Radiography of the Vascular System (Part 1)
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Radiography,
Angiography,
Echocardiography (Ultrasound),
Nuclear Cardiology,
CT,
MRI
Several imaging modalities play an important role in the evaluation of the cardiovascular system and the management of cardiovascular disease. (6)
Chest radiography
provides information about the heart and its shape and size
Chest radiography
It is also excellent for demonstrating the great vessels and vascular changes within the lung fields.
Echocardiography
Encompasses a group of noninvasive sonographic (ultrasound) procedures that can provide detailed information about heart anatomy, function, and vessel patency
Sonographic imaging
may be performed using M-mode, two-dimensional (2-D) imaging, spectral doppler, color doppler, or stress echocardiography
M-mode, 2-Dimensional imaging, Spectral Doppler, color doppler, stress echocardiography
Sonographic imaging may be performed using (5)
Angiography
refers to radiologic imaging of blood vessels after injection of contrast media.
catheter;vessel
In Angiography, To visualize these low-contrast structures, contrast media is injected by a ___ that is placed in the ____ of interest.
Angiography
Positive contrast media are more commonly used, but there are instanced when use of negative contrast media is indicated.
Positive contrast media
Commonly used cm in angiography
Arteriography
imaging of arteries
Venography
imaging of veins
Angiocardiography:
imaging of the heart and associated structures
Nuclear Cardiology
Nuclear medicine procedures used in the assessment of cardiovascular include myocardial perfusion scans, gated cardiac blood pool scans, and PET
Nuclear Cardiology
They are useful in assessing coronary artery disease (CAD), congenital heart disease, and cardiomyopathy.
Myocardial perfusion scan
is the most widely used procedure in nuclear cardiology.
Myocardial perfusion scan
It may be performed on patients with chest pain of an unknown origin, to evaluate coronary artery stenosis, and as a follow-up to bypass surgery, angioplasty, or thrombolysis.
Myocardial perfusion scan
It is especially useful in detecting regions of myocardial ischemia and scarring
Myocardial ischemia and scarring
Myocardial perfusion scan is especially useful in detecting regions of ___ and ___
CT
Is a non-invasive modality used to assess cardiac and vascular disease.
CT
It uses Ct technology with or without IV contrast to visualize the heart anatomy, coronary circulation, and great vessels.
MRI
Is used to detect or monitor cardiac disease and to evaluate the heart’s anatomy and function in patients with both heart disease present at birth and heart diseases that develop after birth.
MRI
It does not use ionizing radiation to produce images, and it may provide the best images of the heart for certain conditions
Circulatory system
consists of the cardiovascular and lymphatic components.
cardiovascular portion
includes the heart, blood, and vessels that transport the blood.
cardio, vascular component
Cardiovascular or blood circulatory, division may be divided further into the ____ (circulation within the heart) and ____ (blood vessel)
vascular or vessel component
is divided into pulmonary (heart to lungs and back) and general, or systemic (throughout the body)
pulmonary, general, or systemic
The vascular or vessel component is divided into ___ (heart to lungs and back) and ____ or ____ (throughout the body).
Heart
is the major organ of the cardiovascular system
Heart
functions as a pump to maintain circulation of blood throughout the body
Vascular Component
comprises a network of blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to body tissues and back to the heart again.
Oxygen, Nutrients, Hormones, Chemicals
Vascular Component Functions:
Transportation of ___, ____, ____, and ____ necessary for normal body activity
waste products
Vascular Component Functions:
Removal of ___ through the kidney and lungs
body temperature, water, electrolyte balance
Vascular Component Functions:
Maintenance of ____ and____ and _____.
Maintenance of body temperature and water and electrolyte balance.
These functions are performed by the red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets suspended in plasma
RBC, WBC, Platelets;plasma
Maintenance of body temperature and water and electrolyte balance. These functions are performed by the ___, ___, and _____ suspended in ____
Arteries
Vessels that transport oxygenated blood from the heart to tissues.
Arterioles
The smaller arteries are called
Capillaries
As blood travels through the arterioles, it enters the tissues through the smallest subdivision of these vessels, known as
Veins
Carries deoxygenated blood to the heart.
venous system
extends from venous capillaries to venules to veins
Pulmonary Circulation
The elements of the blood vessel circuit (veins, venules, capillaries, arterioles, and arteries) that supply blood to the lungs and back make up the ____ components of the cardiovascular system
Veins, venules, capillaries, arterioles, arteries
The elements of the blood vessel circuit (5)
pulmonary arteries
Arteries generally carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the capillaries except for the ____ which carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
heart
is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
mediastinum; diaphragm
Anatomically, the heart lies within the ____ and rests on the ___
myocardium
Cardiac tissue differs from other muscle tissue of the body in its construction and is termed
extensive systemic circulation
The left side of the heart is responsible for the ___
left side; three times
The____ of the heart is responsible for the extensive systemic circulation; the left muscle wall is about ___ as thick as the right side
R&L Atria, R&L Ventricles
The heart is divided into four chambers
Diagnosing heart failure,
Evaluating congenital heart defects,
Checking for valve disorders,
Monitoring heart and lung function,
Investigating symptoms,
Follow-up and placement verification
Radiography of the Chest (Heart) Indications (6)
heart failure.
