Animals - Lab Practical 2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
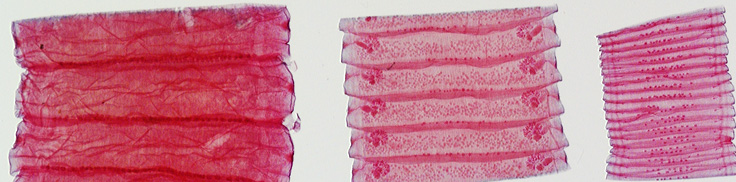
What are these structures and what is their function? What Phylum and Class are these present in?
These are proglottids (gravid, mature, immature), which are reproductive units found in Platyhelminthes of the Class Cestoda (tapeworms).
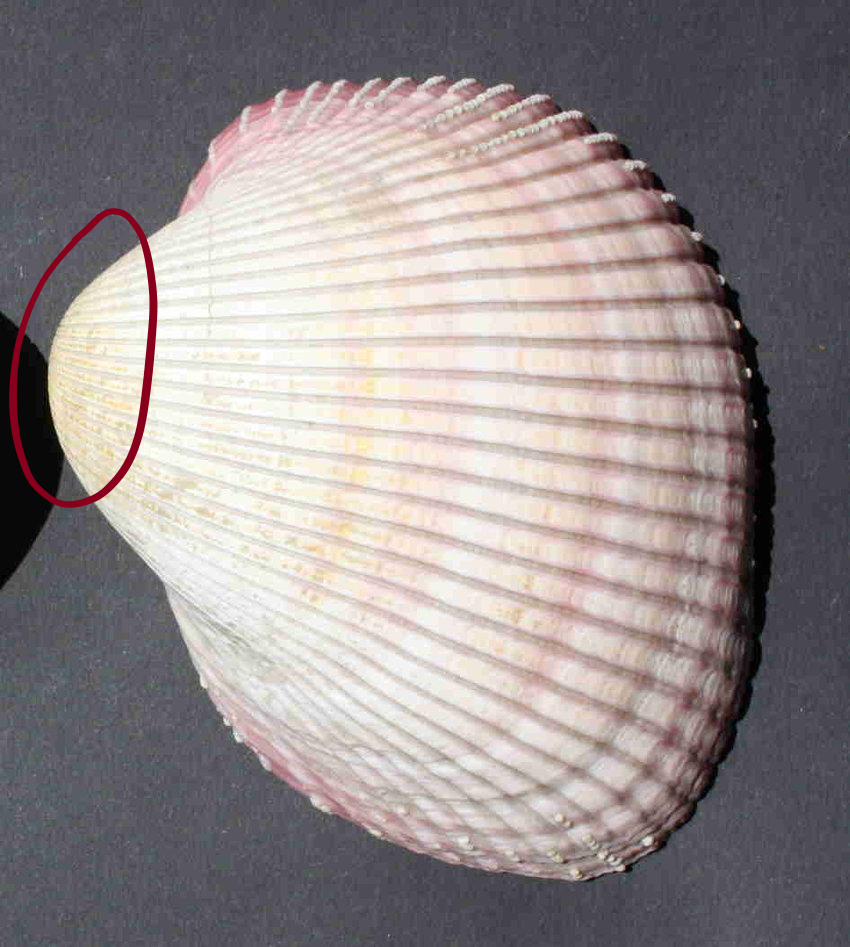

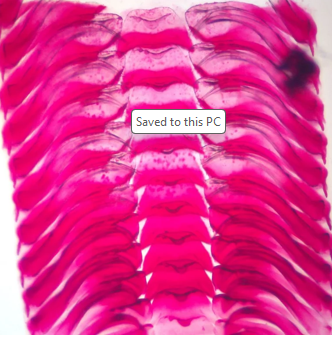
What is this part of the shell called and how old is it relative to the rest of the shell? What Phylum and Class does this animal belong to?
Umbo. It is the oldest part of the shell.
Phylum: Mollusca
Class: Bivalvia
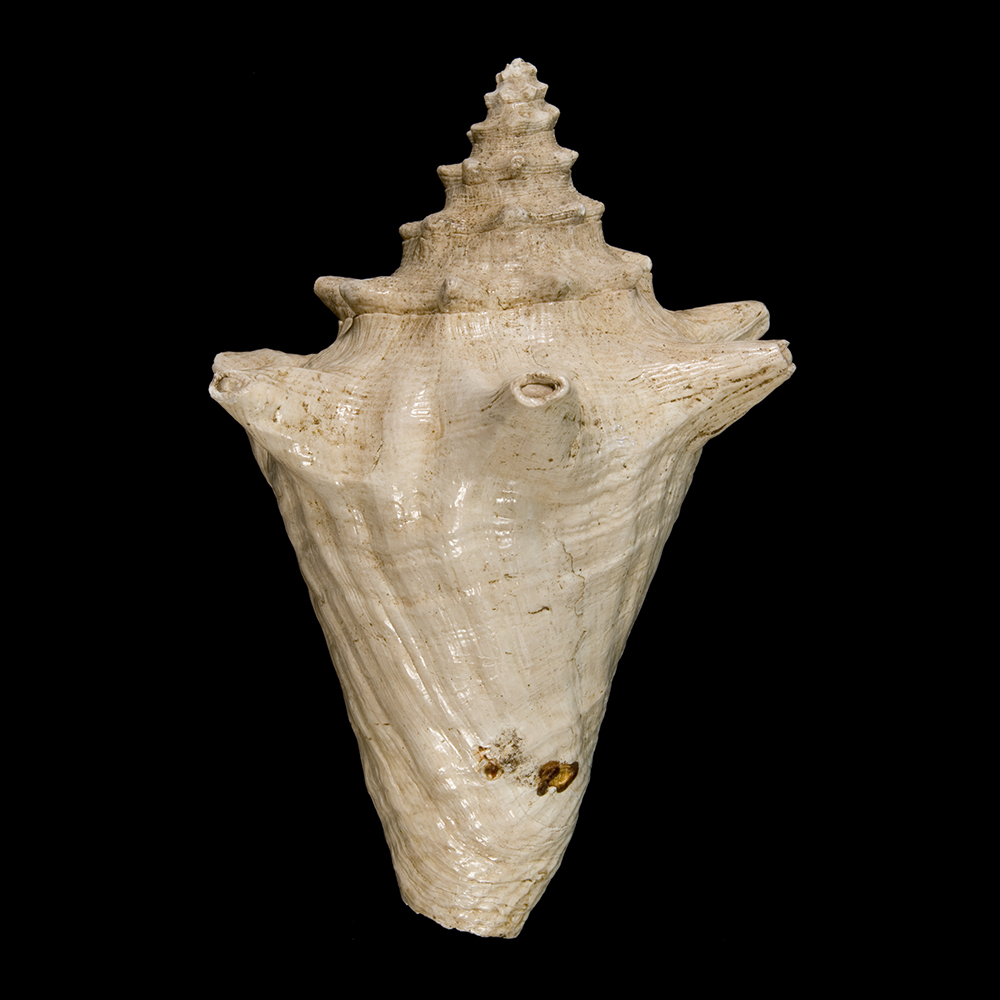

