phys final
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
199 Terms
define homeostasis
the state of dynamic constancy in the internal environment
what is negative feedback
a stimulus causes an opposite reaction by the body to bring the body back to its normal state
list in order the negative feedback mechanisms
stimulus - change that made you move away from set point
sensor - receptors receive and send info
control - CNS receives change and figures out how to correct it; asses change around a set point
effector - fix deviation from the set point
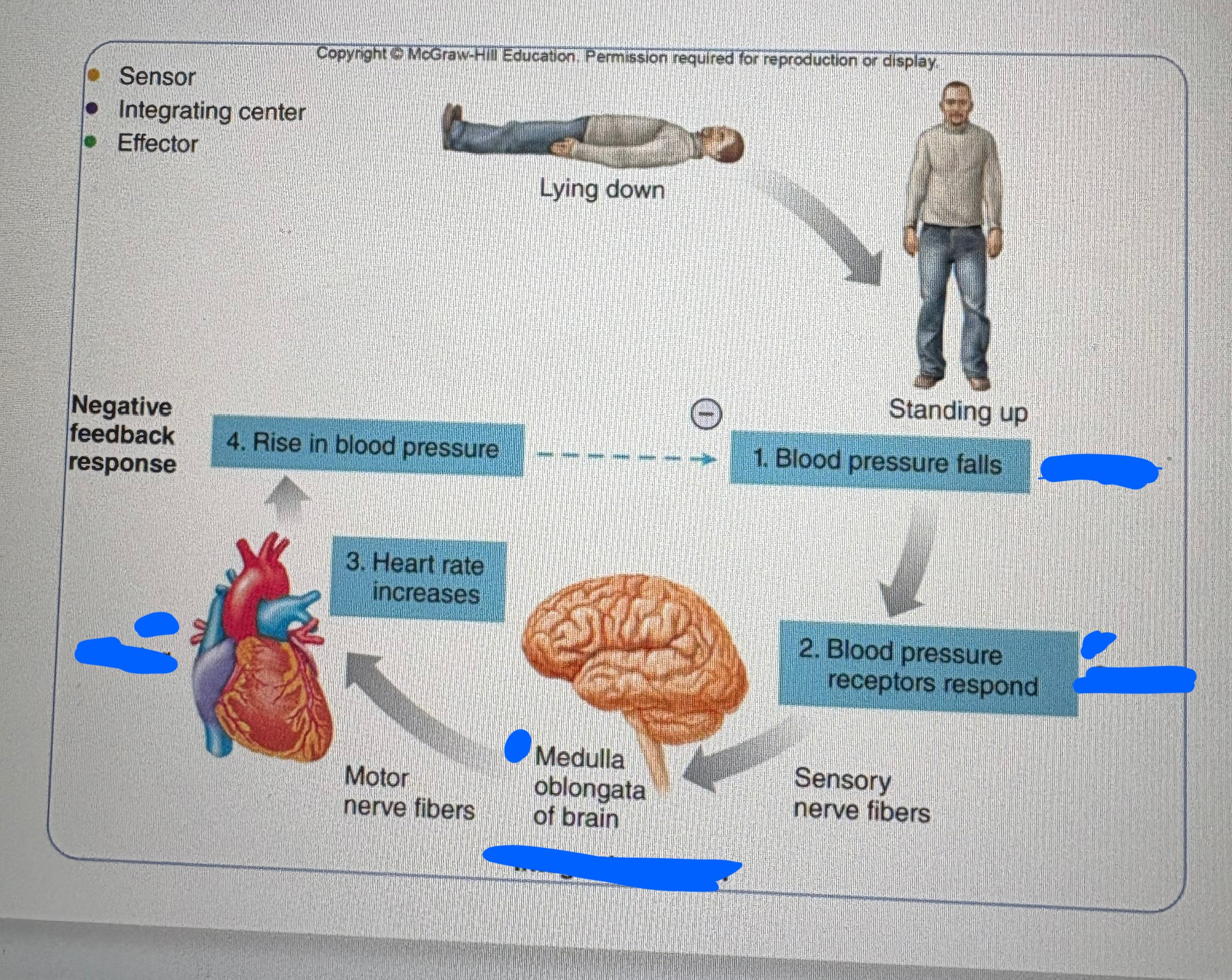
Look at the image and list the stimulus, sensor, integrating center, effector, and negative feedback response
stimulus: 1. BP falls
sensor: BP receptors respons
integrating center: medulla oblongata of brain
effector: heart - HR increases
negative feedback response: rise in BP
explain positive feedback
accelerates a process
stimulus: causes deviation from set point
cellular response amplifies deviation
further deviation leads to additional cellular response
and so on and so on until stimulus stops
end product stimulates process
what are the three muscle types and which ones are voluntary and which ones arent
skeletal - voluntary
cardiac - involunatary
smooth - involuntary
what is the function of muscle and tissue cells
generate mechanical force
what do neurons do and what do they make up
conduct electrical signals/impulses to other cells (communicate); they make up the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
what are epithelaial cells and tissue specialized for (hint - list both single layer epithelium and multiple layer epithelium)
single layer simple epithelium: secretion and absorption
multiple layer stratified epithelium: protection
____ fluid is 65% of all fluid; ___ fluid includes plasma and interstitial fluid
intracellular; extracellular
list the 4 primary tissue types
connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue
What substance helps chemical reactions occur?