Detecting an enlarged heart, which can be a sign of
pulmonary edema
a common sign of congestive heart failure
pulmonary edema
fluid in the lungs
Cardiac size
is measured by drawing vertical parallel lines down the most lateral points of the heart and measuring between them.
Thoracic width
is measured by drawing vertical parallel lines down the inner aspect of the widest points of the rib cage, and measuring between them
Cardiothoracic Ratio (CTR)
is frequently expressed as a percentage.
Abnormal
A CTR of greater than 1:2 (50%) is considered ___
Cardiothoracic Ratio (CTR)
Accurate assessment of heart size assumes the projection is PA and that cardiac size is not exaggerated by factors such as patient rotation
left heart contour
consists of the left lateral border of the left ventricle
right heart contour
is the right lateral border of the Right Atrium (RA)
density; adjacent lung
If the heart contours are not clearly seen, this may indicate increase in ___ of the ___.
middle mediastinum
The heart is located in the ___
Aortic Knuckle
represents the left lateral edge of the aorta as it arches backwards over the left main bronchus.
Mediastinal Contours
Displacement or loss of definition of these contours can indicate diseases such as aortic aneurysm or adjacent lunch consolidation
descending thoracic aorta
The contour of the ____ can be seen in continuation from the aortic knuckle.
aortopulmonary window
is located between the Aortic Knuckle (AK) and the Left Pulmonary Artery (LPA)
Aortic Knuckle (AK), Left Pulmonary Artery (LPA)
The aortopulmonary window is located between the ____ and the ____
aortopulmonary window
It is a space where abnormal enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes can be seen on a chest X-ray.
Cardiomegaly
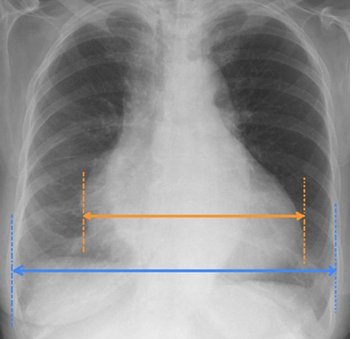
Pulmonary Edema
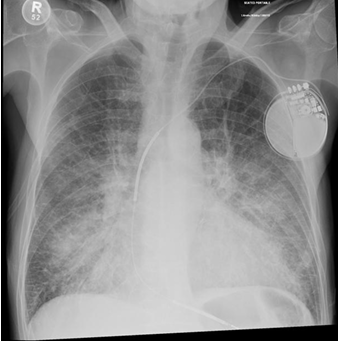
Dextrocardia
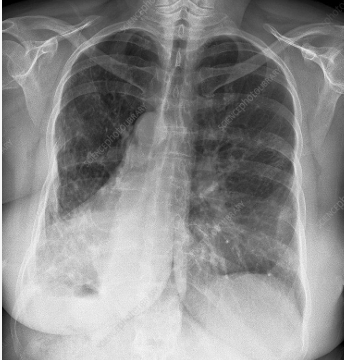
Mitral Annulus Calcifications
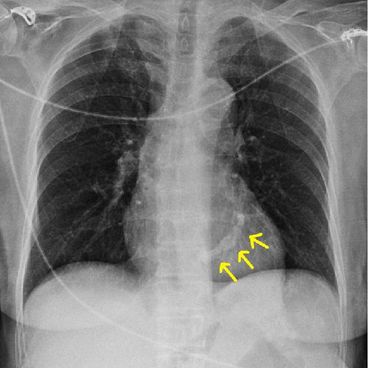
Pacemaker Placement
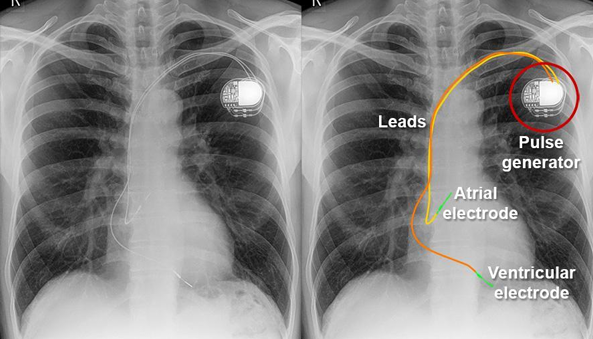
Symptoms of heart disease,
Assessment of critical conditions,
Diagnostic and monitoring,
Screening
Echocardiography Indications (4)
Chest pain, pressure, or shortness of breath
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Palpations or an irregular heartbeat (arrythmia)
Syncope (fainting) or pre-syncope
Echocardiography
Indications
Symptoms of heart disease: (4)
• Cardiac arrest or cardiac standstill
• Trauma to the chest, especially penetrating trauma
• Hypotension (low blood pressure)
• Suspected pulmonary embolism
• Acute heart failure
Echocardiography
Indications
Assessment of critical conditions: (5)
Heart size and function, Heart Valves, Structural and other issues, Blood flow
Echocardiography
Key aspects of Interpretations (4)
• Chamber size
• Pumping strength
• Muscle movement
Echocardiography
Key aspects of Interpretations
• Heart size and function: (3)
• Valve function
• Valve disease
