Topic 1 - Key Concepts
1/287
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
288 Terms
What are eukaryotic cells?
Cells with a nucleus like plant and animal cells.
What are prokaryotic cells?
Cells without a nucleus like bacteria.
Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic - Cells without a nucleus like bacteria. They are smaller, simpler and multicellular.
Eukaryotic - Cells with a nucleus like animals. They are larger, more complex and unicellular.
Are prokaryotes smaller or bigger than eukaryotes?
Smaller.
Are eukaryotes smaller or bigger than prokaryotes?
Bigger.
Are prokaryotes more complex or simpler than eukaryotes?
Simpler.
Are eukaryotes more complex or simpler than prokaryotes?
More complex.
Are animal cells eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Eukaryotic.
Are plant cells eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Eukaryotes.
Are animal cells prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes.
Are plant cells prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes.
Are animal cells uni or multicellular?
Multicellular.
Are plant cells uni or multicellular?
Multicellular.
Name one subcellular structure where genes are found within the eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus.
Name one subcellular structure where genes are found within the prokaryotic cells.
Chromosomal or Plasmid DNA.
List the 5 organelles found in an animal cell.
Cell Membrane.
Nucleus.
Ribosomes.
Mitochondria.
Cytoplasm.
List the 8 organelles found in a plant cell.
Cell Membrane.
Cytoplasm.
Nucleus.
Mitochondria.
Ribosomes.
Cell wall.
Chloroplasts.
Permanent vacuole.
Which 3 organelles does a plant cell have that an animal cell doesn’t?
Cell wall.
Chloroplasts.
Permanent vacuole.
What is the function of the nucleus?
Controls the activities of the cell + stores DNA (genetic information).
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Controls what enters and exits the cell.
What is the function of the mitochondria?
Site of aerobic respiration to release energy to the cell.
What is the function of the ribosomes?
Site of protein synthesis.
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
Jelly like substance where chemical reactions take place + holds other cells in place.
What is the function of the cell wall?
Supports and strengthens the cell.
What is the function of the chloroplasts?
Site of photosynthesis and contains chlorophyll (green pigment) to absorb light energy for photosynthesis to take place.
What is the function of the permanent vacuole?
Cell sap stored here + maintains shape of the cell.
What is the cell wall made out of in plant cells?
Cellulose.
What does the chloroplast contain?
Chlorophyll.
Name the subcellular structure involved in the translation of genetic material in protein synthesis.
Ribosome.
Name the subcellular structure that controls which substances leave the cell.
Cell membrane.
What is the difference between a cell membrane and cell wall?
Cell membrane - Controls what enters and exits the cell.
Cell wall - Made out of cellulose to support and strengthen the cell.
Why do plant roots not require chloroplasts?
They are underground and cannot photosynthesise without sunlight so therefore do not require chloroplasts.
List the 8 organelles found in a bacterial cell.
Cell Membrane.
Cell Wall.
Slime coat.
Plasmid DNA.
Chromosomal DNA.
Flagella.
Ribosomes.
Cytoplasm.
Are bacteria cells prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes.
Are bacteria cells prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Prokaryotic.
Is bacteria uni or multicellular?
Unicellular.
Does bacteria have a jelly or slime coat?
Slime coat.
What are the two types of DNA found in bacterial cells?
Plasmid DNA + Chromosomal DNA.
What is plasmid DNA?
Small circular loops of DNA with useful genes.
What is chromosomal DNA?
Large pieces of DNA floating freely in the cytoplasm to controls the cells activities and replication.
What is the difference between plasmid and chromosomal DNA?
Plasmid - Small circular loops of DNA with useful genes.
Chromosomal - Large pieces of DNA floating freely in the cytoplasm.
What is the function of the flagellum?
Tail used to help the cell move.
What is the function of the slime coat?
Protects the bacteria cell.
Is a bacterial cell smaller or bigger than animal/plant cells?
Smaller.
Is a bacterial cell wall made of cellulose?
No.
