BIOL 2401 CHPT 9: JOINTS
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
What are joints?
where two bones meet and where movement ocurs
What is the tradeoff for joints?
Strength and mobility
What are the two classifications schemes of joints?
Structural and functional
What are the structural classifications of joints?
fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial, and bony
What are the functional classifications of joints?
synarthroses, amphiarthroses, diarthroses
What is a synathrosis joint?
immovable joint
What are the characteristics of a synarthrosis?
- Very strong
- Edges of bones may touch or interlock
- May be fibrous or cartilaginous
What are the four types of synarthrotic joints?
suture, gomphosis, synchondrosis, synostosis
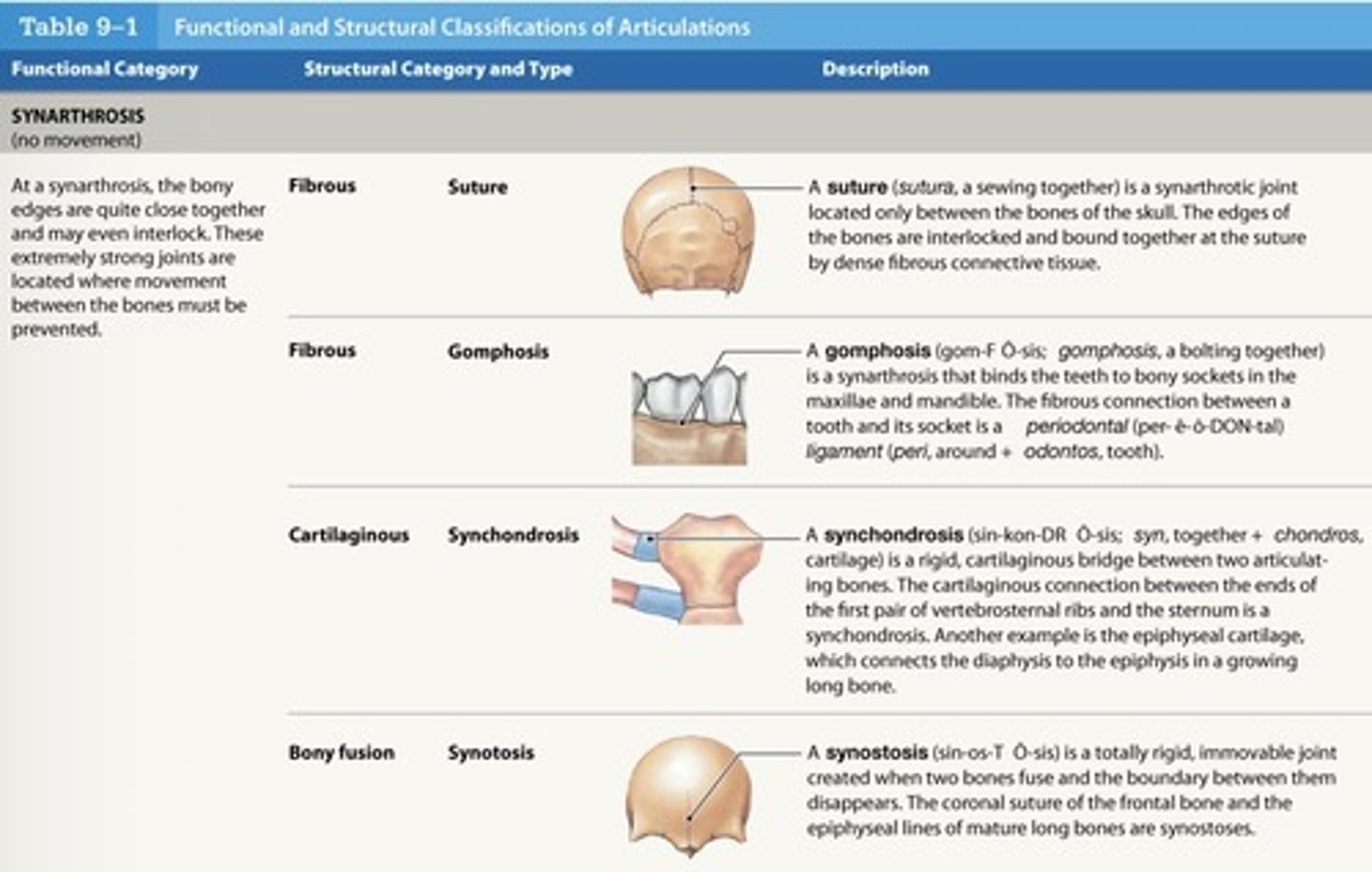
What is a synarthrosis suture joint?
- Found only between bones of skull
- Edges of bones interlock
- Bound by dense fibrous connective tissue
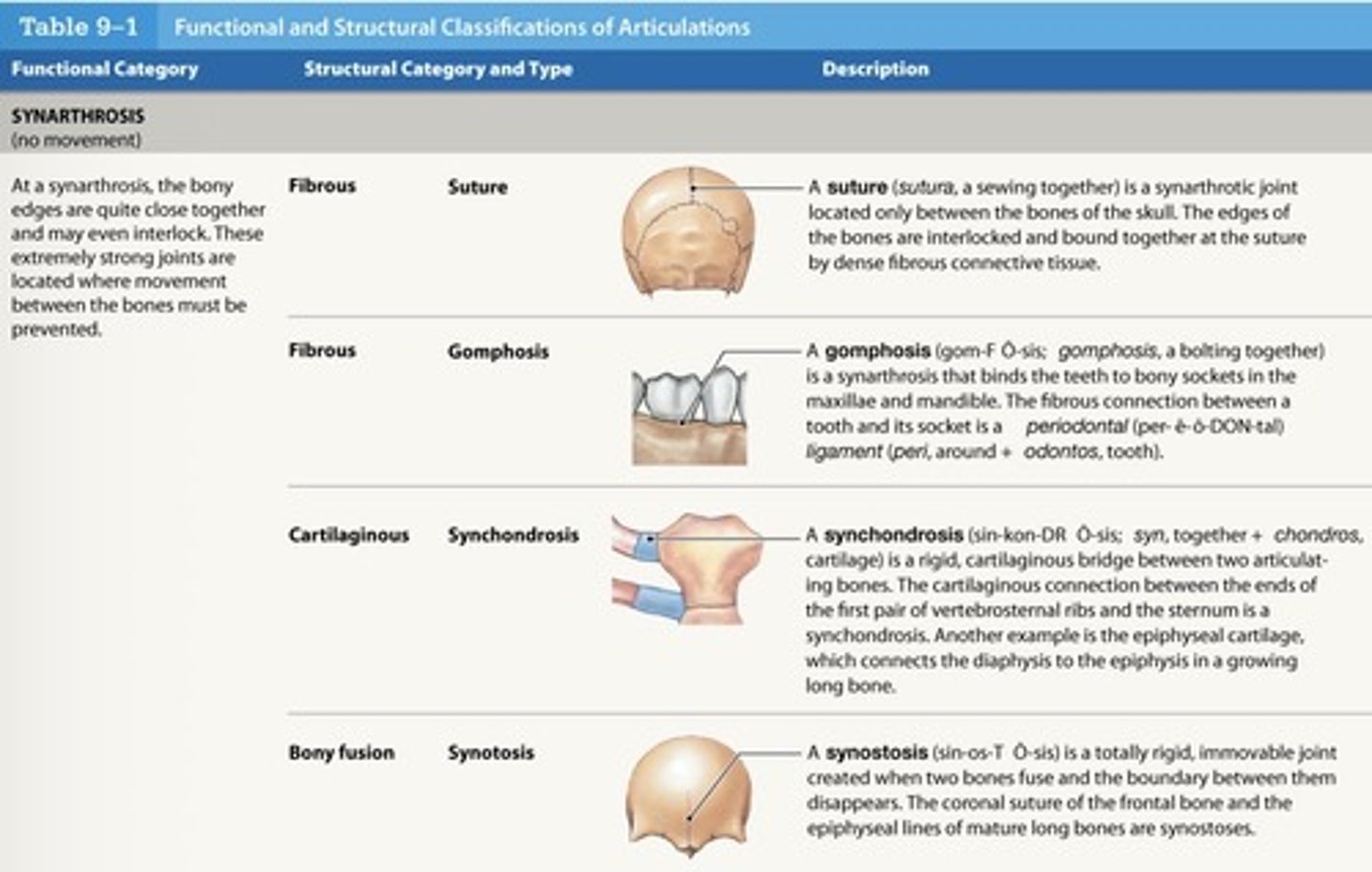
What is a synarthrosis gromphosis joint?
- Binds teeth to bony sockets
- Fibrous connection (periodontal ligament)
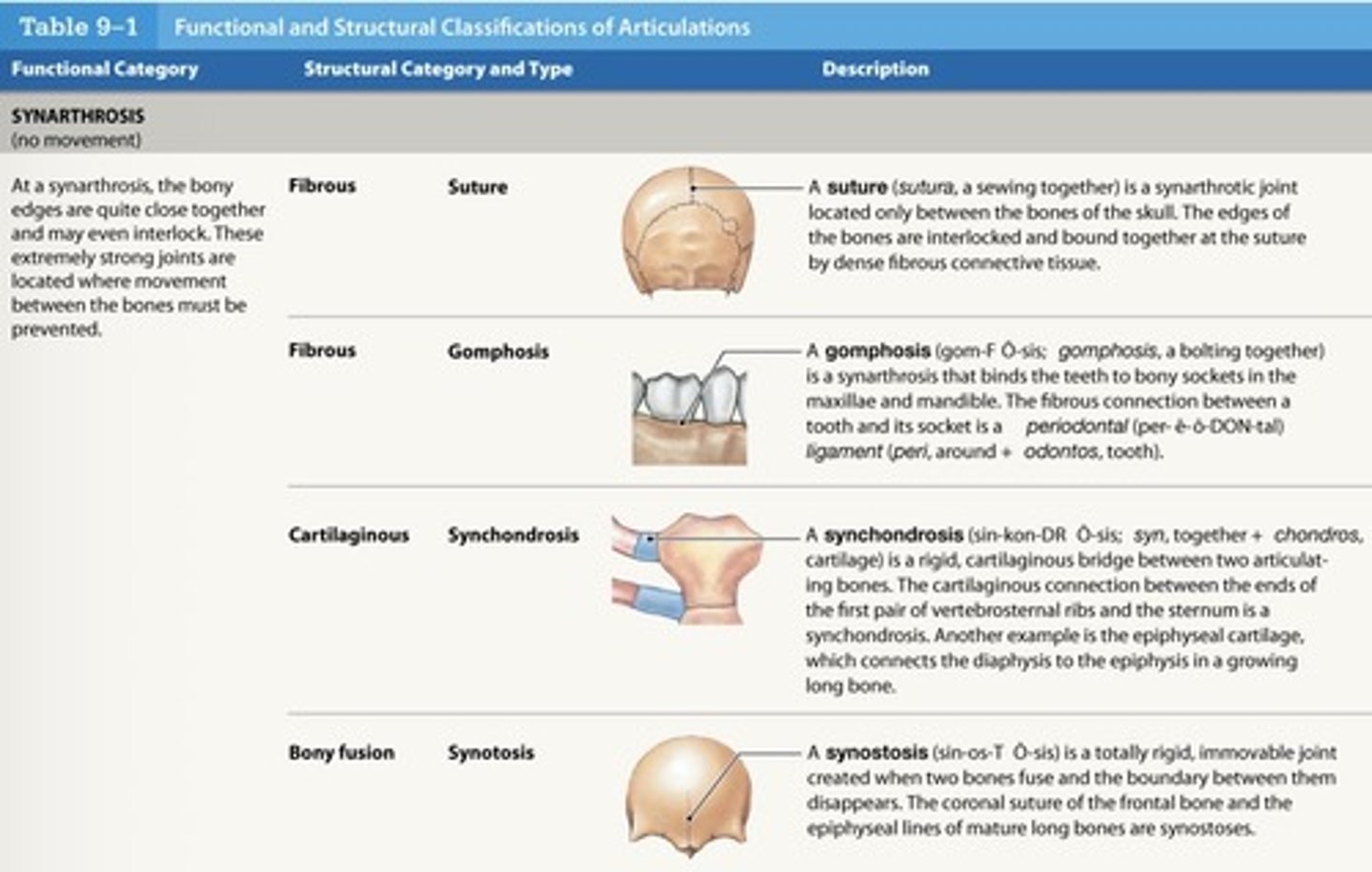
What is a synarthrosis synchondrosis joint?
- Rigid cartilaginous bridge between two bones
- Found between vertebrosternal ribs and sternum
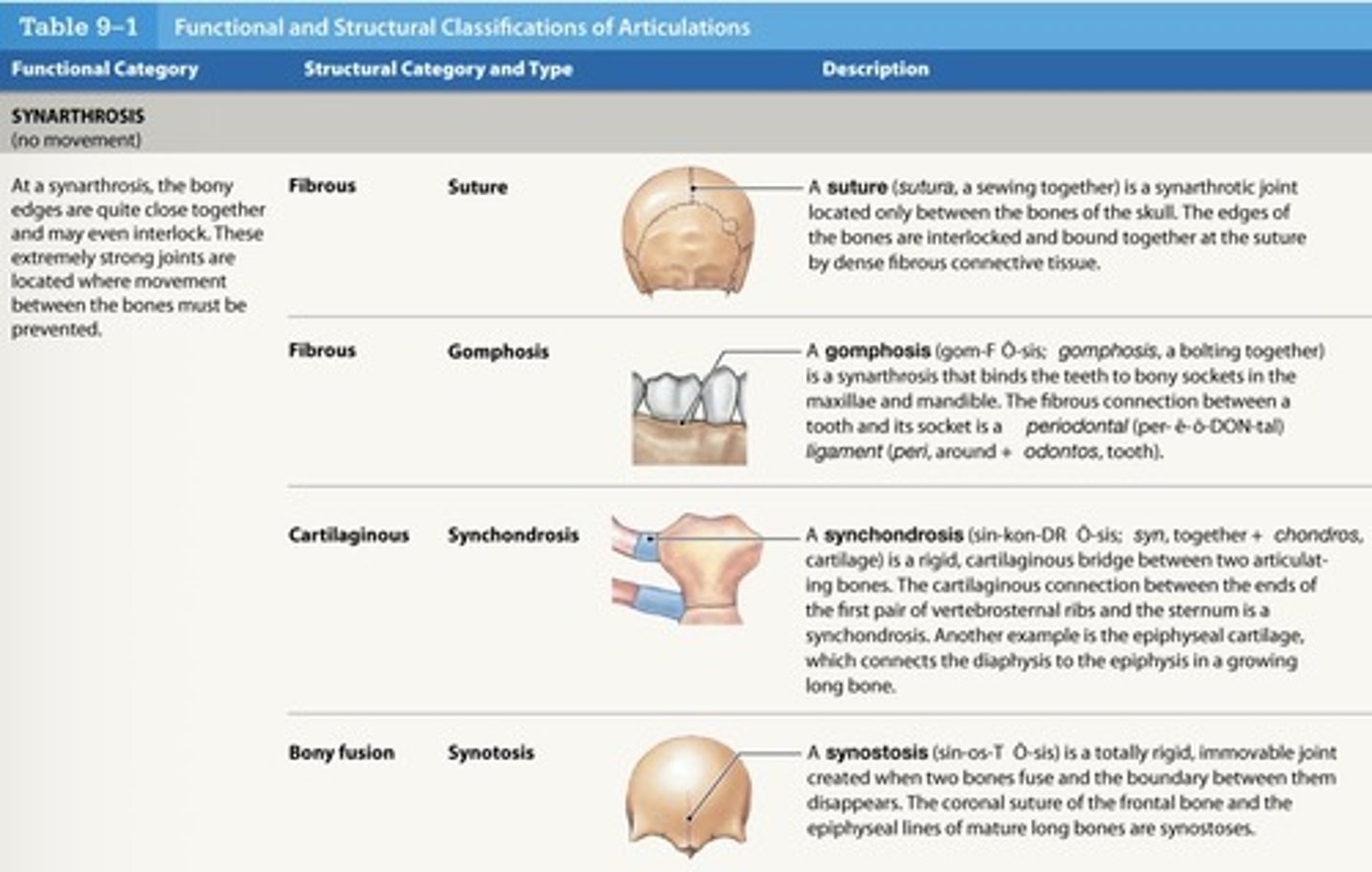
What is a synarthrosis synostosis joint?
- Created when two bones fuse
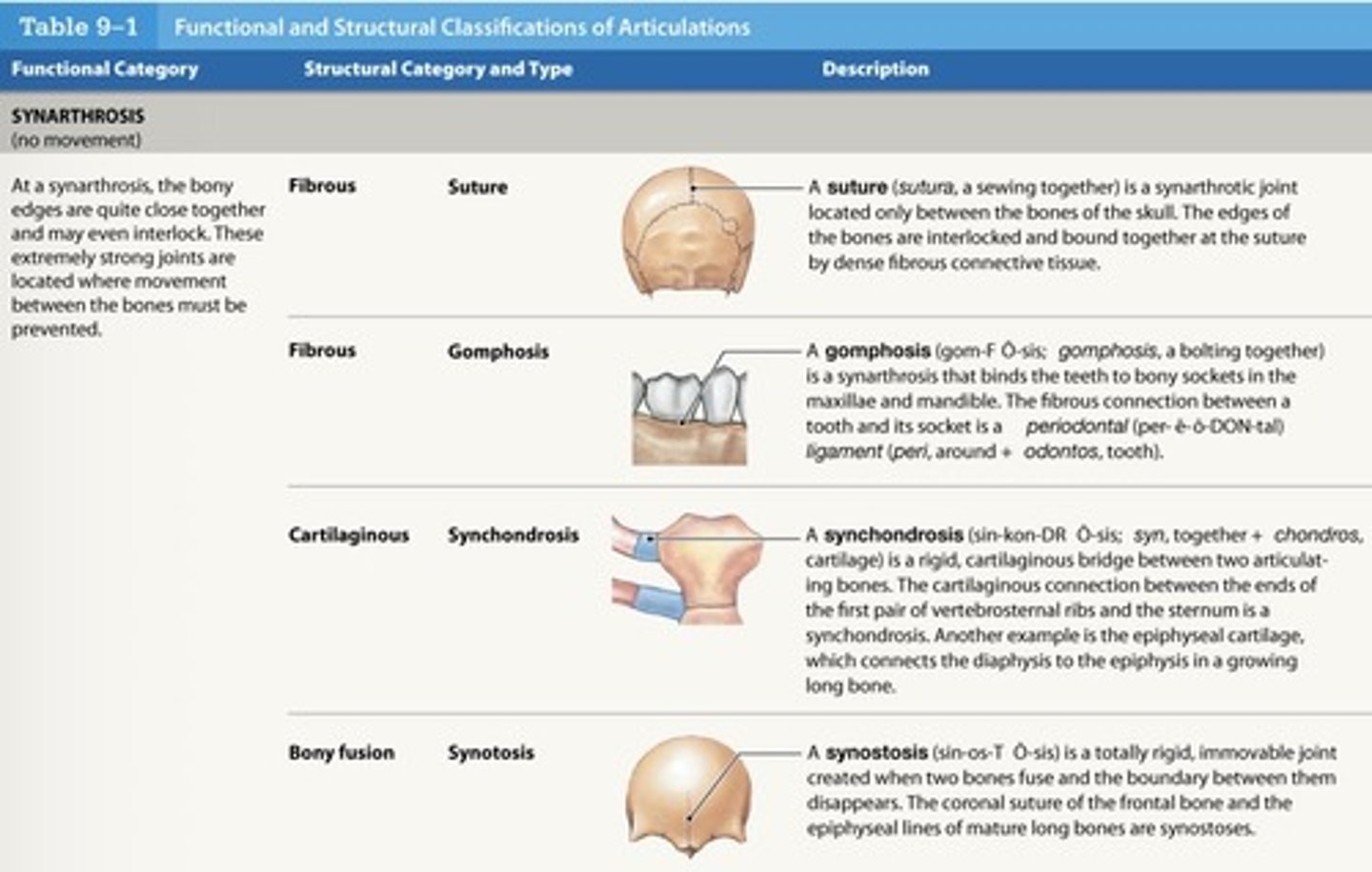
What is an example of synostosis?
epiphyseal lines
What are the characteristics of amphiarthrosis?