catalyst
what are the special molecules that catalyze biochemical reactions
enzymes
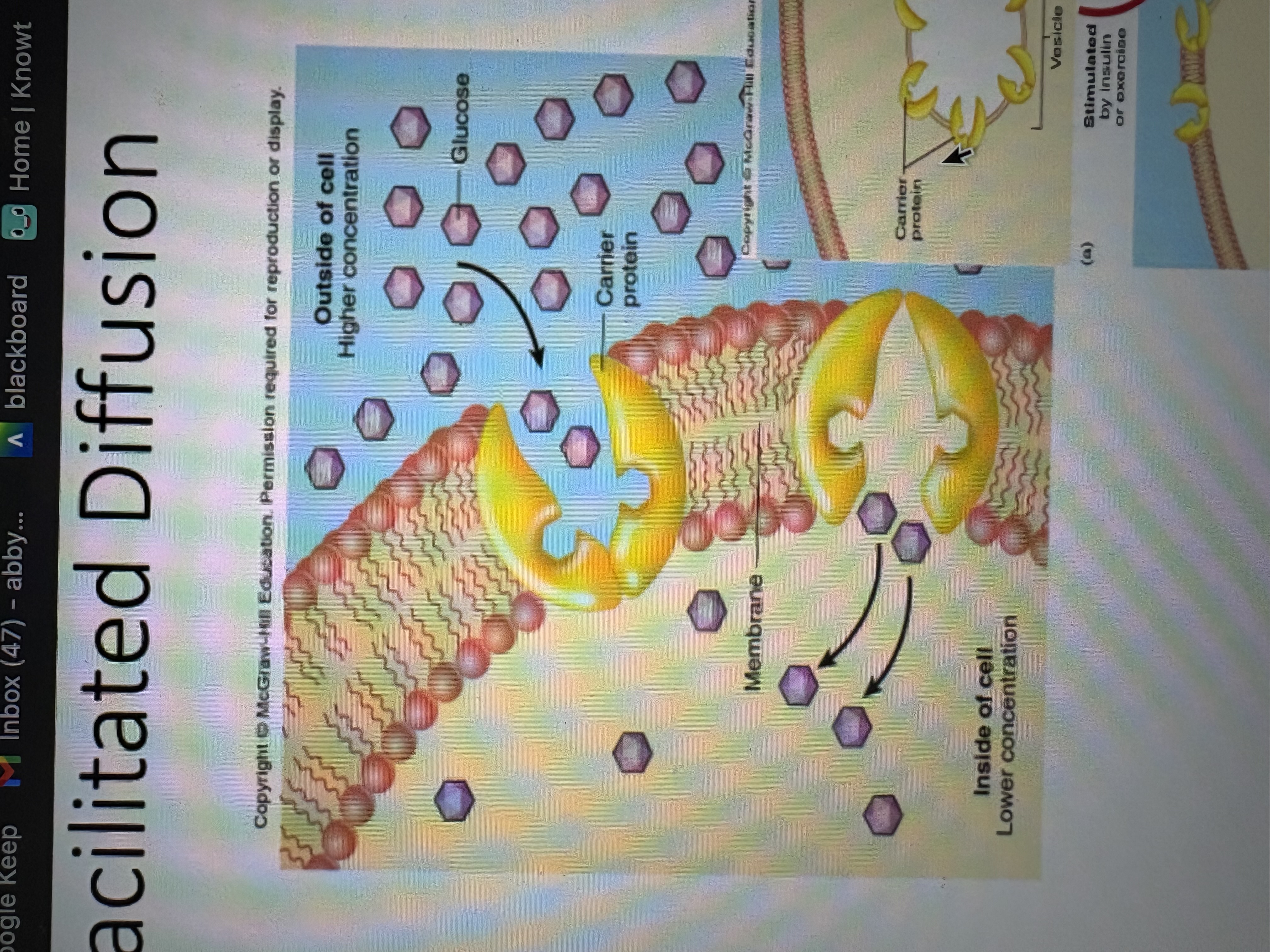
Describe facilitated diffusion
no energy is required
channel is specific and movements are diffusional
an example is glucose - they are polar molecules that need a transported
high to low movement through a membrane via protein channels.
