physiology 201
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
N3 is called what and has what kind of pattern
slow wave; delta rhythm
N2 has what two patterns? what do they look like?
sleep spindles and k complexes
N1 is called what and has what pattern?
is a light sleep stage characterized by theta waves and a transition from wakefulness to sleep.
REM is characterized by what patterns?
beta waves,
fluid outside cell (but not inside vasularture)
ISF
fluid inside cells
intracellular fluid ICF
Plasma
fluid in blood vessels
cytosol
the liquid component of the cytoplasm, excluding organelles and other solids.
specialized (protein lined) intercellular connections that allow for direct communication between adjacent cells (and name the antonym)
gap junctions; tight junctions
tRNA
a molecule that carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis, matching its anticodon with codons on the mRNA.
transcription factors
proteins that regulate gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences.
for template DNA nucleotide sequence CAT, what is the corresponding mRNA codon sequence?
GUA
allosteric modulation
weaker of the two:
NOT the active site being bonded to, and bonds are NOT covalent (two bonding sites must exist, an acti ve site and an allosteric site)
covalent modulation
requires an enzyme to make a strong covalent bond between the protein and something else. This occurs on the active site.
why is the difference in binding site affinity of a secondary active transport protein on the two sides of a membrane an example of allosteric modulation
Ask chatgpt
ligand
molecule that binds to a sensory receptor, ion channel or other macromolecule
Two proteins are found to be 50% saturated with their respective ligands at, one at a high molarity of its respective ligand and one at a low molarity. Which protein has the highest affinity binding site?
kinase
an enzyme that takes the phosphate from an ATP and covalently modulates a protein with it. often this is a mechanism for transport across a membrane.
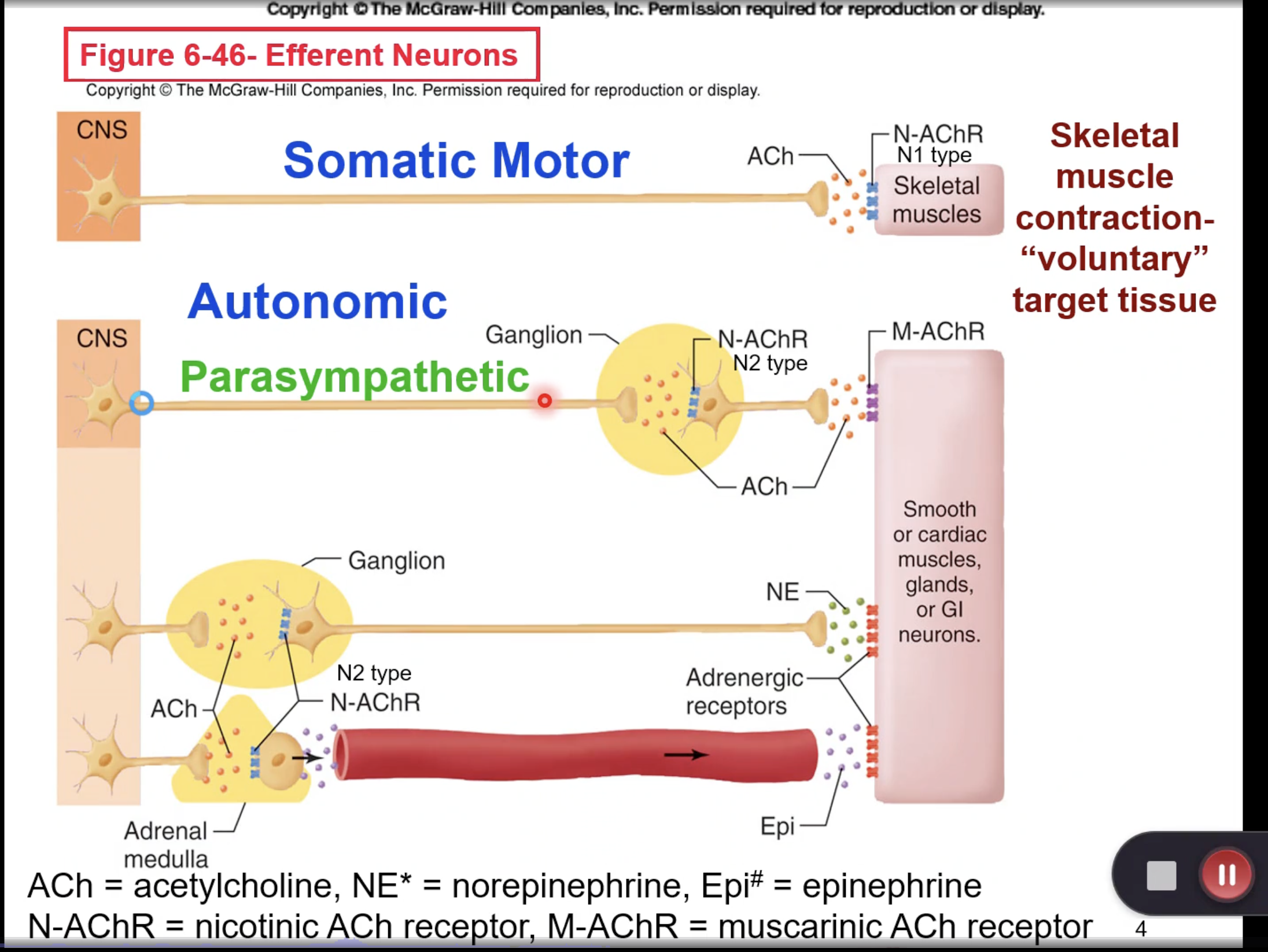
two types of neurons in efferent pathways: what are and what do they do
motor neurons connect to effector tissue of muscles and glands; sympathetic neurons are a type of motor neuron and connect to effector tissue for things that are involuntary (constricting blood vessels for example).
what do you call the thing that processes information from an afferent pathway?
integrating center
this molecule _______ links receptors to second messenger generating systems and is found where?
G proteins, membrane