- More moveable than a synarthrosis
- Stronger than a diarthrosis
- May be fibrous or cartilaginous
What are the two types of amphiarthrosis ?
syndesmosis, symphysis
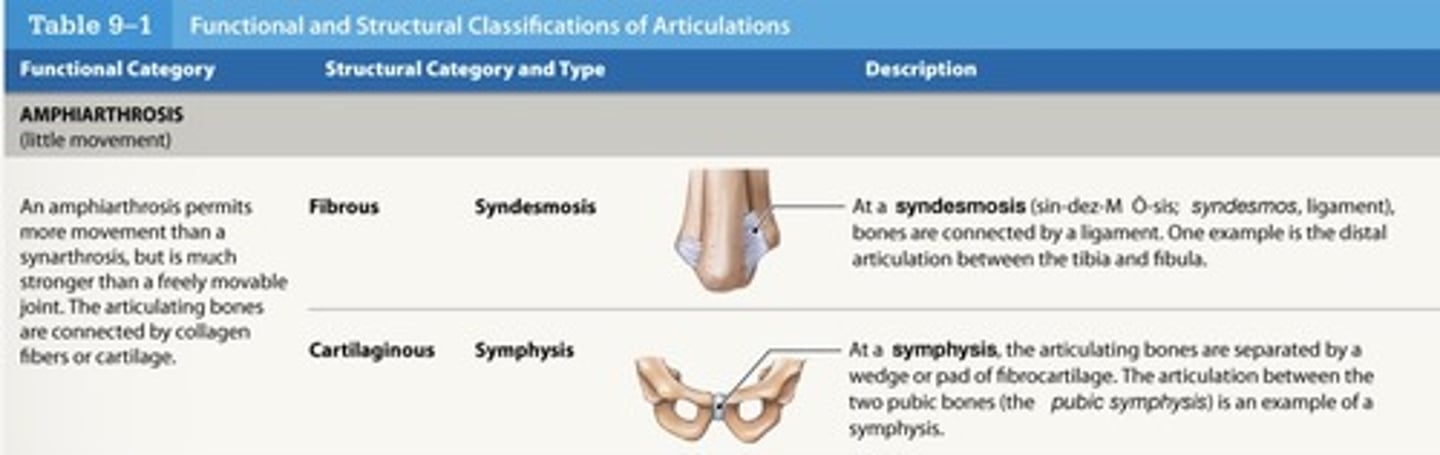
What is a syndesmosis?
bones connected by ligaments
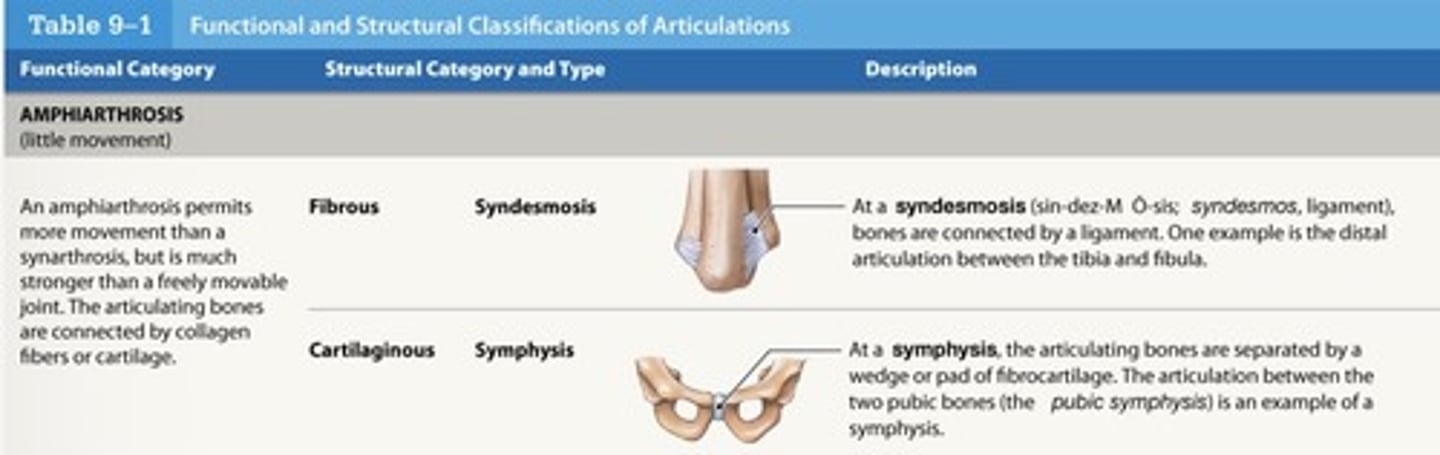
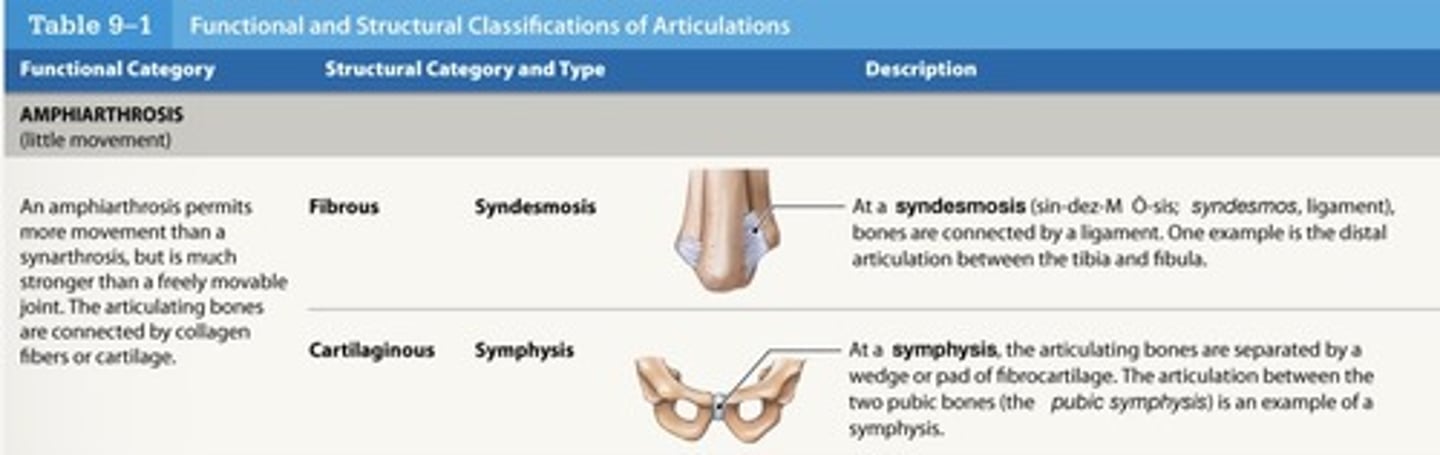
What is a symphysis?
two bones joined by fibrocartilage
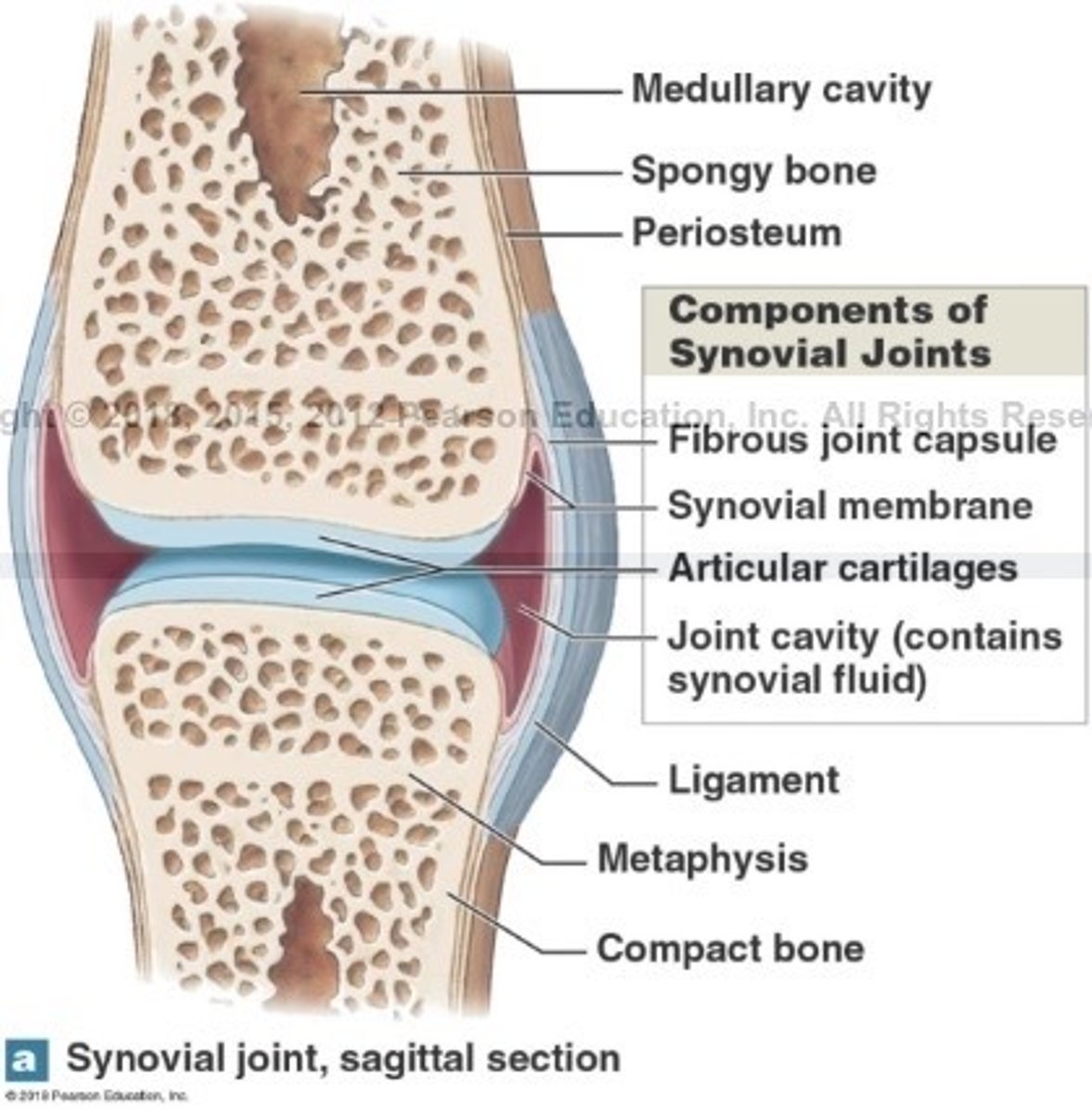
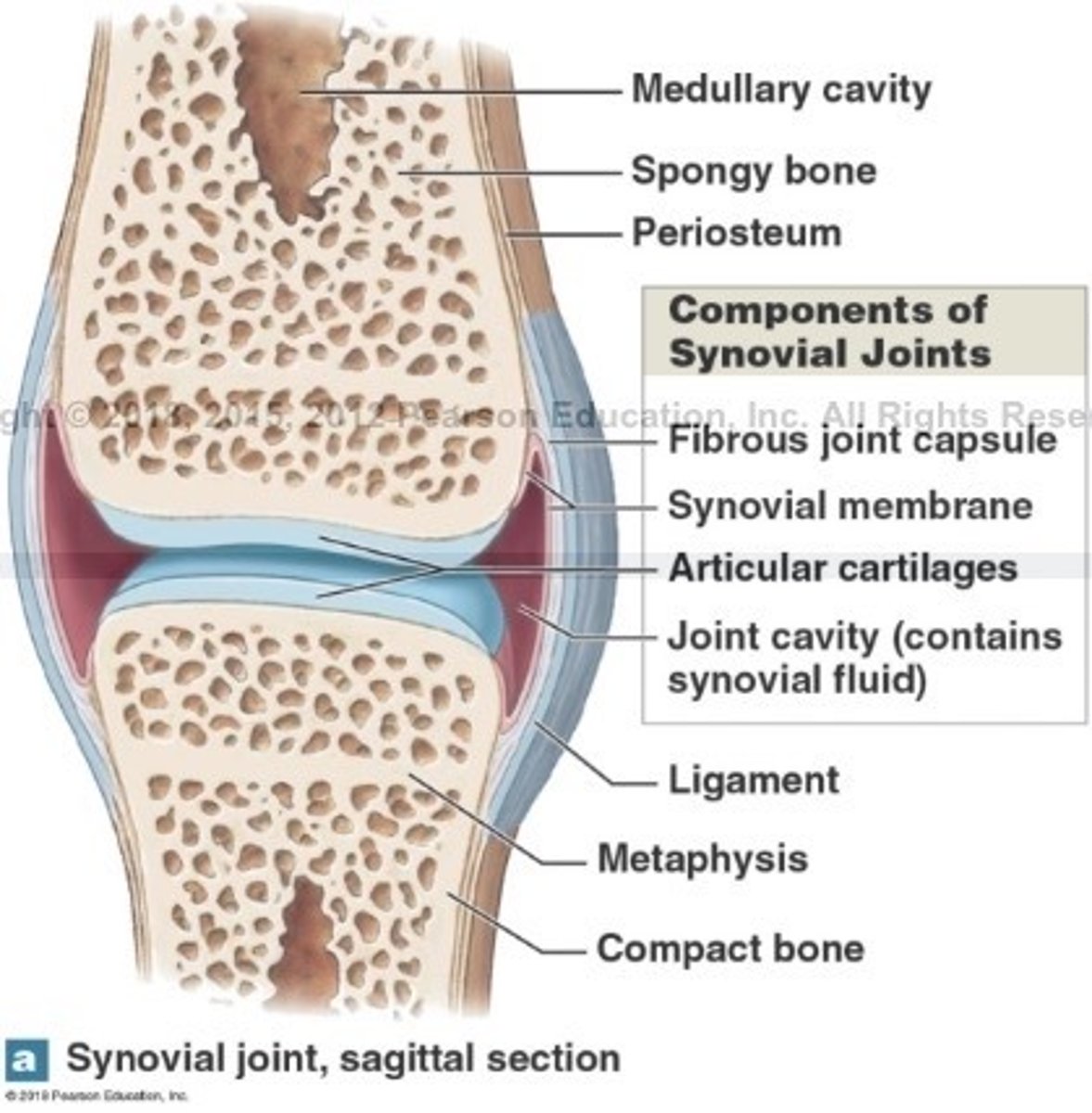
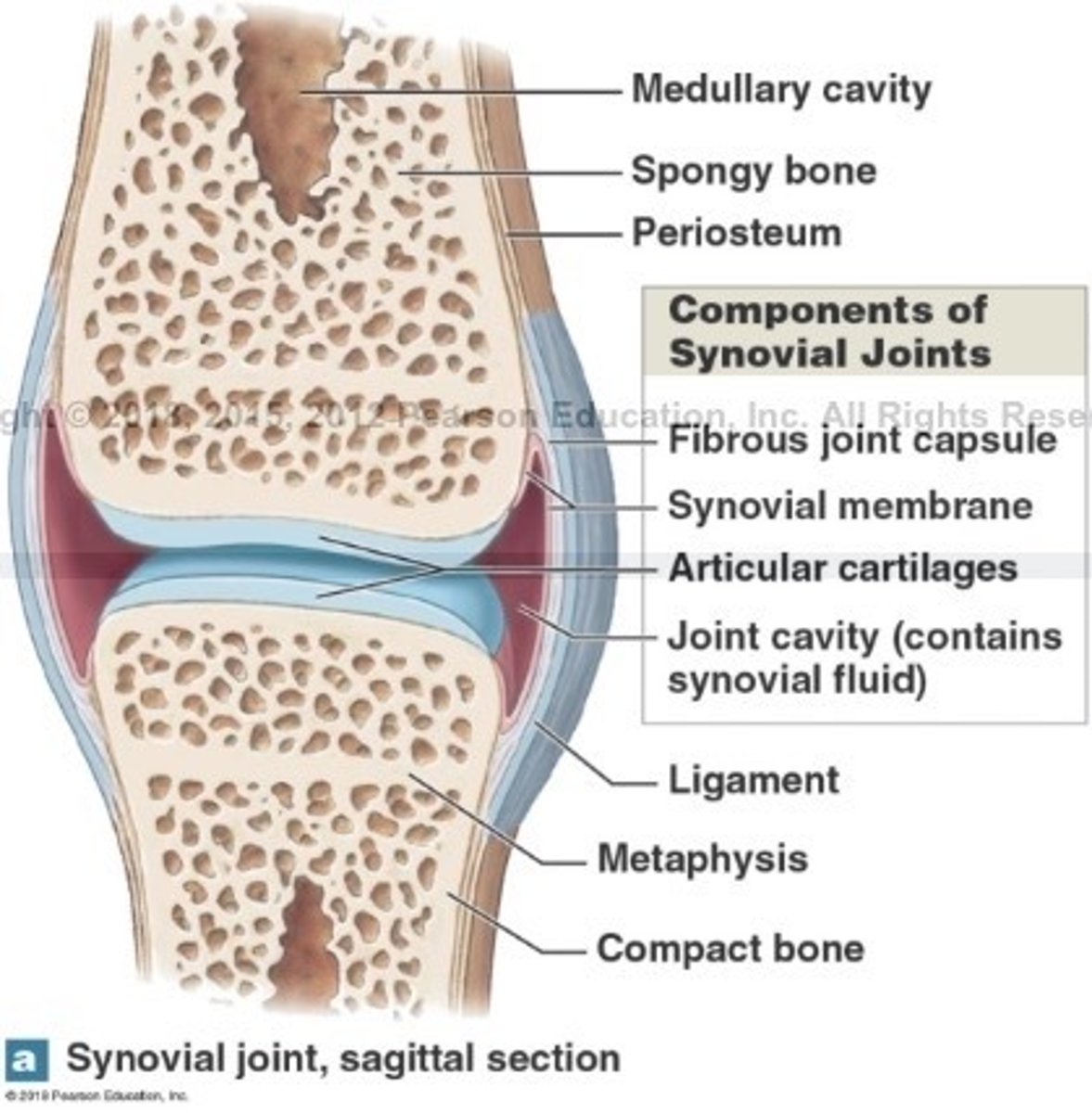
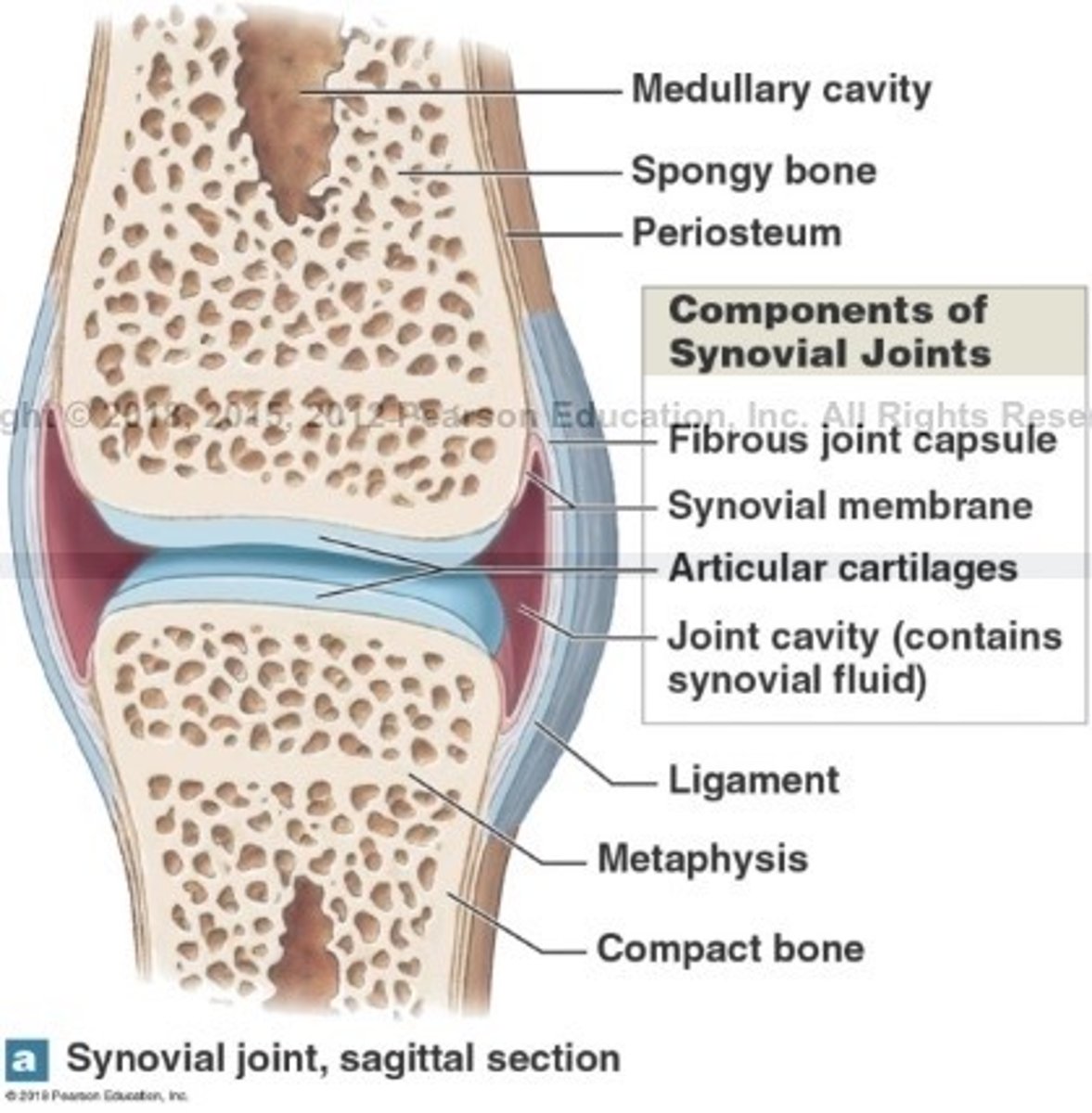
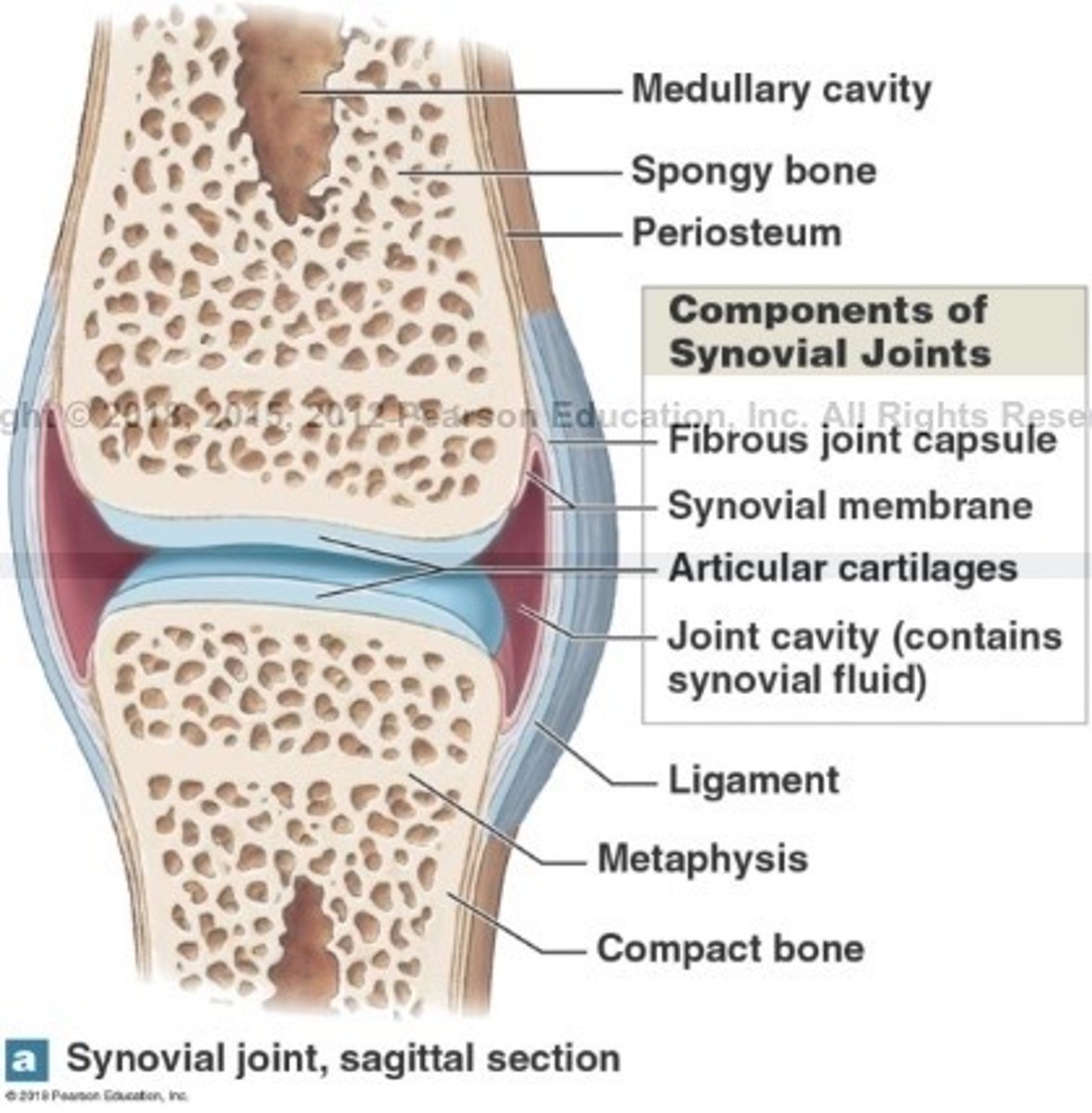
What is synovial joints?