describe active transport (general) - and then list the 2 types (you dont have to decribe the two types yet)
involves energy (ATP) to pump a molecule up its gradient
so low to high gradient
molecule specific and limited by saturation and the rate of conformational change
2 types: primary and secondary
describe Primary active transport
uses ATP pump; pump is an enzyme
The Na/K pump
3 Na⁺ ions out of the cell
2 K⁺ ions into the cell
per ATP molecule hydrolyzed.

describe the Na/K pump
Binding of 3 Na⁺ ions from the cytoplasm (inside the cell) to the pump.
ATP is hydrolyzed – one phosphate group is transferred to the pump (phosphorylation), providing energy.
Pump changes shape and releases 3 Na⁺ ions to the outside of the cell.
2 K⁺ ions from outside bind to the pump.
The phosphate group is released (dephosphorylation), causing the pump to return to its original shape.
2 K⁺ ions are released into the cytoplasm.
describe secondary active transport
like primary active transport, it moves from low to high gradient
differs because it does not directly use ATP
relies on the energy stored in the gradient of another ion (usually sodium, Na⁺) that was established by primary active transport.
requires that proteins have 2 binding sites (one for each molecule)
2 types: co-transport and counter transport
what are the 2 types of secondary active transport
co-transport and counter-transport
compare and contrast co-transport and counter-transport; make sure to list examples of each
both secondary active transport
Co:
symport
substances move in same direction
ex: K+,Cl- (renal system)
counter:
antiport
substances move in opposite direction
ex: HCO3-/Cl-
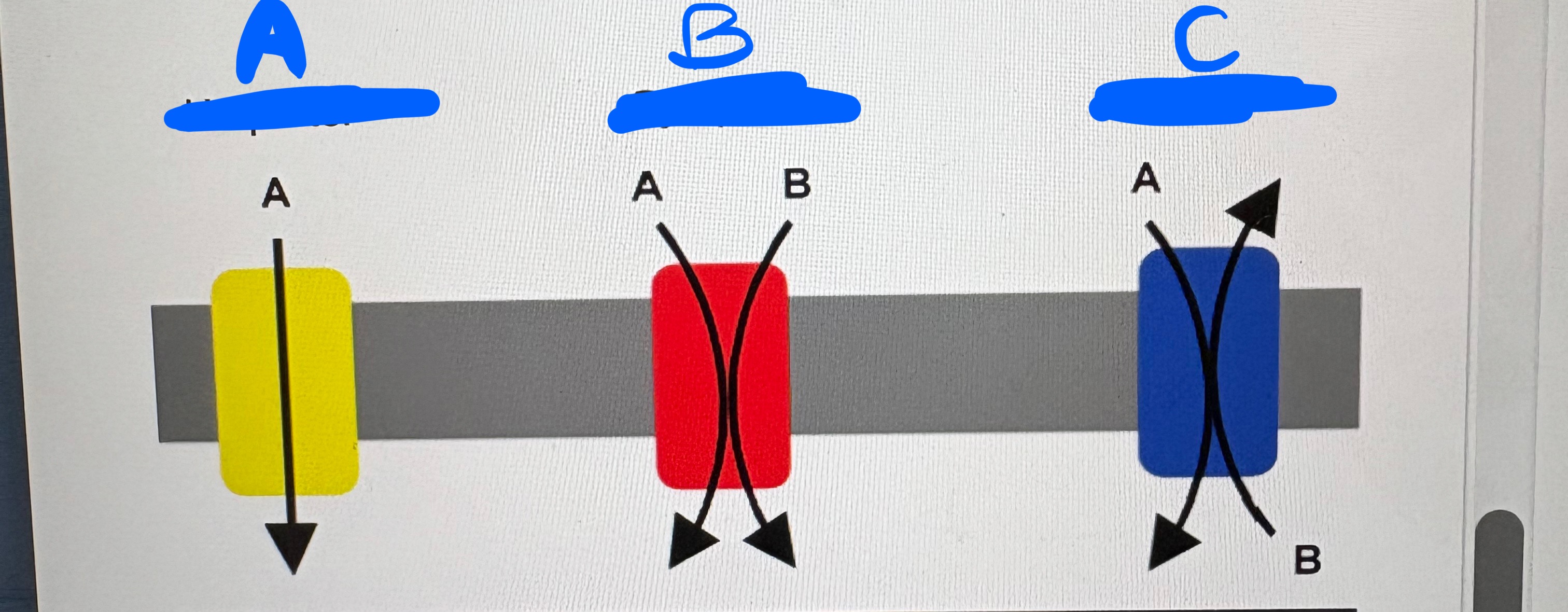
what kind of transport is A, B, and C?
