AP Bio: Unit 4 - Intro to Cell Communication
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Signal Transduction Pathway
A series of steps linking a mechanical or chemical stimulus to a specific cellular response.
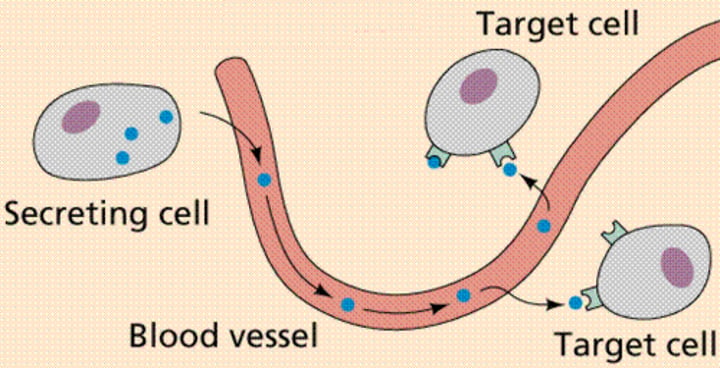
Hormones
In multicellular organisms, one of many types of secreted chemicals that are formed in specialized cells, travel in body fluids, and act on specific target cells in other parts of the body to change their functioning.
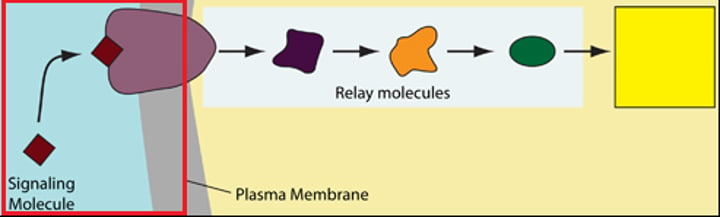
Reception
Reception is the target cell's detection of a signaling molecule coming from outside the cell. A chemical signal is "detected" when the signaling molecule binds to a receptor protein located at the cell's surface or inside of the cell.
Signal Transduction
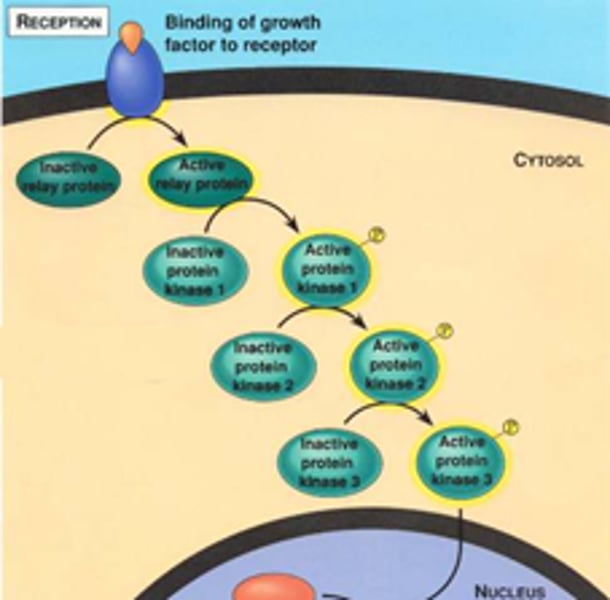
The binding of the signaling molecule changes the receptor protein in some way, initiating the process of transduction. The transduction stage converts the signal to form that can bring about a specific cellular response. Transduction sometimes occurs in a single step but more often requires a sequence of changes in a series of different molecules--a signal transduction pathway. The molecules in the pathway are often called relay molecules.
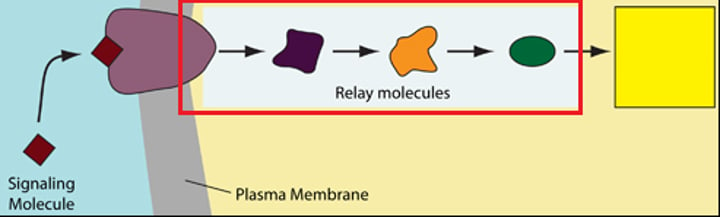
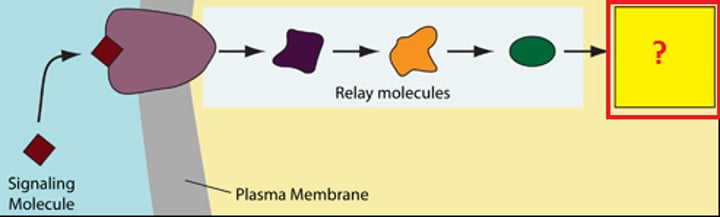
Response
The transduced signal finally triggers a specific cellular response. THe response may be almost any imaginable cellular activity--such as catalysis by an enzyme (for example, glycogen phosphorylase), rearrangement of the cytoskeleton, or activation of specific genes in the nucleus. The cell signaling process helps ensure that crucual activities like these occur in the right cells at the right time, in proper coordination with other cells of the organism.
