normal spirometry (predicted values)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Important measurements
FEV1
FVC
FEV1 / FEV %
PEF
Forced vital capacity
Forced vital capacity- this is the volume of air in litres that can be exhaled from a position of maximum inspiration during a forced expiration, this will usually take 6 seconds to complete in healthy subjects
velocity over time, recorded volume in L and plot against time
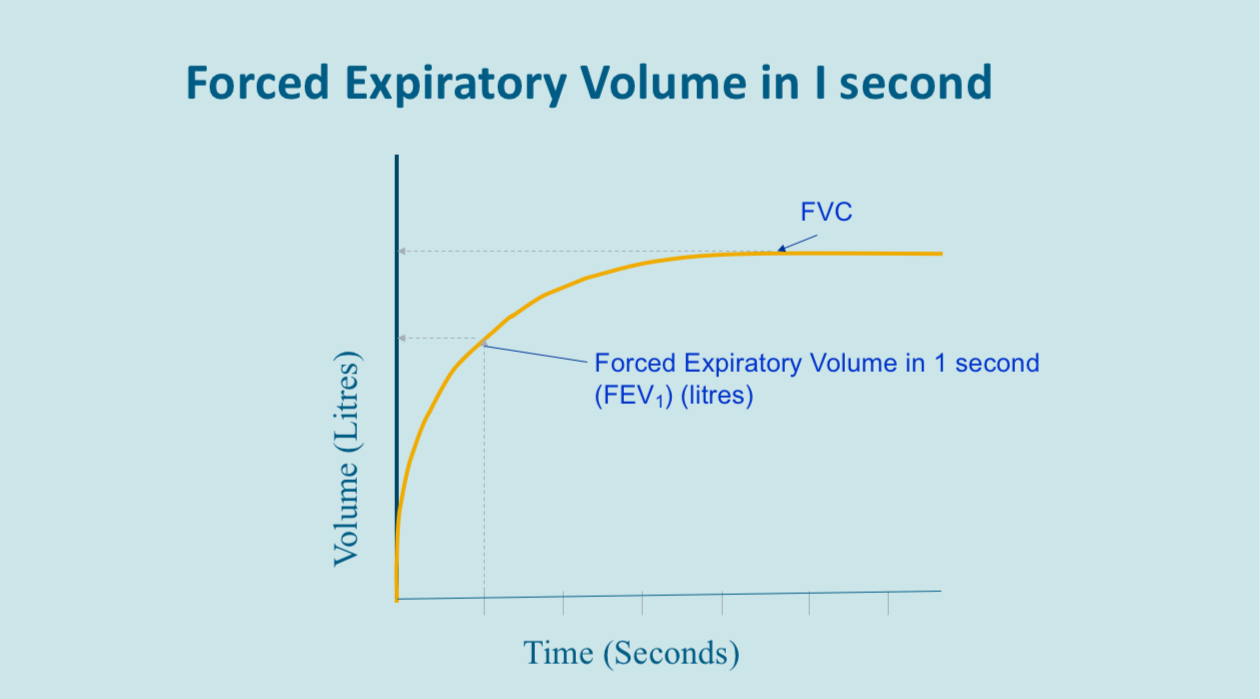
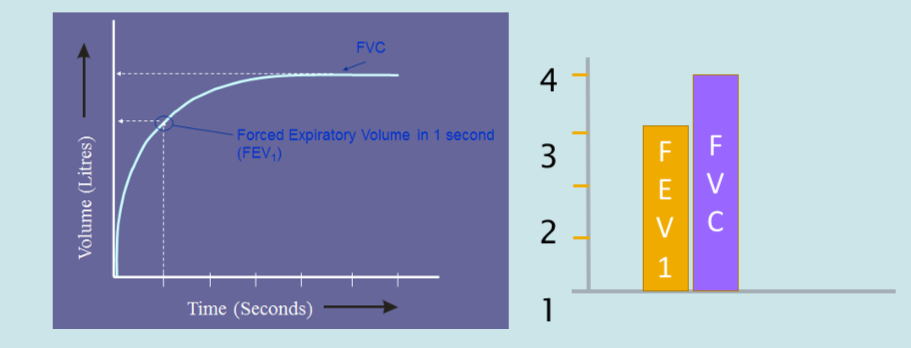
Forced expiratory volume / fvc ratio
This can also be known as the forced expiratory ratio
This is the percentage of the vital capacity which you breath in the first second of a forced expiration, in a normal subject this would be above 70%
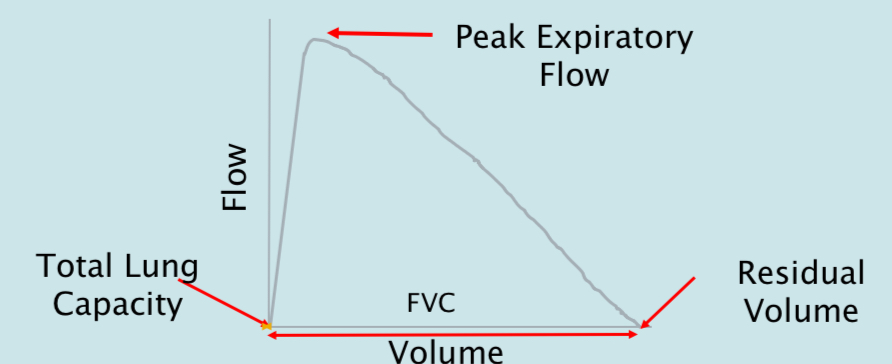
Flow volume curve