A: Uniporter
B: Symporter; co-transport
C: antiporter: counter-transport
why do we have so much K+ in the cell?
The Na/K pump actively brings in K+
the membrane is very permeable to K+
negative anions inside the cell attract the cations outside the cell
this is where the body stores this molecule intracellularly
what are the values for restinf potential and threshold?
resting: -70 mV
threshold: -55 mV
what kind of neuron is located completely within the CNS and integrate the function of the nervous system
association/interneurons
what kind of neurons conduct impulses from the CNS to target organs (muscle or glands)
motor neurons
what kind of neuron conduct impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS
sensory neurons
___ speed up the conduction of electrical signals along an axon
myelin sheath
what forms the myelin sheath
oligodendrocytes
describe Ligand gated channel and where they are located
opening in response to binding of a chemical ligand to its receptors
location: on dendrites
describe voltage gated channels and where they are located
opens in response to + or - changes
protein channel when stimulated depolarizes the membrane to threshhold
specific to an ion
location: on axon
describe mechanical gates channels
open when physical deformation to membrane occurs (like stretching)
define action potential
all or nothing event in a single cell where the membrane potential quickly becomes positive and returns to its resting potentials
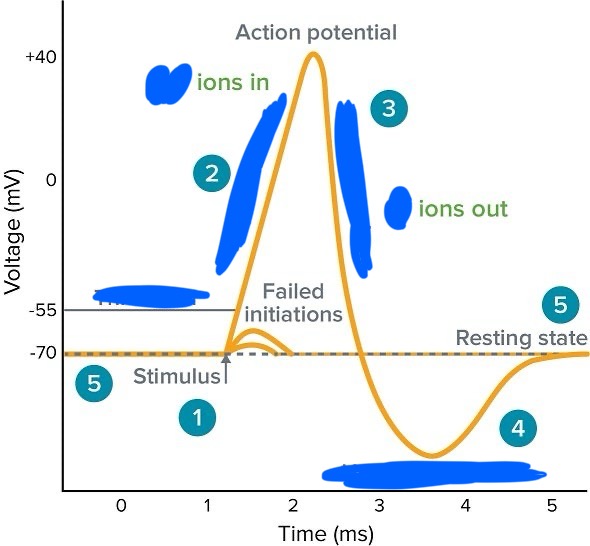
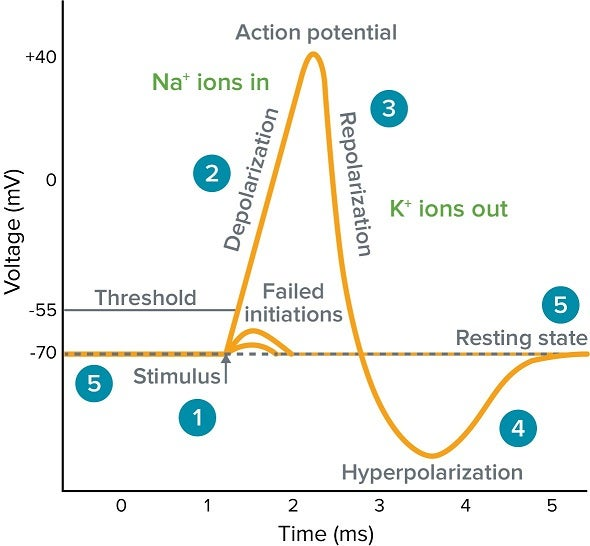
what occurs during hyperpolarization
Dips down past resting potential due to slow K+ moving out of the cell
depolarizaing ____ the permeability for Na+
increases
A second stimulus will not produce an action potential is called what
absolute refractory period
second action potential can happen only if stimulus strength is greater than usual is called what
relative refractory period
why do absolute refractory periods occur
Na+ channels are
inactivatedAs soon as inactivation is
removed and Na+ are
closed, the channel can
reopen to second
stimulus
____ of Na+ allpws action potential to travelw othout decrement (decrease)
positive feedback
synapses can use ____ and ____ stimuli to pass info
chemical and electrical
synapses can be ___ or ____ depending on the neurotransmitter being transmitted
excitatory or inhibitory
define synapse
a junction where impulses are transmitted from neurons and in the PNS the target muscle or gland
what connects electrical pre and post synaptic cells; and what is the speed of the flow
gap junctions; quick flow
where are electrical synapses found; why?
