FBS 31_Plant-Water Relations
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
Water constitutes what percentage of the mass of the plant?
80-95%
Unique characteristic of water which makes it an excellent solvent
Polarity of the molecule H2O
Unique characteristic of water which makes capable of moving through plant tissues by capillary action
Viscosity
Unique characteristic of water which makes it capable of cooling plant tissues
Thermal properties
What do you call a plant cell that is swollen and firm due to high water content
Turgid
What part of the root in plants absorb water
Root hair
Where in the root tip does root hair grow?
Region of maturation
Well-watered plants keep their shape because of the internal pressure of water in the cells that is called?
Turgor pressure
What is the movement of atoms or molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Diffusion
This energy is the power of a moving body to accomplish work
Kinetic energy
A hypothetical term describing the potential ability of a gas, liquid or solid to diffuse from an area of its greatest concentration to an area of lesser concentration.
Diffusion pressure
The direction of diffusion of a substance is determined entirely by the difference in diffusion pressure of the substance and is completely independent of the diffusion pressure of surrounding substances.
Independent diffusion
Factor affecting rate of diffusion where the rate at which a substance (gas) will diffuse increases with increase in what?
Temperature
Factor affecting rate of diffusion that includes Graham’s Law
Density of diffusing molecules
What is being described?
“As density is increased, rate of diffusion is decreased.”
Graham’s Law
Factor affecting rate of diffusion where the more concentrated the medium is, the slower is diffusion.
Medium in which diffusion occurs
Factor affecting rate of diffusion where if there is a large difference in concentration between two areas (the steeper) then the faster the rate of diffusion
Diffusion pressure gradient
Factor affecting rate of diffusion that has to do with size.
Size of diffusing molecule
Factor affecting rate of diffusion that has to do with solubility
Solubility of diffusing molecule
Type of diffusion where the movement of water passes through a semi-permeable membrane
Osmosis
What does DPD stand for?
Diffusion pressure deficit
The pressure needed to prevent the passage of water into an aqueous solution
Osmotic pressure
The pressure needed to prevent the leakage of water from a cell
Turgor pressure
What is the process whereby the water from the cytoplasm of cells is removed causing the cytoplasm to shrink?
Plasmolysis
What do you call the solution where plasmolysis occurs?
Hypertonic solution
What do you call the solution where more water enters the cell, increasing turgidity?
Hypotonic solution
What do you call the solution where the amount of water transported into the cell is equal to the amount of water transported out?
Isotonic solution
What is the formula for Osmotic Pressure?
OP=\frac{22.4MT}{273}
What does M mean in the formula for Osmotic Pressure?
concentration of external solution at incipient plasmolysis
What does T mean in the formula for Osmotic Pressure?
absolute temperature
Importance of imbibition where it initiates seed ____
Germination
Importance of imbibition where it is adhering water to the walls of ____ elements
Xylem
Importance of imbibition where it helps ___ to retain water
Fruits
Importance of imbibition where it plays a major role in young and actively growing ___
Tissues
A DP gradient must exist between the imbibant and the substance imbibed
A certain affinity must exist between components of the imbibant and the imbibed substance
Conditions for imbibition to occur
A DP gradient must exist between the imbibant and the substance imbibed. This means that DP of the water in dry plant materials capable of imbibition is practically ___
Zero
Imbibition of water by dry plants is due to the hydrophyllic colloidal substances as proteins and polypeptides – namely, ____ and ____
Starch, Cellulose
Analogous to Osmotic pressure (OP) in the sense that it represents the potential maximum pressure developed by the imbibant if submerged in pure water.
Imbibition pressure
DPD = IP if imbibant is placed in an ____ condition
Unconfined
Factor affecting rate and extent of imbibition where an increase in this, increases the rate of imbibition
Temperature
Factor affecting rate and extent of imbibition where addition of solute to pure water lowers diffusion pressure of water
OP of substance to be imbibed affects amount and rate of water diffusion
Volume of whole system decreases after imbibition because water molecules are adsorbed tightly and as such are packed closer together. As a result, some KE is lost as heat, therefore an increase in temperature after imbibition.
Volume and energy changes
Term in volume and energy changes that is the binding of molecules or particles to a surface
Adsorption
Term in volume and energy changes that is the filling of pores in a solid
Absorption
Term in volume and energy changes that is the release of an adsorbed substance from a surface
Desorption
Process whereby water is lost in the form of vapor through the leaves
Transpiration
Only __% water vapor is utilized. Most of it is lost in the form of vapor through transpiration.
5
Type of transpiration occurring in the stomata of the leaves
Stomatal
Type of transpiration that is the loss of water from the cuticle of the leaves, fruits and stem
Cuticular
The term used when water, not water vapor, is released from the plant
Guttation
Type of transpiration that is the loss of water through a pore-like structure found in the branches or stem; slow
Lenticular
Method of measuring transpiration that involves loss of weight of plant from one period of time to another surface of soil covered so as to eliminate water loss due to evaporation.
Gravimetric method
Method of measuring transpiration where bubble is introduced in the capillary. The measurement is how far will the bubble travel per minute. Assumption: amount of water loss is the same as the amount of water absorbed.