What is the very top part of the shell called and how old is it relative to the rest of the shell? What Phylum and Class does this animal belong to?
Apex. It is the oldest part of the shell.
Phylum: Mollusca
Class: Gastropoda
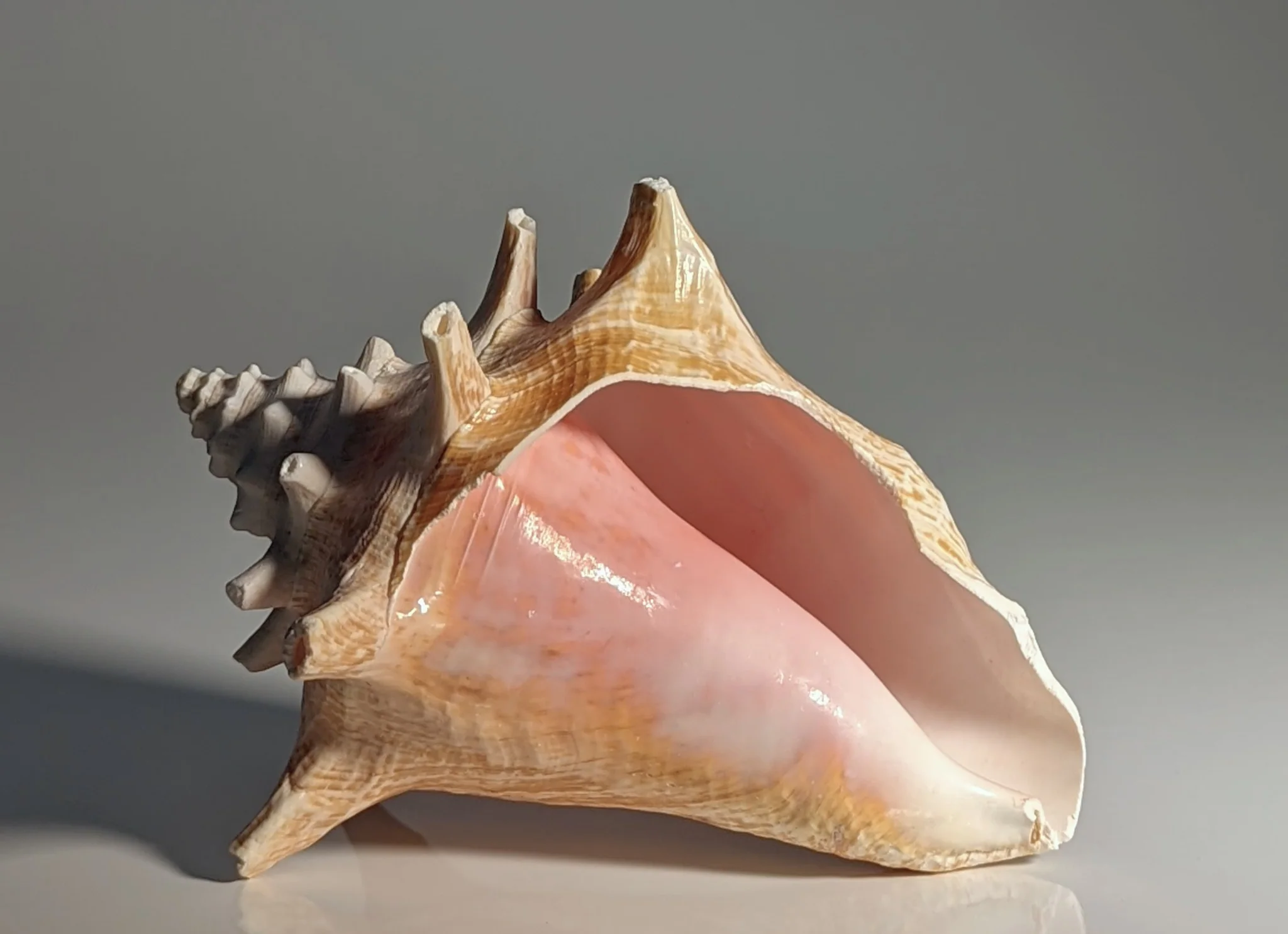

Is this shell right (dextral) or left handed (sinistral)? How do you know?
This shell is right handed or dextral. When you orient the shell so the apex is at the top, the opening is on the right side.
Name this structure and its function. What Phylum and Class(es) can this be found in?
This is a radula, a hard feeding organ with central plates that scrape algae or other food sources from their surfaces.
It can be found in all Classes in the Phylum Mollusca except for Bivalvia.
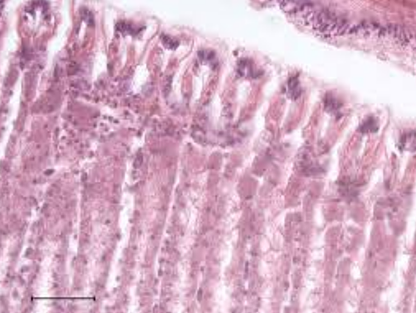
Name this structure and its function.
This is a gill. It is a soft respiratory organ.
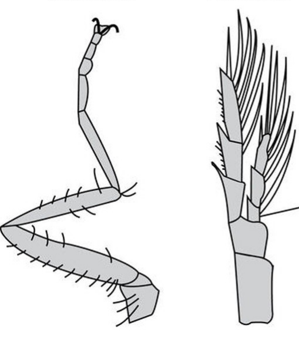
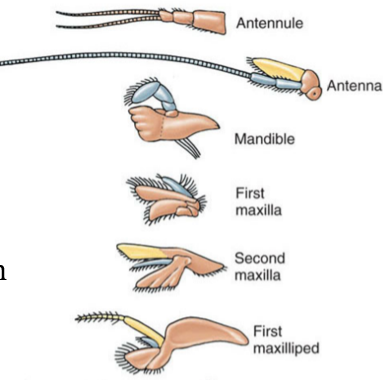
What is the major difference between these two appendages? What phylum are these found in?
The one on left is uniramous and does not branch
The one on right is biramous and branches
These are in arthropods
Explain the color coding scheme for this diagram.
Peach: Protopod (most basal branch)
Blue: Endopod (medial outer branch)
Yellow: Exopod (lateral outer branch)
What phylum does this animal belong to?
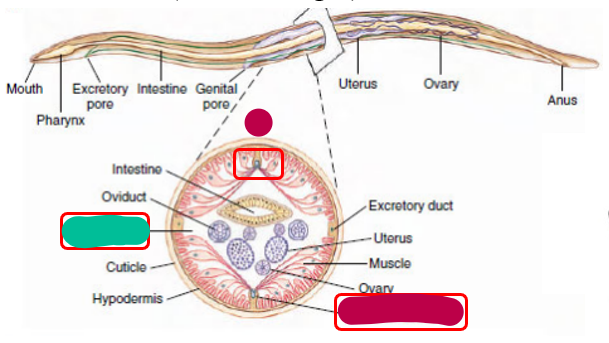
What are the structures whose names are censored by magenta?
What is the structure whose name is censored by teal?
Nematoda
Magenta: Dorsal AND ventral nerve chords
Teal: Pseudocoelom