cardiac and smooth msucle; allows for contractions as a unit to occur
describe an excitatory post synaptic response
Opening Na+ or Ca2+ channels results in a graded depolarization called an excitatory postsynaptic potential; activated
on the ligand gated channels on the dendrites
The dendrite is the area for graded potential
Na or Ca go into the cell
describe an inhibitory post synaptic response
Opening K+ or Cl- channels results in a graded hyper-polarization called inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Hyper-polarization
K+ moves out and Cl- moves in
what are the characteristics of graded potentials
summation and lack of refractory period
AcH channels are ___ gated channels
ligand
step by step explain how an action potential is produced
1. Resting Potential (~ –70 mV)
The neuron is at rest.
The Na⁺/K⁺ pump maintains high Na⁺ outside and high K⁺ inside.
Inside of the cell is negatively charged compared to the outside.
Voltage-gated channels are closed.
2. Stimulus and Threshold (-55 mV)
A stimulus (e.g., neurotransmitter binding) causes local depolarization.
If the membrane potential reaches threshold (~ –55 mV), an action potential is triggered.
Voltage-gated Na⁺ channels open.
3. Depolarization (rises to +30 to +40 mV)
Na⁺ floods into the cell due to concentration and electrical gradients.
The membrane potential becomes more positive.
Rapid upward spike in voltage.
4. Peak of Action Potential (+30 to +40 mV)
Voltage-gated Na⁺ channels close (inactivate).
Voltage-gated K⁺ channels open.
5. Repolarization
K⁺ exits the cell, making the inside more negative again.
Membrane potential starts to return toward resting level.
6. Hyperpolarization (~ –80 mV)
K⁺ channels stay open slightly too long, causing the membrane to become more negative than the resting potential.
Prevents immediate firing again (refractory period).
7. Return to Resting Potential
Voltage-gated K⁺ channels close.
Na⁺/K⁺ pump and leak channels restore original ion concentrations.
Neuron is back to –70 mV, ready to fire again.
Explain how ligand-gated channels produce synaptic potentials, using the nicotinic ACh receptor as an example.
An action potential reaches the presynaptic neuron terminal.
This triggers release of acetylcholine (ACh) into the synaptic cleft.
ACh Binds to Nicotinic Receptors
ACh diffuses across the cleft and binds to nicotinic ACh receptors on the postsynaptic membrane.
These receptors are ligand-gated ion channels.
Binding of ACh opens the channel, allowing Na⁺ to enter and K⁺ to exit the postsynaptic cell.
However, more Na⁺ enters than K⁺ leaves, leading to a net positive charge inside.
This net inward flow of positive charge depolarizes the postsynaptic membrane.
If the EPSP is strong enough to reach threshold, it can trigger an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron.
To end the signal, acetylcholinesterase breaks down ACh in the synaptic cleft.
