Trihybrid Maps
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIO 239: Genetics Laboratory: Week 4: Wednesday, September 17th: Trihybrid Fly Test Cross & Gene Maps; Week 6: Monday, September 29th: Forked Diagrams; Probability; Trihybrid Maps
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
_______ indicates the location of a gene on a chromosome
gene mapping
_______ is the cause of which genes that are close together are inherited together
linkage
true or false: genes that are far apart are more likely to separate via crossing over
true
early linkage analysis used a _______ of 1: Rf = 1 map unit (centiMorgan, cM)
recombination frequency (Rf)
the formula for Rf is
(recombinants/total)100
Sturtevant explained gene mapping with a _______ trihybrid test cross
heterozygote
F2 phenotypes that dont return a 1:1:1:1/1:1:1:1:1:1:1:1 ration indicate _______
linkage
this test cross reveals gene order, estimates distacne between genes, and finds double cross-overs (DCOs)
3 point test cross
with 3 genes, a test produces _______ possible phenotypes, which is _______
8, 23
mendelian ratios suggest independent assortment. if the ratios are skewed, it means that _______ occurred
linkage
_______ are the parental types; they’re identical to the parents, are reciprocals of one another, and are most frequently if genes are linked
non-recombinants (NRC)
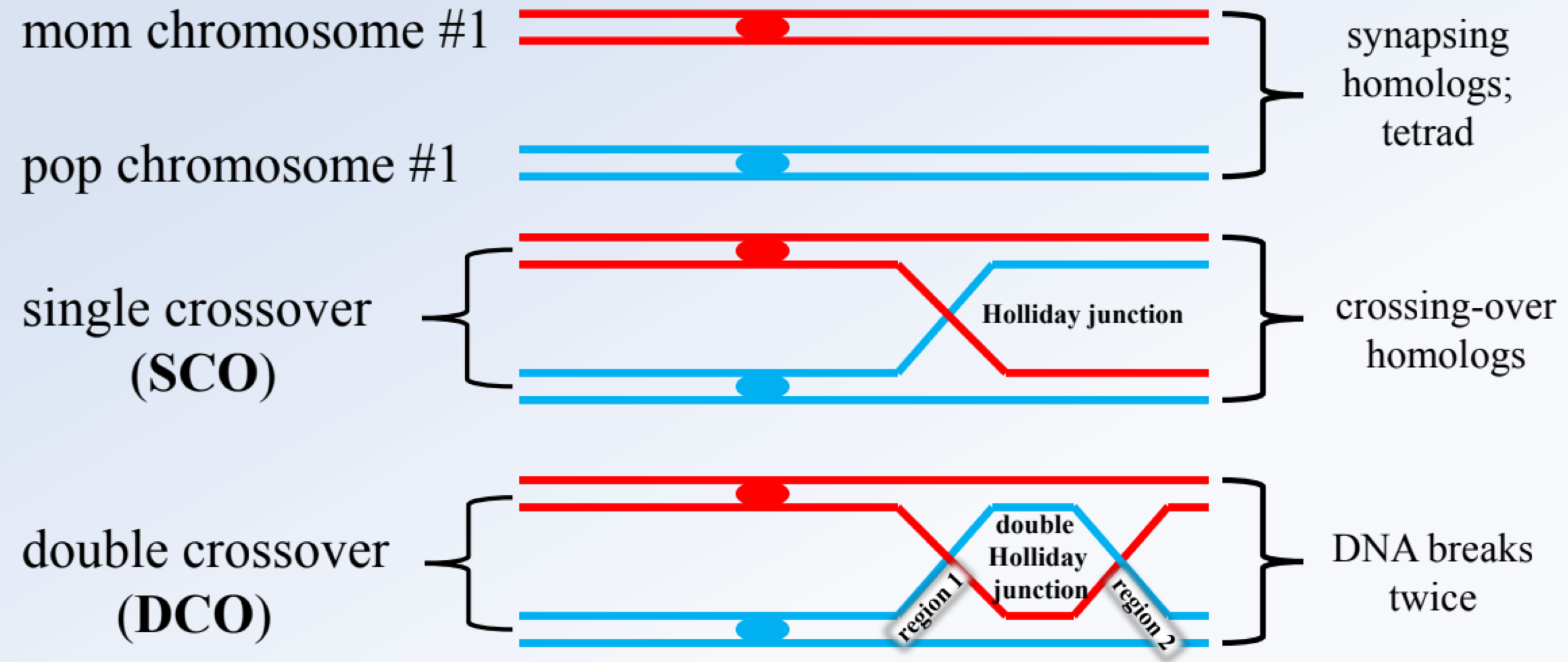
_______ occur in two types from regioun 1 (between genes 1-2) and two from region 2 (between gene 2-3)
single crossovers (SCO)