A messenger molecule is not soluble in lipids! What is one way to get the information across the membrane?
by causing generation of the second messenger cAMP
know the 4 steps of most cell responses to extracellular chemical messengers
Binding of the chemical messenger to a receptor protein (first step).
Generation of second messenger molecules (cAMP, IP₃, DAG, Ca²⁺, etc.).
Allosteric activation of protein kinase enzymes (second messengers activate kinases like PKA, PKC, CaM-kinase).
Phosphorylation of specific cell proteins (kinases phosphorylate target proteins → cellular response) ()
What is an inactive G protein bonded to? what about an active G protein?
inactive is bonded to GDP, active is bonded to GTP.
fatty acids undergo ______ to form ________, which enters the_________.
β-oxidation, acetyl-CoA, Krebs cycle.
glycolytic pathway
T/F: fatty acids are broken down to molecules that can enter the glycolytic pathway
false, they never enter it, they instead go through β-oxidation into acetyl-CoA.
anticipatory mechanism to avoid the effects of a stimulus before they set in
feed forward
Differentiate acclimatization and resetting set point for the stimus of cold weather
acclimatization would be the improvememt of the warming up system while resetting the set point
resetting set point
membrane potential
seperation of charge across membrane
two kinds of gradients: _______ and ________
electircal and chemical
symbol for equil. pot.
Eion
membrane potential symbol
Vm
hydronium
water molecule with a proton + [H3O]+
baroreflex
Parasymphathetic nervous system
the part of the nervous system associated with heart rate DECREASE, as well as other functions
sympathetic nervous system
INCREASES heart rate (fight or flight servous system)
baroreceptor
label parts of neuron
dendrites, cell body (where grtaded potentials happen), initial axon segment (where action pots. happen first), axon, axon terminals
axosomatic
attaches to the cell body of the postsynaptic cell
axoaxonic
presynaptic neuron attaches to axon termials and makes it release neurotransmitters without graded/action potentials
the idea that graded potential signals will get weaker over distance without action potentials
decremental conduction
excitable cell
cell that is capable of generating action potential
oligodendricyte
myelin forming cell in Central NS
schwan cell
myelin forming cell in peripheral NS
node of ranvier
interneurons
glycosylated
having sugar molecules linked (often on the extracellular surface of integral proteins)
when a signal comes from the same cell quickly so the waves overap a bit; when the signal comes from multiple cells and overlaps.