What is happening in this image? What is structure A and what is structure B?
Ecdysis or molting.
A: Old cuticle
B: New cuticle
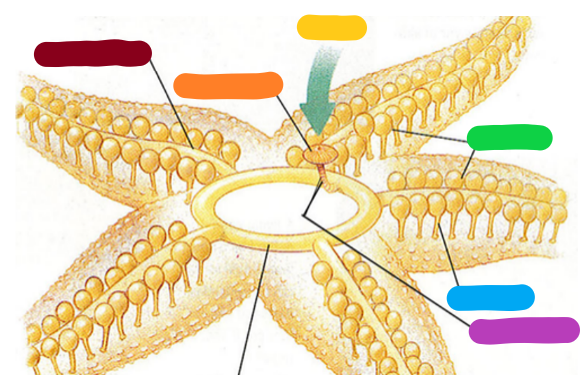
Provide the anatomical term for the color coded structures in this diagram.
Red: Radial canal
Orange: Madreporite
Yellow: Water
Green: Ampulla
Blue: Tube foot
Purple: Stone canal
Pink: Ring canal
Describe the movement of water through the echinoderm water vascular system.
Madreporite
Stone Canal
Ring Canal
Radial Canals
Lateral Canal
Ampulla
Tube Feet
What two main purposes does the echinoderm water vascular system serve?
Locomotion and nutrient transport
What germ layer is the echinoderm endoskeleton/test derived from?
Mesoderm
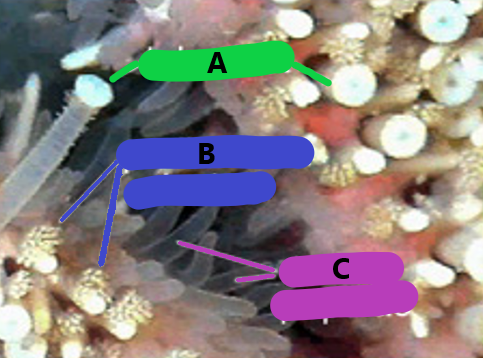
What structures correspond with these letters? What phylum is this?
A: Tube feet
B: Pedicellaria
C: Dermal papule
This animal is in the phylum Echinodermata
What are ambulacra in echinoderms?
Radial areas along which nerves and structures of the water vascular system run
What are dermal branchiae/papulae in echinoderms?
Projections of the coelom lined with skin that are used for respiration and excretion
What are dermal pedicellariae in echinoderms?
Sensory pincer-like “jaws/claws” that keep the body free of debris, protect papulae, and aid in food capture
What class of echinoderms includes sea stars?
Asteroidea
What class of echinoderms includes brittle stars?
Ophiuroidea
What class of echinoderm includes sea urchins and sand dollars?
Echinoidea
What class of echinoderm includes sea cucumbers?
Holothuroidea

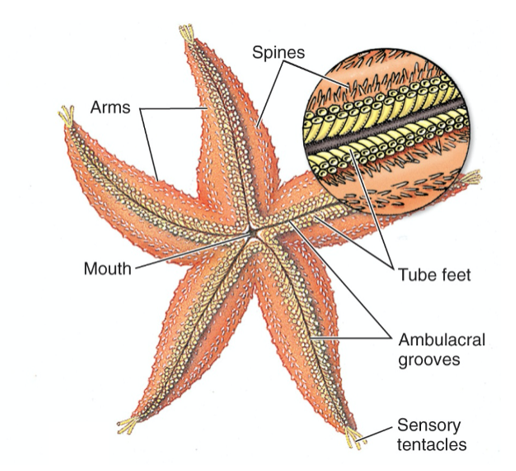
Asteroidia oral surface diagram
Red: Spines
Orange: Tube feet
Yellow: Ambulacral grooves
Green: Sensory tentacles
Blue: Mouth
Purple: Arms
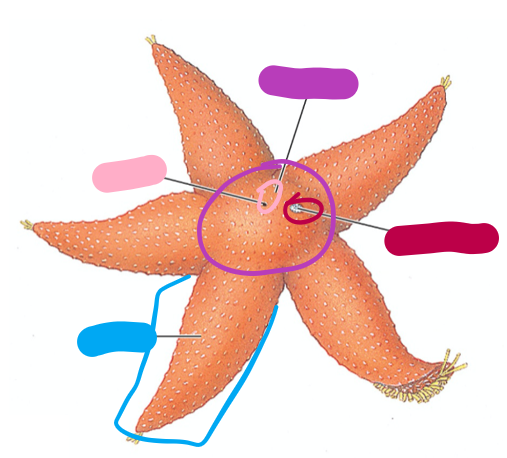
Asteroidia aboral surface diagram
Purple: Central disc
Magenta: Madreporite
Pink: Anus
Blue: Arm
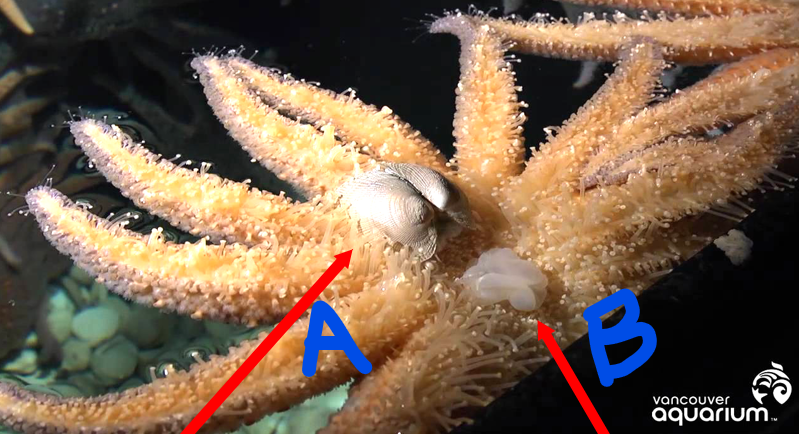
Describe what is happening at points A and B.
What phylum/class is this animal from?
A: Tube feet are prying open a bivalve
B: The cardiac stomach is everted for digestion
Phylum Echinodermata, Class Asteroidea

What are these structures and what Phylum/Class can they be found in?
Placoid scales
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Chondrichthyes
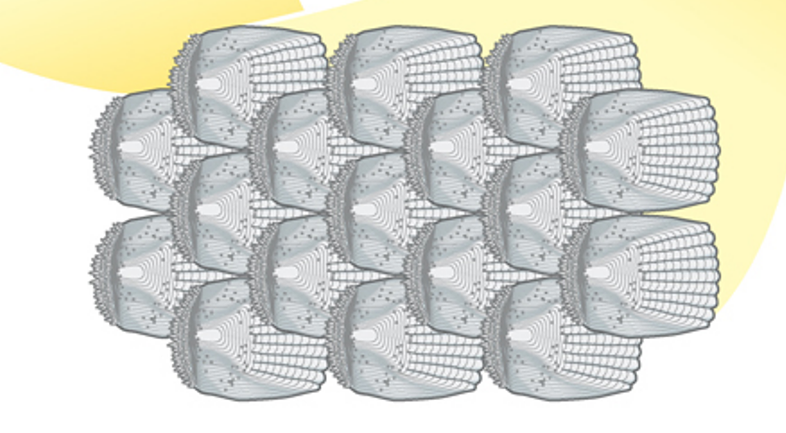
What are these structures and in what Phylum can they be found?
Ctenoid scales
Phylum: Chordata
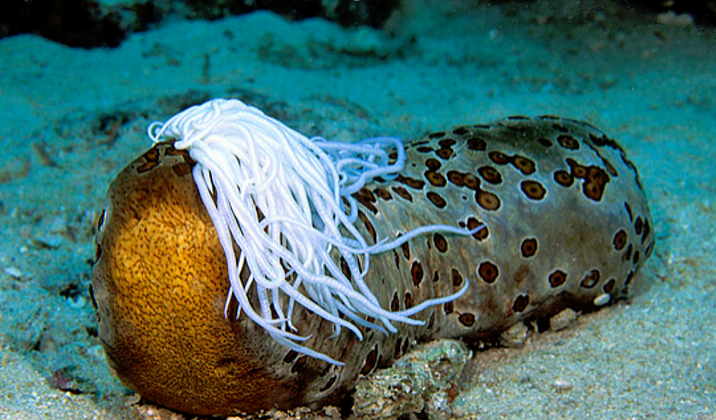