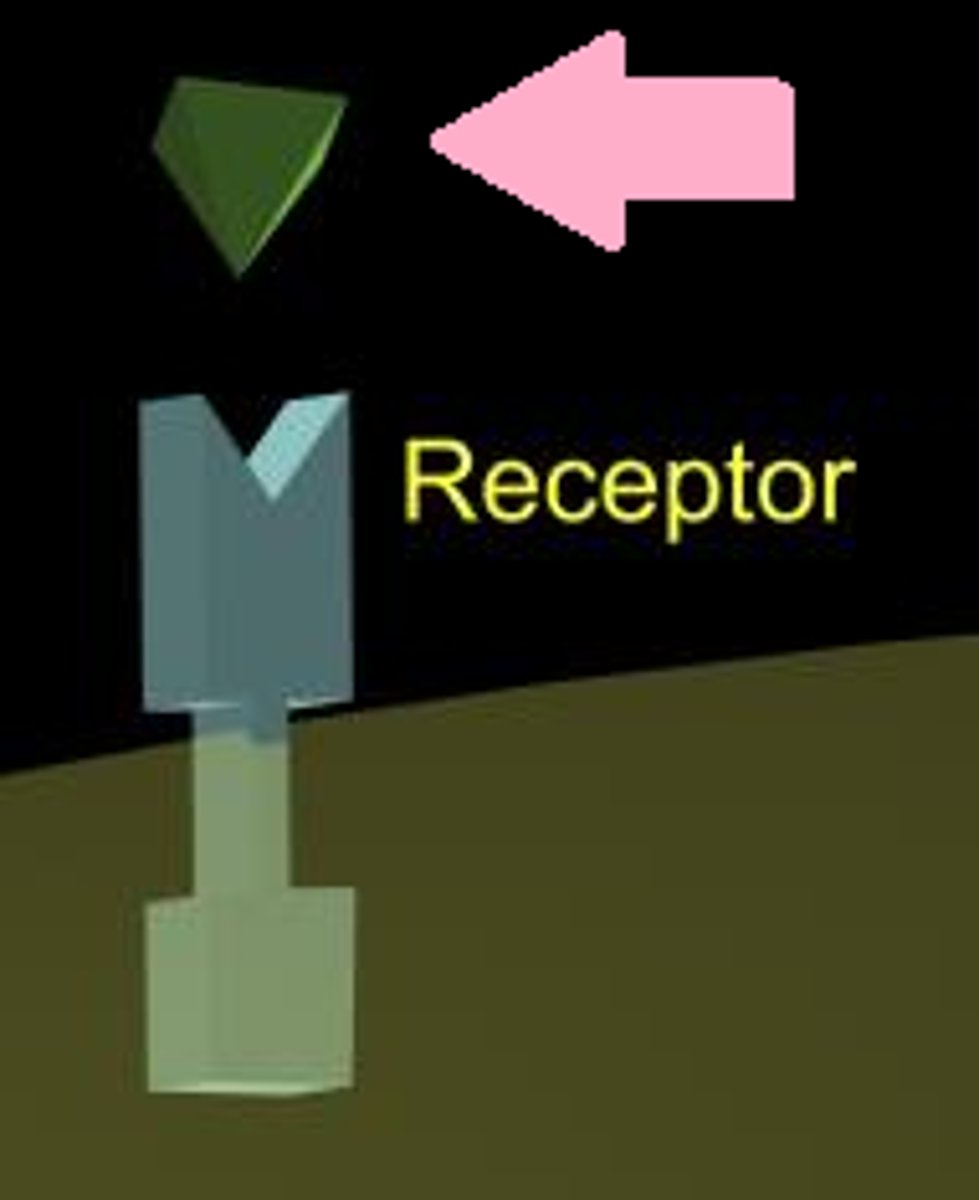
Ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to another molecule
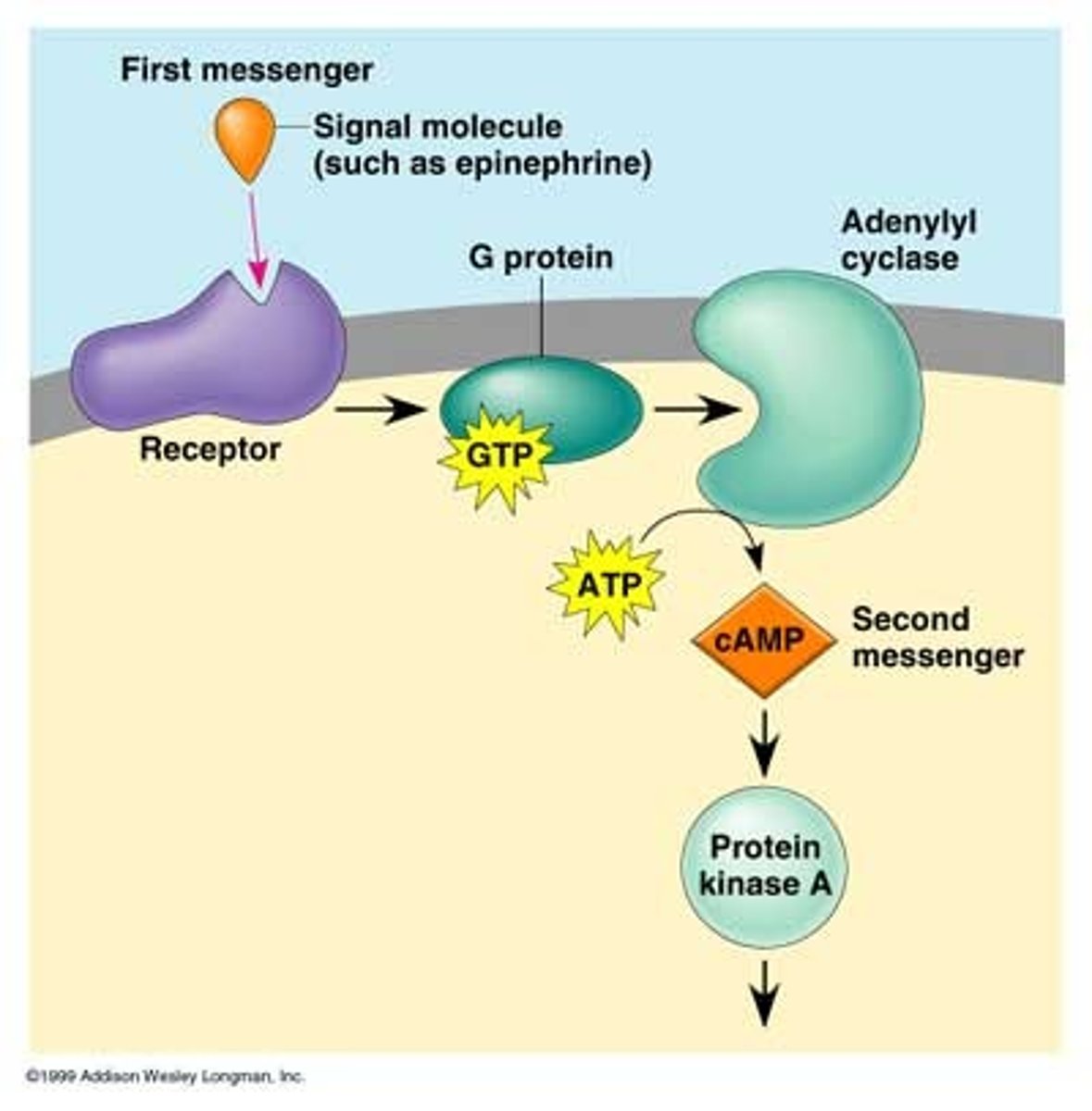
G-protein coupled receptor
A signal receptor protein in the plasma membrane that responds to the binding of a signaling molecule by activating a G protein. Also called a G protein-linked receptor.