The receptor channels close, and the membrane potential returns to baseline.
what are the receptors that Ach can bind to
nicotinic and muscarinic
MODULE 7
MODULE 7
what are the functions of the CNS
.1. Receives input from sensory neurons and
directs activity of motor neurons
2. Association neurons integrate sensory
information and help direct the appropriate
response to maintain homeostasis and respond
to the environment
what portion of the brain controls emotion
limbic system
what all does the hippocampus do
Formation and retrieval of memory
• Helps form cognitive maps that help make mental models
of our world
• Stress and emotion (via thelimbic system) can affect
memory
• Contain Cortisol receptors
what is the master command center for neural and endocrine coordination
hypothalamus
what regulates the pituitary gland
hypothalamus
what two hormones does the hypothalamus produce
antiduretic (ADH) and oxytocin
what is the limbic system made up of
thalamus and hypothalamus
what does the thalamus do
relay center for sensory info (except smell); direction of traffic; helps the flow of info, allowing you to prioritize what is received
what do opioid neurotransmitter bind to
opioid receptors
what are opioid receptors activated by
stress to block the transmission of pain
what is the part of the hindbrain that has the ability to control rates; ex: heart rate
medulla oblongata
what neurotransmiter is involved in memory, sensory, and learning
glutamate
what is dopamine involved in
mood, sleep, reward pathway, effected by increase in pressure
what are beta endorphine involved in
released when the body feels pain
runners high
will decrease anxiety
what is GABA involved in
its your inhibitory neurotransmitter
involved in brain function and sleep
Lets help someone sleep by reducing senses
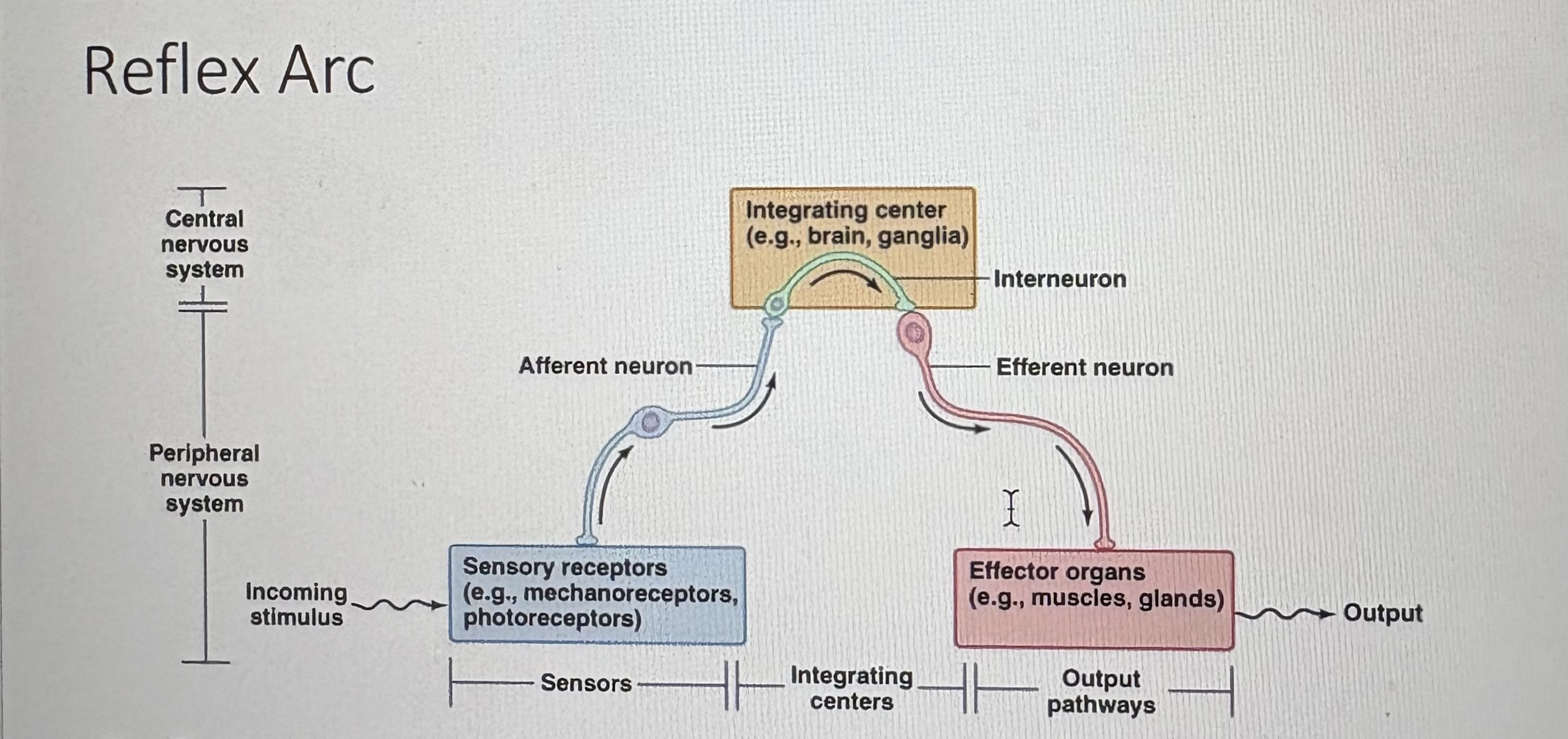
in the reflex arc, A ___ occurs at the receptor of a ____. This is sent along the _____ as a nervous impulse and is received by the ___
stimulus; sensory neuron; afferent neuron; CNS
in the reflex arc, the interneuron makes connections to the ____. the ____- transmits the impulse to the ____
motor neuron; motor neuron; effector organ
MODULE 8
MODULE 8
what are the subdivisions of the autonomic division
parasympathetic, sympathetic, and enteric
Which neurotransmitter is only in the sympathetic division
norepinephrine
what are the types of adrenergic receptors and what do they use
a(alpha) - a1 and a2; use cAMP
B (beta) - B1 and B2; use a Ca2+ second messenger system
___ receptors are more sensitive to norepinephrine
Alpha (α) receptors
____ receptors are more sensitive to blood epinephrine
beta (β) receptors
what is dual innervation
One organ receiving sympathetic and parasympathetic input, usually with opposing effects that help maintain balance (homeostasis).
Apply examples of dual innervation of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic system
Ex 1: Heart
Sympathetic: Increases heart rate and force of contraction