Explain what is happening in this photo. What Phylum and Class does this animal belong to?
The animal is discharging its Cuvierian tubules through its anus for defense.
Phylum: Echinodermata
Class: Holothuroidea (sea cucumbers)
What are these structures and in what Phylum can they be found?
Cycloid scales
Phylum: Chordata
What are these structures and in what Phylum can they be found?
Ganoid scales
Phylum: Chordata
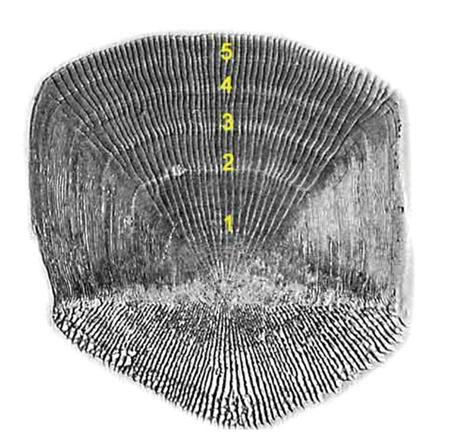

What is being shown with the numbering in this image? What is the overall structure called and what phylum can it be found in?
Age estimation of a fish made by counting the number of annuli in a scale.
Structure: Cycloid scale
Phylum: Chordata
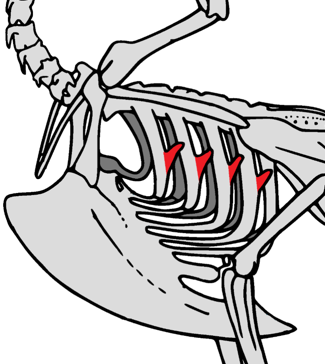
What two main structures, visible within this diagram, aid in flight in birds?
Keeled sternum
Uncinate processes on ribs
Define tagmata in Arthropoda.
Groupings of segments into discrete functional units
(Ex. Spiders and ticks have a cephalothorax and abdomen)
What is the key trait of the subphylum Chelicerata? Is this trait present in any other subphyla?
Their first pair of appendages has been modified into fanglike structures or mouthparts.
Trilobites are extinct now, but had chelicera as well.
What tagmata are present in Chelicerata?
Cephalothorax and abdomen (usually unsegmented)
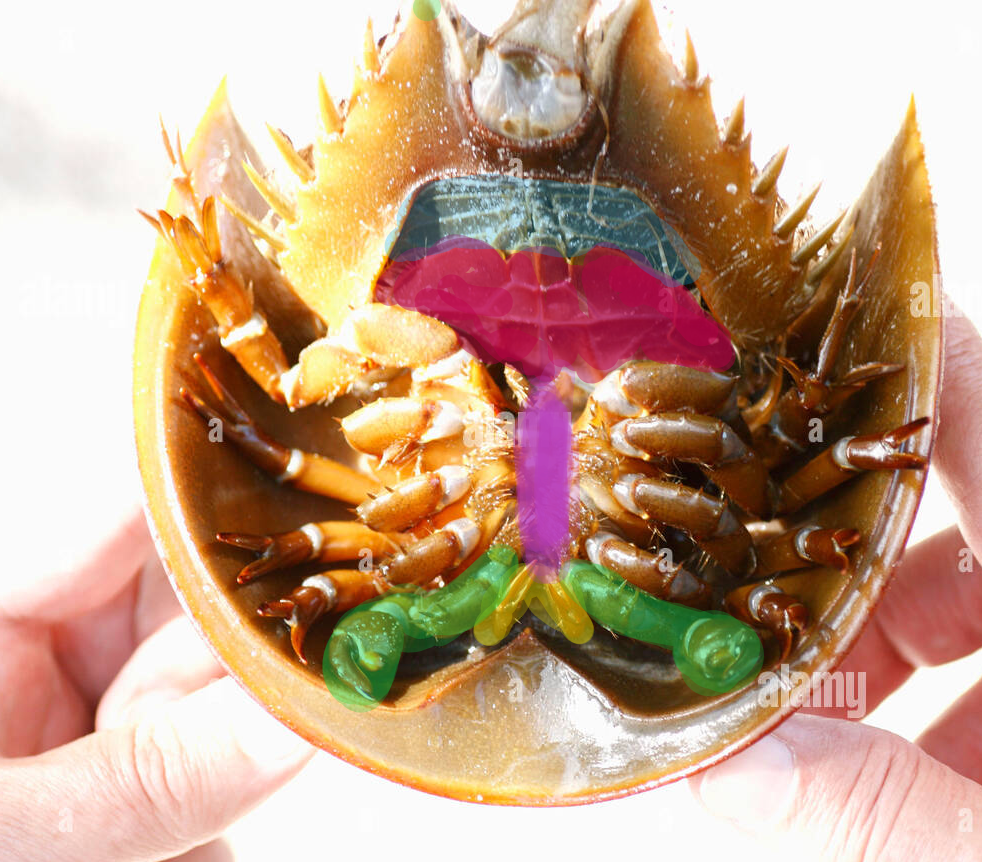

