BU288 - Midterm 1: Important Topics
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topics that could show up on final: Midterm 1: Lecture 2 - Research (Slides 1-4) Lecture 3 - Personality (Slides 5-11) Lecture 4 - Learning (Slides 12-15) Lecture 5 - Perception (Slides 16-35 Lecture 6 - Values, Attitudes, and Work Behaviour (Slides 36-59)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What is the difference between an Independent Variable (IV) and a dependent variable (DV) ?
An Independent variable is a predictor
A Dependent variable is the outcome
→ An independent variable predicts the dependent variable
What is a mediating variable?
A mediating variable explains a relationship between an IV and DV
Ex:
Sleep → Alertness → Performance
Sleep (IV) increases alertness (mediating) which increases performance (DV)
What is a moderating variable?
Moderating variables CHANGE a relationship between an IV and DV
Ex: Sleep or work motivation is zero, performance is going to be zero
What is the Hawthorne Effect?
Refers to a favorable response of subjects in an experiment to a factor other than the IV or treatment
Research subjects tend to change their behaviour because they’re being studied.
What is Personality?
How they think, feel and behave - psychological characteristics influence how they act
Predicts behaviour
Ex: Performance
How to describe personality?
The most researched ‘comprehensive model’ of personality suggests that there are 5 major dimensions of personality
“The Big Five”
What is the Five-Factor Model of Personality?
Openness to Experience
Curious, imaginative, artistic, and original
Conscientiousness
Responsible, dependable, persistent, and organized
Extraversion
Sociable, gregarious, and assertive
Agreeableness
Good-natured, cooperative, and trusting
Neuroticism
Nervous, depressed, and insecure under stress
→ All on their own continuum from low to high
Ex: Introversion to extraversion
What is the Locus of Control?
Locus of Control: A set of beliefs about whether one’s behavior is controlled mainly by internal or external factors
→ Internals believe that the opportunity to control their own behaviour resides within themselves
→ Externals believe that external forces determine their behaviour
What is self-esteem?
The degree to which a person has a positive self-evaluation
People with high self-esteem have favourable self-images
People with low self-esteem have unfavourable self-images
What is General Self-Efficacy?
Refers to an individual’s beliefs in his or her ability to perform successfully in a variety of challenging situations
What are implications of Employee’s Personalities?
Person-Job Fit
Match/compatibility of individuals’ traits and job requirements (tasks) is important for performance
Person-Organizational Fit
Match/compatibility of individuals’ traits and organization’s values and culture is important for satisfaction, (decreased) turnover, and a number of other work outcomes.
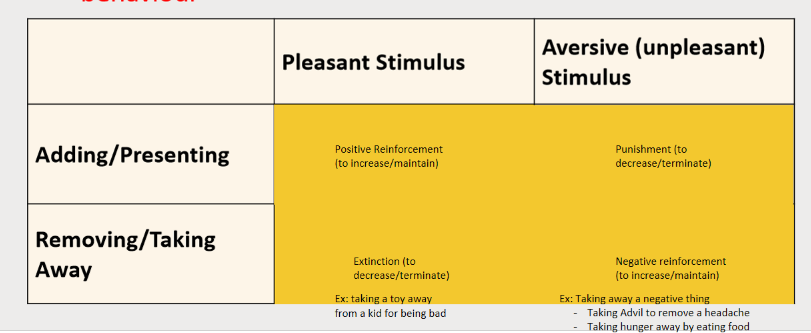
What is the Operant Learning Theory:
Uses rewards and punishment to modify behaviour
People repeat behaviours that bring them satisfaction and pleasure, and stop those that bring them dissatisfaction and pain
Explain more about decreasing and reinforcing behaviour in the Operant Learning Theory:
Increase probability of behaviour: 2 ways to reinforce behaviour
Decrease probability of behaviour: 2 ways to decrease behaviour
What is Social Cognitive Theory?
Emphasizes the role of cognitive processes in regulating people’s behaviour
People Learn by:
Observing the behaviours of others and regulating their own behaviour
Personal Factors and environmental factors work together and interact to influence people’s behaviour
What are the components of SCT?
Observational Learning
Process of imitating the behaviour of others
Self-Regulation
The use of learning principles to regulate one’s own behaviour
Self efficacy beliefs
What is Perception?
Process used to organize and interpret sensory impressions to give meaning to the environment
Perception is the basis for understanding others and their behaviour
Often bias or flawed
What are factors that influence perception?
The Context
Time, Work Setting, Social Setting, etc.
The Target
Size, Background, Proximity, Similarity, Motion, etc.
The Perceiver
The attitudes, motives, experience, expectations, interests, social identity, etc.
What are the Basic Biases in Perception?
Primacy and Recency Effects
Reliance on Central Traits
Implicit Personality Theories
Projection
Stereotyping
What is the Primacy Effect?
The reliance on early cues
Primacy often has a lasting impact
What is the Recency Effect?
The tendency for a perceiver to rely on recent cues or last impressions
What are Central traits?
Central traits are personal characteristics of a target person that are of particular interest to a perceiver
Common central traits: Physical appearance, height, weight
What is an Implicit Personality Theory?
Personal theories that people have about which personality characteristics go together
Perhaps you expect hardworking people to also be honest, or people of average intelligence to be most friendly
What is Projection?
Projection: The tendency for perceivers to attribute their own thoughts and feelings to others.
Sensible perceptual strategy
Can serve as a perceptual defence
What is Stereotyping?