Potometer method
Specially prepared filter paper coated with cobalt-chloride is used, placed and pressed over a transpiring leaf blade, when not saturated it is colored blue, when saturated colored pink – time it takes to change color is compared to a given table to give the rate of water loss.
Cobalt-chloride method
Plant is enclosed in a box, CaCl2 is used, oven-dried first then weighed, placed inside U- tube, blow in air into box for plant to transpire. The pump will aid CaCl2 to absorb the water transpired.
Box method
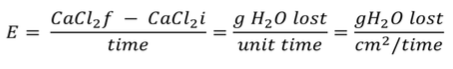
What is the method of transpiration being represented in this equation?
Box method
Movement of stomata is dependent upon the turgidity of the ____
guard cells
What does E in physiology mean?
Transpiration
What does G in physiology mean?
Stomatal conductants
When guard cells are swollen the stoma is?
Turgid
When guard cells are shrunken the stoma is?
Flaccid
C3 and C4 Plants have their stomata opening in what time?
Day
Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) plants have their stomata opening in what time?
Night
Factor affecting stomatal movement where stomates open in light and close in dark; some will not open when exposed to far red or UV while some will open
Light
Subtopic of factor affecting stomatal movement where under light condition, chloroplasts of the guard cell photosynthesize resulting in an increase of osmotically active substances
Photosynthesis
Subtopic of factor affecting stomatal movement where illumination of the guard cells increases its pH; at high pH opening of the stomates is favored and at low is closing.
A high pH is accompanied by a decrease in starch and an increase of the reducing sugars which are osmotically active resulting in an increase of turgor.
pH
Factor affecting stomatal movement where the greater the degree of water deficit, the sooner the stomates close
Water
Factor affecting stomatal movement where as air temperature increases, stomates open
Air temperature
Factor affecting rate of transpiration that involves, root-shoot ratio, leaf area, leaf structure, and leaf orientation.
Plant factors
Transpiration ____ with increased root-shoot ratio
increases
Greater leaf area, greater amount of water ___
loss
Factor affecting rate of transpiration that has to do with the plant’s surroundings
Environmental factors
Subtopic of factor affecting stomatal movement that causes opening of stomates
Light
Subtopic of factor affecting stomatal movement where increased relative humidity of air decreases rate of transpiration because vapor pressure between the leaves and the atmosphere is not very steep.
Humidity of air
The ratio of the actual vapor pressure to the vapor pressure of atmosphere when saturated at the same temperature.
Relative humidity
Subtopic of factor affecting stomatal movement where where all other factors constant – increase in temperature within a certain physiological range almost increases the rate of transpiration.
Temperature
Factor affecting stomatal movement where this disperses vapor accumulating or concentrating in the vicinity of the leaf as a result of transpiration and thus may increase transpiration at the immediate onset of application.
Wind
Factor affecting stomatal movement whether there is soil water or not
Availability of soil water
Significance of transpiration where some would say this is not at all important because some plants transpire negligibly do not overheat
Cooling effect
Significance of transpiration where protein synthesis is inhibited and protein breakdown is enhanced
Effect on growth and development
Significance of transpiration where transpiration stream provides an efficient means of transport and distribution once salts have been absorbed
Effect of mineral salt absorption
Xylem tissue cell type where they are:
Cells most concerned with water translocation in the plants
They are elongated
Dead at maturity
Tracheids and vessels
Subtopic of Xylem tissue cell type where they are:
Restricted to Angiosperms
Formed by several cells arranged end to end and dissolved cross walls
Vessel or Xylem duct
Subtopic of Xylem tissue cell type where they are:
Found in all types of Vascular plants
Form the main pathways in gymnosperms due to absence of vessels
Smaller than vessels
Tracheids
Xylem tissue cell type where they are:
Dead at maturity
Function for support
Water translocation through these are uncertain
Xylem fibers
Xylem tissue cell type where:
Components of xylem rays called wood and ray parenchyma
Function as storage
Xylem parenchyma
What facilitates lateral distribution of water and nutrients?
Xylem ray parenchyma
Increase in ___ concentration of cell or decrease in TP will increase DPD
solute
Water is absorbed most in the ___ ___ zone, it diffuses into the root hair as a result of DPD gradient
root hair
This structure are extensions of the epidermal cells. They lack cuticle and provide a large surface area.
Root hairs
Water movement in the roots occurs exclusively through cell wall without the involvement of any membranes. Majority of the amount of water goes through this
Apoplast pathway
Water movement in the roots is from cell to cell through the plasmodesmata
Symplast pathway
This specialized pathway forms a network of the cytoplasm of all cells
Plasmodesmata
This separates the cortex and the endodermis. It is composed of a wax like substance called suberin.
Casparian strips
This is a wax like substance which blocks water and solute molecules through the cell wall of the endodermis.
Suberin
Water is forced to go through the cell membranes of different cells leading to what pathway?
Transmembrane pathway

What do you call the dots on the tracheids?
Pits
Mechanism of water absorption where rapidly transpiring plant vessels and tracheids are generally in state of negative tension or reduced pressure
Passive
Mechanism of water absorption that does not concern the shoot
Active
Factor affecting rate of absorption of water where a decrease in this, water mobility is reduced, also the protoplasm is less permeable and root growth is inhibited.
Soil temperature