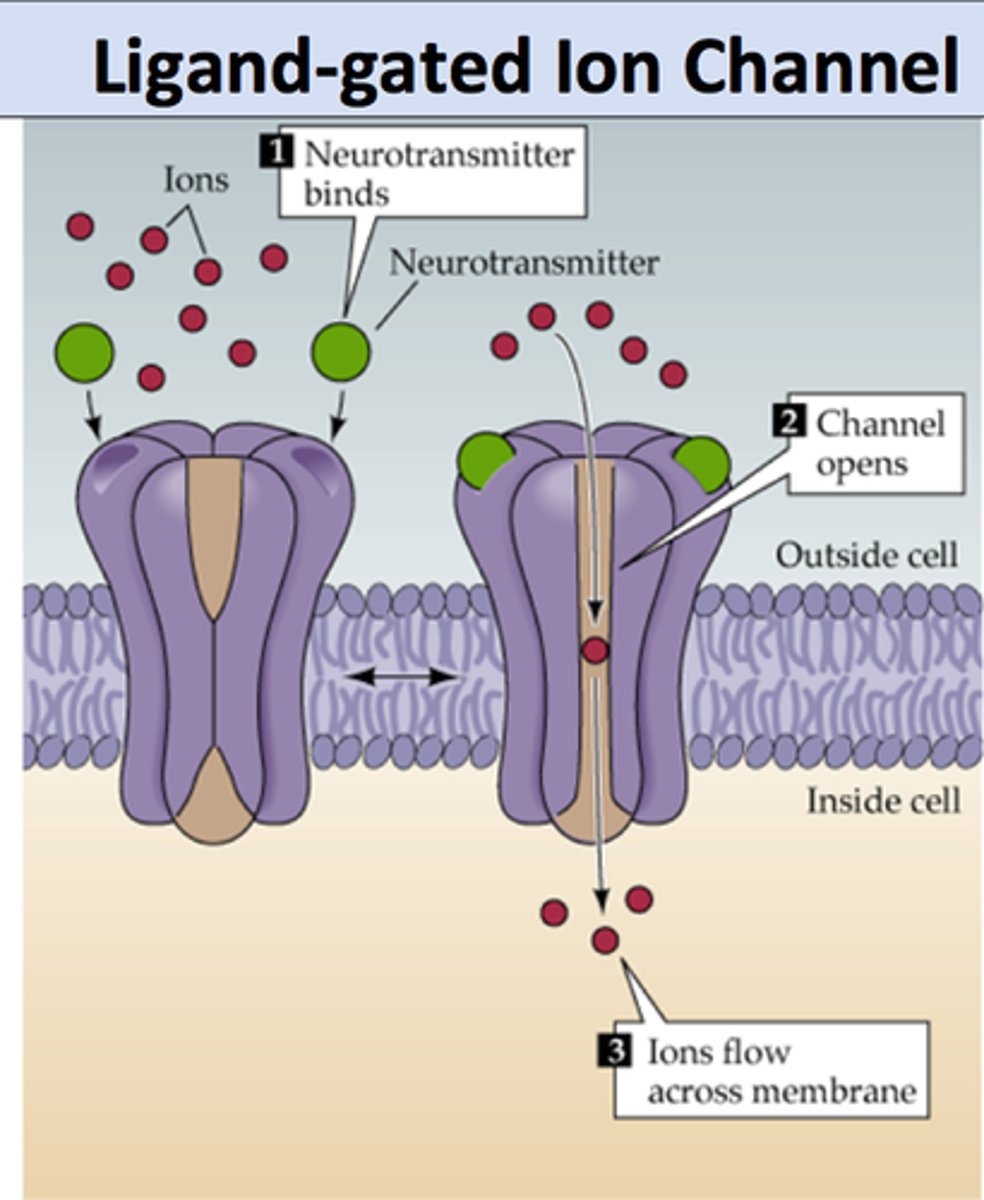
Ligand-gated ion channel
A protein pore in cellular membranes that opens or closes in response to a signaling chemical allowing or blocking the flow of specific ions.
