Genes and Biological models
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:12 PM on 3/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
1
New cards
What did FJ Gall believe about phrenology?
That there was a 1-1 link between a brain region and function
2
New cards
Why do some people argue that brain imaging studies are “modern” phrenology?
Because there’s a very high rise in brain imaging studies, trying to connect brain regions to specific functions
3
New cards
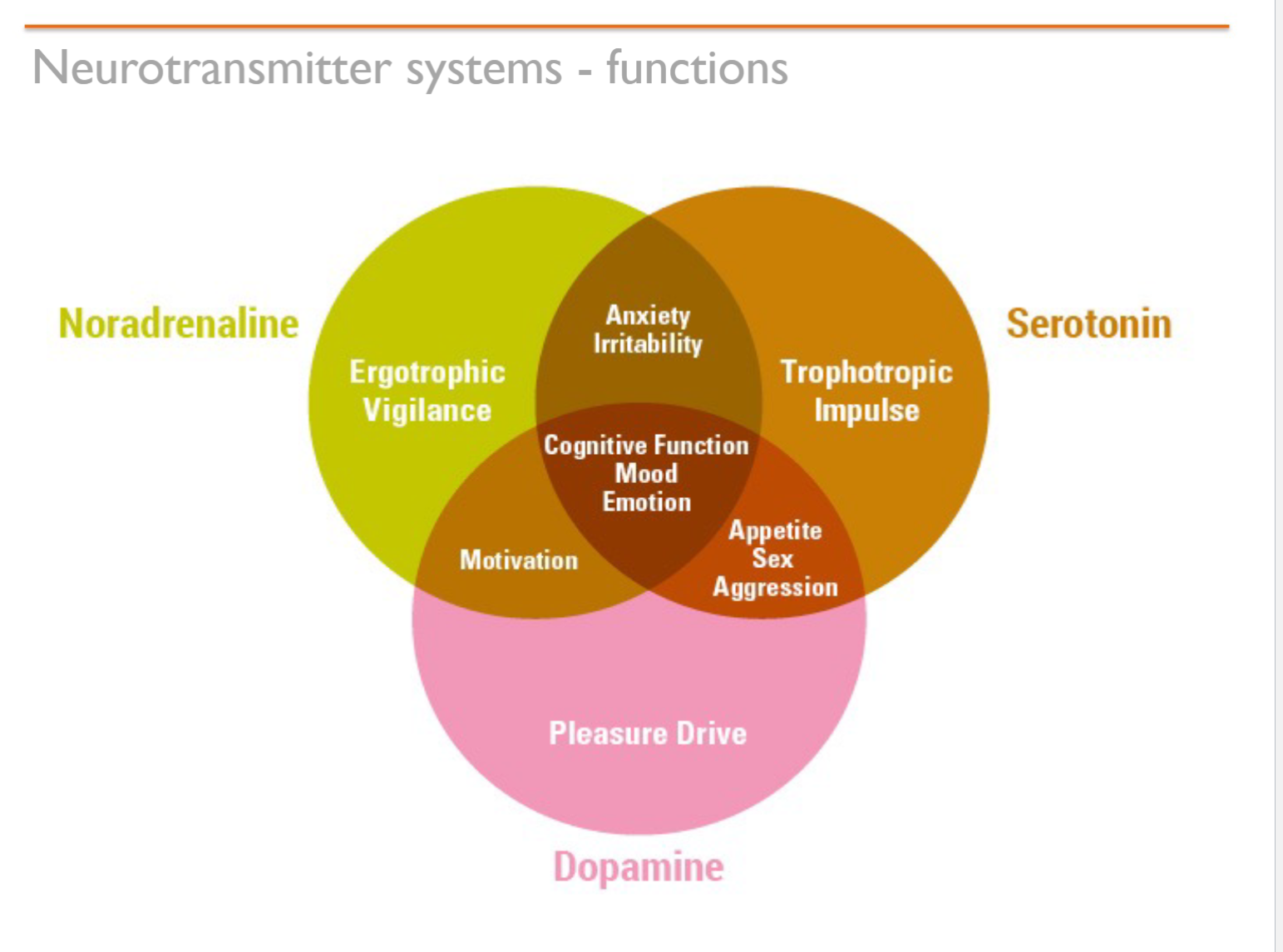
Neurotransmitters are proteins in the brain, of which there are three basic systems. What are they called and which is important for MAPD?