Explain the color coding in this image.
Yellow: Chelicera
Green: Pedipalps
Purple: Gnathobase
Pink: Genital operculum
Blue: Gill opercula (book gills underneath)
How do horseshoe crabs eat?
By crushing its prey with front legs and ingesting it.
What is the scientific term for the tail of a crustacean or chelicerate?
Telson
Describe unique adaptations of key echinoderm traits in Echinoidea.
Closed ambulacral grooves, fused ossicles/calcareous plates, aboral madreporite
no papulae
Describe unique adaptations of key echinoderm traits in Holothuroidea.
Closed ambulacral grooves
Internal madreporite
No papulae, pedicellariae, or spines
What structures do members of Holothuroidea use for respiration and excretion?
Respiratory tree (internal, but can be discharged in defense as a last resort)
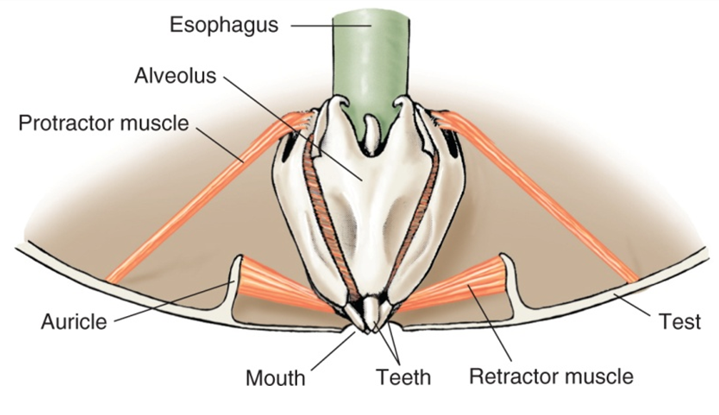
What is this structure known as and what Phylum/Class is it found in? Describe any other unique features.
Aristotle’s lantern
Phylum Echinodermata, Class Echinoidea
5 self-sharpening teeth that are replaced as needed
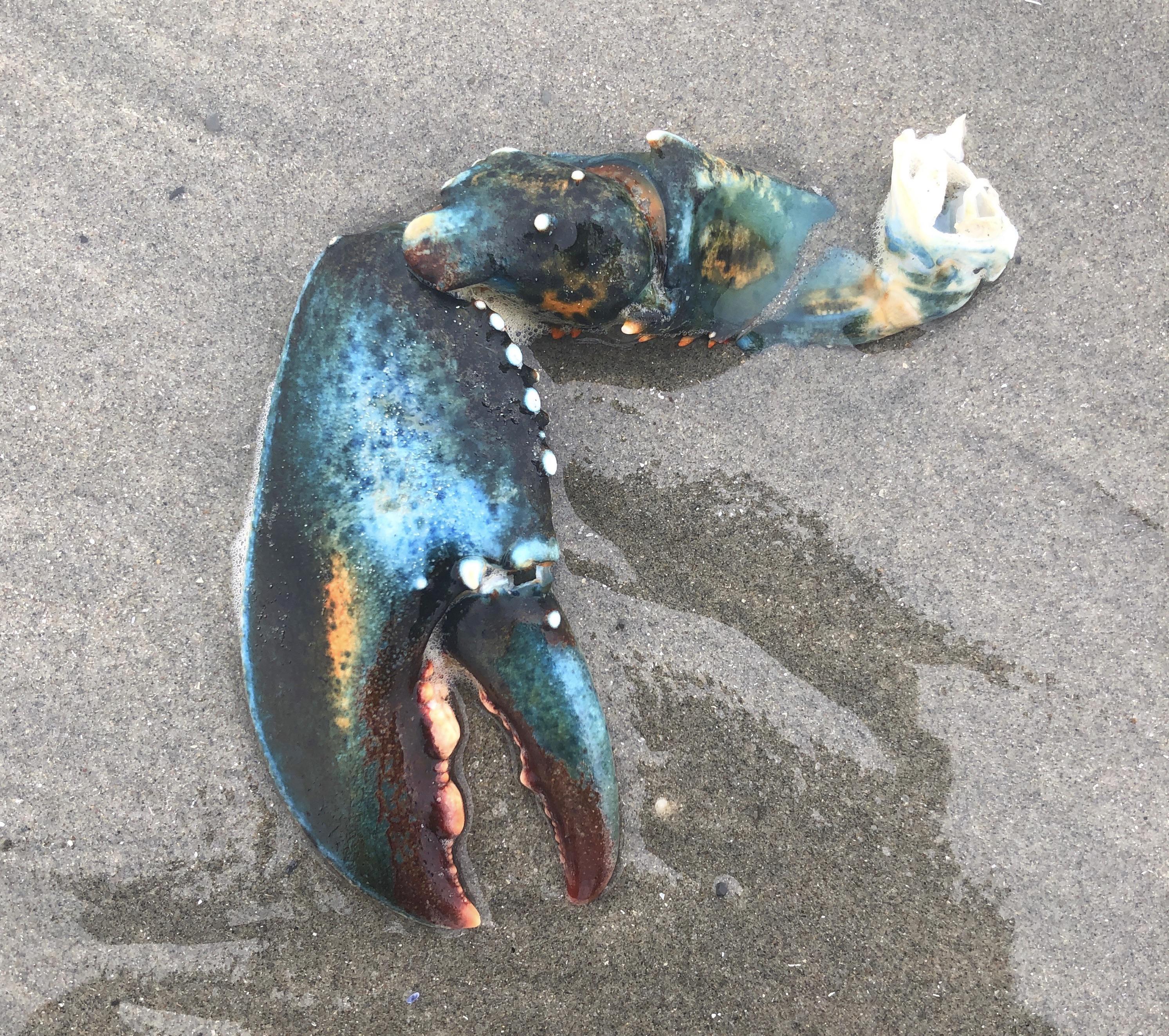

What is the scientific term for this kind of appendage and what phylum is it found in?
Cheliped
Arthropoda
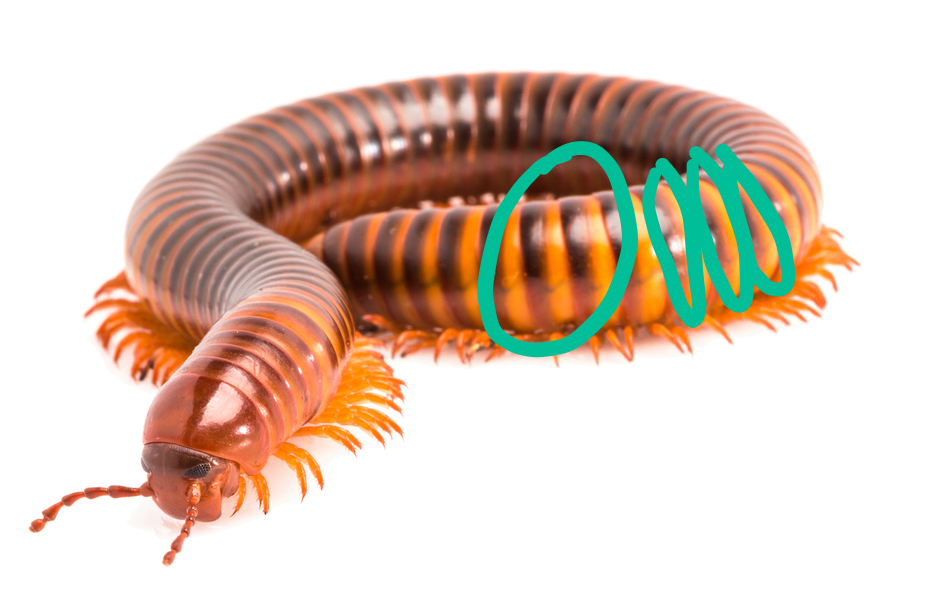