Stereotyping: The tendency to generalize about people in a social category and ignore variations among them.
Race, gender, ethnic
What are some consequences of Stereotyping?
Can result in unfairness for individuals
Can result in decreased organizational performance
What is the Self-Fulfilling Prophecy?
Tendency for someone’s expectations about another to cause that individual to behave in a manner consistent with those expectations
What is the Pygmalion Effect?
“someone's high expectations improves our behavior and therefore our performance in a given area. It suggests that we do better when more is expected of us.”
What is the Golem Effect?
“Low expectations placed on individuals lead to poorer performance.”
What is a Stereotype Threat?
The feeling of being at risk of confirming negative stereotypes about his/her social group
What is Attribution?
Attribution: The process by which we assign causes or motives to explain people’s behaviour
About understanding why
Dispositional (internal) or situational (external) factors
Explain Kelley’s Attribution Model:
Motives are judged through:
Consensus: Do most people engage in the behaviour, or is it unique to this person?
Consistency: Does the person engage in the behaviour regularly consistently?
Distinctiveness: Does the person engage in the behaviour in many situations, or is it distinctive to one situation?
What are the Three Biases in Attribution?
Although observers often operate in a rational, logical manner in forming attributions, our attributions are NOT always correct
Fundamental attribution error
Actor-observer effect
Self-serving bias
What is Fundamental Attribution Error?
To explain other people’s behaviour, we tend to over-emphasize dispositional explanations and under-emphasize situational explanations
We blame people first, not the situation
What is Actor-Observer Effect?
Actors and observers tend to view causes of actor’s behaviour differently
Observer: Emphasizing dispositional factors (FAE)
Actor: Emphasizing situational factors
What is Self-Serving Bias?
Tendency to take credit for successful outcomes but not for failures
We succeed because of our intelligence; we failed because of bad luck
What are values?
Values: A broad tendency to prefer certain states of affairs over others
Have to do with what we consider “good” and “bad”
Define Culture:
A shared meaning system that includes norms, values, symbols, and behavioural scripts
What is Work Centrality?
The valuation of work differs across cultures
People for whom work was a central life interest work more hours
What are the four basic dimensions of Hofstede’s Study?
Power Distance
Uncertainty avoidance
Masculinity/Femininity
Individualism/collectivism
Explain High Power distance Vs. Low Power Distance
High Power Distance: Accept and expect a hierarchy of power, where everyone has their place within the hierarchy (Mexico, China, Russia)
Low Power Distance: Dislike of hierarchy/inequality, prefer to equalize the distribution of power (Canada, U.S.A)
Define Uncertainty Avoidance:
The extent to which a culture feels threatened by, and avoids, uncertainty and ambiguity.
Explain High Uncertainty Avoidance Vs. Low Uncertainty Avoidance:
High Uncertainty Avoidance:
Stress rules and regulations, hard work, conformity, and security
Low Uncertainty Avoidance:
Less concerned with rules, conformity, security, and hardwork
Risk taking is valued
Define Masculinity/Femininity:
The valuing of achievement, competitiveness, assertiveness, and materialism (Masculinity).
Explain More Masculinity Vs. More Femininity:
More Masculine:
Firmer gender roles, focus on economic performance
More Feminine:
Looser gender roles, sexual equality, and focus on quality of life
Define Individualism/Collectivism:
The preference to act as individuals rather than as member of groups
Explain Individualistic cultures Vs. Collectivistic cultures:
Individualistic Cultures:
Stress independence, individual initiative, and privacy
Collectivistic Cultures:
Favour interdependence and loyalty to one’s group
Tighter social framework, expectations that group members to look after and protect each other
Define Attitudes:
A tendency to evaluate a specific target in a consistent way
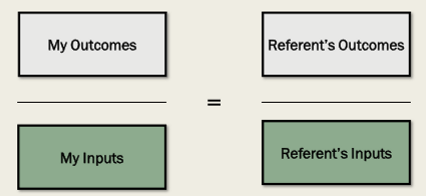
Define Equity Theory:
Individuals compare their job inputs and outcomes with those of others and then respond in ways to eliminate inequities
Equity is perceived when the following ratio is satisfied:
How do people respond to inequity?
Change inputs
Change outcomes
Adjust perceptions of self
Adjust perceptions of Others
Choose a Different Referent
Leave the field (job, etc.)
Three Basic Kinds of Fairness:
Distributive Fairness
Procedural Fairness
Interactional Fairness
What is Distributive Fairness?
Perceived fairness of outcomes people receive in social relationships
Allocation of rewards, resources
What is Procedural Fairness?
Perceived fairness of the way/process allocation decisions are made
Process is consistent, unbiased, allows 2-way communication, welcomes appeals
What is Interactional Fairness?
Perceived fairness of the treatment received during the decision-making process
Communicated all important information with respect and dignity
Three types of Organizational Commitment:
Affective commitment
Continuance commitment
Normative Commitment
What is Affective Commitment?
Want to stay
Interesting, satisfying work
Meeting expectations
What is Continuance Commitment?
Need to stay
Dependent on the job/organization (e.g. money)
Lack of alternative options for work
What is Normative Commitment?
Ought to stay
Identified with the organization, product, service, work team (i.e. loyalty)
Benefits that build a sense of responsibility to reciprocate; “owing” to the organization.
What are the consequences of Organizational Commitment?
All three forms of commitment REDUCE turnover intentions and actual turnover
Affective commitment is positively related to performance