4.1.8.1 How markets & prices allocate resources
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What’s the price mechanism?
way in which prices are determined in a market economy.
How are prices determined in the price mechanism?
through the interaction of buyers and sellers in the marketplace.
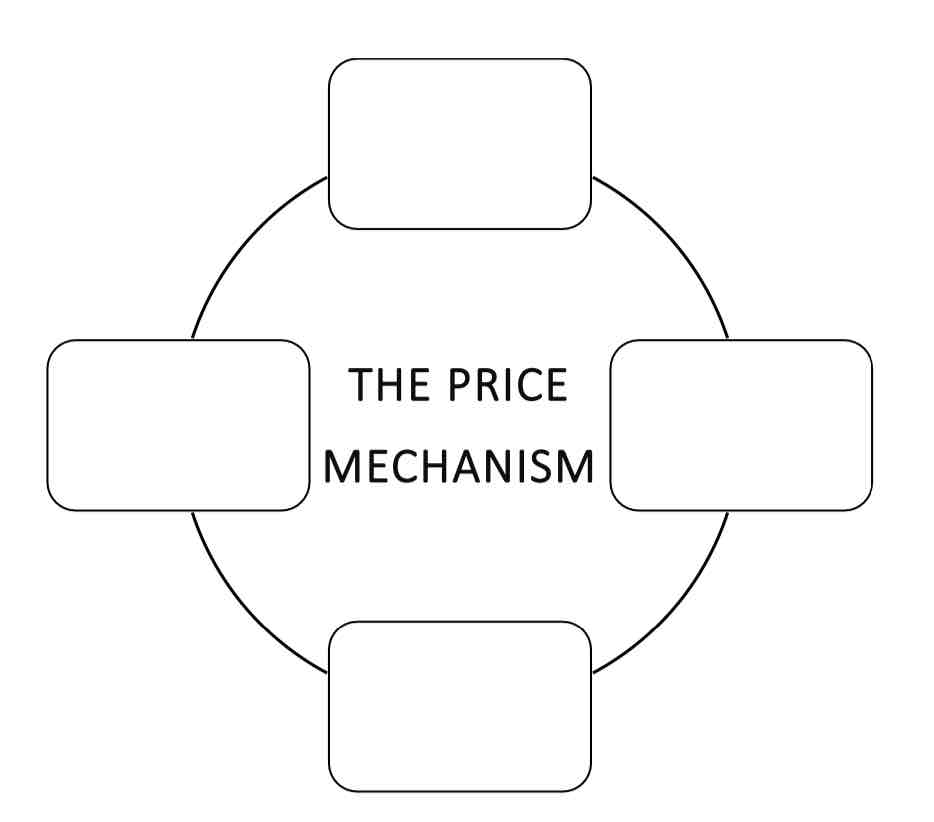
What are the 4 functions of price?
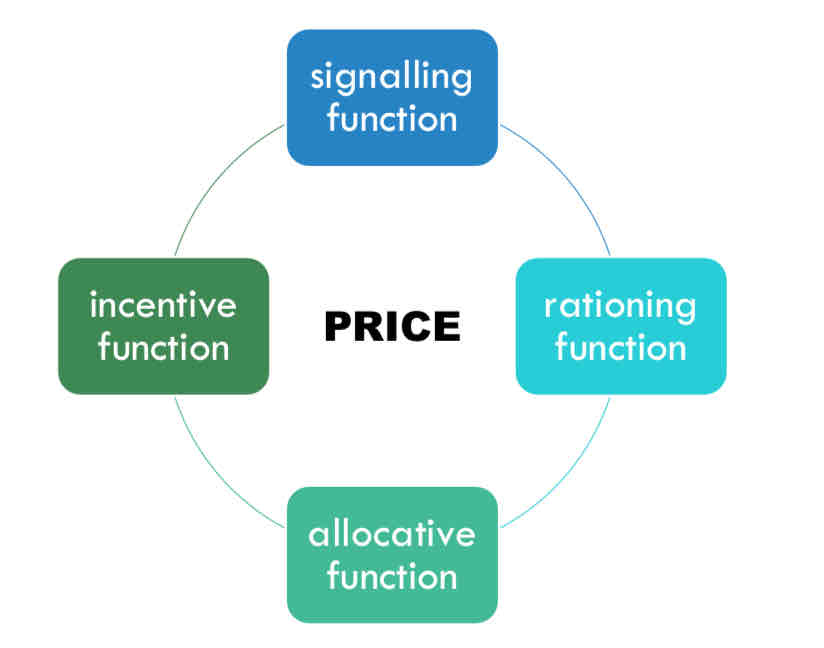
What does the signalling function of price mean?
Prices provide information to buyers and sellers
What does the incentive function of price mean?
Prices create incentives for people to alter their economic behaviour (SUPPLY mainly)
What’s the rationing function of price?
Rising prices ration demand for goods/services (DEMAND) – only the more serious/wealthy consumers will continue to demand the good
What does the allocative function of price mean?
Changing prices allocates scare resources away from markets exhibiting excess supply and into markets where there is excess demand.