What are these segments called? Is this a centipede or millipede and how do you know?
Tergites
Millipede (two legs per segment)
How do you tell if a millipede is male or female?
A male millipede is missing the leg pair on the 6th segment from the head.
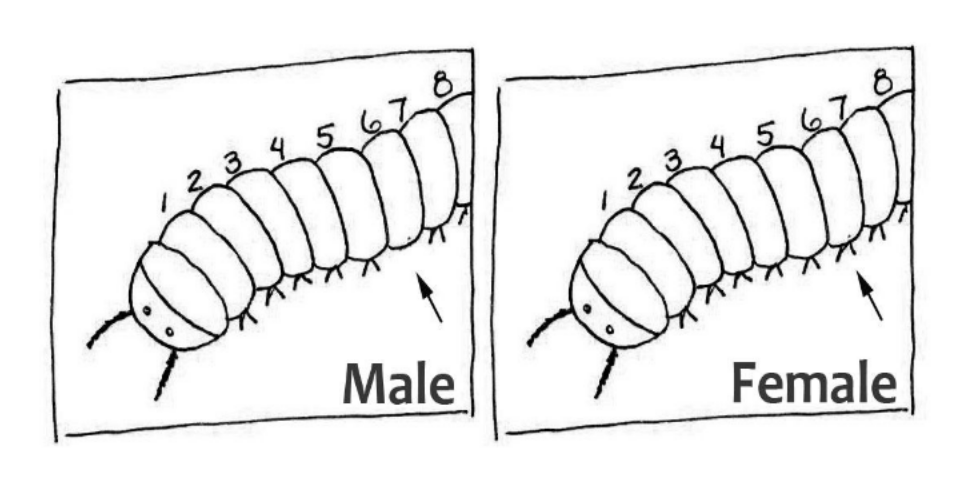
How do myriapods breathe?
Via a tracheal system
What Order of Insecta contains beetles and how is it diagnosed?
Coleoptera
Elytra (hard wing covering)
What Order of Insecta contains butterflies and how is it diagnosed?
Lepidoptera
Scales/modified setae
What Order of Insecta contains flies and how is it diagnosed?
Diptera
1 pair of wings and halteres (club shaped organs that aid in proprioception during flight)
What Order of Insecta contains ants/bees and how is it diagnosed?
Hymenoptera
Waist
What Order of Insecta contains true bugs and how is it diagnosed?
Hemiptera
The wings fold to create an X
What structures do hexapods use for excretion/osmoregulation and respiration?
Excretion/osmoregulation: Malpighian tubules
Respiration: Tracheal system (spiracles and tracheal tubes)
What are nematodes commonly known as? How big is this phylum relative to others?
Roundworms
Second largest phylum
Describe the coelom and nervous system of nematodes
pseudocoelom
Have both ventral and dorsal nerve chords and cerebral ganglia
What phyla exhibit eutely?
Rotifera, Nematoda, Tardigrada
What is this structure known as, what does it do, and what kind of animal is it found in?
Furcula — A springing mechanism that propels springtails forward
Springtails are a kind of hexapod (not insects)
How do nematodes move?
Nematodes only have longitudinal muscles, so they move in a thrashing or whipping motion.
What is the key synapomorphy for Tunicata?
The tunic, an outer protective covering made of cellulose
What else are tunicates known as?
Ascidians or sea squirts
What is interesting about the development of Cephalochordates/lancelets compared to tunicates?
All 5 chordate characteristics persist throughout life
What key trait defines the subphylum Vertebrata?
Enlarged brain enclosed in a cranium
(not all vertebrates have a vertebral column, like jawless fish, but most have bony or cartilaginous vertebrae surrounding the nerve chord)
What are lamprey larva known as? What kind of research are these used in?
Ammocoetes
Model for vertebrate evolution
Describe the function of the different kinds of paired fins
Pectoral fins control direction
Pelvic fins control stabilization
Describe the function of non-paired fins in dorsal and caudal positions.
Dorsal: Stabilization
Caudal (such as a heterocercal tail): Thrust and lift
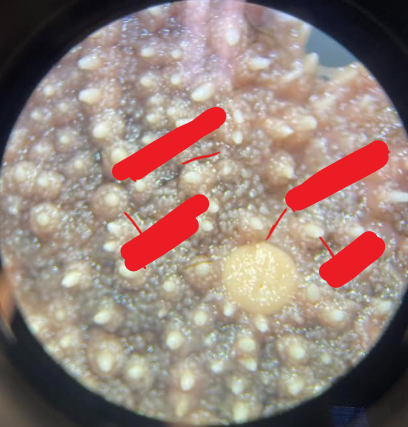
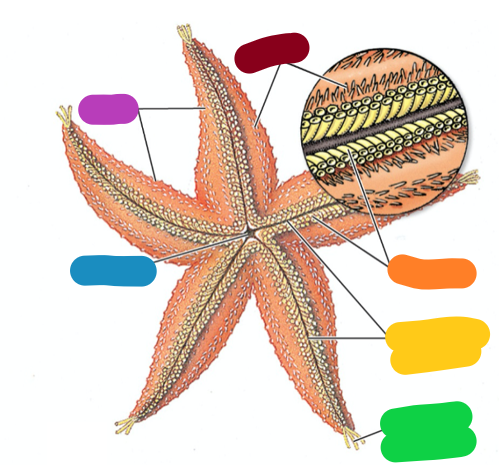
What Phylum and Class is this animal in and what structures are the labels referring to?
Phylum: Echinodermata
Class: Asteroidea (sea stars)
Aboral surface
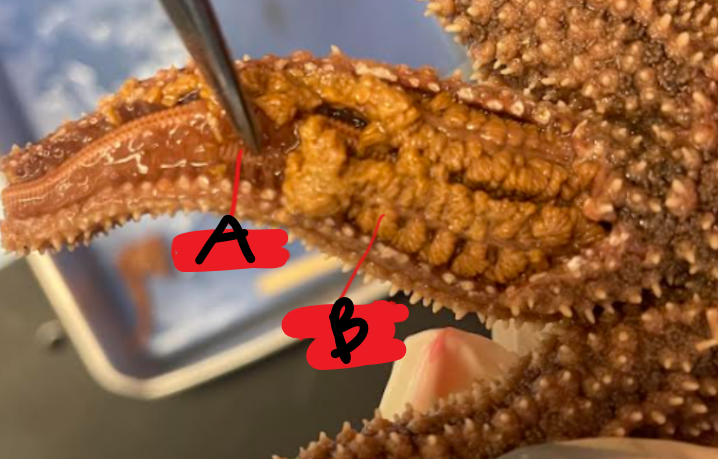
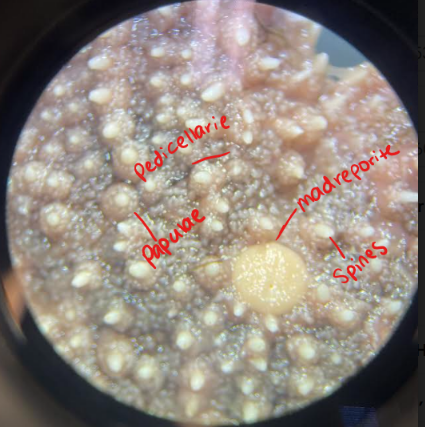

What structures are indicated by these labels?
A: Ossicles
B: Pyloric ceca
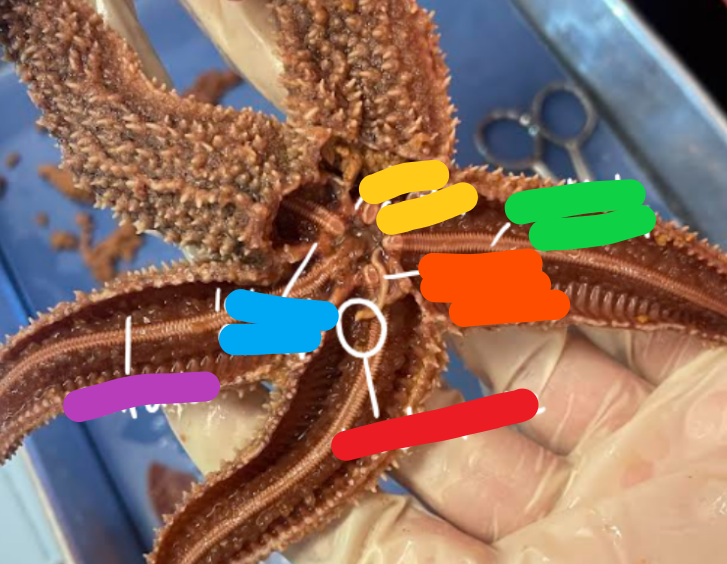