Free moving joints, at the ends of long bones
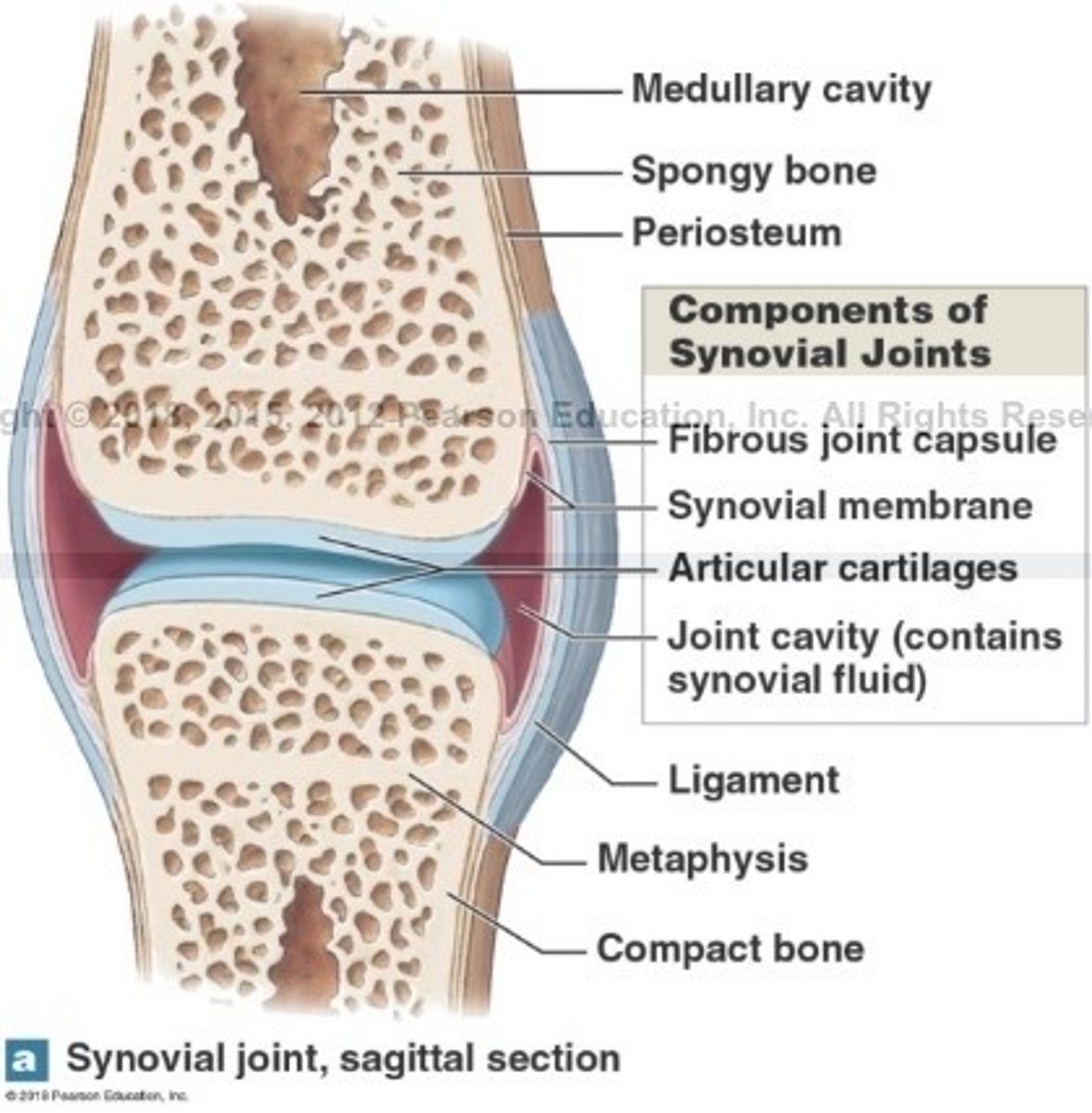
What are synovial joints surrounded by?
A 2 layered joint capsule that contains a synovial membrane
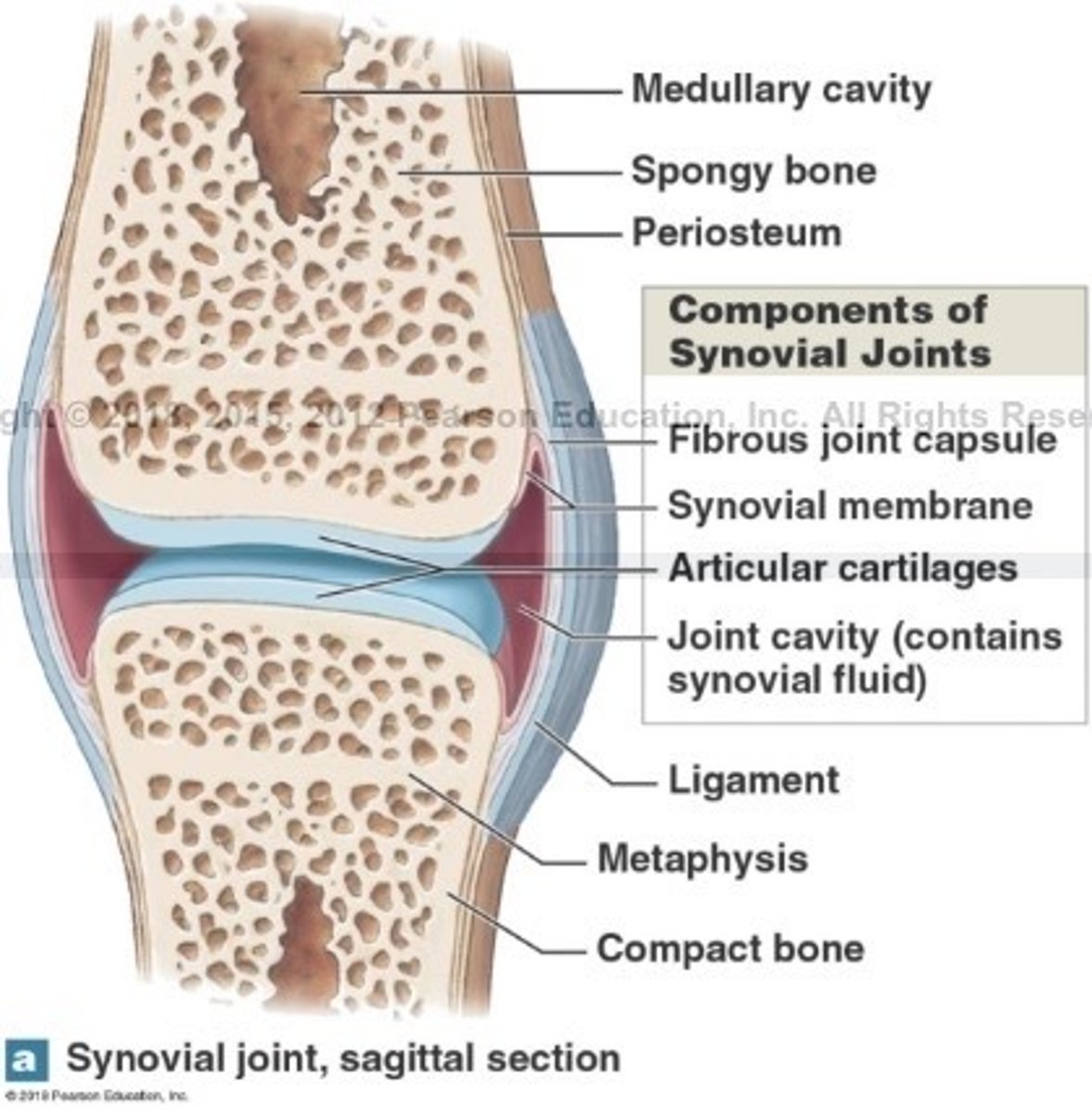
What is the function of synovial fluid?
Fills joint cavity and reduce friction
What is articular cartilage of the synovial joint?
It covers articulating surfaces
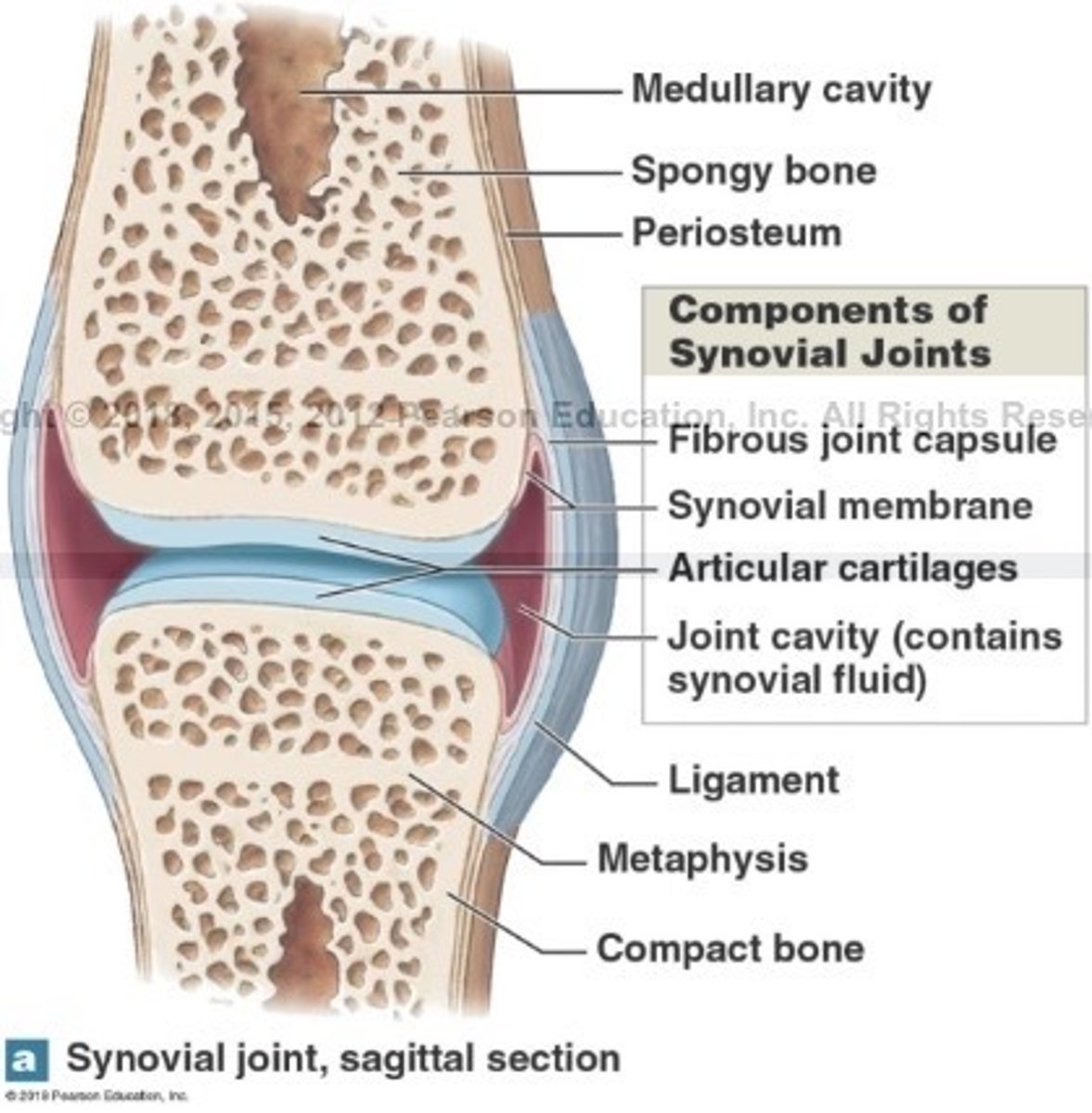
What is the function of articular cartilage?
reduces friction and absorbs shock
What is synovial fluid?
It resembles interstitial fluid that has the consistency of egg yolk
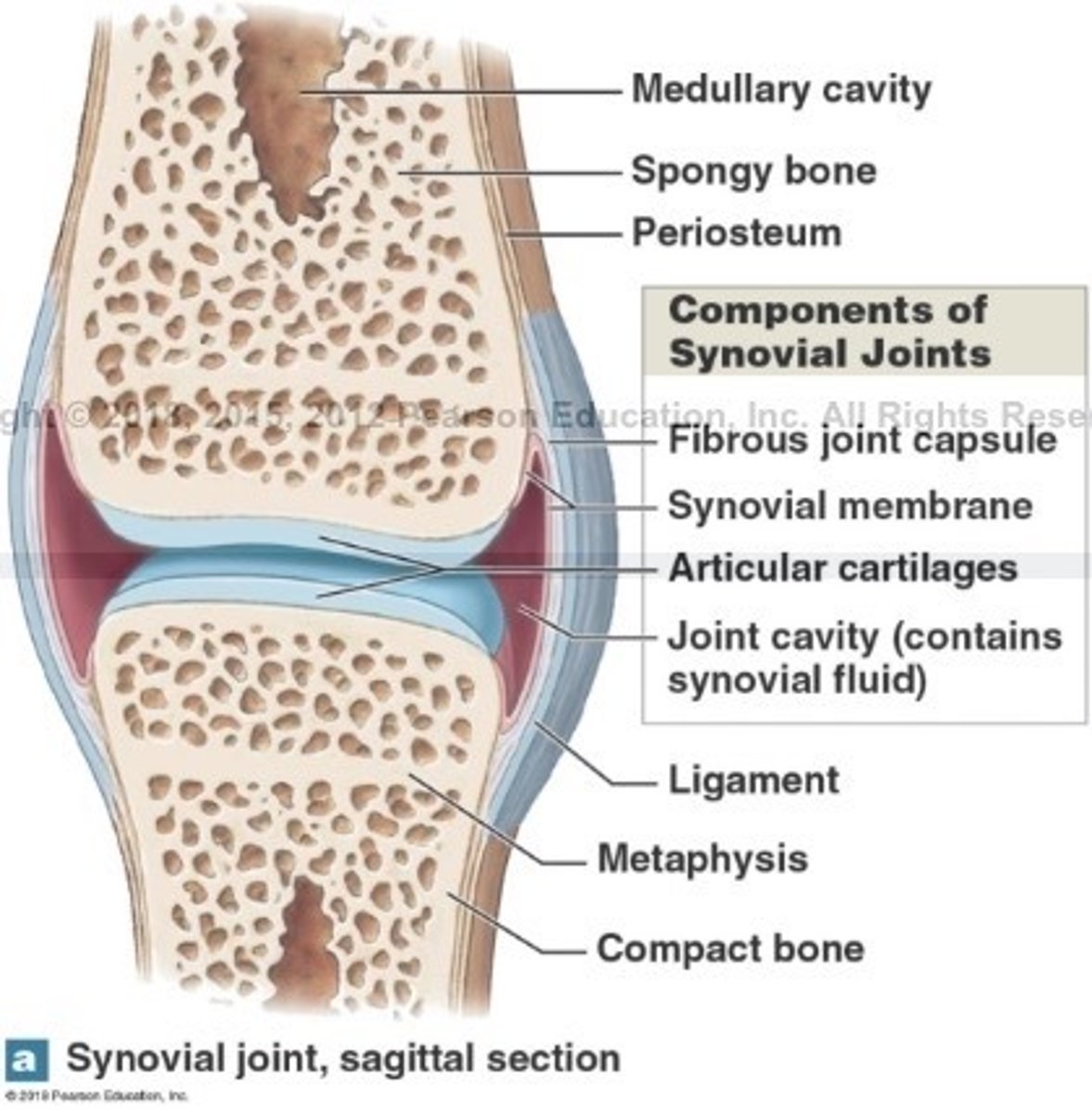
What are the primary functions of synovial fluid?
lubrication, nutrient distribution, shock absorption
Are synovial joints mobile?
Yes, but relatively weak
What accessory structures are stabilized by synovial joints?
- Cartilages and fat pads
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Bursae
What cartilages are in synovial joints?
Meniscus
What is a meniscus?
a fibrocartilage pad that provides padding between bones
What is the function of fat pads in synovial joints?
Adipose tissue covered by synovial membrane that protect articular cartilages.
What is the function of ligaments in synovial joints?
Support, strengthen joints
What is the function of tendons in synovial joints?
Attach muscles around joint
What is bursae?
Small pockets of synovial fluid
What is the function of bursae in synovial joints?
Cushion areas where tendons or ligaments rub against other tissues
What are the factors function that stabilize synovial joints?
Responsible for preventing injury by limiting range of mostion, and for stabilizing the joint
What are the factors that stabilize synovial joints?
Collagen fibers of joint capsule and ligaments
Shapes of articulating surfaces and menisci
Other bones, muscles, or fat pads
Tendons attached to articulating bones
What is dislocation (luxation)?
articulating surfaces forced out of position and damages articular cartilage, ligaments, joint capsule
What is subluxation?
partial dislocation
Movements are described in terms that reflect the
-Plane or direction of movement
-Relationship between structures
What is monaxial?
Movement in one plane
What is an example of monaxial?
Elbow and ankle
What is biaxial?
movement in two planes
What is Triaxial?
movement in three planes
What is an example of biaxial?
wrist and ribs
What is an example of Triaxial?
shoulder and hip
What are the types of movement at synovial joints?
gliding, angular movements, rotation, special movements
What is gliding movement?
when two flat surfaces slide past each other
What is angular motion?
rotation around an axis
What is Flexion?
decreasing the angle of a joint
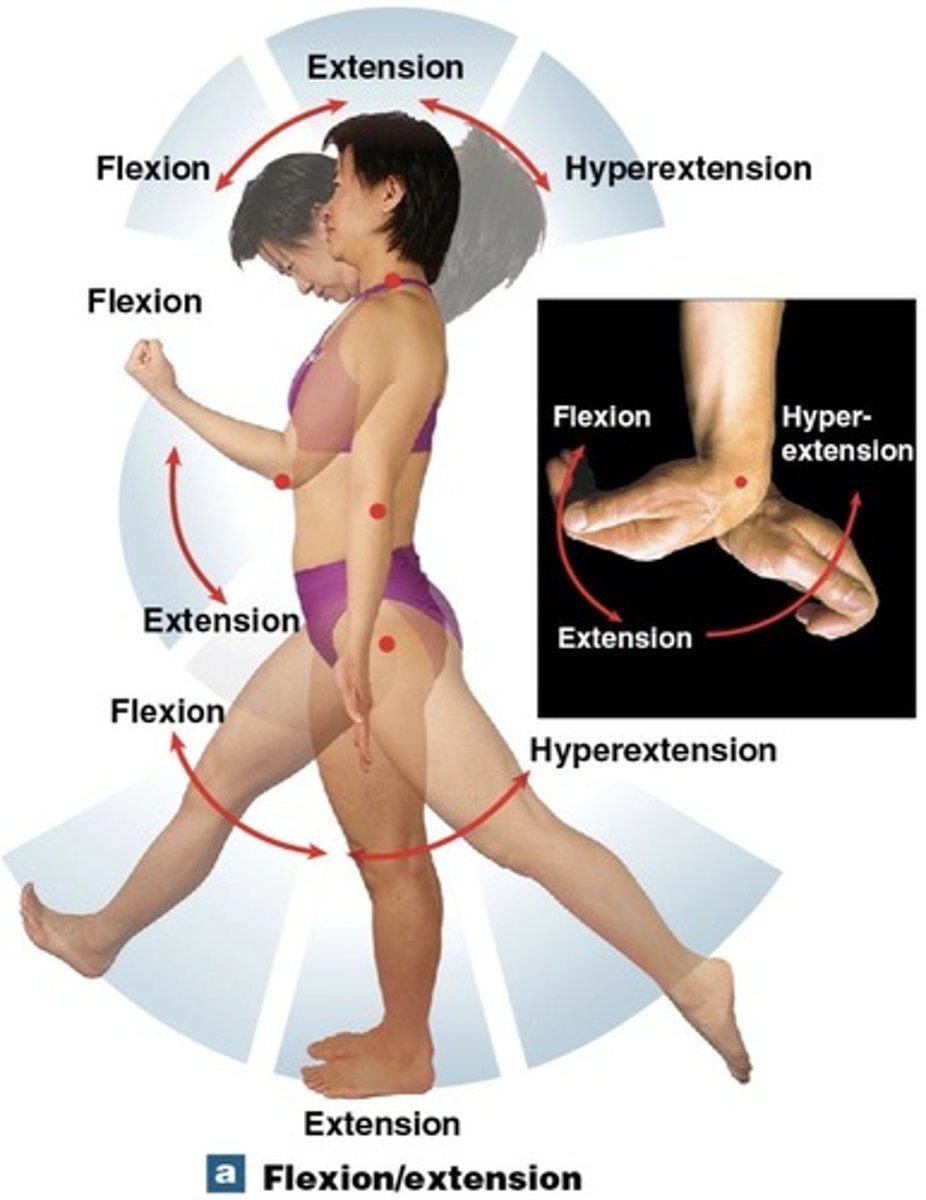
What are the types of angular movement? (6)
flexion, extension, hyperextension, abduction, adduction, circumduction
What is extension?