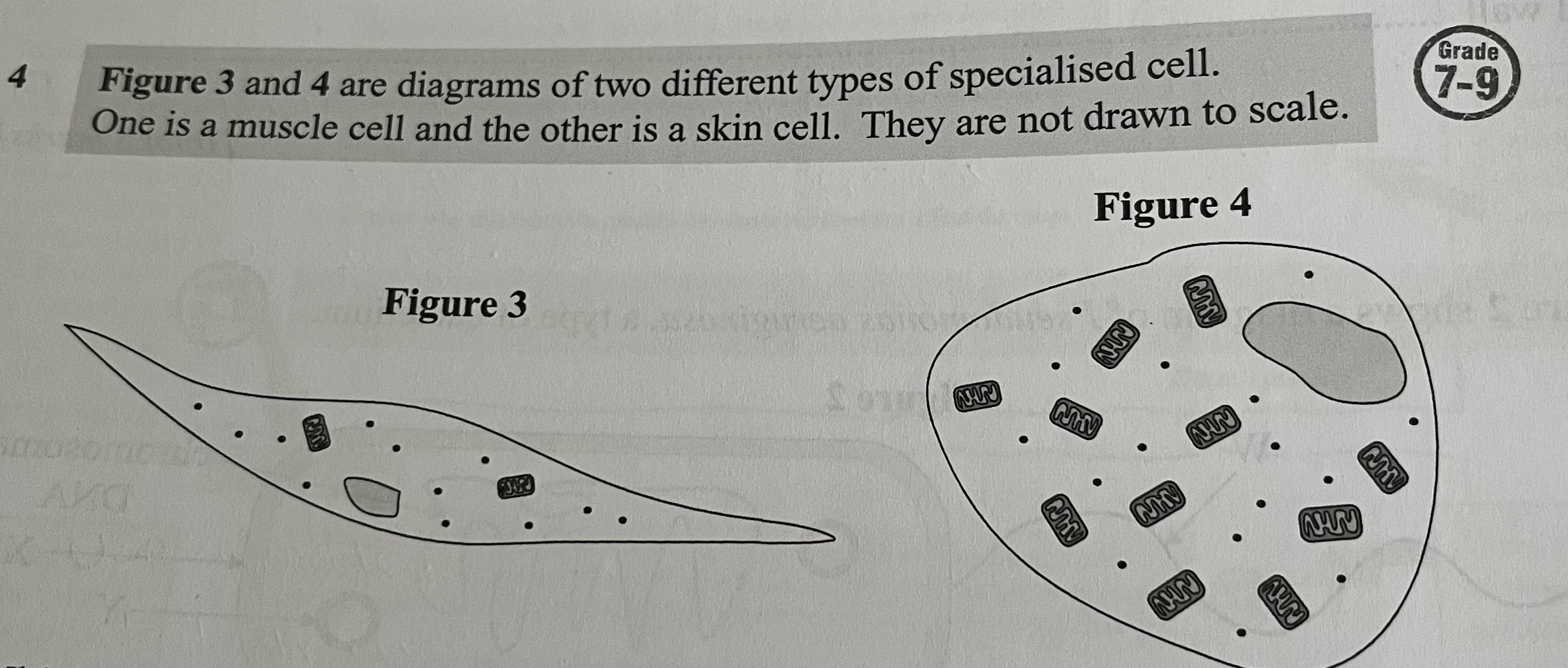
Which cell is more likely to be a muscle cell? Explain your answer.
Figure 4 since it contains more mitochondria. Muscle cells require a lot of energy to contract so will need lots of mitochondria as this is the site of respiration which transfers energy to the cell.
Define: Specialised cell
Cells adapted to carry out a particular function in the body.
What is the egg cell?
Female gamete.
What is the female gamete?
Egg cell.
What is the function of the egg cell?
Carry female DNA.
Be fertilised by sperm cell.
Develop into an embryo.
What adaptations do egg cells have?
Cytoplasm.
Haploid nucleus.
Cell membrane.
Jelly coat.
What is a sperm cell?
Male gamete.
What is the male gamete?
Sperm cell.
What is the function of the sperm cell?
Fertilise egg cell.
Transport male’s DNA to egg cell of the female.
What adaptations do sperm cells have?
Flagellum.
Mitochondria.
Acrosome.
Haploid nucleus.
What is a haploid nucleus?
Nucleus containing half the number of chromosomes as a diploid nucleus - 23 chromosomes.
What is the name of a nucleus containing 23 chromosomes?
Haploid nucleus.
How many sets of chromosomes does a haploid cell have?
1 set.
What is a diploid nucleus?
Nucleus containing 23 pairs of chromosomes - 46 chromosomes.
What is the name of a nucleus containing 46 chromosomes?
Diploid nucleus.
How many sets of chromosomes does a diploid cell have?
2 sets.
What type of nucleus does a sperm cell have?
Haploid.