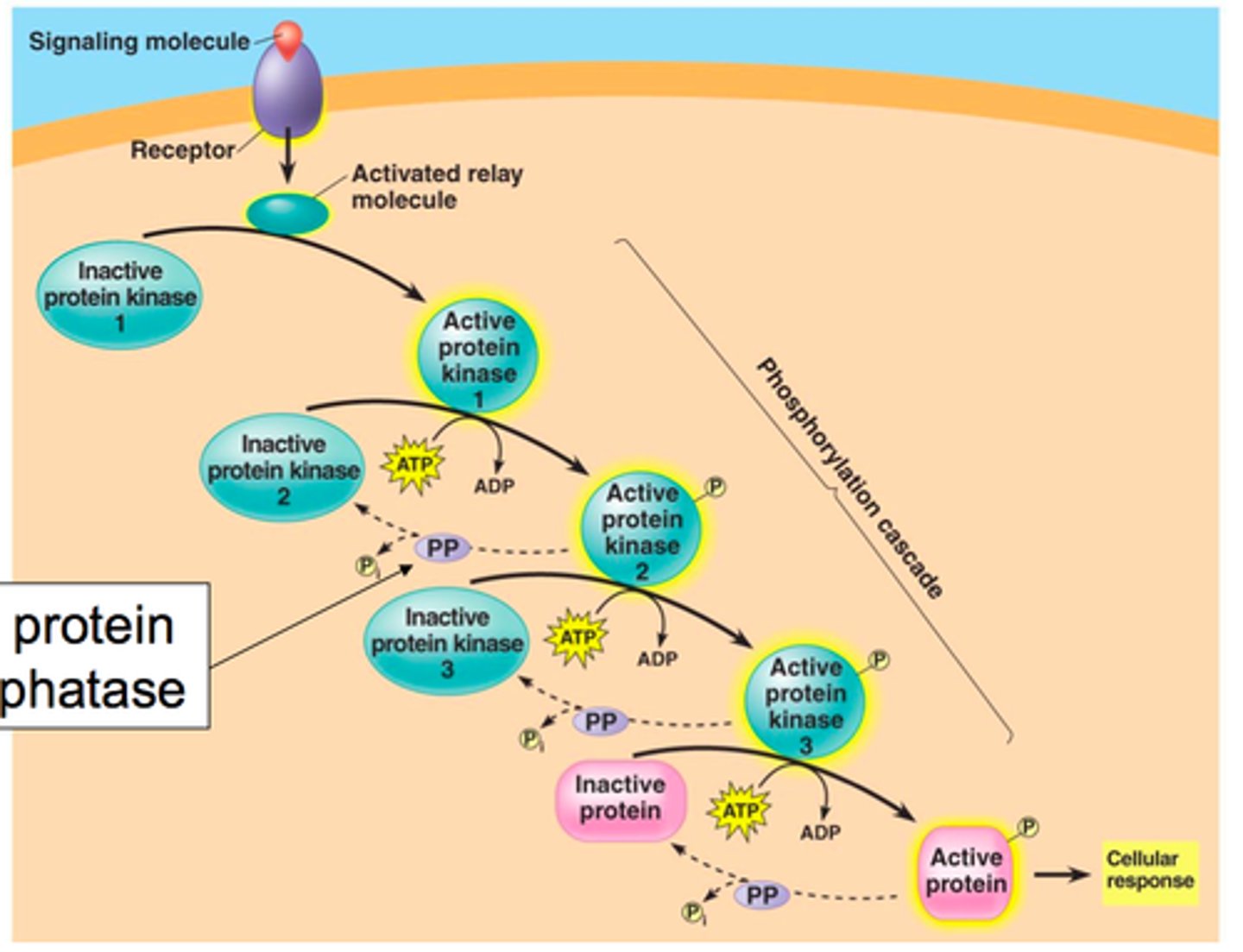
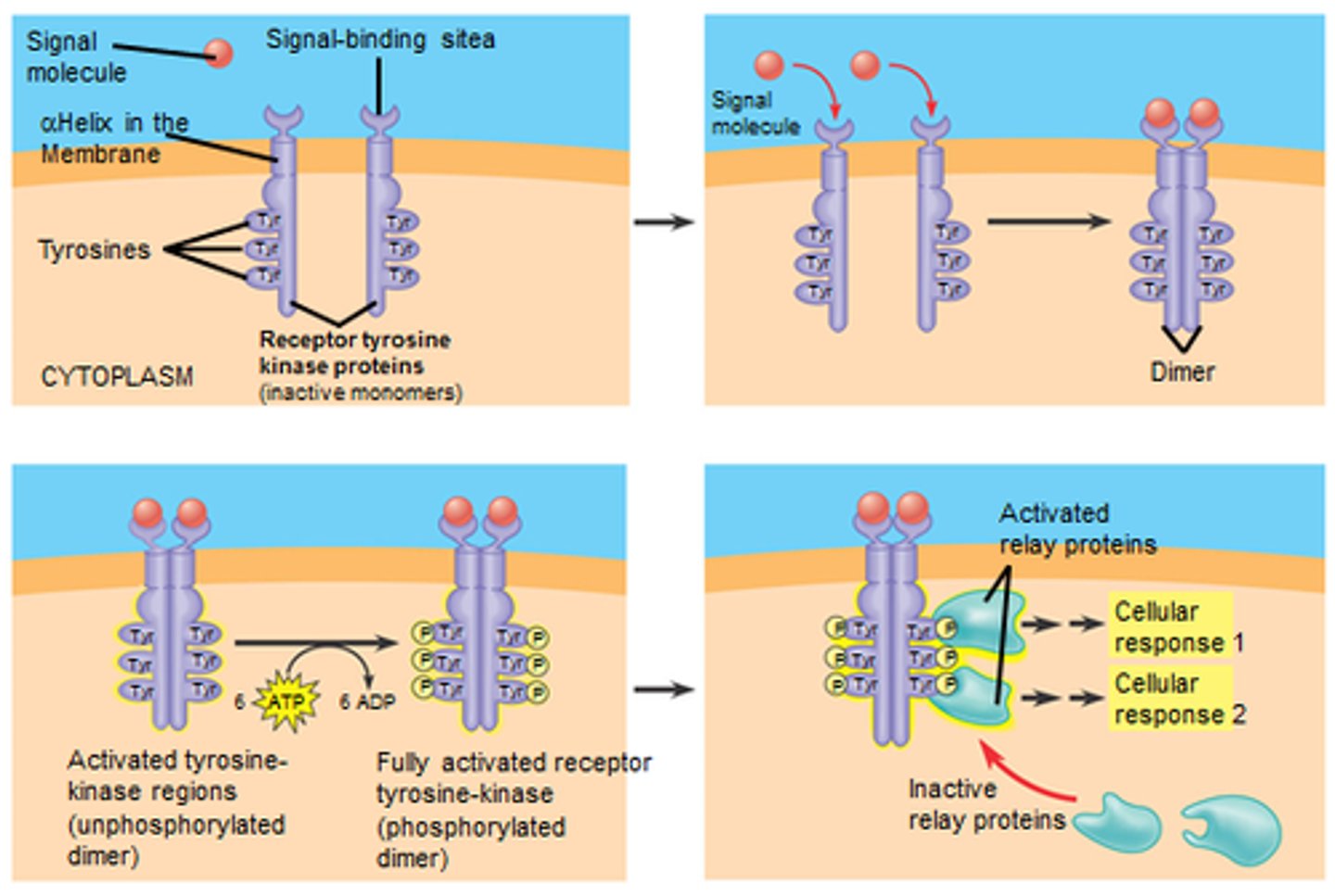
Protein kinase
An enzyme that transfers phosphates groups from ATP to a protein, thus phosphorylating the protein.
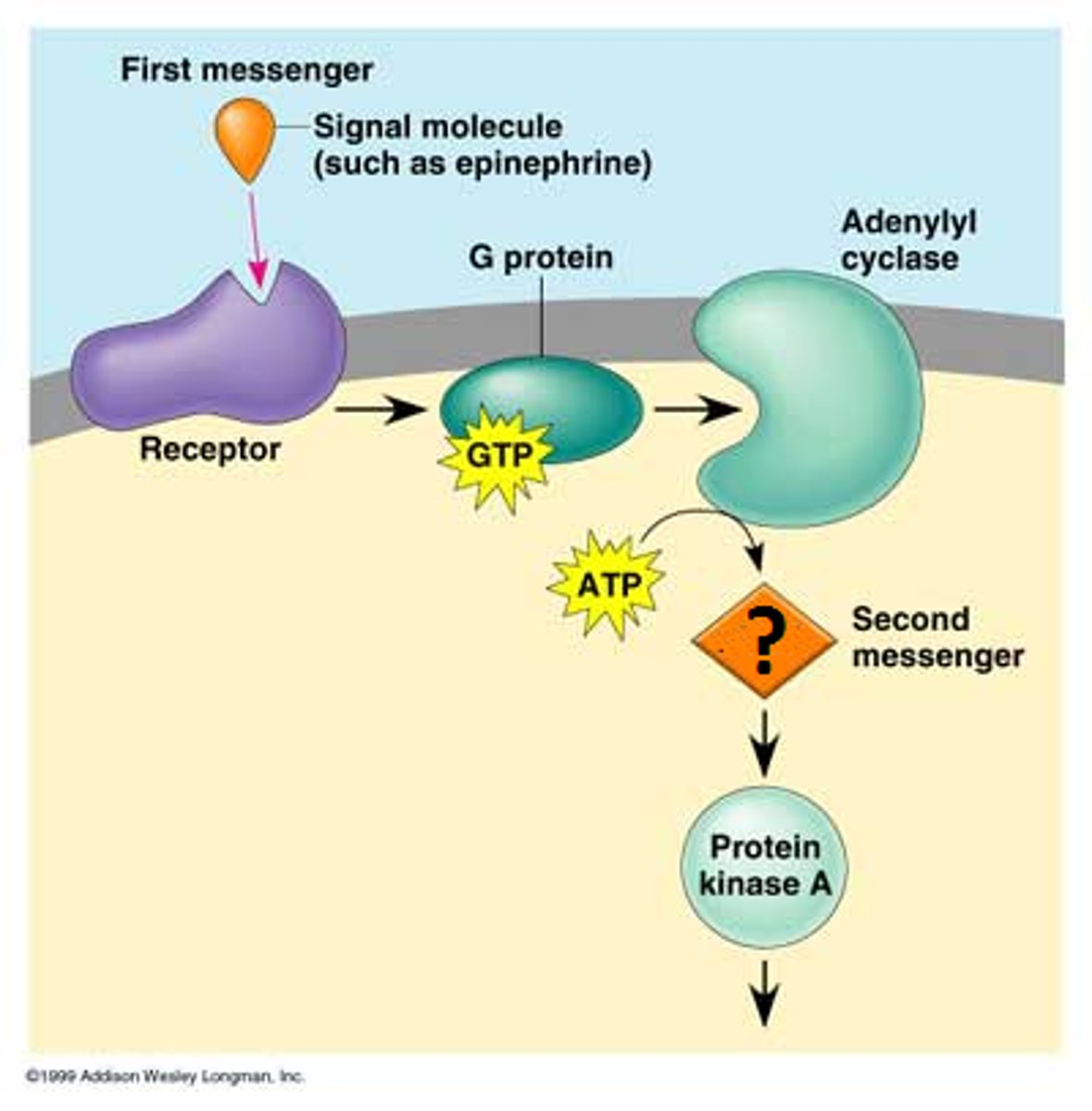
secondary messengers
A small, nonprotein, water-soluble molecule or ion, such as a calcium ion or cyclic AMP, that relats a signal to a cell's interior in response to a signaling molecule bound by a signal receptor protein.