Increasing the angle of a joint
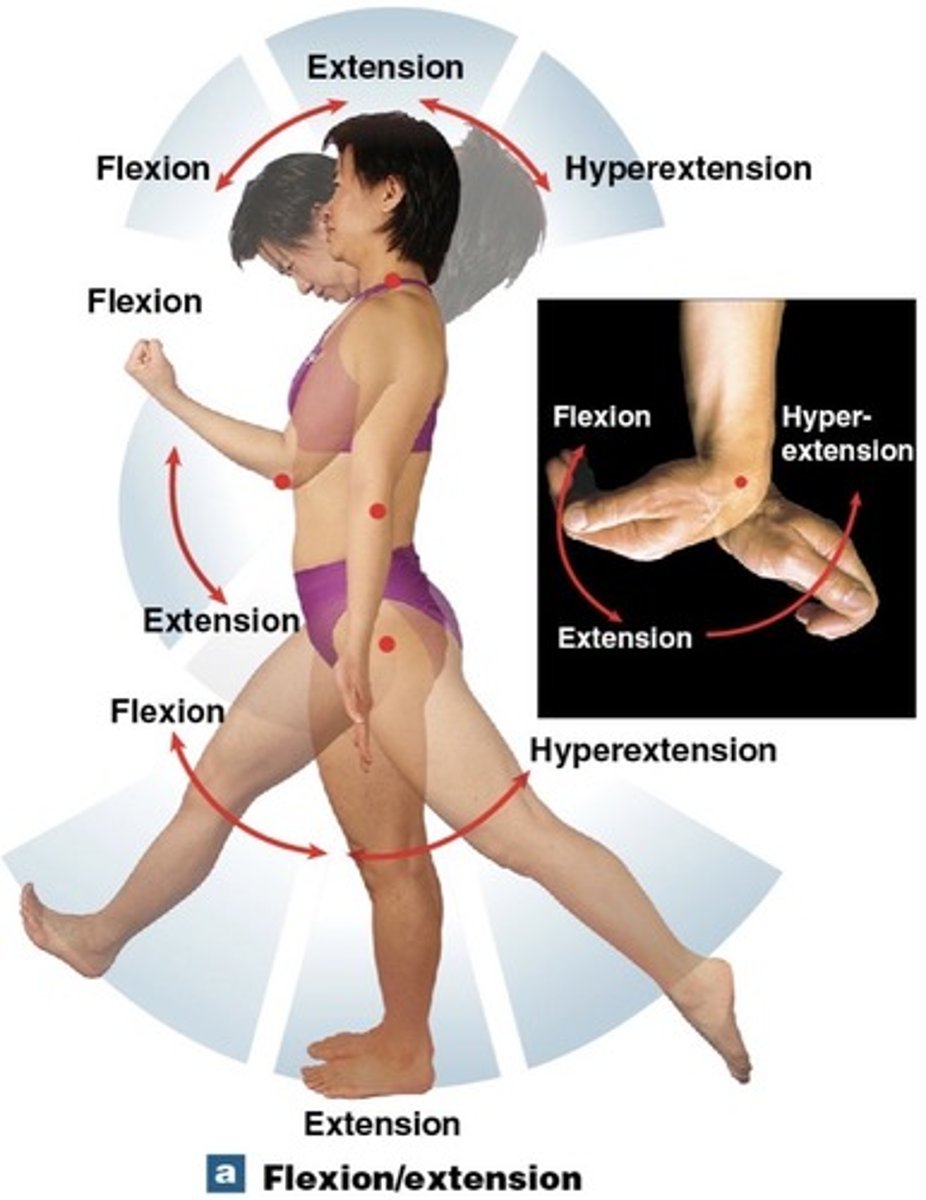
What is hyperextension?
extension beyond anatomical position
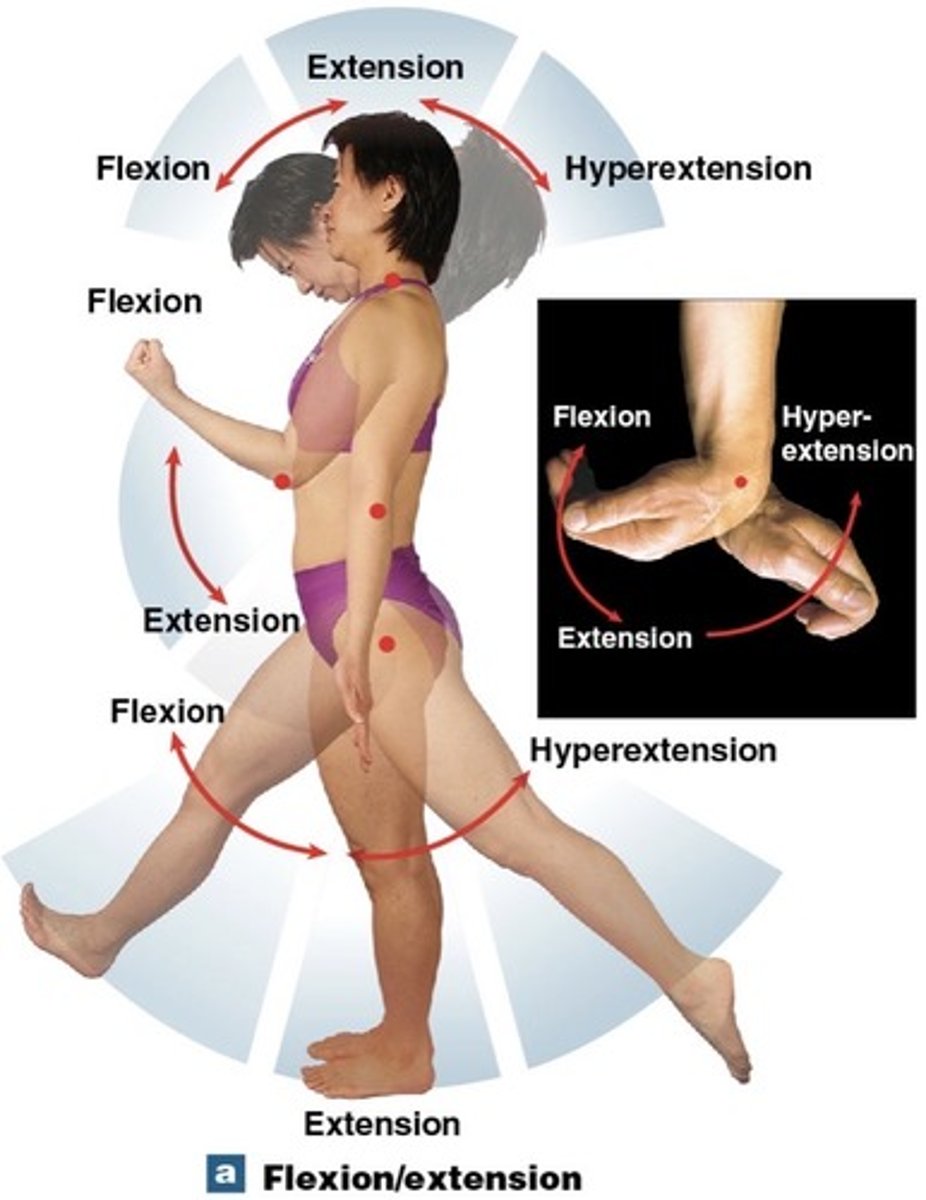
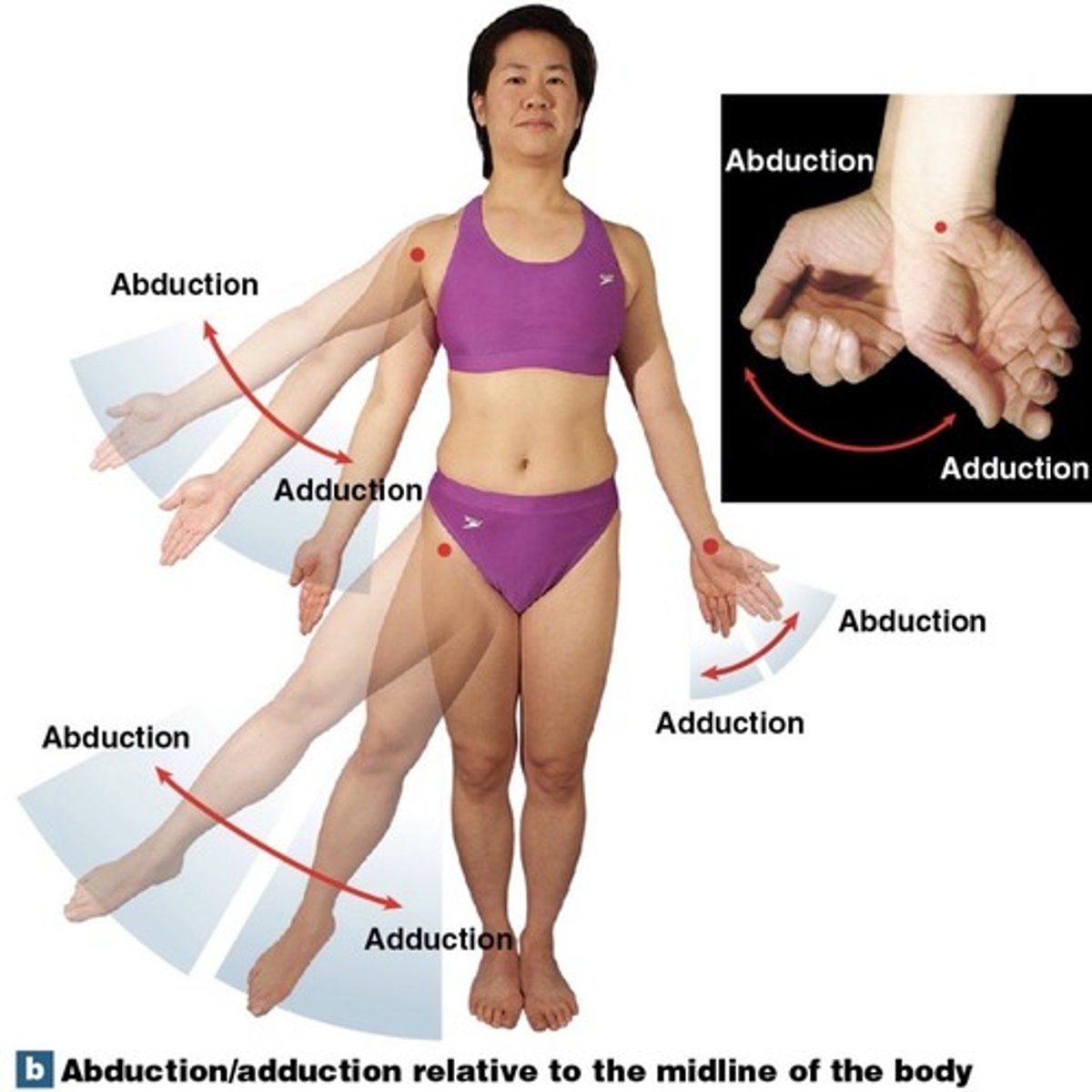
What is abduction?
movement away from the midline
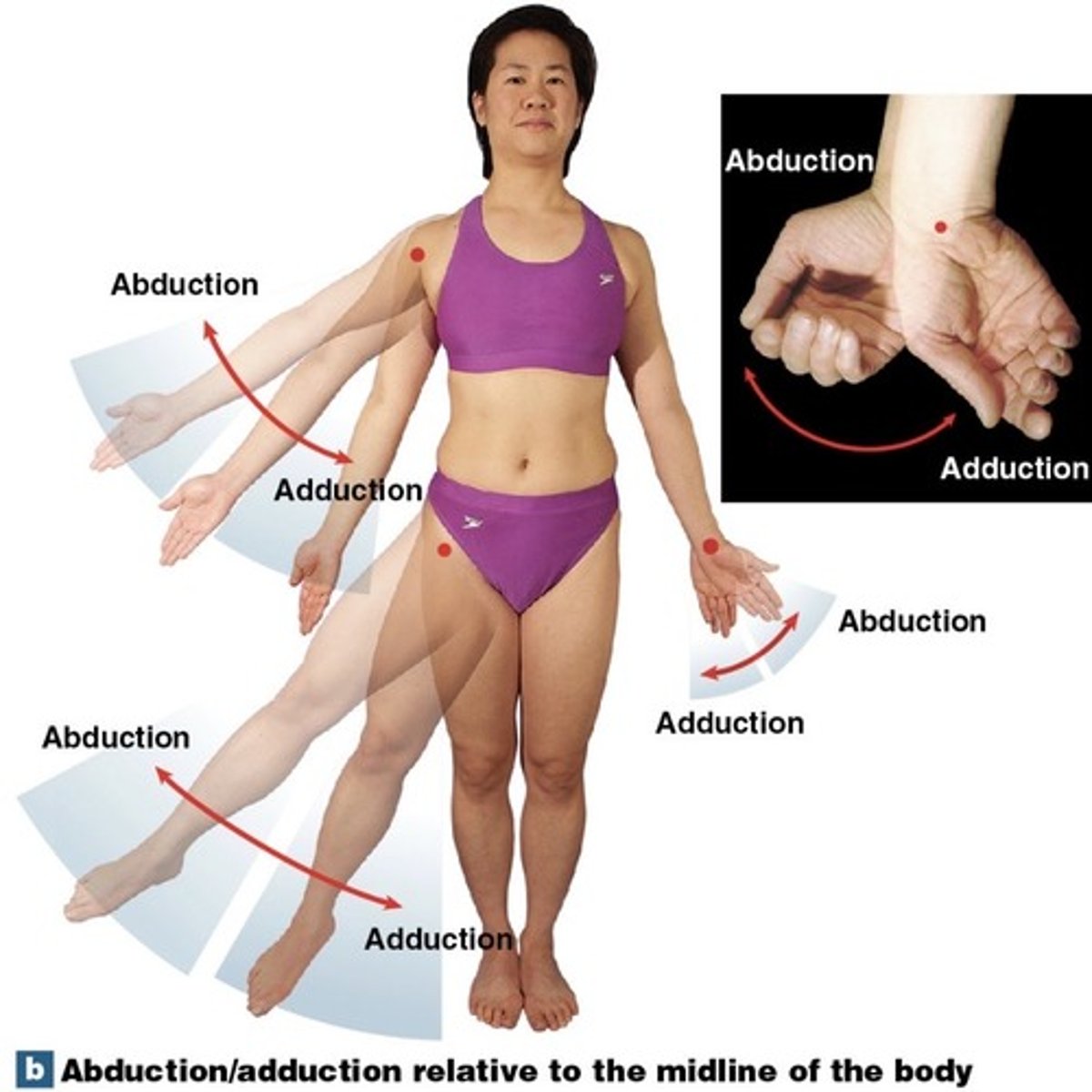
What is adduction?
movement toward the midline
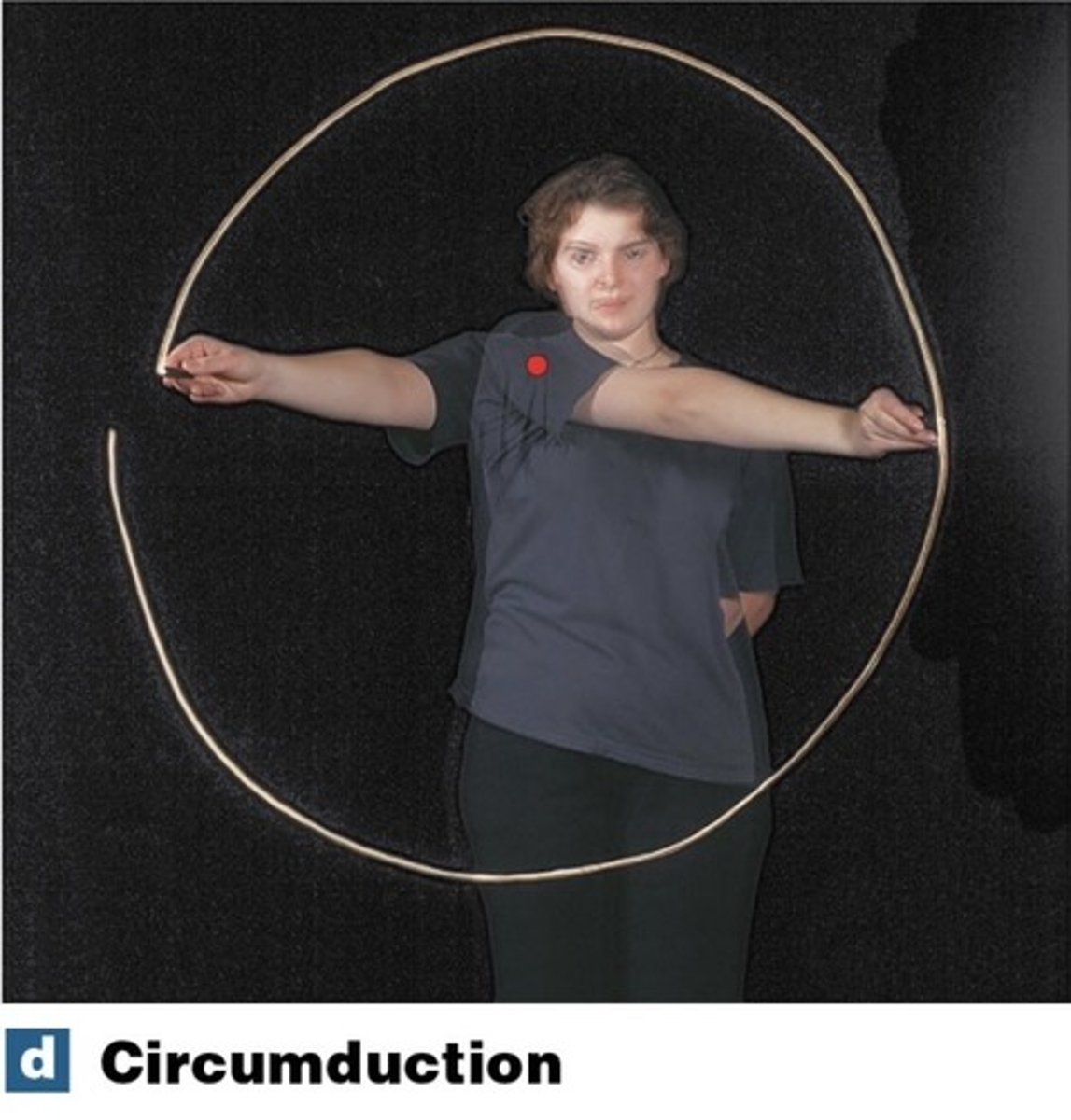
What is circumduction?
moving the arm in a circle around the shoulder

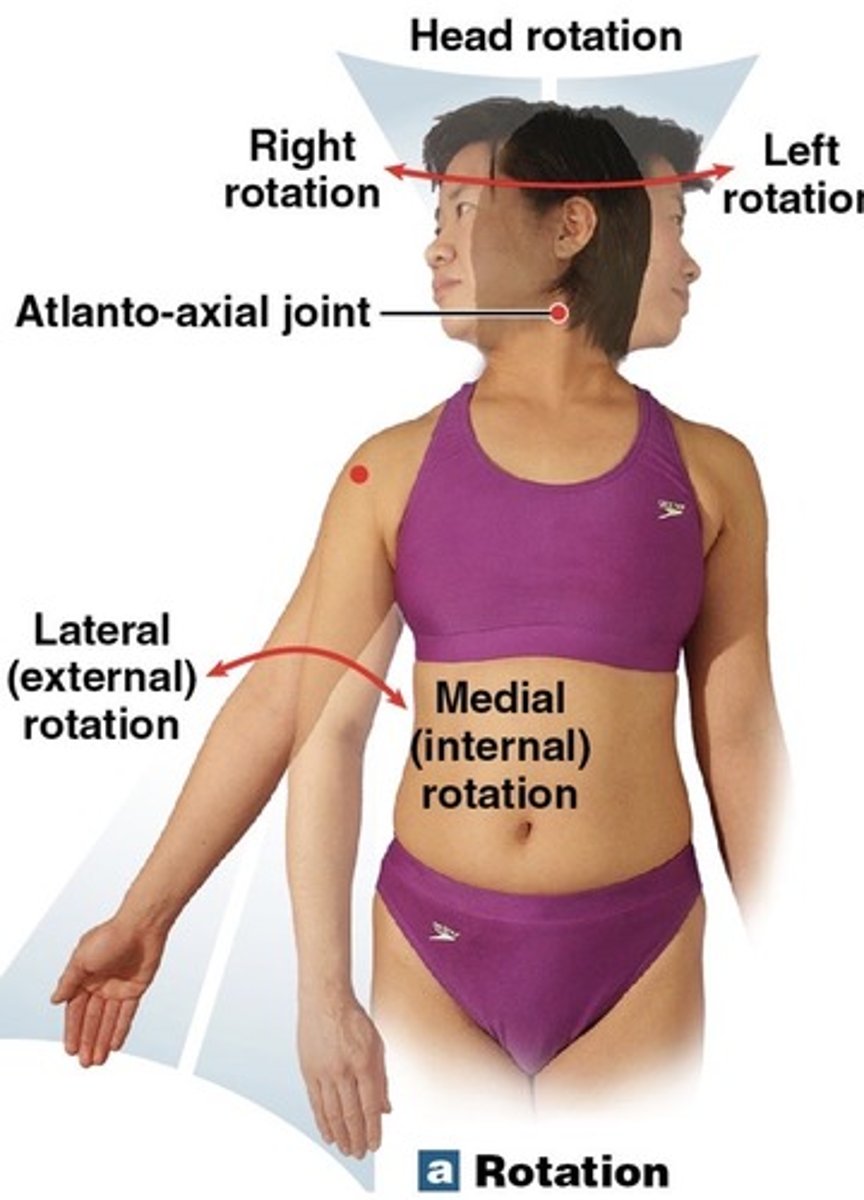
What is rotational movement?
the movement of a bone as it rotates around its longitudinal axis
What is medial rotation?