(via norepinephrine on β1 receptors)
Parasympathetic: Decreases heart rate
(via acetylcholine on muscarinic receptors)
Ex 2: Urinary Bladder
Sympathetic: Relaxes bladder wall, contracts internal sphincter
(inhibits urination)Parasympathetic: Contracts bladder wall, relaxes sphincter
(promotes urination)
what hormone does the medulla oblongata secrete
epinephrine
what do the postganglionic neurons release
norepinephrine
___ is released; ___ is secreted
norepinephrine; epinephrine
during fight or flight, HR ____ and BP _____
increases; increases
the parasympathetic division is ____ to the sympathetic division
antagonist
what does the parasympathetic division do/rest and digest
Releases ACh from postganglionic neurons
Slows heart rate (decreases rate of pacemaker cells), and
increases digestive activities
the automatic system is moves ___ from the spinal cord, making it ___
away; efferent
what are the neuotransmitters and receptors for the parasympathetic division - acknlowledge pre and post ganglionic
Preganglionic neurotransmitter: Ach
Preganglionic receptor: nicotinic
Postganglionic neurotransmitter: Ach
postganglionic receptor: muscarinic
what are the neuotransmitters and receptors for the sympathetic division - acknlowledge pre and post ganglionic
Preganglionic neurotransmitter: Ach
Preganglionic receptor: nicotinic
Postganglionic neurotransmitter: norepinephrine
Postganglionic receptor: adrenergic (alpha and beta)
MODULE 9
MODULE 9
The function of the endocrine system is to ____
regulate
define hormone
a chemical message produced by an endocrine tissue and travels through the bloodstream to target cell receptor
what hormones are released by the posterior pituitary and what do they do
oxytocin - involved in milk ejection reflex
ADH (vasopressin) - involved in regulation of water
the ___ pituitary is controlld via releasing and inhibiting hormones transported through the ______
anterior; hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system
what is the sequence of events of the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system?
regulatory hormone controls secretion of anterior pituitary
anterior pituitary hormone then controls the secretion of a hormone from another endocrine gland
the last hormone does the action on its target cell
ex: thyroid releases T3 and T4 hormones to do the action intended of this sequence
what are the pancreatic hormones and what do they regulate
glucagon and insulin; Regulates blood glucose levels, causes an antagonistic effect (blocking)
insulin ___ blood glucose levels; glucose ____ blood glucose levels
lowers; raises
The hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract is a neural pathway that connects the ___ to the _____ (neurohypophysis)
hypothalmus to the posterior pituitary gland
MODULE 10
MODULE 10
What are thick filaments made up of; thin filaments?
myosin; actin
____ is on actin and blocks the cross bridge
tropomyosin