Temporal summation; spatial summation
afferent neurons that allow conscious sensing of touch, pain, temp, pressure, etc
somatic sensory neurons
internal sensing neurons (info from organs, fullness, stretch, etc)
visceral sensory neurons
light, taste, smell
special sensory neurons
control skeletal movement, shivering, etc
somatic motor neurons
cranial vs spinal nerves
spinal nerves all have BOTH afferent and efferent cells, while some cranial nerves can be specialized to one of the two.
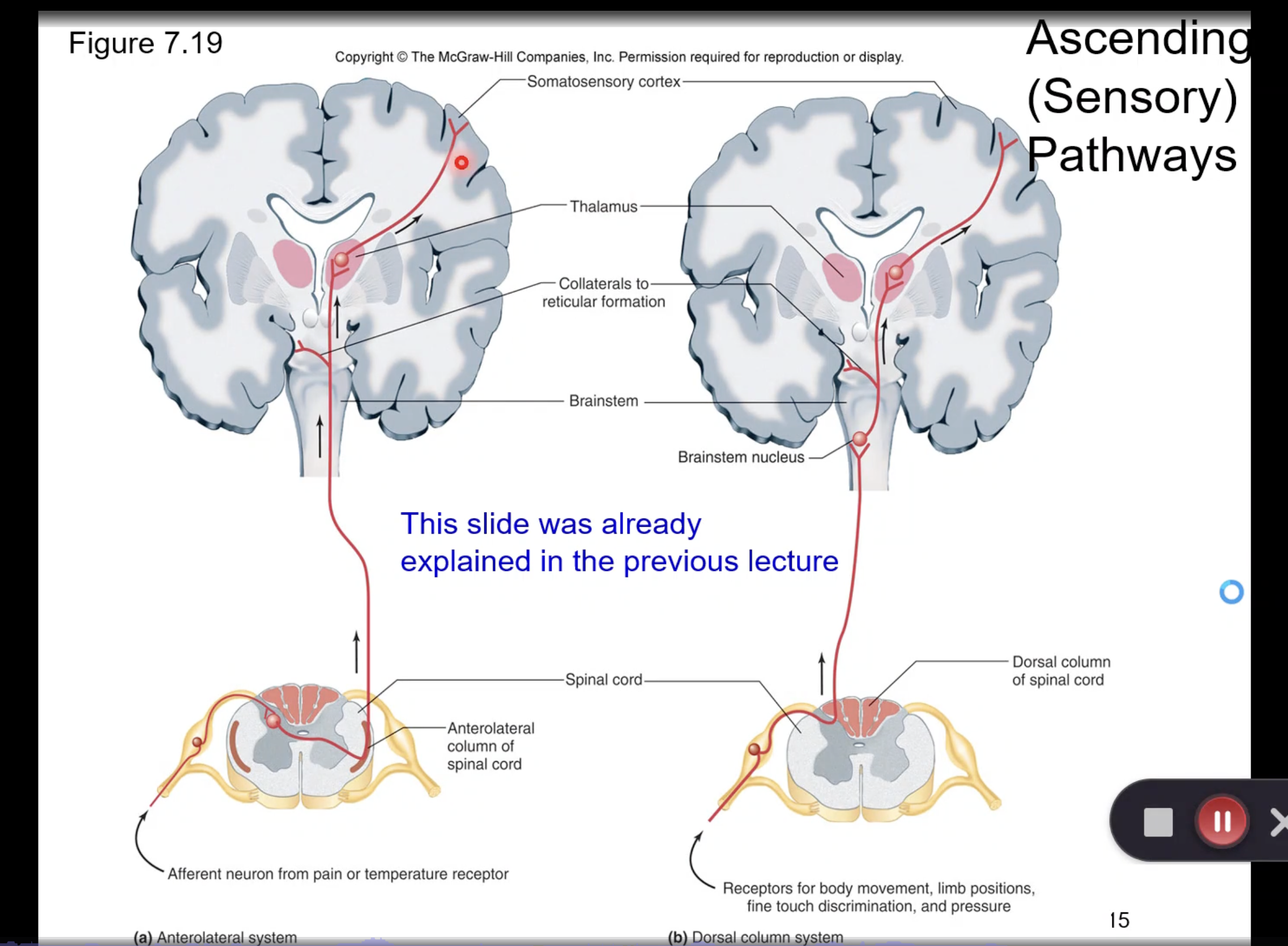
anterolateral system
carries pain/temp info
proprioceptor
this molecule ________senses an influx of Ca2+ and accelerates fusion of membrane and vesicle (which is done by _________ to release neurotransmitters)
synaptotagmin; SNAREs