this is a right triangle shape, flows are repoed in litres per second or litres per minute, to convert seconds into minutes you would need to multiply by 60
Quality control
this is a series of checks to ensure that results generated are as accurate and precise as possible, the results should be the best possible representation of the patient’s status at the time of testing. In order to make clinical decisions from lung function tests, these measurements need to have good repeatability (within visit) and reproducibility (between visits)
The source of error on these can be equipment, environment, patient, physiologist and procedures / protocols
Repeatability and reproducibility
This is the variation in measurement using repeat measurements under identical conditions, for example performing spirometry on the same patient on the same piece of equipment by the same operator under the same environmental conditions
This is the variation in measurement when there are different conditions - for example performing spirometry on a patient on different days or using a different spirometer and reformed by a different operator
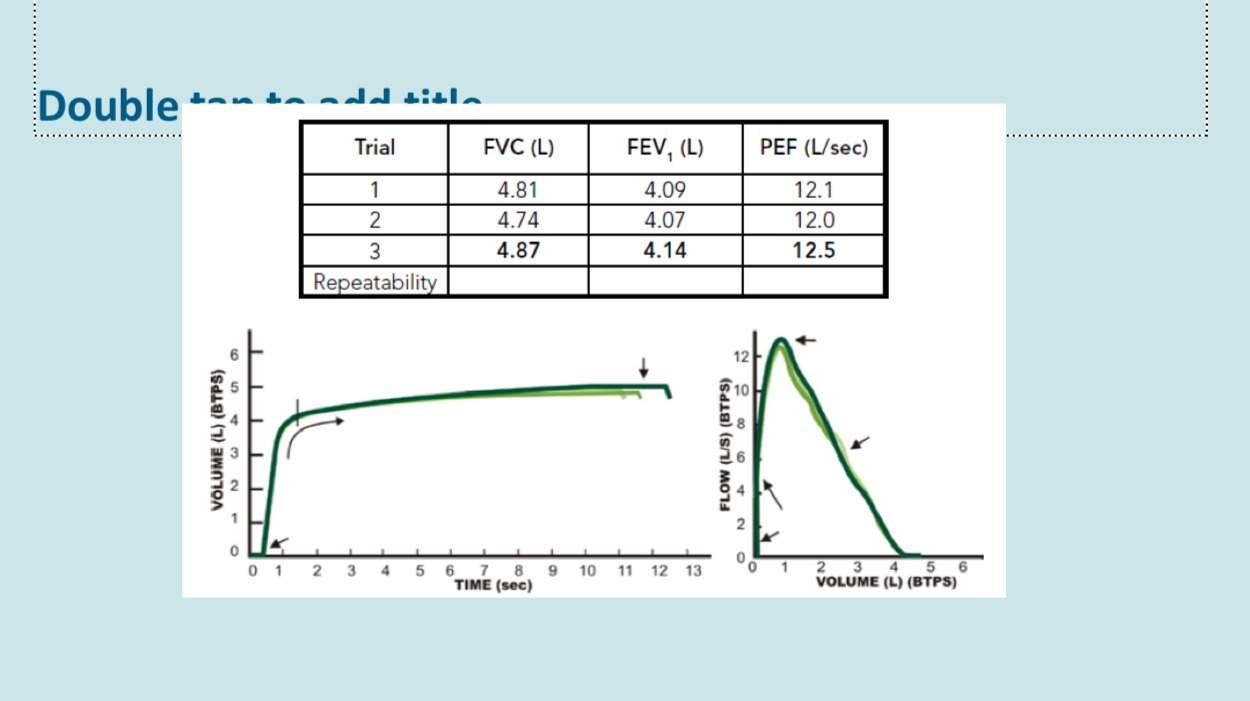
Repeatability criteria
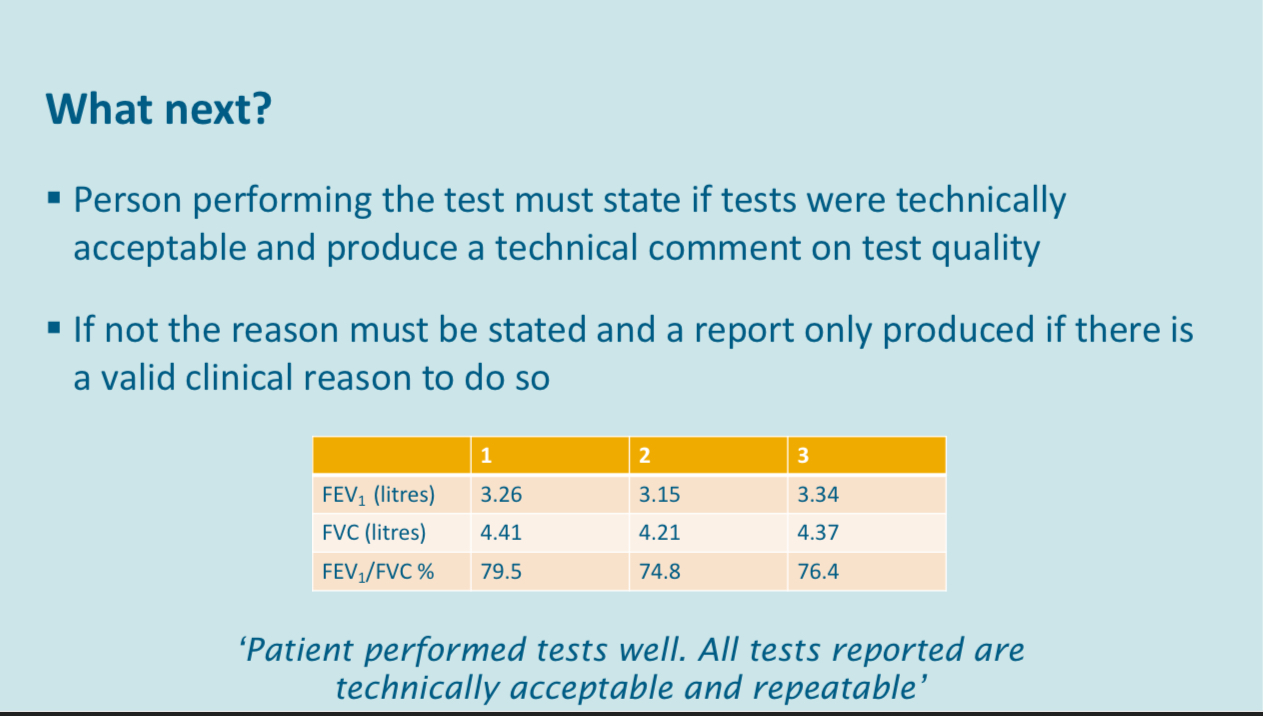
3 technically acceptable results selected from up to 8 efforts
The chosen values for FVC and FEV1 should not differ from the next best values for FVC and fev1 by more than 150 ml
Reported the highest FEV1 and FVC - these can come from any one of the 3 efforts meeting repeatability criteria, some of the equipment will select the best calculated from a combination of FEV1 and fvc, but this is not recommended