• Color doppler
Echocardiography
Key aspects of Interpretations
• Heart Valves: (3)
• Congenital defects
• Blood clots and tumors
• Inflammation
• Aorta
Echocardiography
Key aspects of Interpretations
• Structural and other issues: (4)
• Doppler effect
• Normal vs. abnormal flow
Echocardiography
Key aspects of Interpretations
• Blood flow: (2)
Parasternal Long Axis View
Parasternal Short Axis View- Slide the probe towards the mitral valve; Tilt the probe towards the base of the heart
Apical Views
Subxiphoid View
Inferior Vena Cava View
Echocardiography- Step 1:
Echocardiography- Step 2: (movement of the probe for mitral valve level) & (movement of the probe for aortic valve level)
Echocardiography- Step 3:
Echocardiography- Step 4:
Echocardiography- Step 5:
• LV: Left Ventricle
• RV: Right Ventricle
• LA: Left Atrium
• RA: Right Atrium
• TV: Tricuspid Valve
• MV: Mitral Valve
• AO: Aortic Valve
Apical 5 Chamber (A5C) View: •Structures to identify (7)
Echocardiography- Step 4: Subxiphoid View & Echocardiography- Step 5: Inferior Vena Cava View
What views
Allows to see similar structures as the Apical 4 Chamber view but just approached from a different angle
Useful when having difficulty getting adequate parasternal views.
Cardiac CT Scan
Also known as Coronary CT Angiography (CCTA)
Coronary CT Angiography (CCTA)
Cardiac CT Scan Also known as
• Chest pain evaluation
• Coronary artery disease
• Aortic issues
• Heart valve assessment
• Congenital heart defects
• Planning for surgery or procedures
• Cardiac masses
• Pericardial diseases
• Post-surgery evaluation
Cardiac CT Scan (9)
Evaluating the anatomy and function of the heart chambers
Diagnosing a variety of cardiovascular disorders
Evaluating the effects of coronary artery disease
Planning a patient’s treatment for cardiovascular disorders
Monitoring the progression of certain disorders over time
Evaluating the effects of surgical changes, especially in patients with congenital heart disease.
Cardiac MRI- Indications (6)
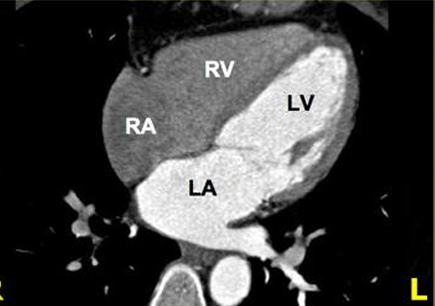
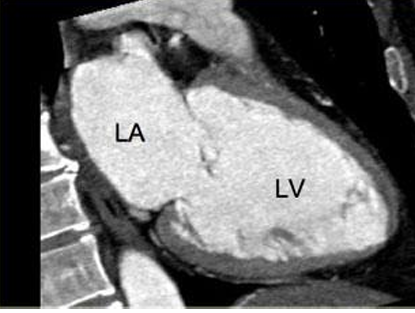
4 chamber view
Cardiac MRI- Cardiac Axes
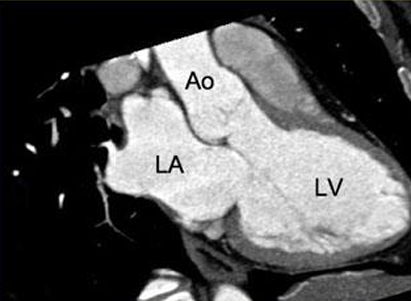
3 chamber view
Cardiac MRI- Cardiac Axes
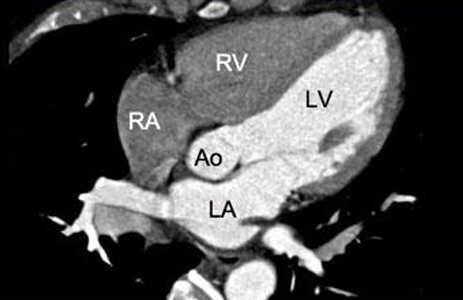
2 chamber view, 3 chamber view, 4 chamber view, 5 chamber view
Cardiac MRI- Cardiac Axes (4)
5 Chamber View
2 Chamber View
Thoracic Aortography
X-ray examination of the aorta’s main artery in the chest (including the root, ascending aorta, aortic arch, and the descending aorta).
Thoracic Aortography
It uses a catheter to inject a contrast dye directly into the aorta
Thoracic Aortography
Done to diagnose and assess conditions like aortic aneurysms (bulges), dissections (tears), or congenital heart diseases.
Thoracic Aortography
To evaluate the extent of a condition and its effects on the aorta’s branches
Thoracic Aortography
To help plan surgery by providing a detailed map of the aorta and any potential blockages