Amino acids, Mono-amines and peptides
Mono-amines (Serotonin, Dopamine & Adrenaline) are important for MAPD
Mono-amines (Serotonin, Dopamine & Adrenaline) are important for MAPD
4
New cards
What does the “emotion” network of the brain consist of?
•Amygdala \n •Conditioning, face processing \n •Serotonin \n •Norepinephrine
\
This network is also related a lot to other regions (for example, the cognitive control one)
\
This network is also related a lot to other regions (for example, the cognitive control one)
5
New cards
What does the “motivation” network of the brain consist of?
•Striatum \n •Motivation, Pleasure \n •Dopamine
\
It’s there for processing motivation and related to goal-directed activity and obtaining a reward
\
It’s there for processing motivation and related to goal-directed activity and obtaining a reward
6
New cards
What does the “cognitive control” network of the brain consist of?
•Prefrontal cortex \n •Working memory, emotion regulation \n
There for regulating emotions and motivational systems. In mental disorders, there’s often something off with the balance of the regulation (often lack of regulation in anxiety or mood disorders)
There for regulating emotions and motivational systems. In mental disorders, there’s often something off with the balance of the regulation (often lack of regulation in anxiety or mood disorders)
7
New cards
What does the “default mode” network of the brain consist of?
•PCC & vmPFC \n •Introspection
\
Also rumination, which is overly present in people w depression
\
Also rumination, which is overly present in people w depression
8
New cards
What did the study where people had to anticipate making a speech show?
They had higher heart rate and more stress, but in the control group, cognitive control kicked in whereas in the SAD group, cognitive control part barely communicated with the emotion part -- the emotion part takes over
9
New cards
Why is there an issue with statistical power in FMRI studies?
The sample sizes are very low (around 20-30), but the brain areas they’re studying are about 200,000, meaning there’s about 200,000 variables
Furthermore, you need a lot of subjects if the relationship between the brain regions and constructs is diffused and weak
Furthermore, you need a lot of subjects if the relationship between the brain regions and constructs is diffused and weak
10
New cards
How are MAPD represented in specific brain areas?
There are many more brain regions related to multiple terms than just one specific one
11
New cards
How do antidepressants work?
They affect the levels of serotonin, adrenaline and dopamine in the brain
12
New cards
Why is there the theory that depression is a disorder of the neurotransmitter systems?
Because antidepressants affect the neurotransmitter system. However, this is like saying headaches are caused by a lack of aspirin
13
New cards
How effective are antidepressants?
Not very effective if compared to placebo (Cohen’s D= 0.3), but the total effect (not compared to placebo) is quite high (0.8-1.4)
14
New cards
What are the placebo responses composed of?
* Effect of clinical management
* Expectations
* Natural course
* Regression to the mean
\
* Expectations
* Natural course
* Regression to the mean
\
15
New cards
What might be the future of placebo pills?
Open-labelled placebo has also been shown to work to some degree, but placebo in general is not as effective as psychotherapy
16
New cards
Why has it taken so long to realise the caveats of antidepressants?
* Publication bias
* Outcome reporting bias: results are initially negative, then positive (distorted reporting)
* Spin: negative results are interpreted positively
* Outcome reporting bias: results are initially negative, then positive (distorted reporting)
* Spin: negative results are interpreted positively
17
New cards
Candidate gene studies
Gene studies where you find a link between a specific gene and a mental illness and then test that gene
18
New cards
Fill in what goes where in the Venn diagram