Honors Chemistry - Chapter 3
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Atom
Smallest piece of an element that has all of the properties of that element
Nucleus
The central location of atoms, with protons and neutrons
Proton
1 amu
2nd discovered
positive charge
Neutron
1 amu
3rd discovered
no charge
Electron
0 amu
1st discovered
negative charge
Atomic number
# of protons in the nucleus of an atom
Atomic mass
# of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
Isotope
Atoms of the same element having different atomic masses
Ion
Atoms of the same element having different amounts of electrons (have charges)
Democritus
greek philosopher
believed that the universe was made of tiny uncuttable pieces
atomos → not to be cut, referring to the smallest piece of matter
John Dalton postulates
all matter is made of extremely small particles called atoms
atoms of the same element are alike in mass and size
atoms of different elements have different masses and sizes
atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed
atoms combine to form compounds in simple numerical ratios
in chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or destroyed
What does Dalton’s hard sphere model look like
A pool ball
What were JJ Thomsons conclusions from the cathode ray tube experiement
the electron is negatively charged
atoms can be divided
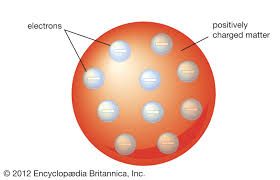
What did Thomsons plum pudding model look like and how does it differ from Daltons model
a chocolate chip cookie
it has electrons throughout positive base instead of all one thing
What did Robert Millikan discover form the oil drop experiment
the mass and charge of the electron
What are Ernest Rutherfords conclusions from the gold foil experiment
the atom is mostly empty space
most of the atoms mass is in the nucleus
the proton is positively charged
What did Rutherfords empty space or nuclear model look like and how does it differ from thomsons model
a cherry
the positive charge is only present in the middle instead of all throughout the atom

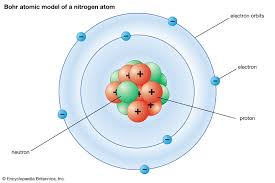
what did the Bohr model or planetary space model look like and how is it different form Rutherfords model
the solar system
the electrons orbit around the nucleus instead of staying put
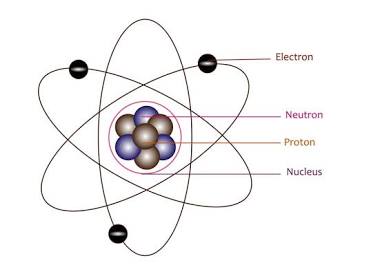
What did the quantum mechanical model look like and how is it different from Bohrs model
the electrons don’t orbit in definite paths, not fixed orbits
Law of multiple proportions
Atoms of two or more elements can combine in different ratios to form more than one compound
Law of conservation of mass
Total mass or reactants in any chemical reaction is exactly equal to the total mass of the products
Law of definite composition/proportion
A compound always contains two or more elements combined in definite proportions by mass
What particles belon in the nucleus of an atom
Protons and neutrons
What particles go in the orbitals or shells of an atom
Electrons
Which particles have mass
Neutrons and protons
What subatomic particles influence the average atomic mass
Protons and neutrons