Label the structures in the water vascular system.
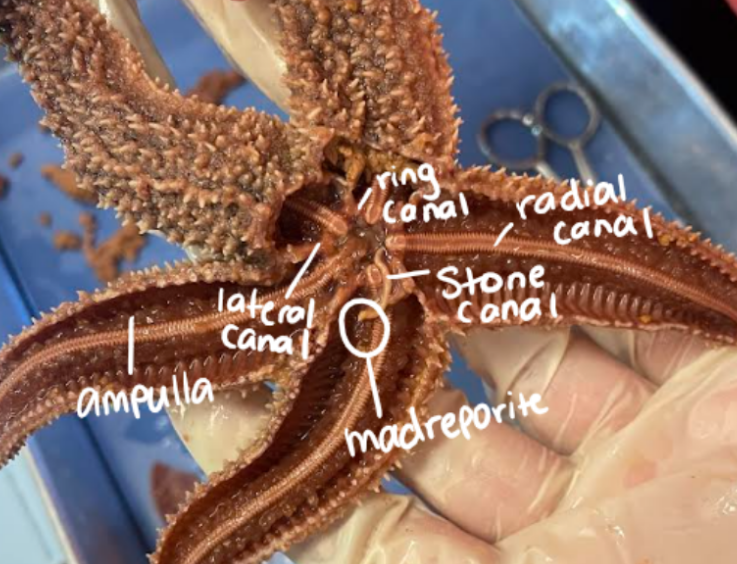
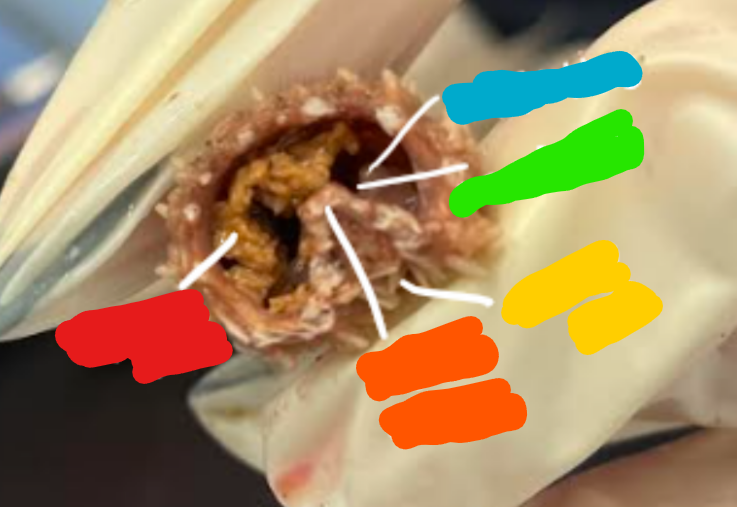


Label the structures in the cross section of the sea star arm
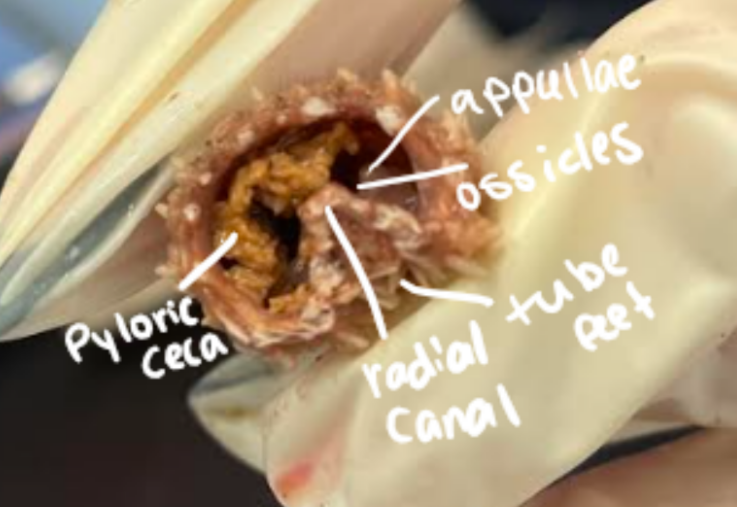
What are the functions of the tube feet?
They aid in locomotion, but they can also capture and pry open prey such as clams.
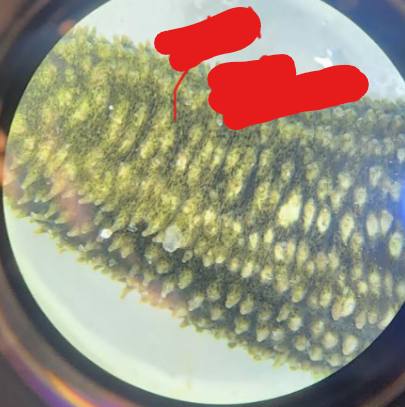

What are these structures and what Phylum/Class are they found in?
Radial longitudinal muscles
Phylum: Echinodermata
Class: Holothuroidea
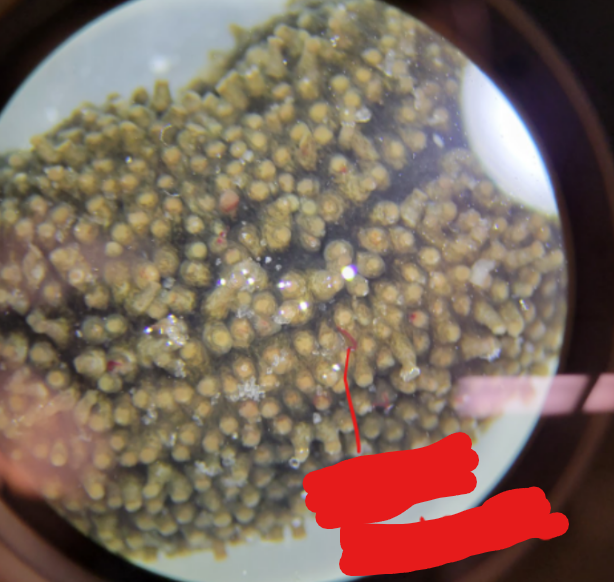

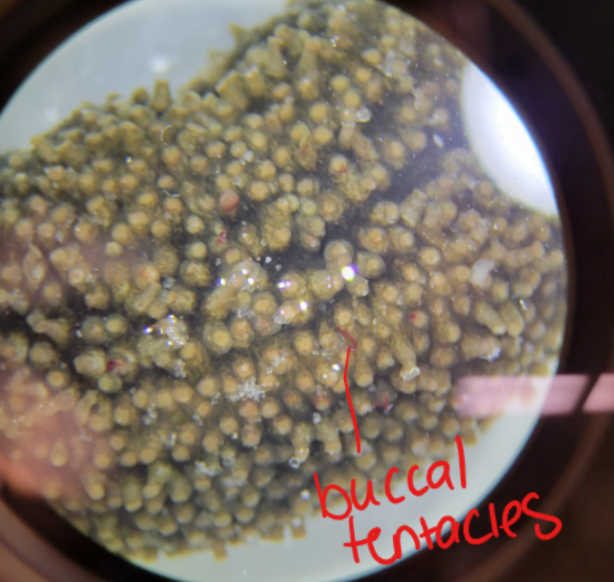
What are these structures and what Phylum/Class are they found in?
Buccal tentacles
Phylum: Echinodermata
Class: Holothuroidea
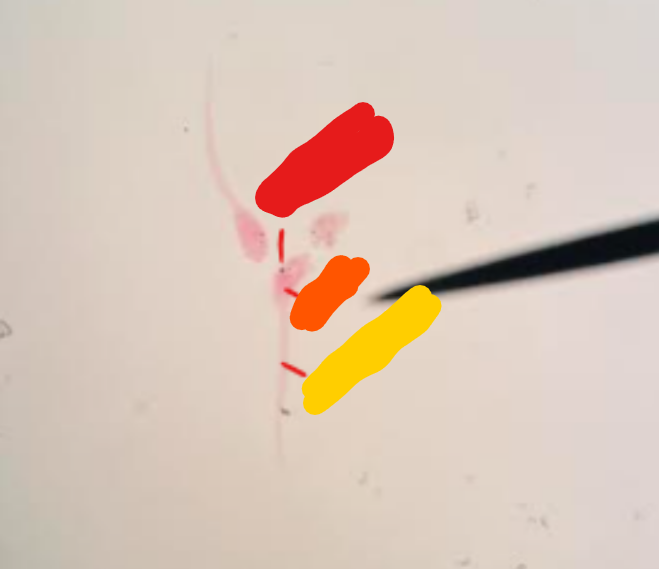