What type of nucleus does an egg cell have?
Haploid.
Why do gametes need a haploid nucleus?
When the gametes join to form a zygote, it will have a diploid nucleus with the correct number of chromosomes (2 sets, 23 pairs, 46 chromosomes).
Why do sperm need flagellum?
To move to the egg cell and fertilise it.
Why do sperm cells have lots of mitochondria?
So they can respire to release energy to the cell and have therefore have enough energy to move to the egg cell and fertilise it.
What does the acrosome contain?
Digestive enezymes.
What is the function of the acrosome?
Contains digestive enzymes to break down/digest the egg cells cell membrane.
Describe the role of a sperm's acrosome in fertilisation.
Contains digestive enzymes to break down/digest the egg cells cell membrane.
How can we describe a sperm cells head?
Streamlined head.
What does the head of the sperm cell contain?
Acrosomes.
How does a streamlined head help a sperm cell to function?
Helps sperm cell to move faster and contains acrosomes to break down egg cells membrane.
What is the function of the cytoplasm in the egg cell?
Contains nutrients for the growth of the embryo.
Does an egg cell have a jelly or slime coat?
Jelly coat.
What does the cell membrane and jelly coat do after fertilisation?
They harden so only 1 sperm cell can enter the egg cell.
Why can only 1 sperm cell enter the egg cell?
Cell membrane and jelly coat harden after fertilisation, only allowing 1 sperm through.
Why do egg cells not need a tail?
Cilia line the oviducts to sway the egg from the oviduct to the uterus.
Describe how the egg cell is adapted for its function.
Cell membrane/Jelly coat - Hardens after fertilisation so only 1 sperm can enter.
Cytoplasm - Contains nutrients for developing embryo.
Haploid nucleus - Contains half of the DNA (23 chromosomes) so when it merges with the sperm cell, it forms a zygote with a the correct number of chromosomes in a diploid nucleus (46 chromosomes).
Describe how the sperm cell is adapted for its function
Flagellum - Tail to move towards the egg cell and fertilise it.
Lots of mitochondria - Respires to provide energy for the cell to swim towards the egg cell.
Acrosome - Contains digestive enzymes to break down the egg cells cell membrane.
Haploid nucleus - Contains half of the DNA (23 chromosomes) so when it merges with the egg cell, it forms a zygote with a the correct number of chromosomes in a diploid nucleus (46 chromosomes).
Elephant body cells contain 56 chromosomes. How many chromosomes will an elephant egg cell contain?
28.
What are ciliated cells?
A cell that lines certain tubes in the body and has cilia on its surface.
Where are ciliated cells found?
Oviducts and respiratory system.
What adaptation does the ciliated cell have?
Cilia.
What are cilia?
Microscopic hairs that sway to move substances/particles.
Describe how the ciliated epithelial cell is adapted for its function.
Has microscopic hairs called cilia that sway to move substances like mucus up the throat.
When an egg cell is ready to be fertilised, it moves through the fallopian tubes towards the uterus explain how the ciliated epithelial cell might be involved in this process.
Cilia cells beat backwards and forwards to move the egg cells along the inner surface of the fallopian tubes towards the uterus.
What adaptations do the small intestines have?
Villi, microvilli and capillaries.
What are the villi?
Folds in the small intestine.
What are the microvilli?
Microscopic folds in the small intestine.
How do microvilli increase the rate of absorption in the small intestine?
Increase surface area to increase rate of absorption/diffusion of substances as there are more places for substances to be absorbed.
How do capillaries increase the rate of absorption in the small intestine?
Increase constant blood supply to increase rate of absorption of nutrients.
Describe how the small intestine is adapted for its function
Viili + Microvilli - Increase the surface area, allowing absorption of nutrients into the blood to take place faster and more efficiently.
Thin cell membrane - Increase the rate of absorption of nutrients into the blood.
Capillaries - Increase constant blood supply so that nutrients can be absorbed quickly.
What is the role of a microscope?
To magnify cells so that we can see the actual structures in more detail.
Where is the slide viewed from on microscope?
Stage.
What is the function of the stage?
Where the slide is viewed from.
Which lens on a microscope do we look through?
Eyepiece lens.
Which lens on a microscope magnifies the image?
Objective lens.
What is the function of the eyepiece lens?
To look through.
What is the function of the objective lens?
To magnify the image.
A microscope has three different objective lenses - x4, x10 or x40. Which lens should a students select first when viewing her cells?
x4.