Rotation toward the midline
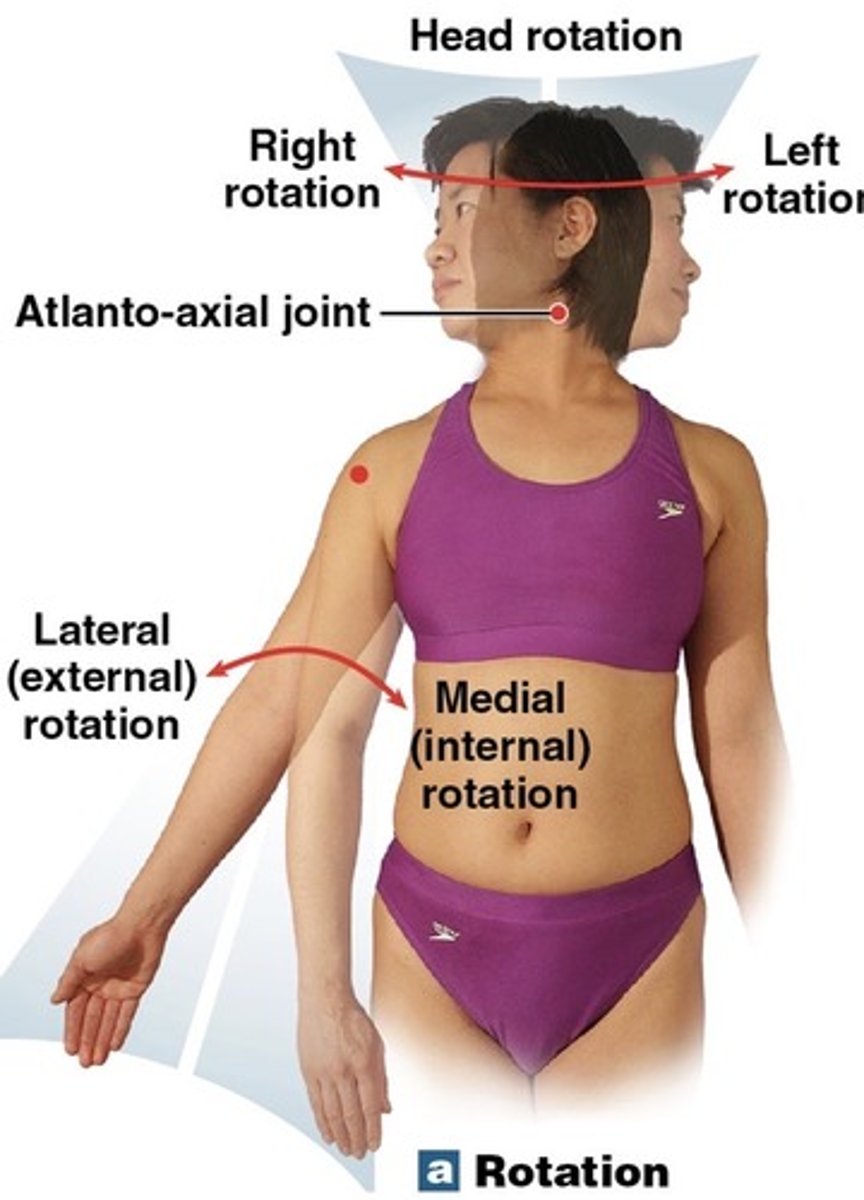
What is lateral rotation?
rotation away from the midline
What movements are in rotational movement?
Medial and lateral rotation, pronation, supination
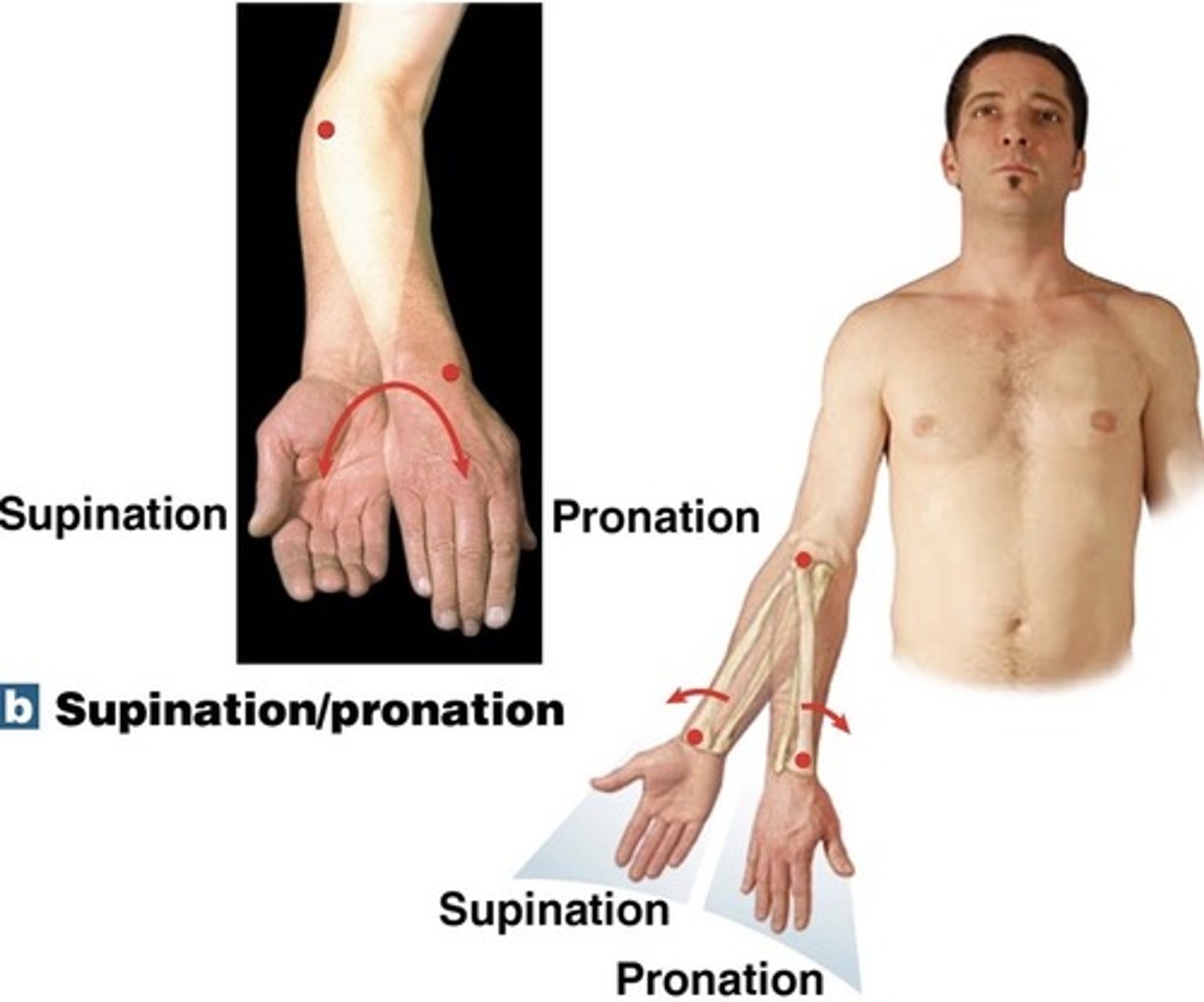
What is pronation?
turning the forearm so that the palm is down
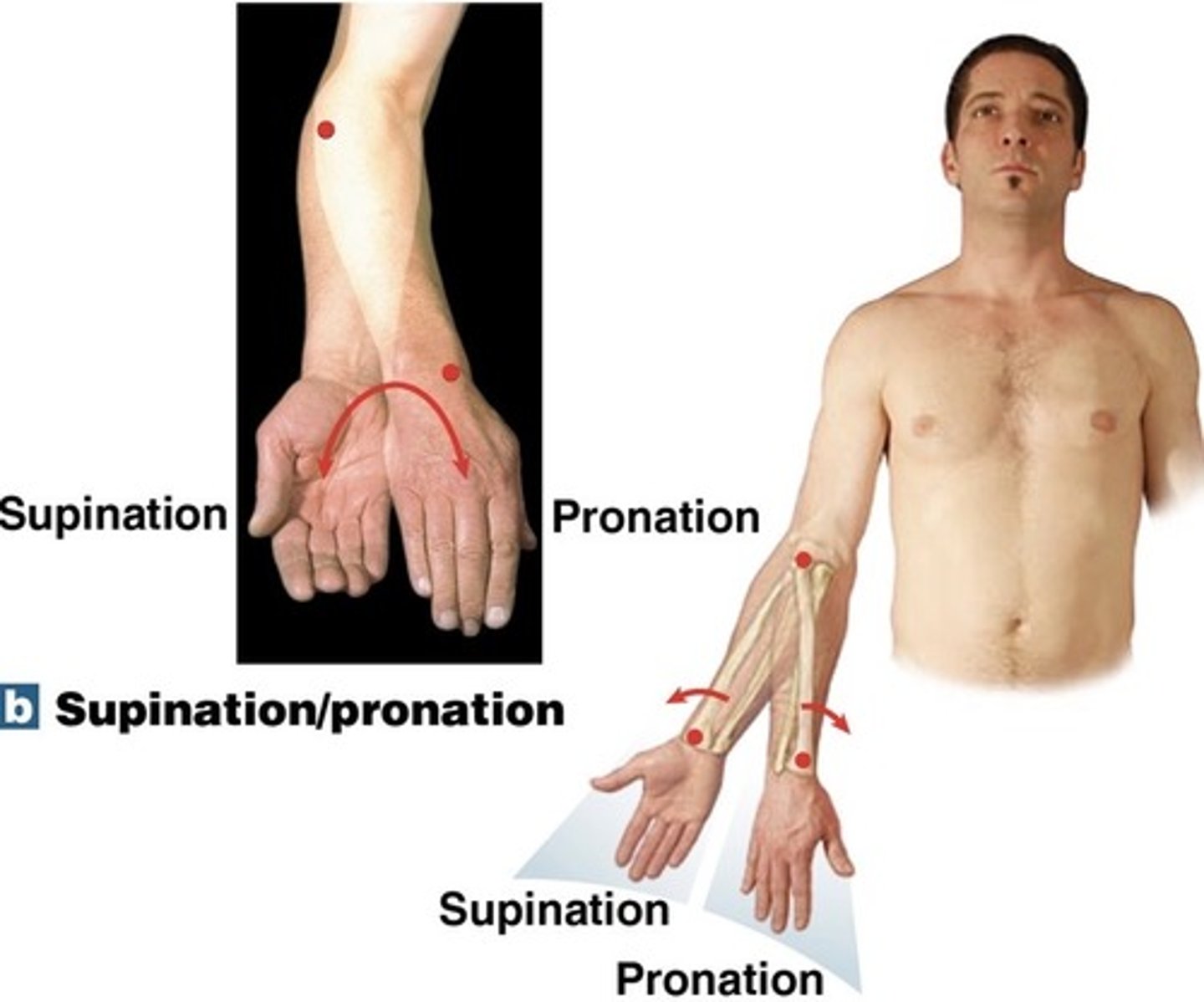
What is supination?
turning the forearm so the palm is up
What are the special movements?
supination, pronation, inversion, eversion, protraction, retraction, elevation, depression, opposition
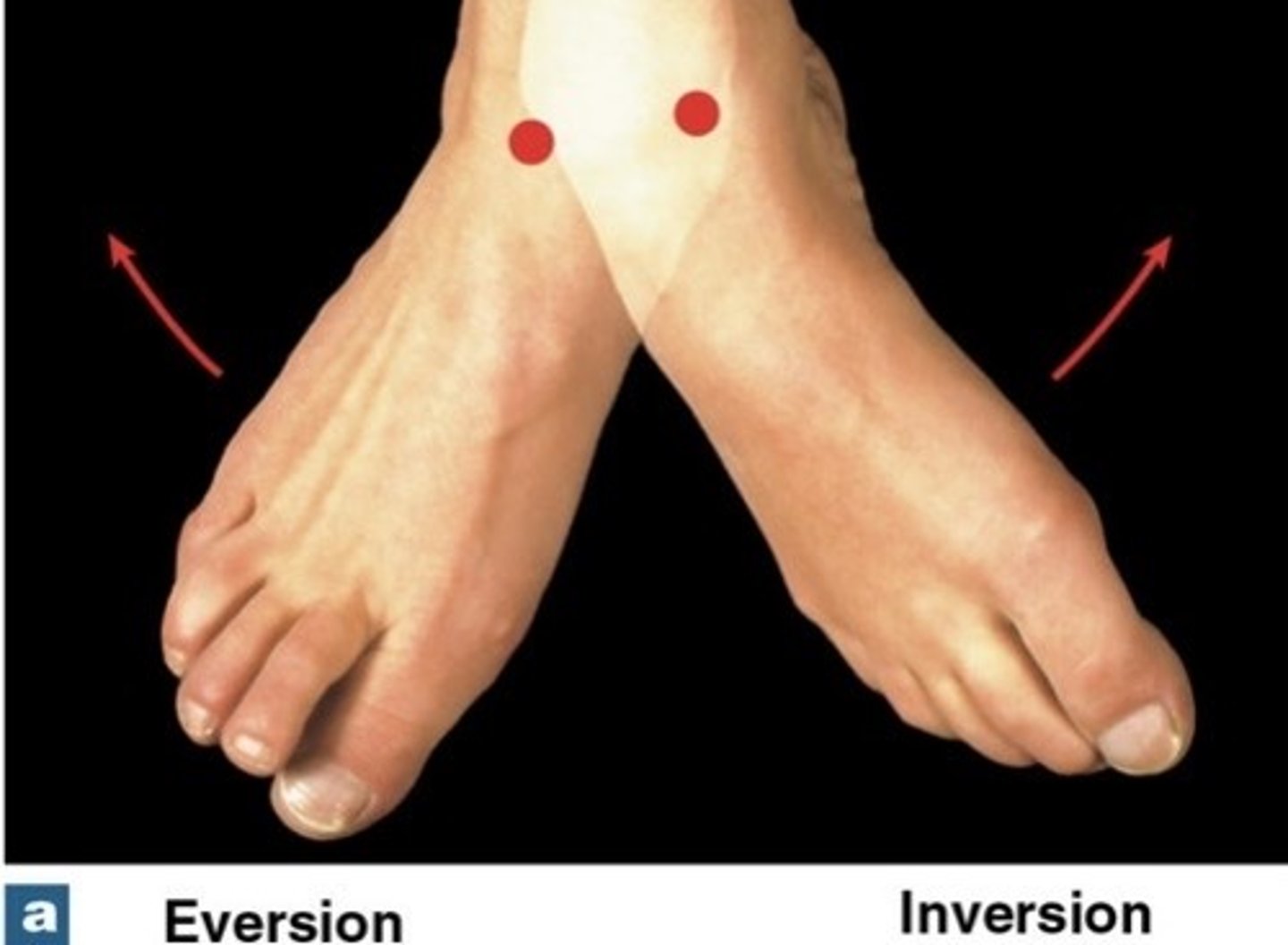
What is inversion?
twists sole of foot medially
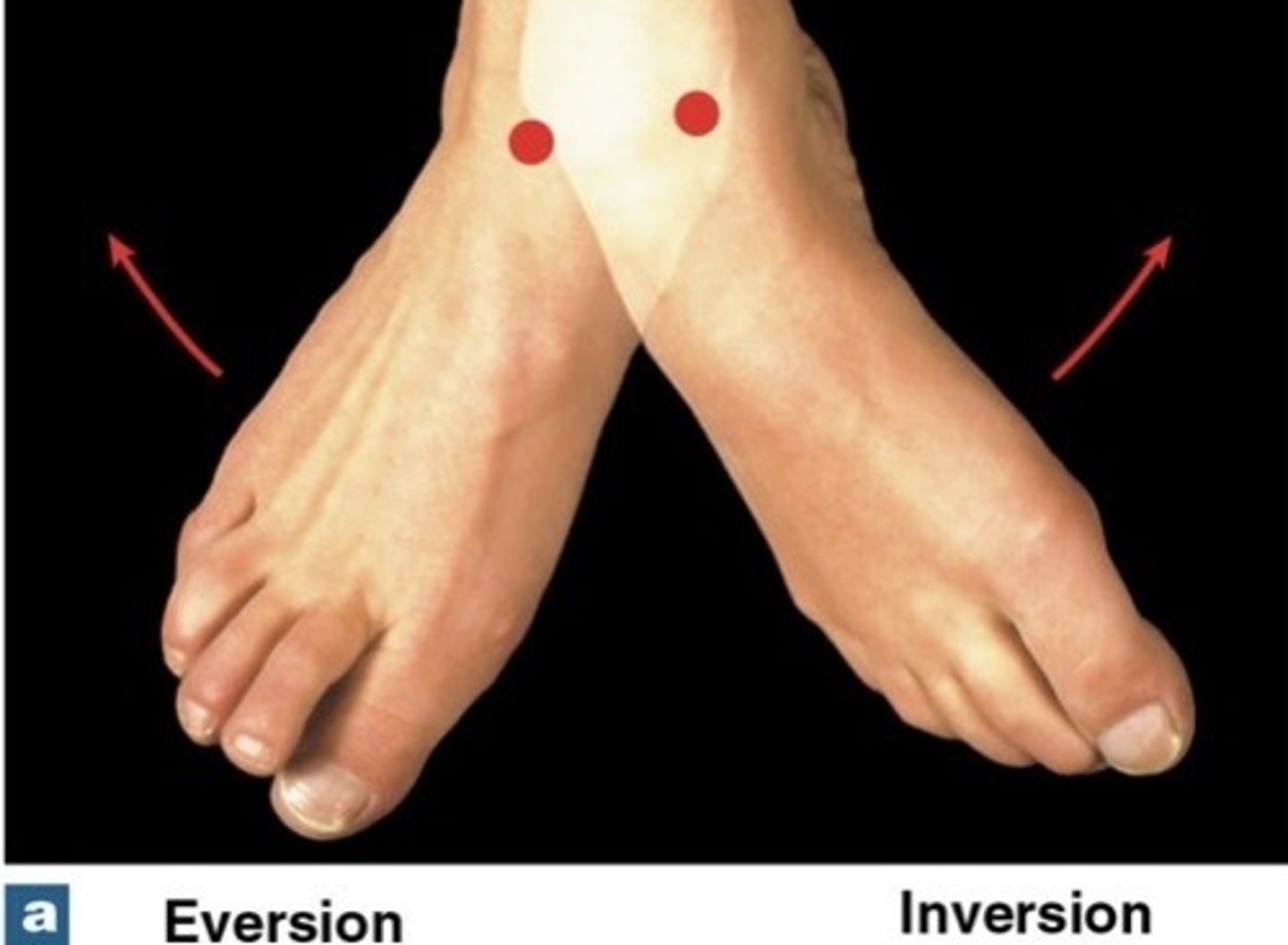
What is eversion?