interneuron
sensory transduction
receptive field
map of spine/regions that control parts of body
all _________ nerves have efferent and afferent while ______ mostly do but can also specialize
spinal; cranial
corticospinal pathway
permissive actions
HPA axis
hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis
the protein ________is voltage sensor inbedded in the t tubule and as an action potential is generated it changes shape of ________ to allow Ca2+ to flow from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the ICF
DHP (Dihydropyridine) receptor, Ryanodine receptor
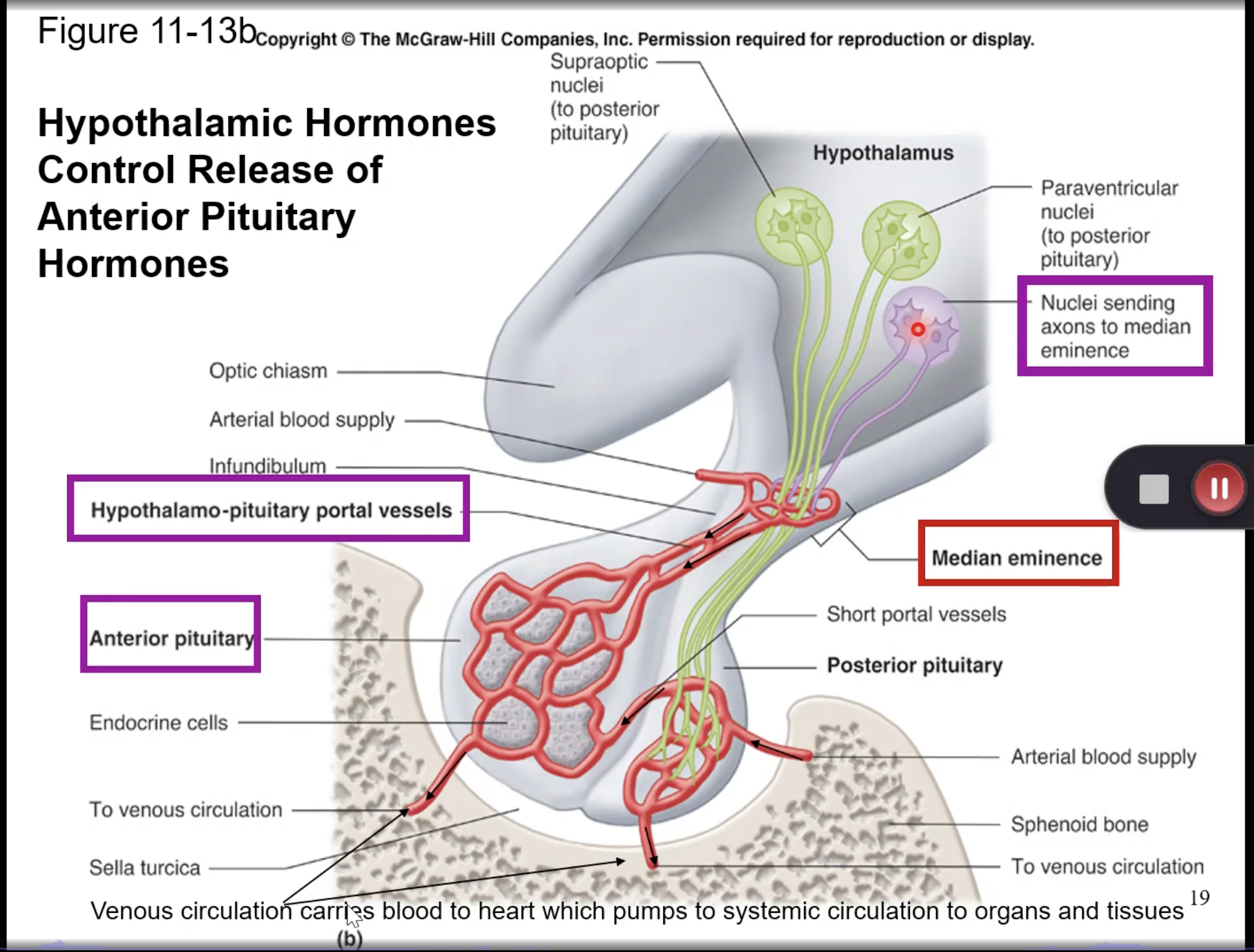
the hormone _____ is released by neurons of the ________ part of the brain into the _______, location which contains the _________ .