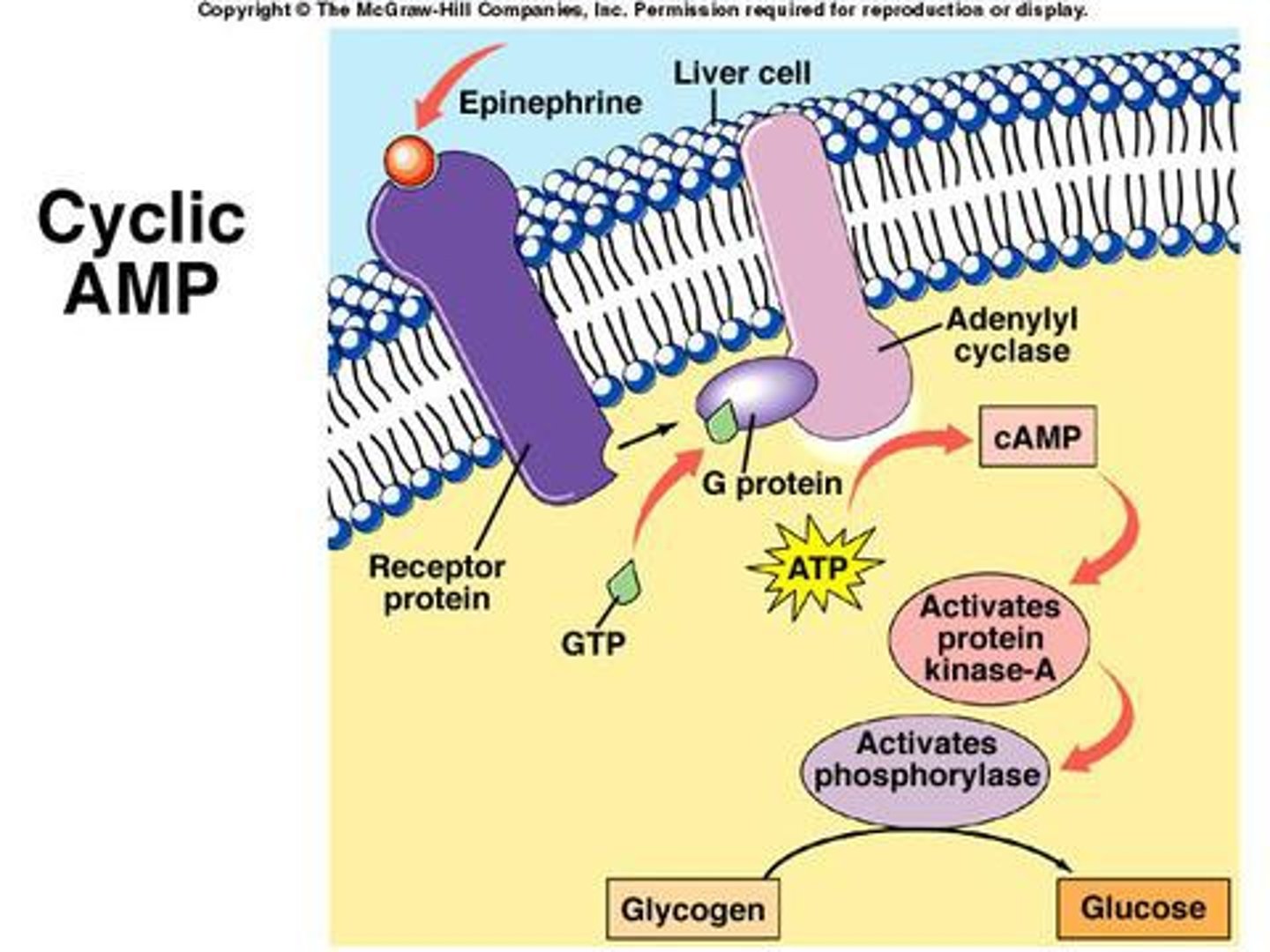
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, a ring shaped secondary messenger made from ATP that is a common intracellular signaling molecule (second messenger) in eukaryotic cells. It is also a regulator of some bacterial operations.