twists sole of foot laterally
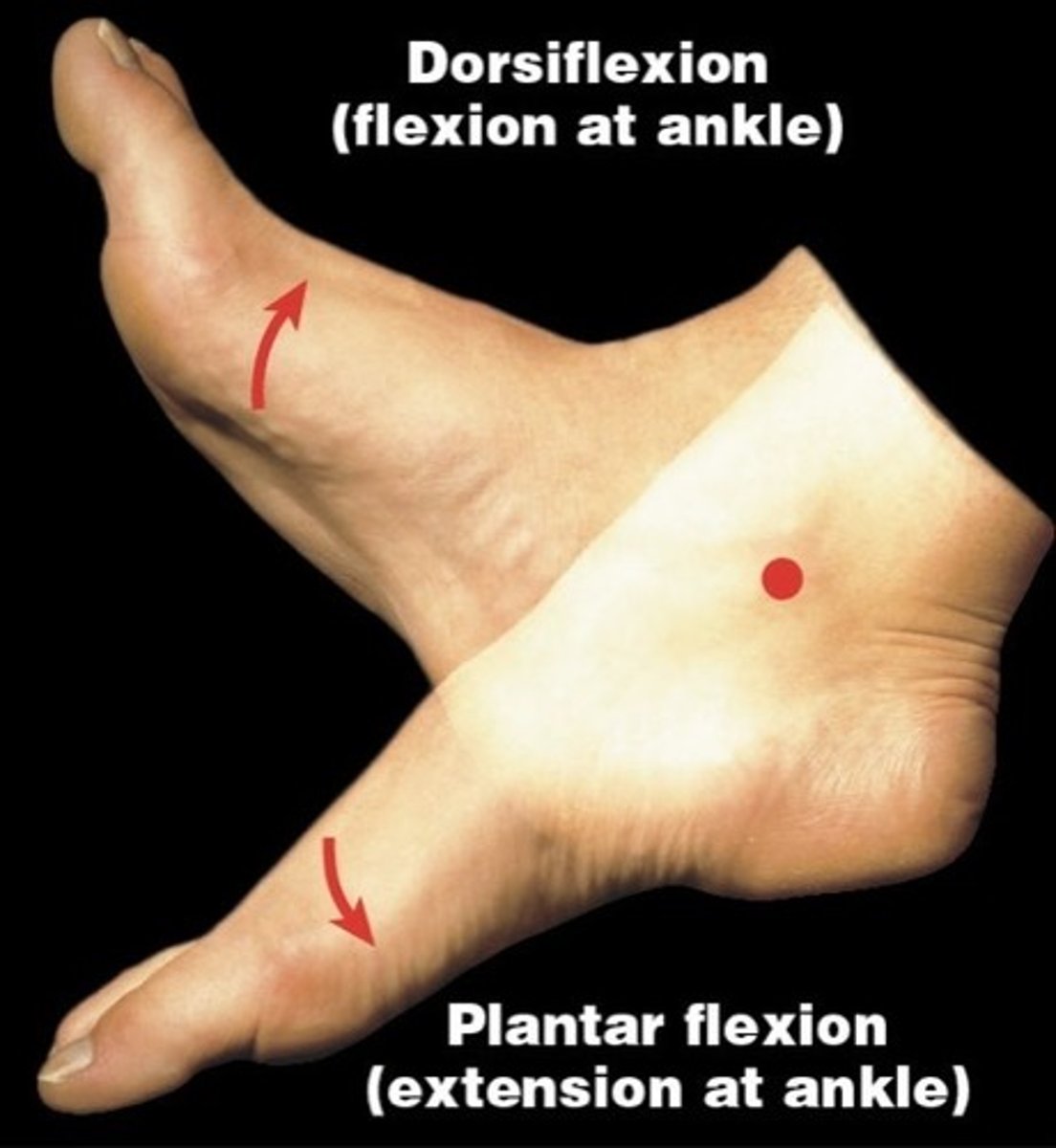
What is dorsiflexion?
flexing the foot and toes upward
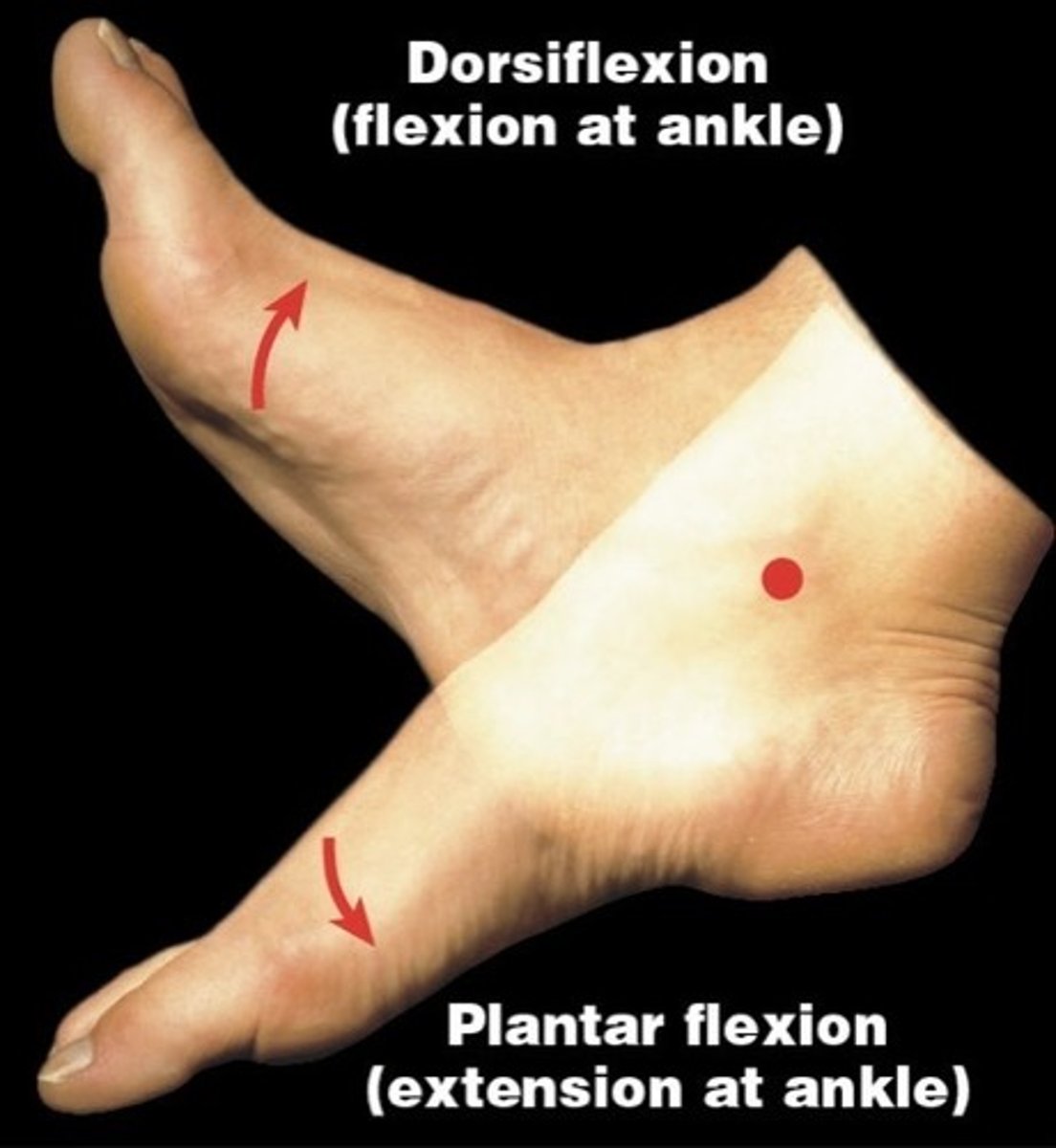
What is plantar flexion?
bending the foot and toes downward
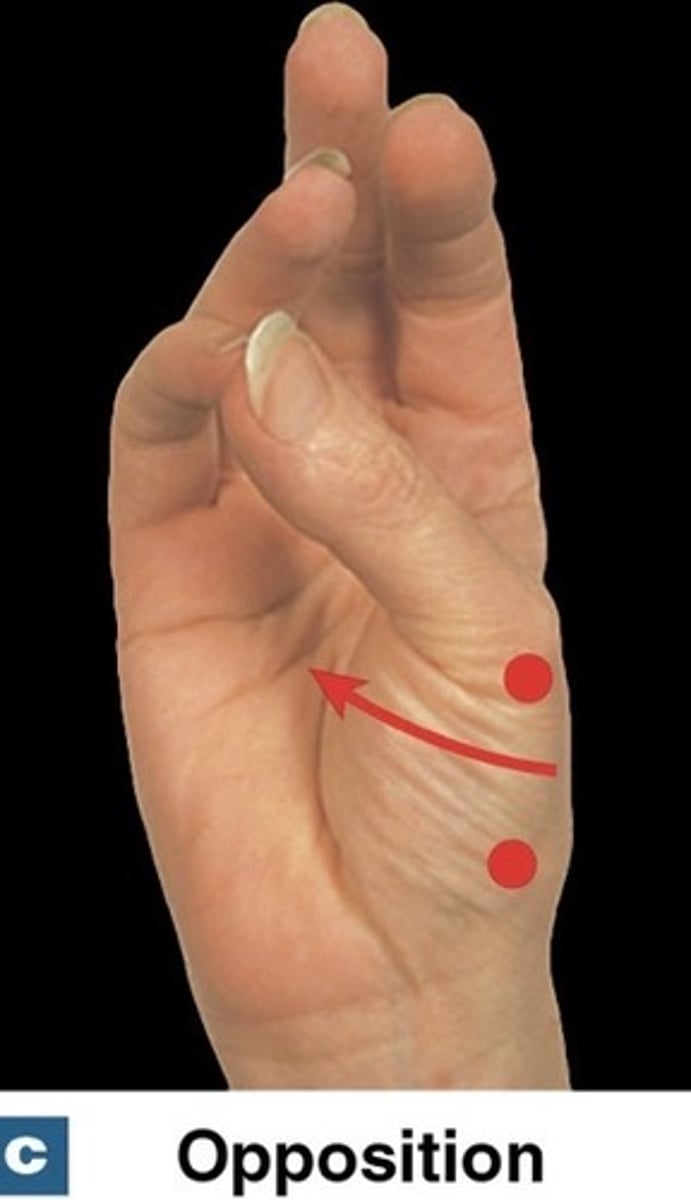
What is opposition?
brings thumb to touch tips of fingers
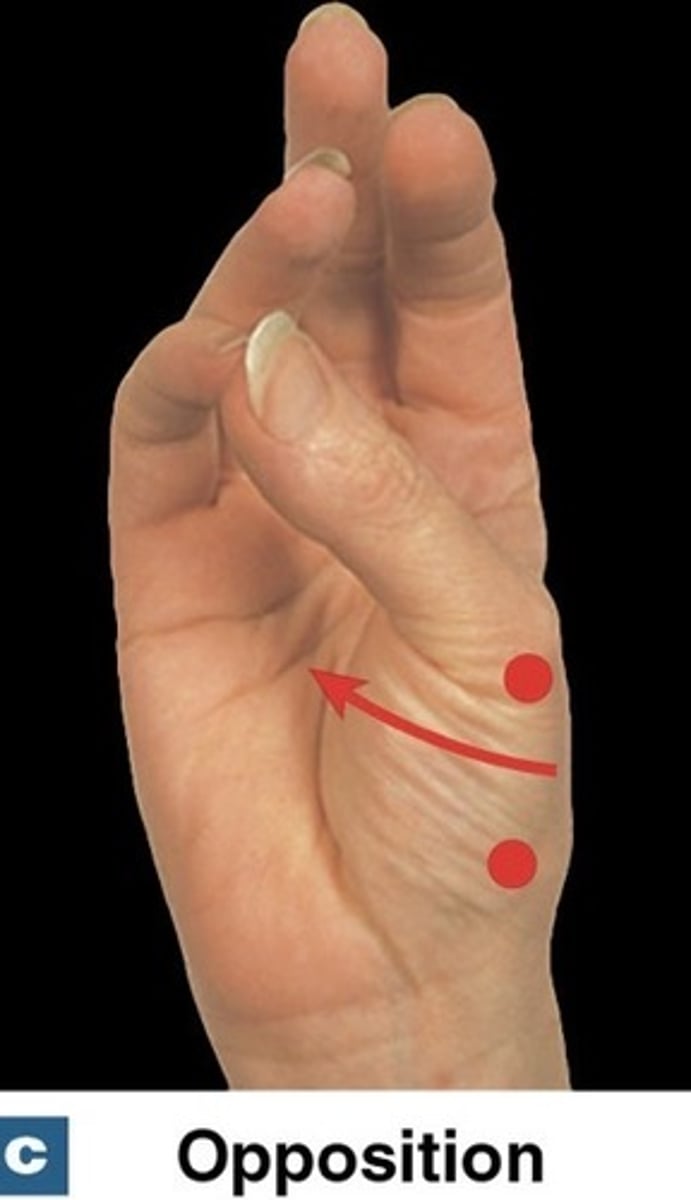
What is reposition?
returning thumb to the zero position
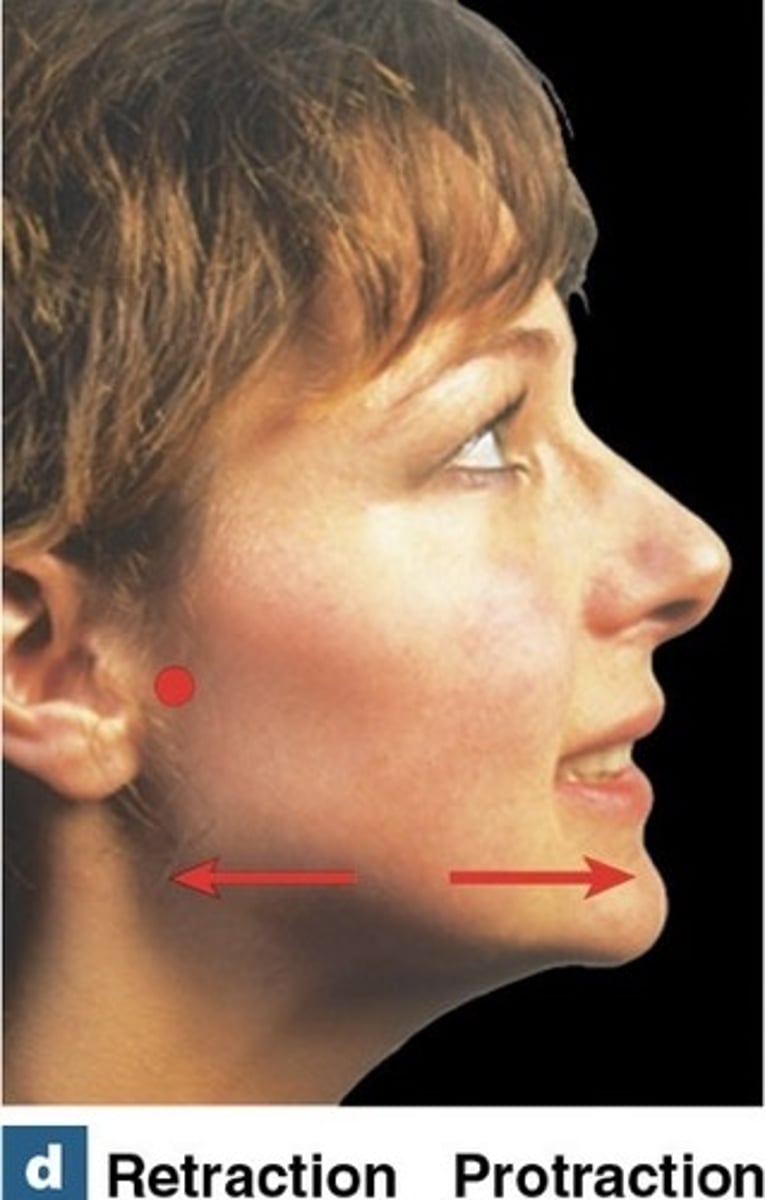
What is protraction?
Moving a body part forward, away from the middle of the body.
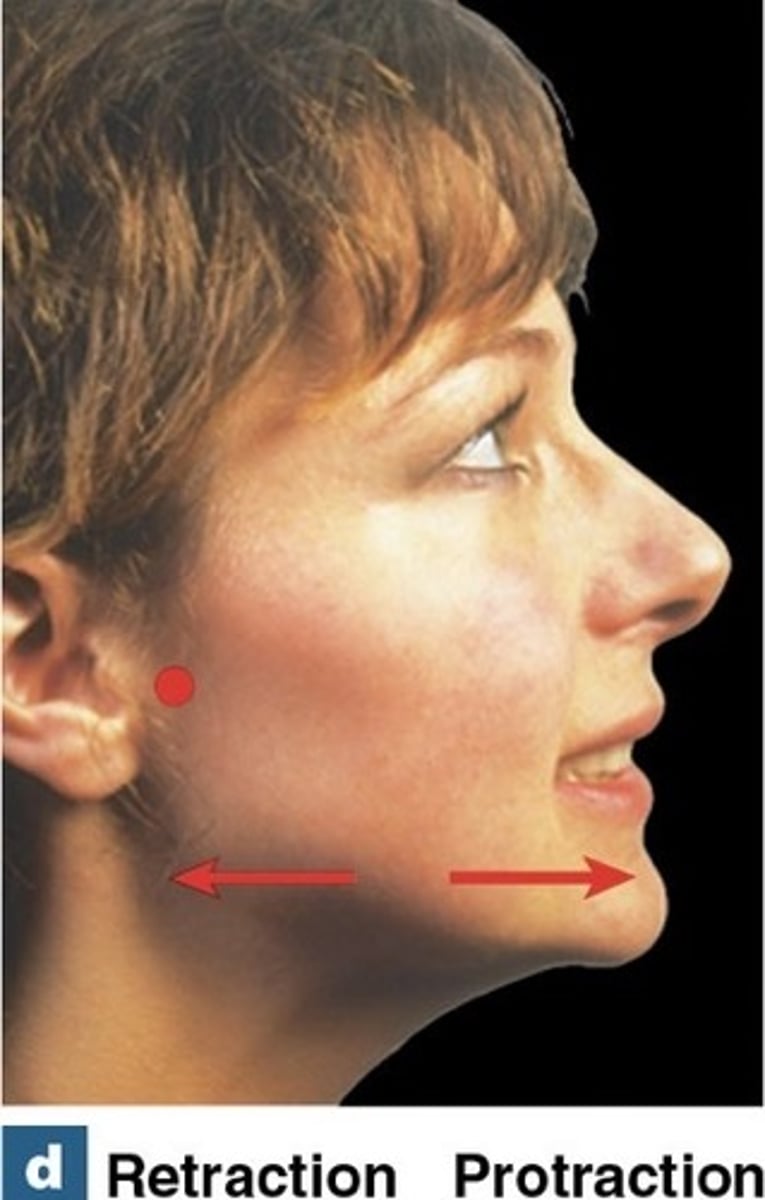
What is retraction?
moving a body part in the posterior direction
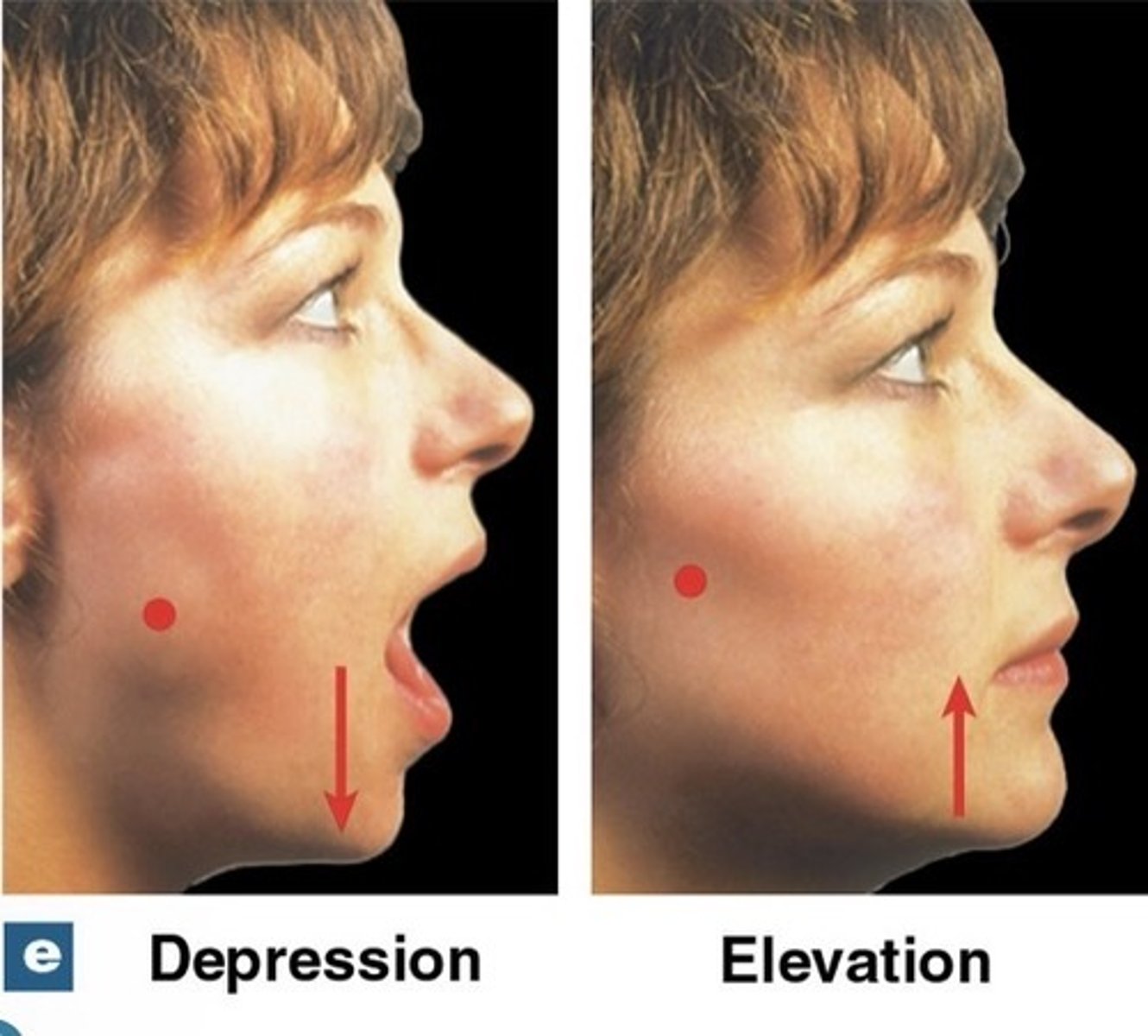
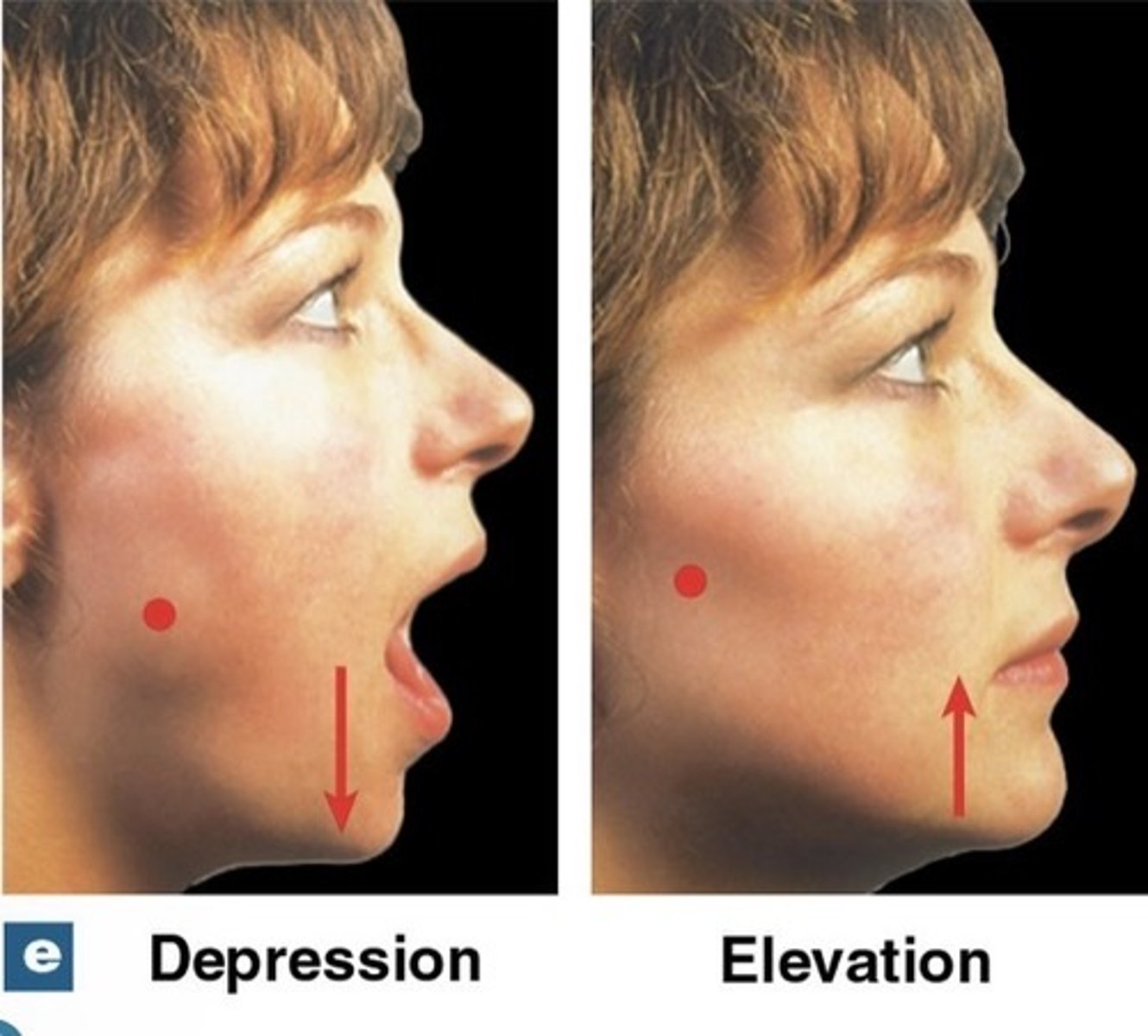
What is depression?