Acceptability criteria
aim to achieve the best results possible, the patients may n to achieve all the acceptability criteria but the results may still be used with clinical discretion, as long as these documented and taken into consideration when interpreting results
The patient needs to be continually observed to ensure that their test technique is correct, and encouraged throughout in order to exhale both as hard and fast as possible, and until they are completely empty
What factors may affect lung volume
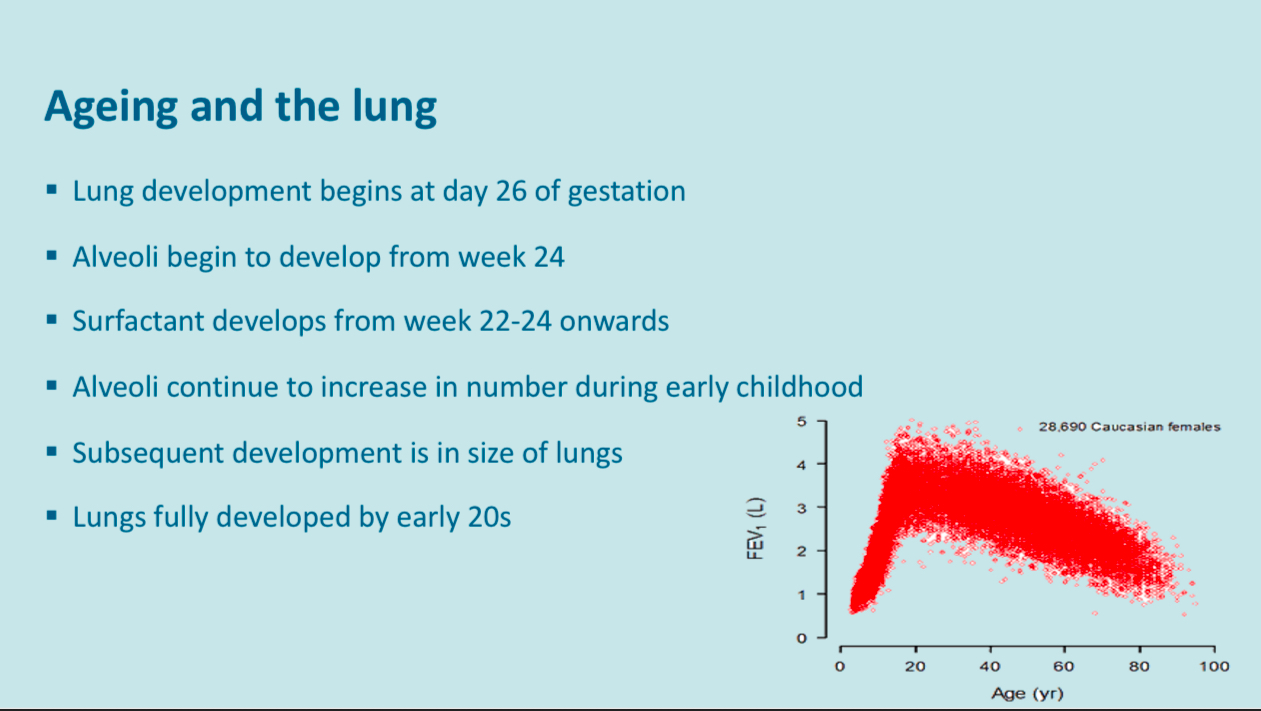
age
Height
Sex
Ethnicity
Children with similar lungs until puberty, males have broader shoulder and increase in trunk and chest digestions, for a given height, males lung volumes will be greater than female
Caucasians have a greater lung volume than any other ethnicity