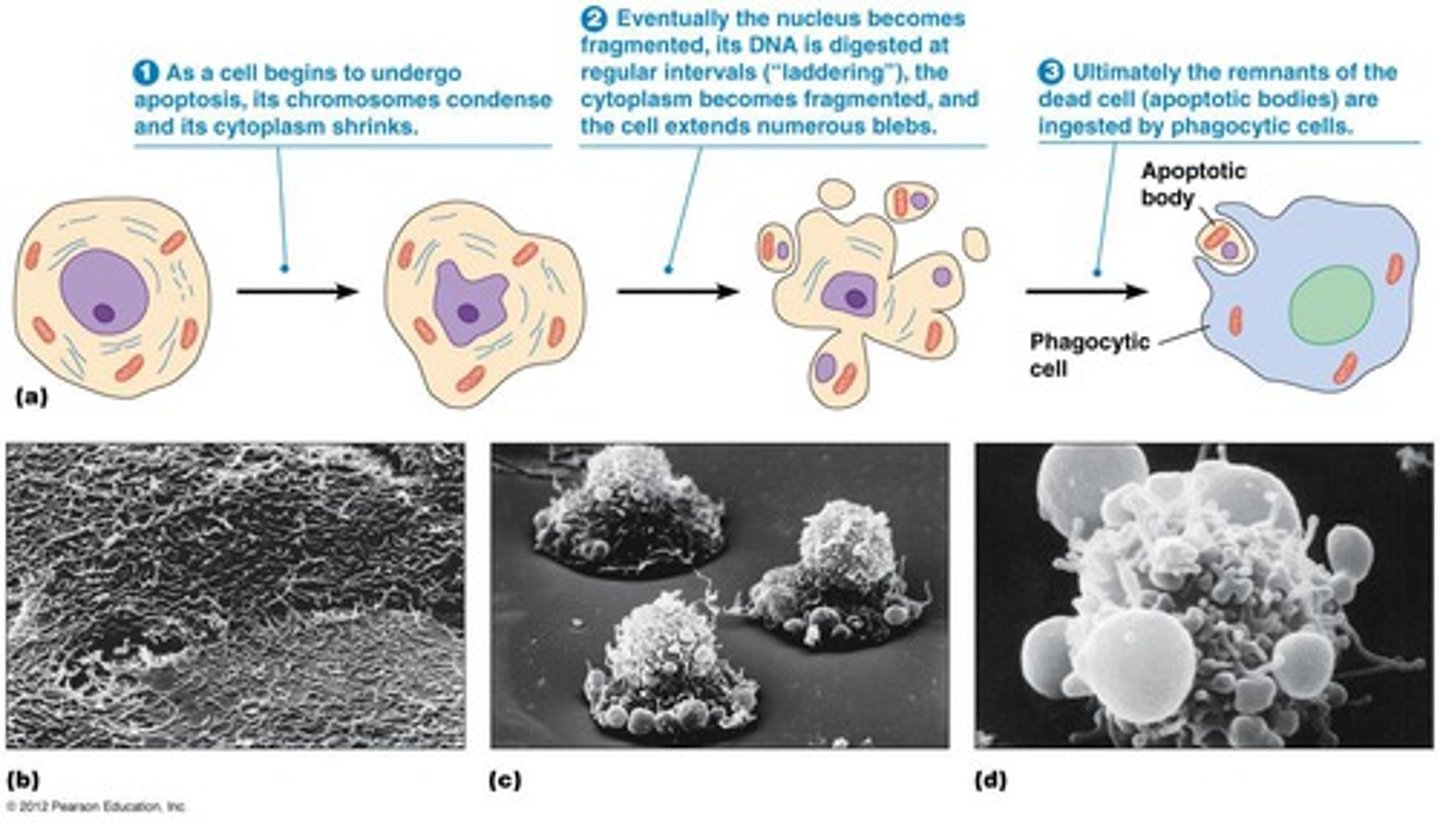
apoptosis
A program of controlled cell suicide, which is brought about by signals that trigger the activation of a cascade of suicide proteins in the cell destined to die.
phosphorylation cascade
A series of enzyme-catalyzed phosphorylation reactions commonly used in signal transduction pathways to amplify and convey a signal inward from the plasma membrane.