lowering a body part
What is the classification of synovial joints by shape?
Plane, hinge, condylar, saddle, pivot, ball-and-socket
What is elevation?
raising a body part
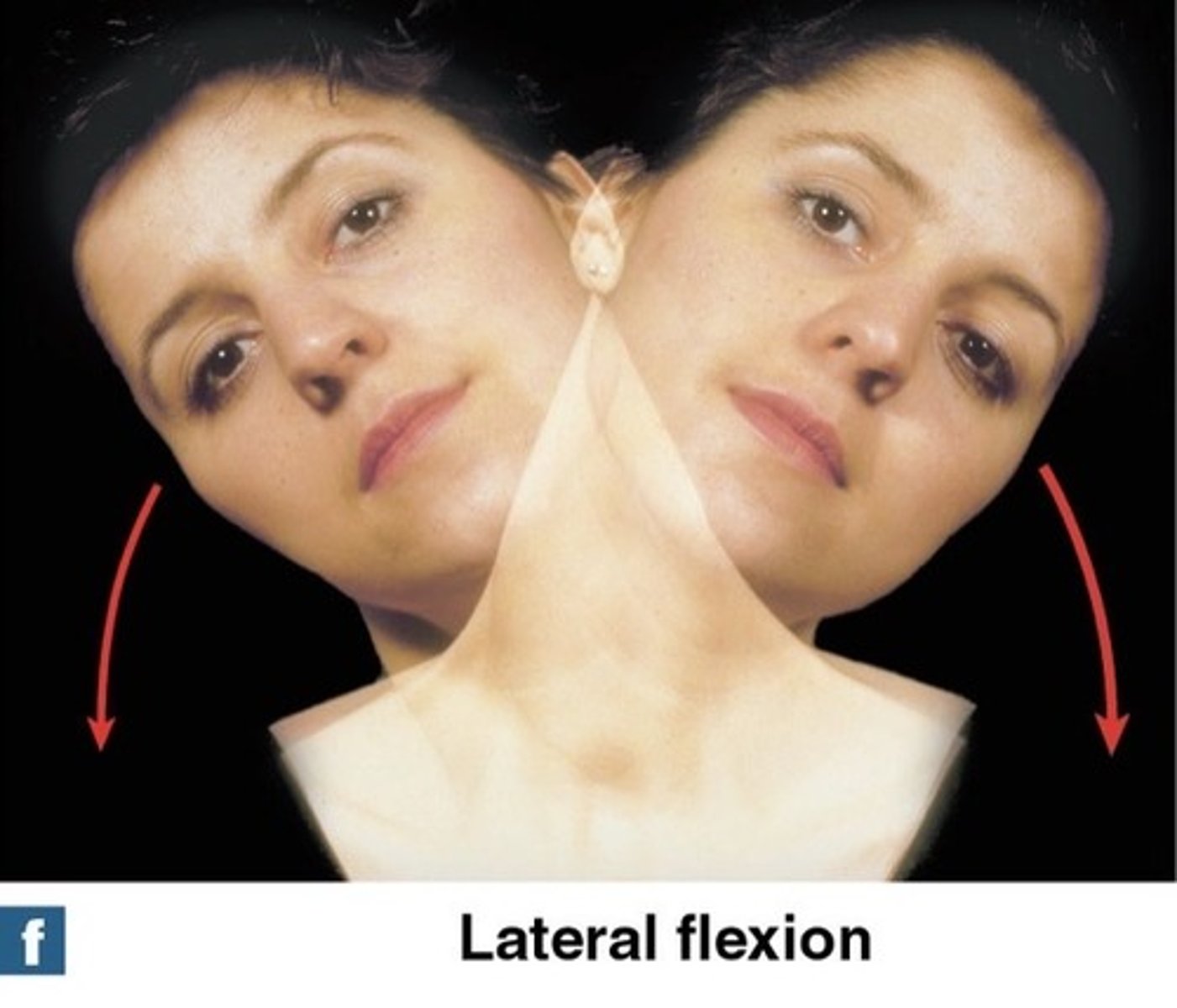
What is lateral Flexion?
bends vertebral column from side to side
What are the examples of the plane joint?
- Intercarpal joint
- Vertebrocostal
What is the plane joint?
Flattened or slightly curved surface litmited mostion nonaxial

What is an example of a hinge joint?
elbow and knee
What is hinge joint?
angular motion in a single plane (monaxial)

What is an example of a condylar joint?
metacarpophalangeal joint
What is a condylar joint?
Oval articular face within a depression (biaxial)

What is an example of the saddle joint?
carpometacarpal joint of the thumb
What is a saddle joint?
Articular faces fit together like a rider in a saddle - Biaxial

What is an example of a pivot joint?
Alanto-axial joint
Proximal radio-ulnar joint
What is a pivot joint?
Allows a bone to rotate around an axis - monaxial

What's is an example of a ball-and-socket joint?
Shoulder and hip joint
What is a ball-and-socket joint?
Round head in a cup-shaped depression - Triaxial

What type of joint is a elbow joint?
hinge joint
What type of joint is a shoulder joint?
ball and socket
What are the degenerative changes of joints?
Rheumatism, arthritis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gouty arthritis
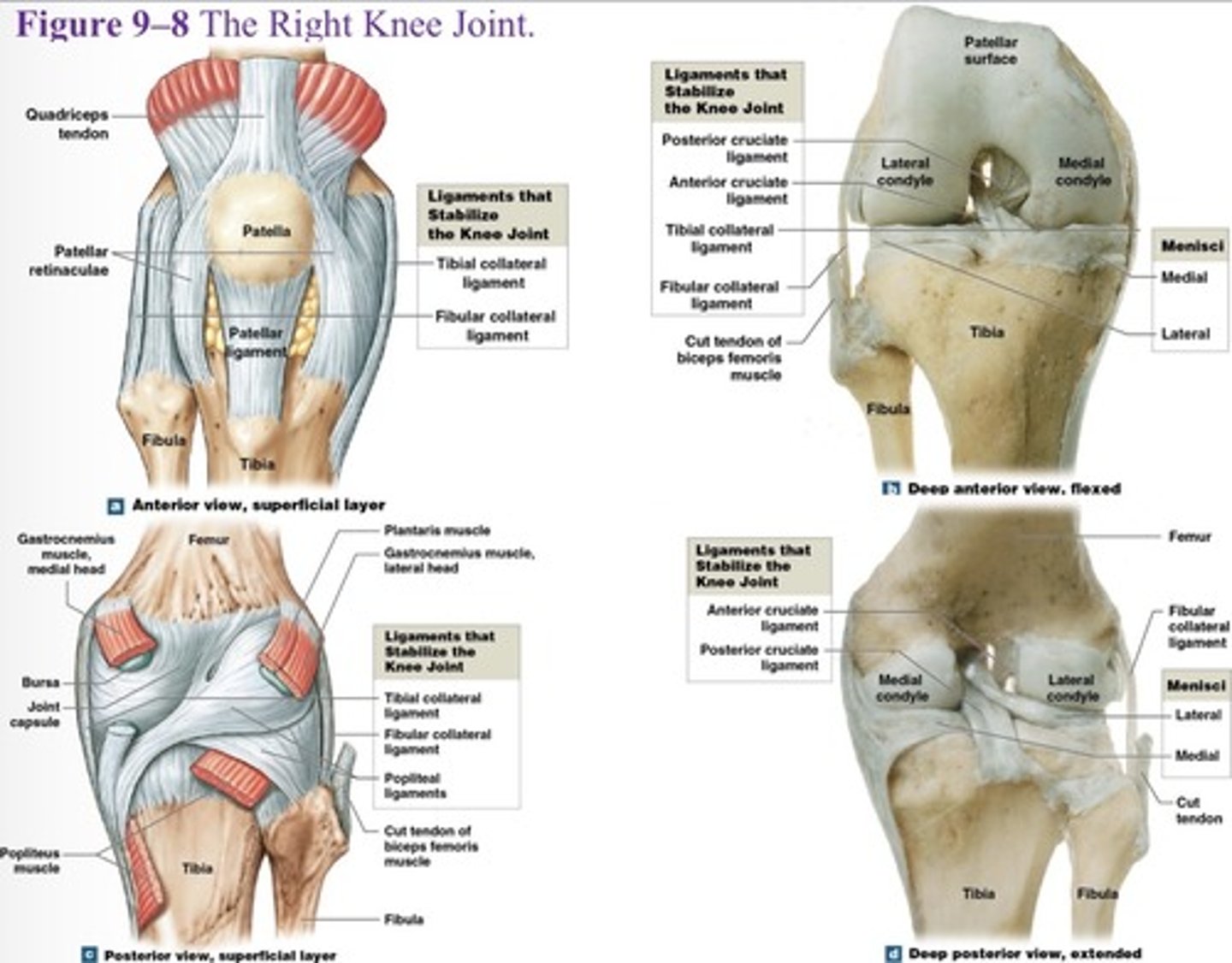
What type of joint is the knee joint?
Complex jingle joint
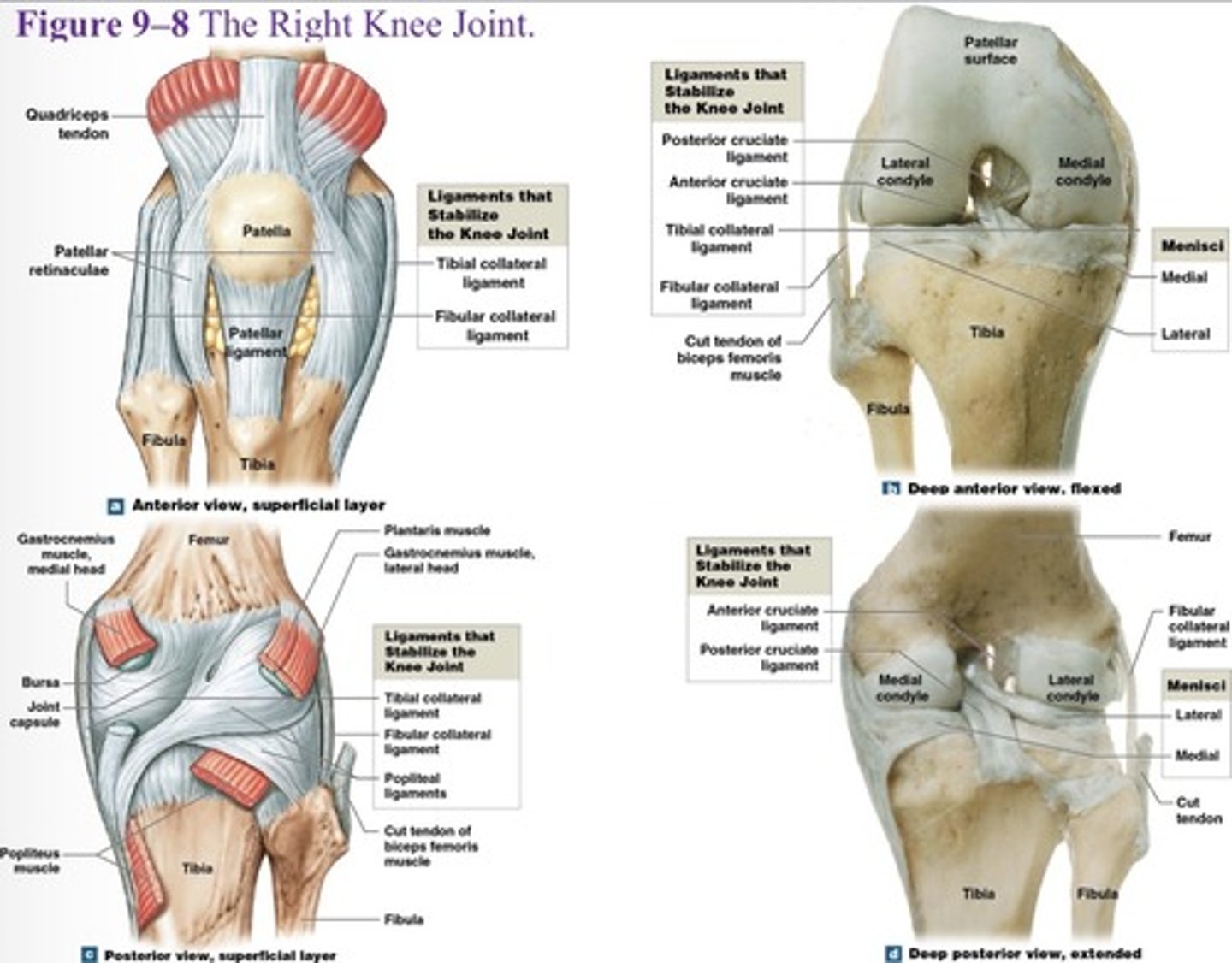
What is the function of the knee joint?
transfers weight from femur to tibia
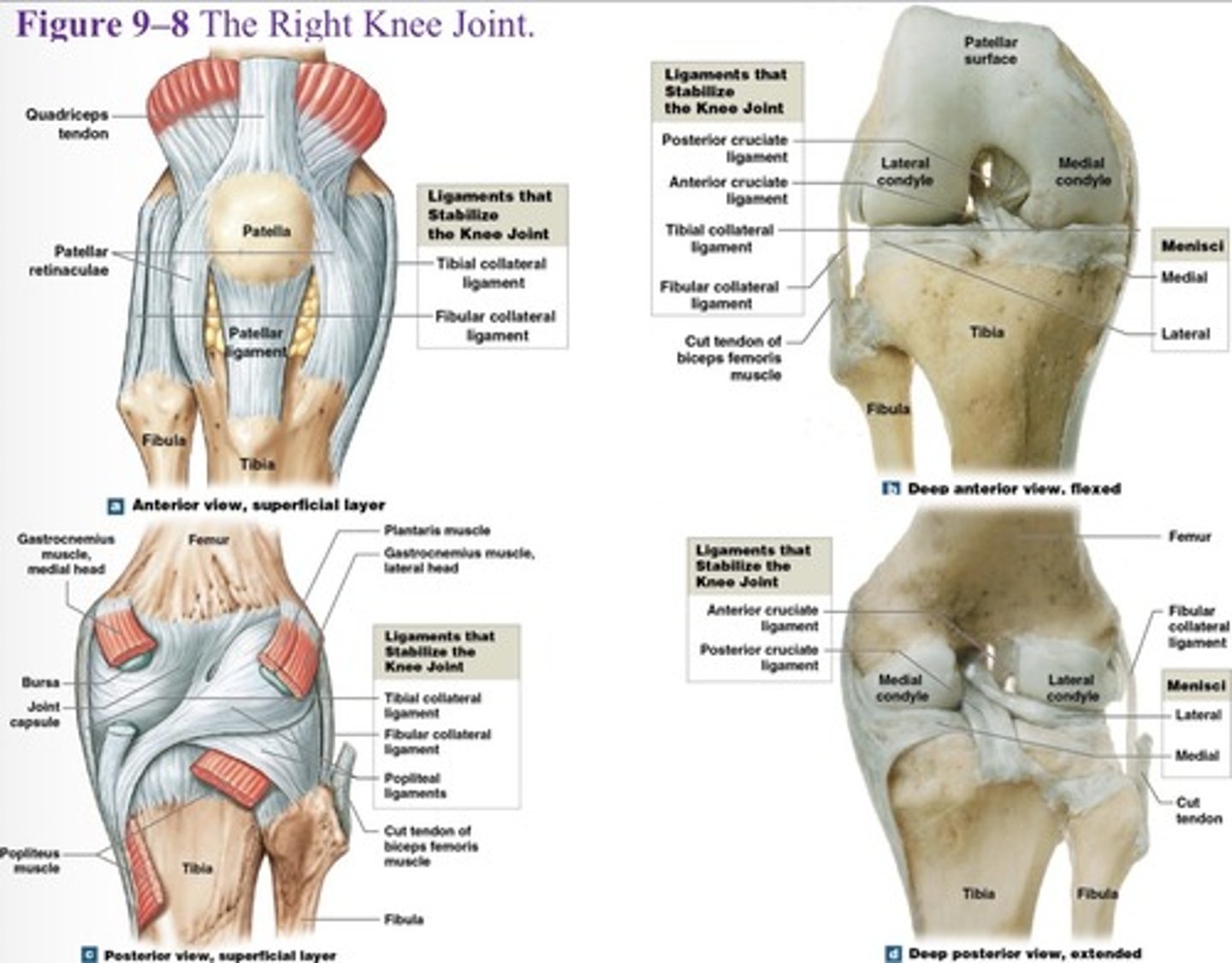
What are the three articulations of the knee joint?