CRH; hypothalamus; median eminence; hypothalamic-pituitary portal system/vein.
the hormone _____ acts on the ______ (what structure) to release ________, which then acts on the ________ to release cortisol.
CRH; anterior pituitary gland; ACTH; adrenal glands
long loop vs short loop and all examples in the HPA axis
the ____________ is made up of which 3 proteins
thin filament: actin, tropomyosin, troponin
muscle cells have long things called ________ made up of smaller units called ___________
myofibrils, sarcomeres
membrane of the muscle is called _______
sarcolemma (plasmalemma can refer to any type of cell membrane)
the __________ is the part of a sarcomere that is dark and made up of the protein _________
thick filament; myosin
Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA)
4 steps of cross bridge cycle
latent period
the length of time between x=0 and first sign of tension in muscle fiber
this is where a motor nueron attaches to one of its muscle fibers (and it has many ACh receptors)
motor end plate
thick filament is made up of 2 ______ and 4 ______ chains
heavy, light
free vs. calcium bound troponin
differentiate m line, z line, I band, A band, and H zone
Three functions of ATP (and name of protein that puts Ca away back into SR)
Hydrolysis by myosin (energy for cross bridge during energuie faze - puts myosin head in energized position), detachment (attracted to myosin and dissociates it from actin), hydrolysis by SERCA t
name the three muscle relationships and give examples
firce-frequency, length-tnesion, load-velocity
three sources of energy/ATP for muscle cells (and name enzyme for the one that lasts 10 seconds)
creatine phosphate (mediated by creatine kinase, only 8-10 seconds worth of ATP), oxidative phosphorylation (if enough O2), Glycolysis
oxidative phosphorylation
glycolysis at max can be maintained for _______
at maximum can be maintained for 1.3-1.6
three types of fibers and their names
fast glycolytic fibers (IIb), fast oxidative fibers (IIa), slow oxidative fibers (I)
IIb has _______
fast myosin ATPase, fewer mitochondria, less blood/myoglobin. high intensity activities
IIa has______
fast myosin ATPase (not as fast as IIb), moderate intensity excersice but still used in high intensity
I fiber has _____
slow myosin ATPase, high blood supply/myoglbin, used for all types of activities
ciliary muscles are controlled by the ______ system
parasympathetic
this second messenger ______ opens receptor _______ on the SR membrane to release Ca2+ without needing an action potential
IP3; IP3R
the enzyme _________ is activated by Ca2+ in smooth muscle and activates ______, this second enzyme phosporylates myosin to allow the cross bridge cycle to occur
calmodulin (CM); MLCK (myosin light chain kinase)
T/F smooth muscle has sarcomeres
F
where the neuron connects to the muscle cell is called ___________. The name the specialized region of the muscle cell here is __________ . what receptor is found there and what happens to the Ach?
neuro muscular junction; Motor end plate; N-AchR is used and then broken down by AChesterase on the surface of the motor end plate into choline which can be reuptaken buy the neuron and acetic acid
this is the name of the graded potential that occurs at the end plate
EPP (end plate potential)
things that cause fatigue during high intensity excercise
slight decrease in ATP, too much ADP, less Ca2+ and decreased Ca2+ sensitivity
T/F all fibers in a given motor unit are of the same type
T
four types of hormones
catecholamine (like epi), peptide, steroid, thyroid