Creating predicted values
representative sample of healthy subjects so non smokers
Drawn from the general population (ideally)
Exclude those with respiratory disease
Past and present medical history
Physical examination
Chest x ray
Step in transition from paediatric to adult reference values, reference values for Caucasians only need to adjust for non - Caucasian patients and extrapolate values for patients > 70 years old
The reference values are calculated for each patient on their ages birth, height, sex and ethnicity. The predicted values are created from populations of subject with no known lung disease and who are non smokers. There are many difference references values available and the results should state which predicted values are being used
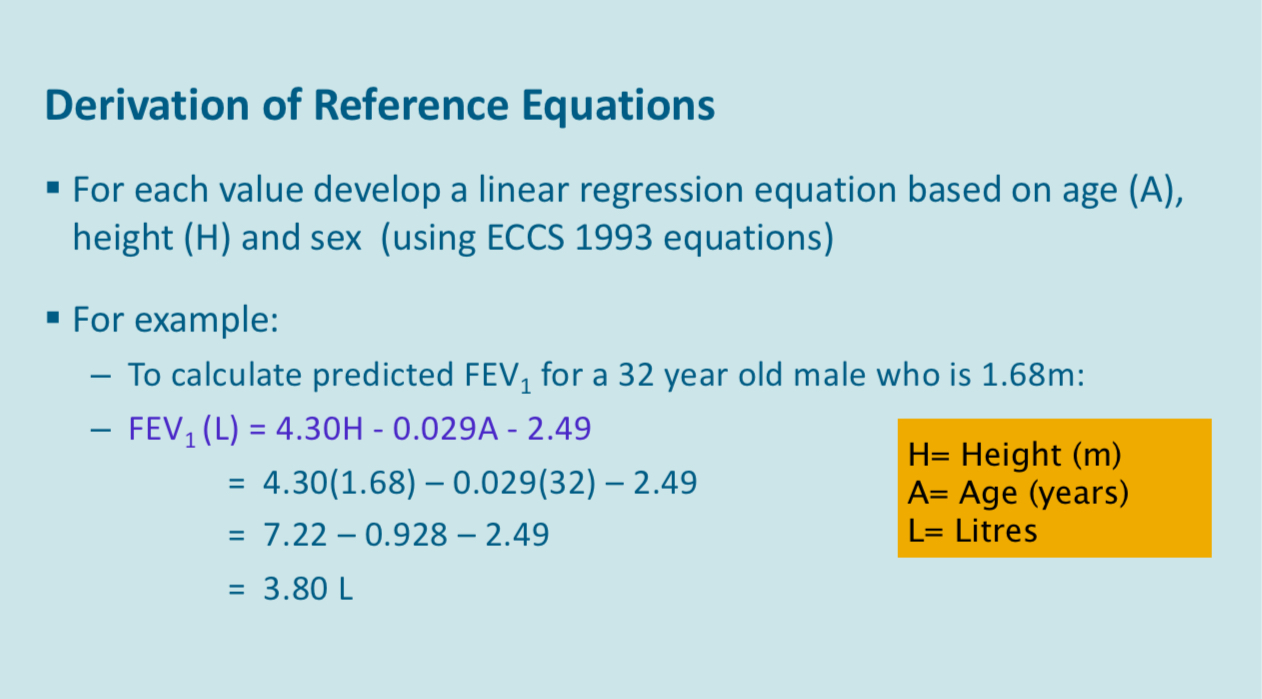
Extra info