Two femur-tibia articulations
At medial and lateral condyles
One between patella and patellar surface of femur
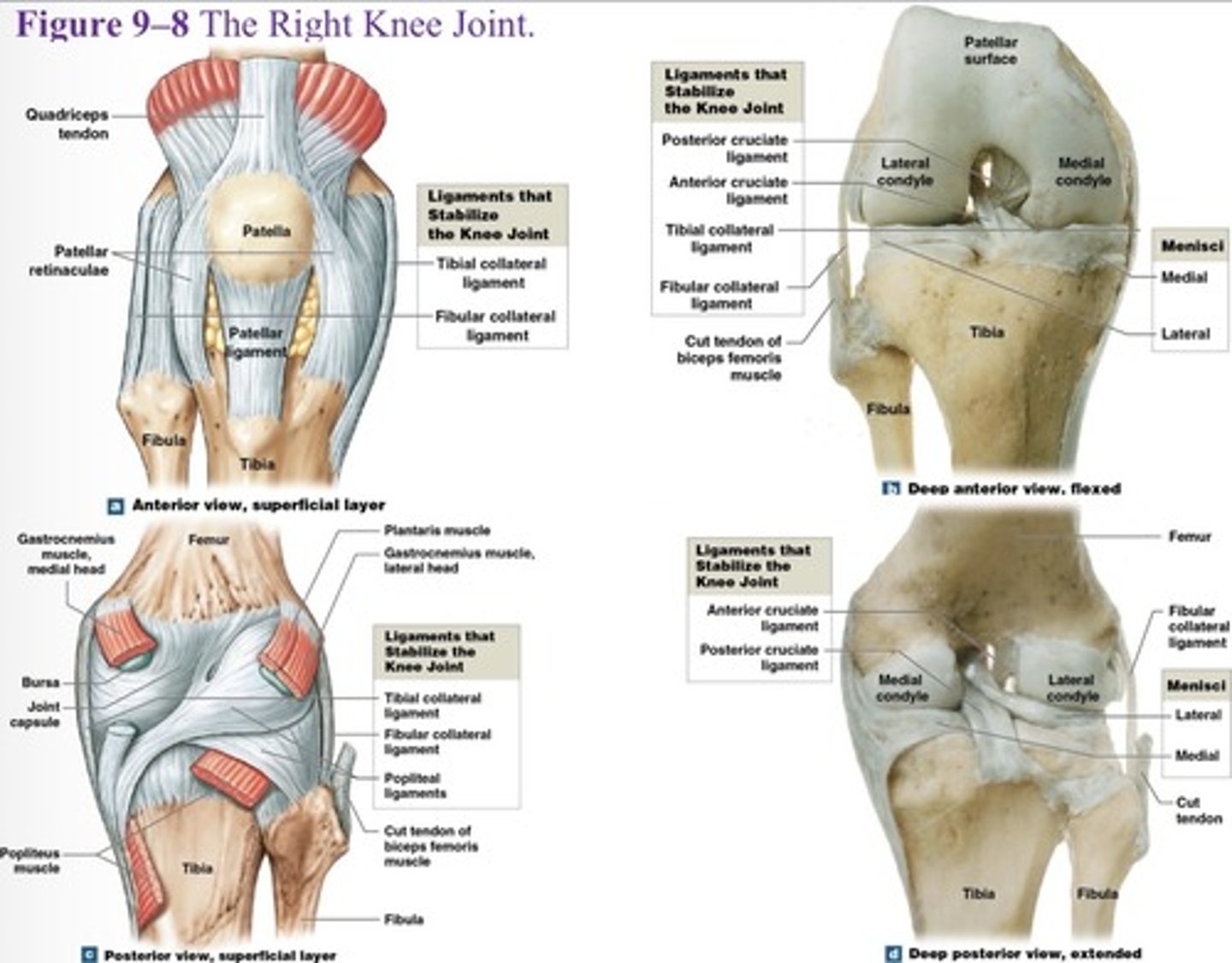
What is a joint capsule and joint cavity of the knee?
Medial and lateral menisci
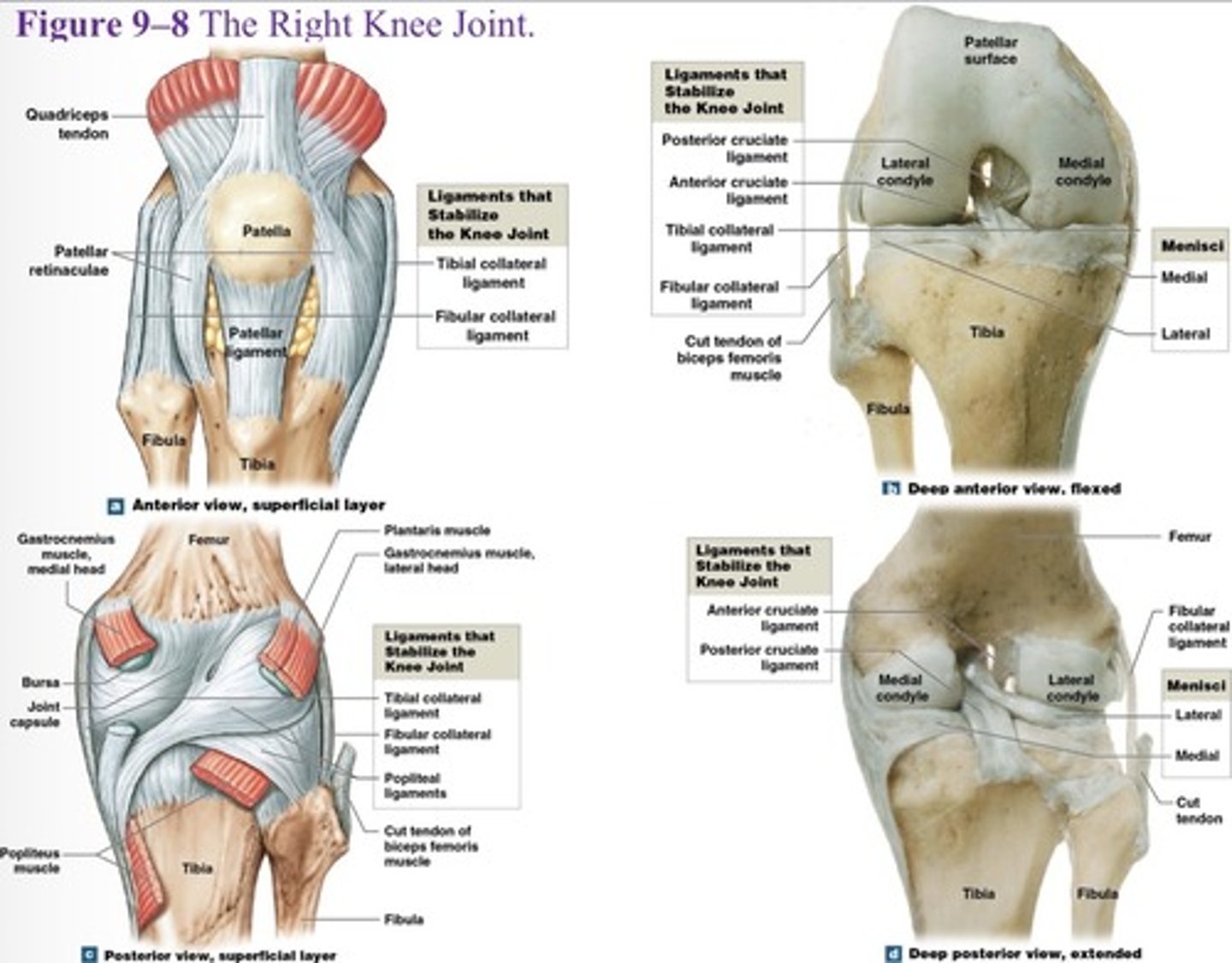
What is the function of the medal and lateral menisci of the knee?
They contain fibrocartilage pads at femur-tibia articulations, that cushion and stabilize the joint
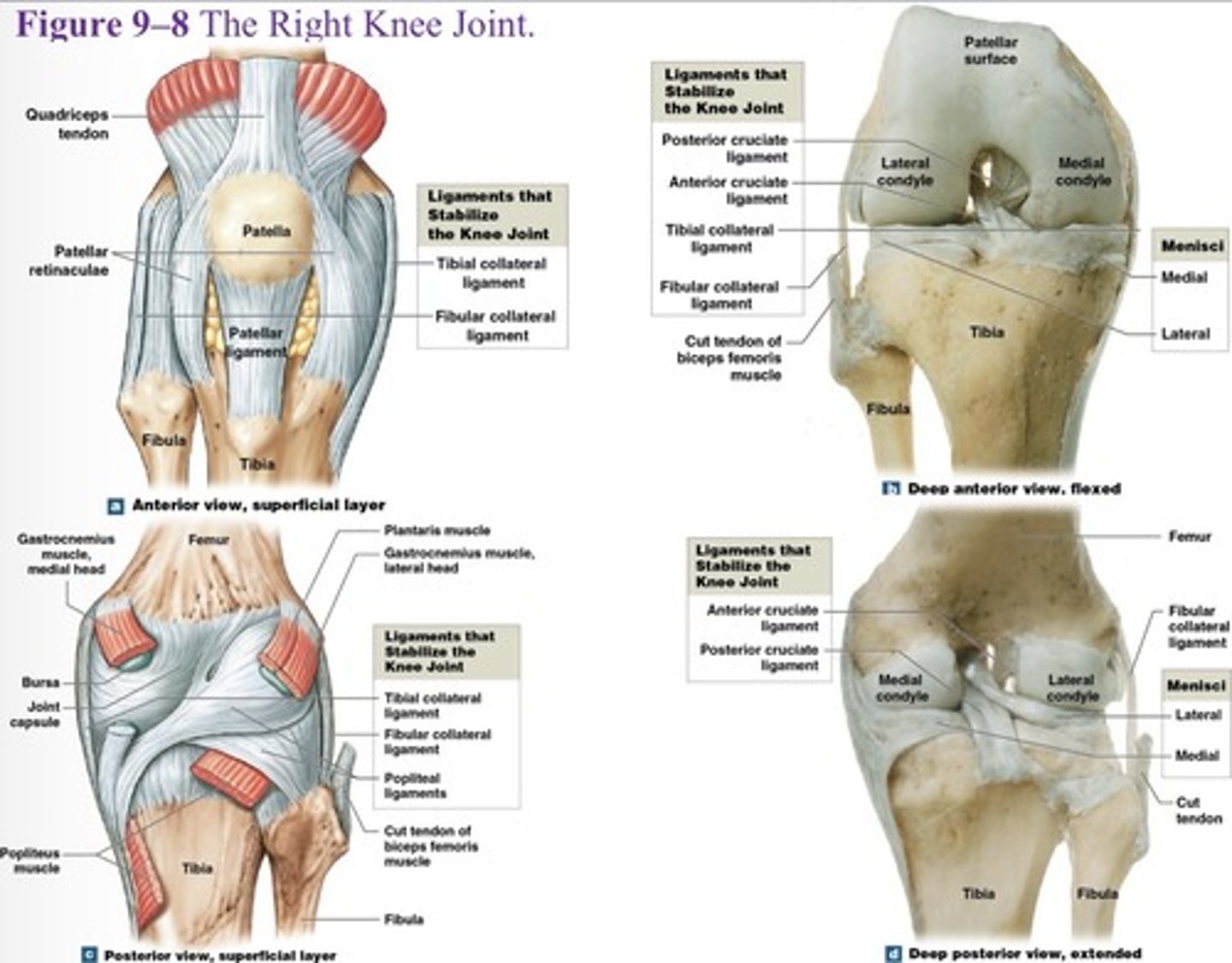
What is the first knee joint ligament?
Patellar ligament (anterior)
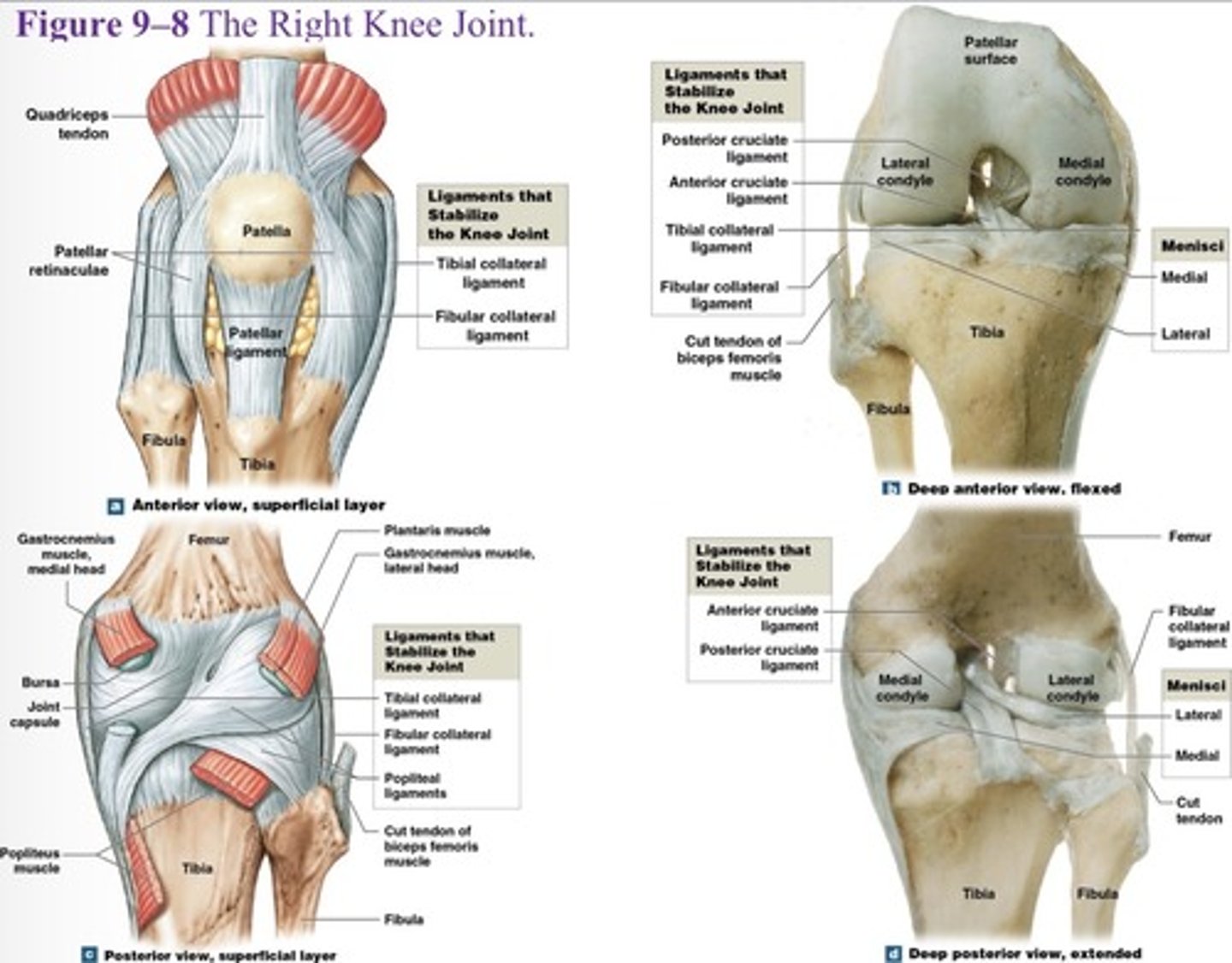
What is the 2 and 3 knee joint ligament?
Two popliteal ligaments (posterior)
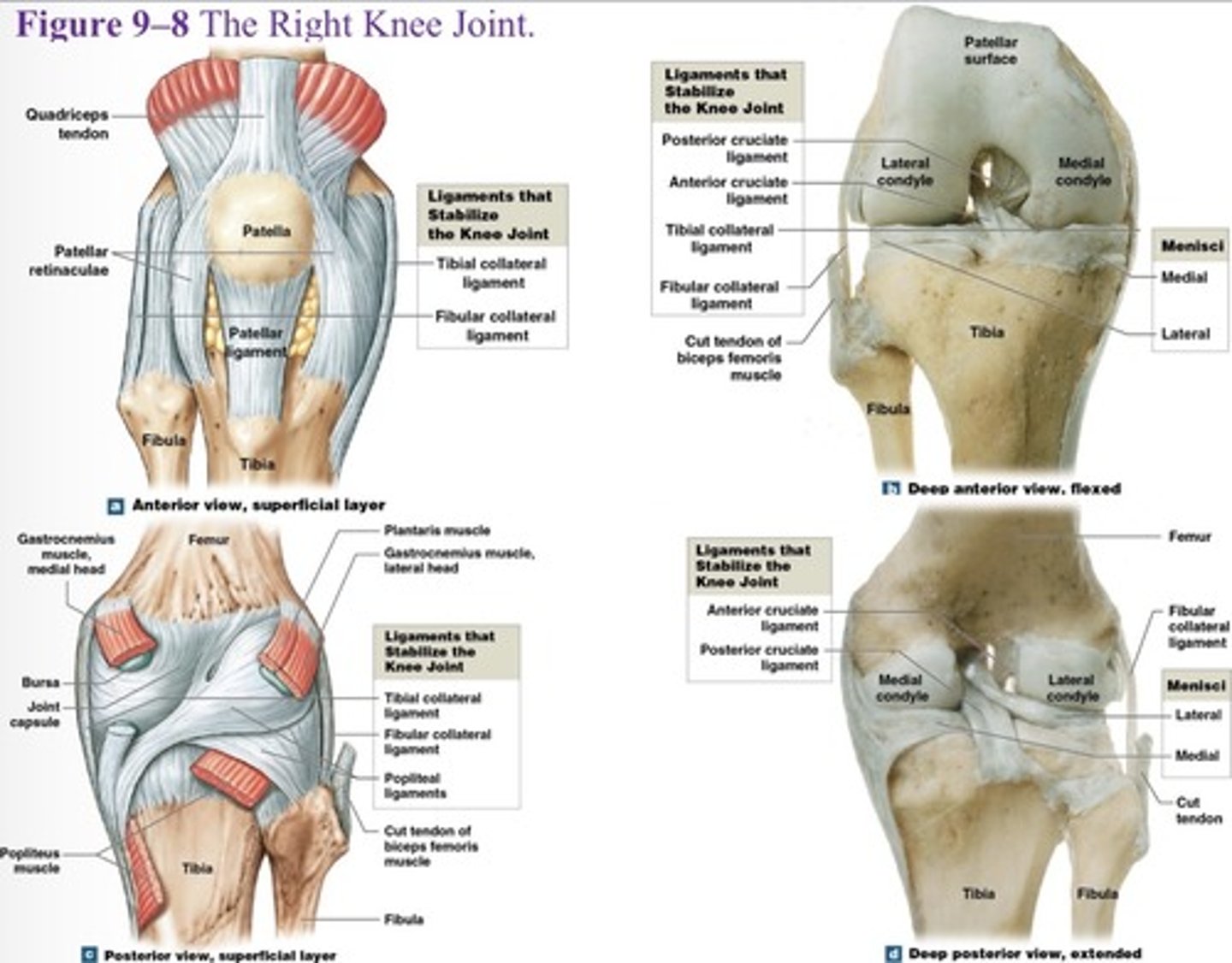
What is the 4 and 5 knee joint ligament?
Anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments
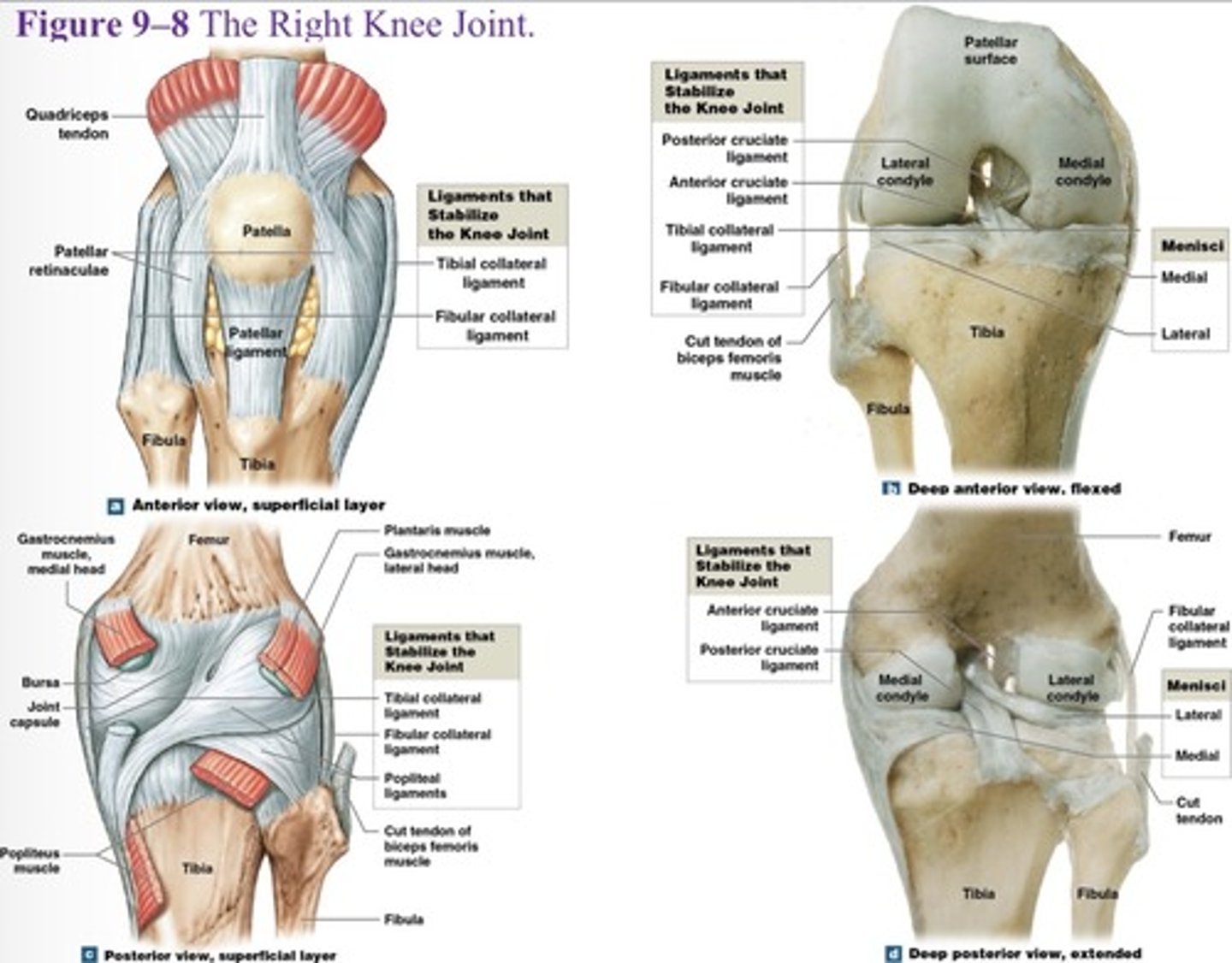
What are the major supporting ligaments in the knee joint? (7)
Patellar ligament, two popliteal ligaments, anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments, tibial collateral ligament, and fibular collateral ligament.
What is rheumatism?
Pain and stiffness in musculoskeletal system
What is arthritis?
inflammation of the joints
What is osteoarthritis?
Caused by wear and tear of joint surfaces, or genetic factors affecting collagen formation