Expand on the rationing function:
◎ Excess demand for a good or service will lead to a rise in the price of a good or service
◎ This is due to the scarcity of the product
◎ The price rise will lead to a reduction in demand
◎ The more scarce a product the higher the price
◎ This leads to a rationing of the product as its use is restricted
◎ There will be a movement along the demand curve showing a decrease in quantity demanded and a decrease in price
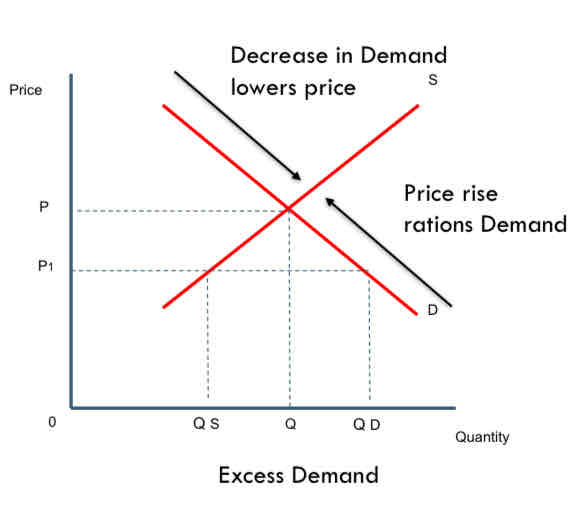
Draw a diagram to show the rationing function
At price 𝑃 1 (below market equilibrium P) the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied, thus creating excess demand.
A price rise will ration the demand, a movement (up) along the demand curve
Expand on the incentive function:
◎ Higher prices act as a motivator for producers to increase the supply of a good or service
◎ This is due to greater contribution per unit i.e. the difference between selling price and variable cost
◎ As prices rise so do revenue and profit
◎ There will be a movement along the supply curve showing an increase in quantity supplied
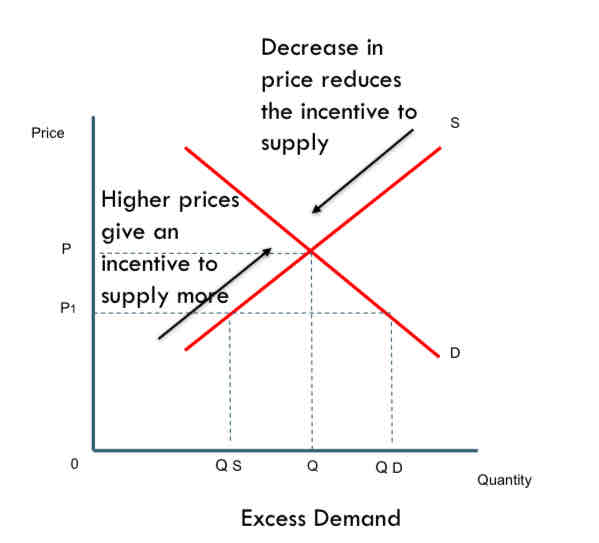
Draw a diagram to show the incentive function
At price 𝑃 1 (below market equilibrium P) the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied, thus creating excess demand.
A price rise will give an incentive to increase the supply, a movement (up) along the supply curve
Expand on the signalling function
◎ An increase in price will give an indication to producers that they should increase supply
◎ An increase in price will give an indication to consumers that they should reduce demand
◎ A decrease in price will give an indication to producers that they should decrease supply
◎ A decrease in price will give an indication to consumers that they should increase demand
◎ All of these signals will lead to shifts in the supply or demand curves
What are the types of efficiency?
economic
Productive
Allocative
When does EE occur?
when the maximum amount of products are produced at their minimum cost whilst maximising their benefit to society.
occurs where we have allocative and productive efficiency at the same time
When does productive efficiency occur?
occurs when an economy uses the minimum inputs to produce the maximum output at lowest cost
occurs where no additional (or maximum) output can be produced from the factor inputs available at the lowest possible average or unit cost
When does allocative efficiency occur?
occurs when society is producing goods to match the needs of consumers.
occurs where consumer satisfaction is maximised in the production of goods and services
How can productive & allocative efficiency be illustrated?
using a PPF
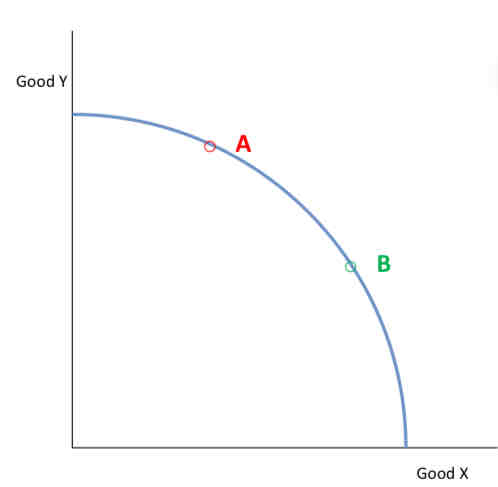
Show allocative efficiency on the PPF:
Allocative efficiency takes into account the desires of consumers.
If good Y is in greater demand than good X then production at point A will be more efficient than that of point B.
Therefore, allocative efficiency can be found somewhere on the PPF but at what point depends upon consumer preference.