What are these animals? Identify the labeled structures.
Larval tunicates
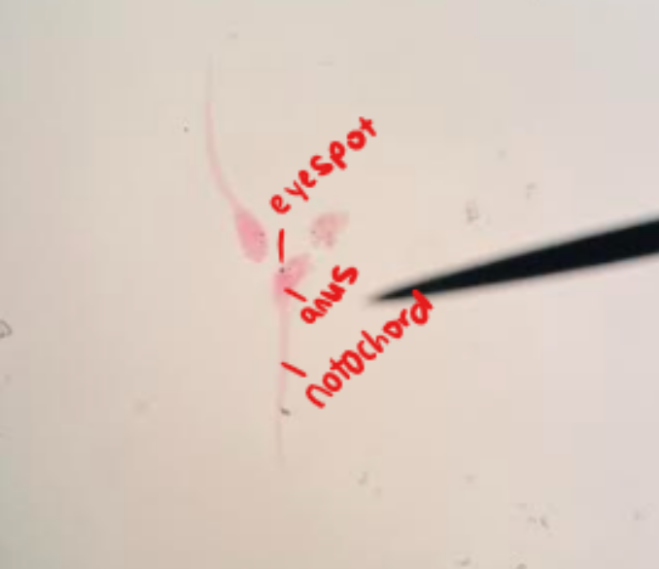

Stained lancelet/amphioxus (this is a prompt card— Draw out the anatomy of this animal)
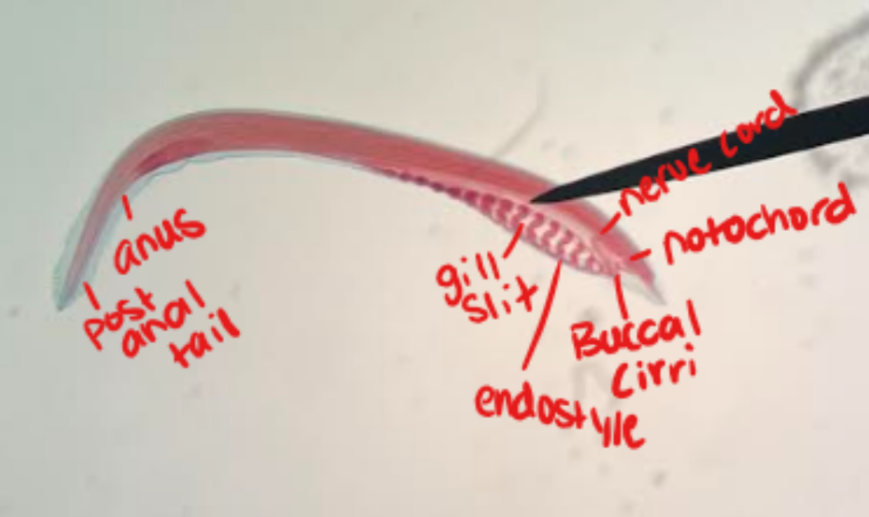

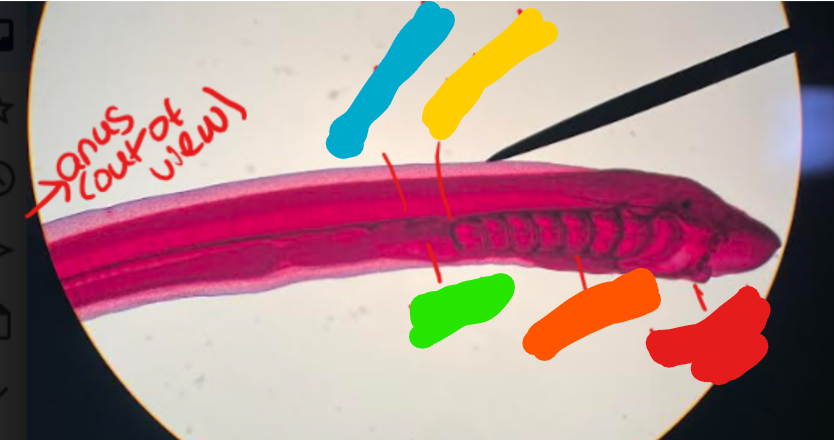
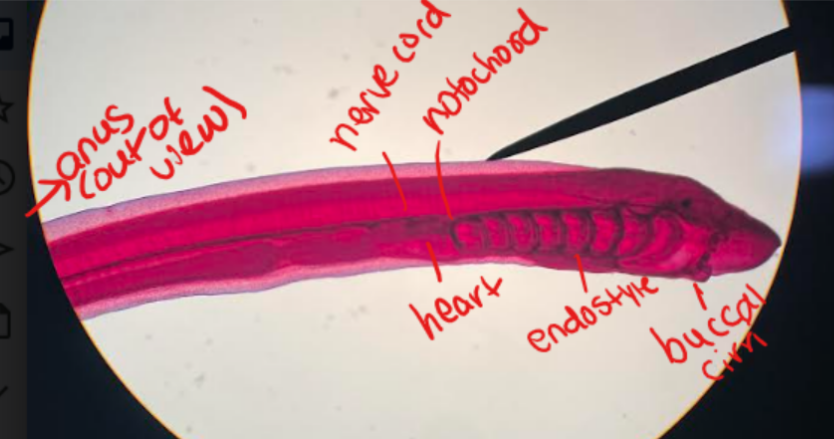
What animal is this? What Phylum/Subphylum is it part of? Identify the labeled structures.
Larval lamprey (ammocoete)
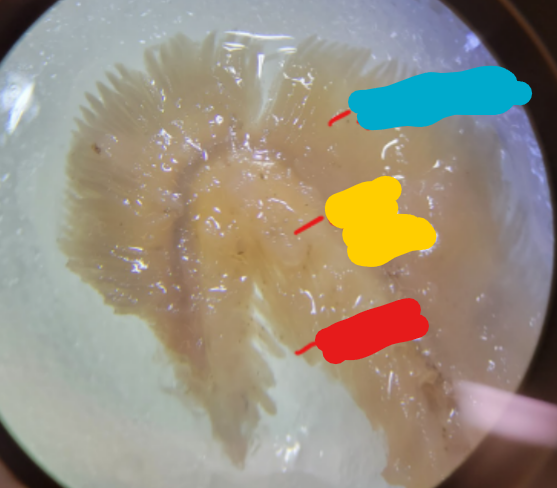

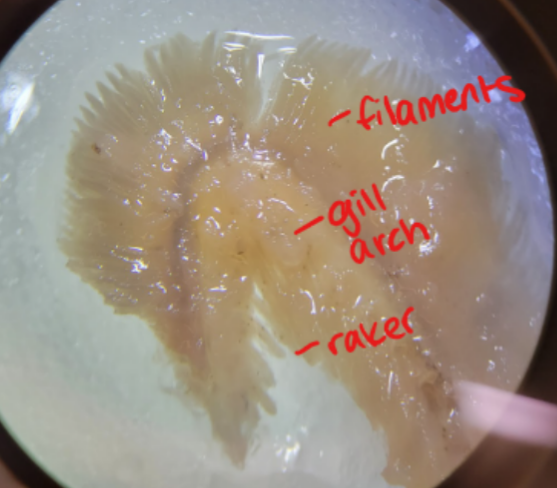
What is this structure and what kind of animal is it found in? Identify the labeled structures.
This is a gill from a fish.
What is the pygostyle and what is its purpose?
A bony muscle attachment site for tail feathers, which serve essential functions in steering and balance during flight.