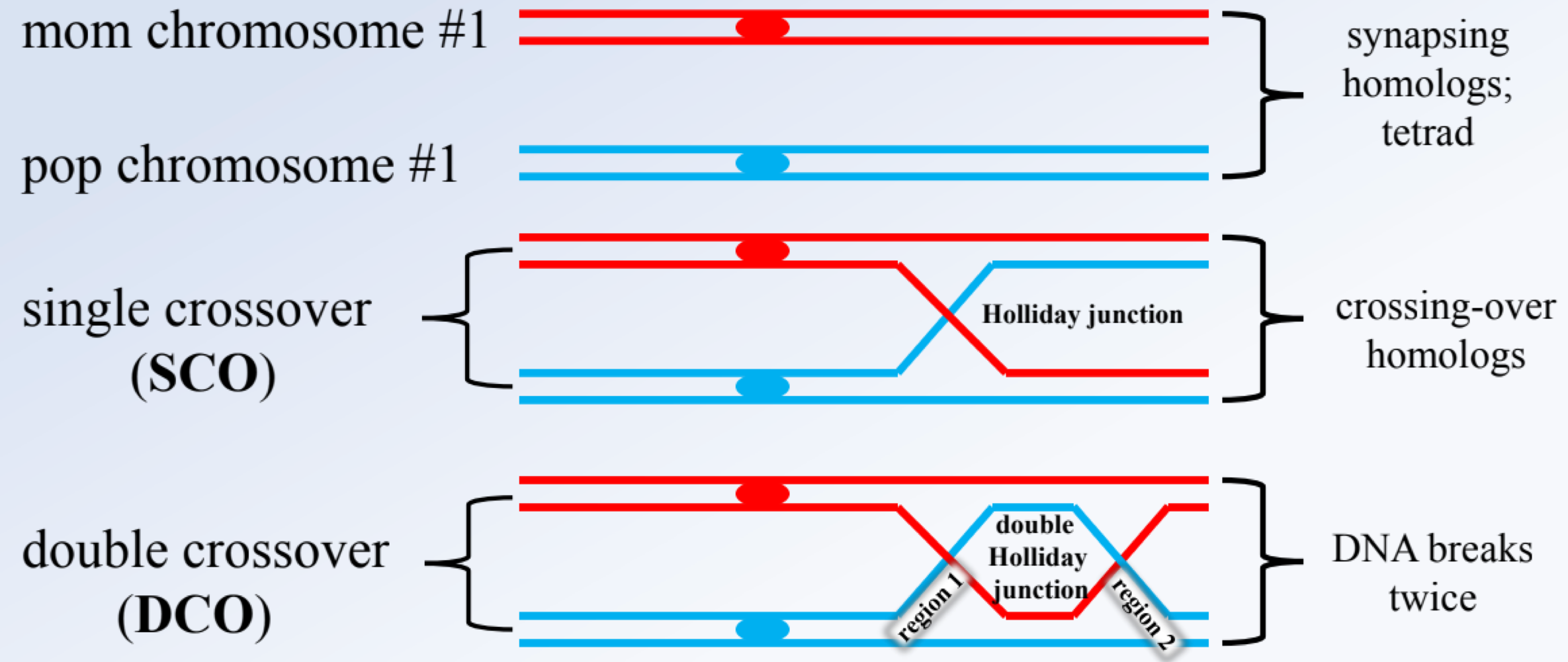
_______ reflects crossing over in both regions, are least frequent, and used to identify the middle gene by comparing them with the NRC
double crossovers (DCO)
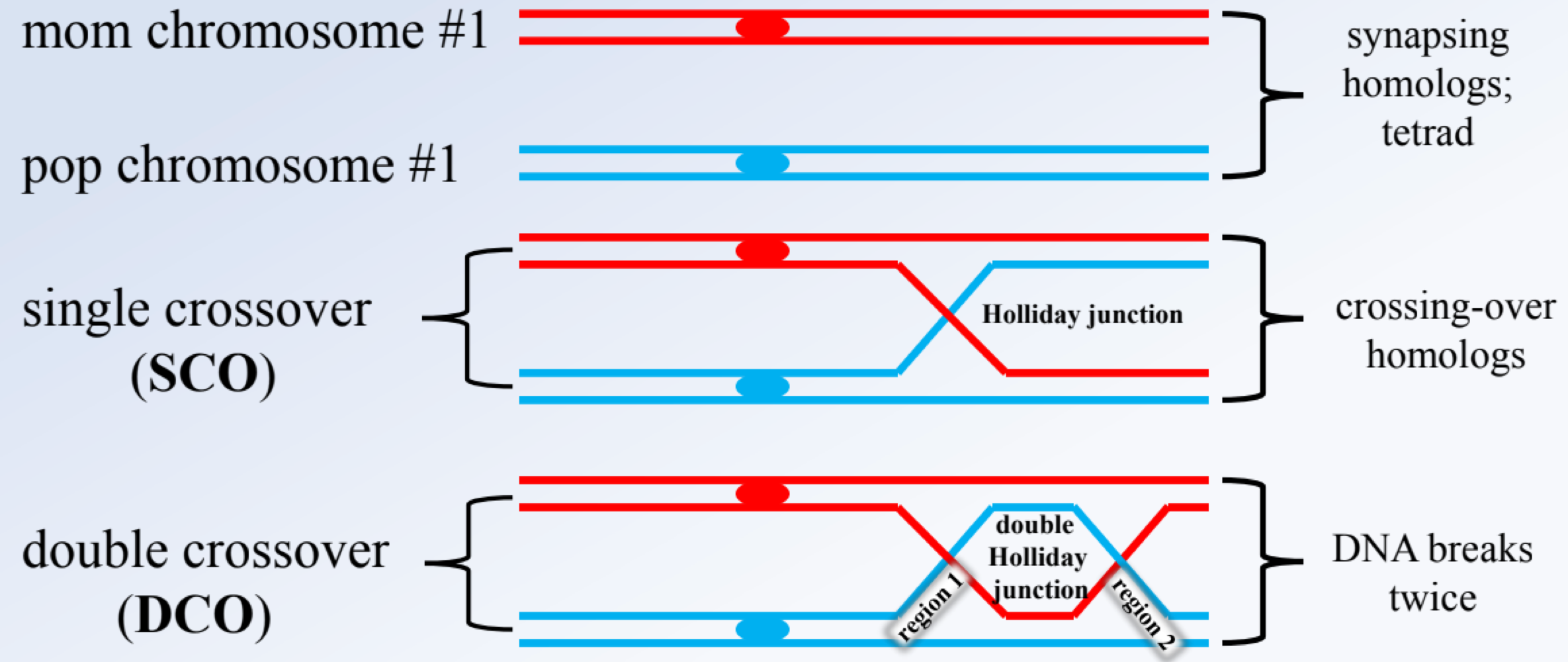
the _______ is the allele that changes compared to the NRC and DCO
middle gene
_______ is when one crossover reduces the likelihood of another crossover
interference (I)
if interference is 0, that means _______
no interference occured, and genes are independently assorted
if interference is 1, that means _______
interference occured, and no cross overs occurred
the formula for interference is _______
1- COC
the _______ is how much interference occurred based o the number of DCos observed compared to how many were estimated
coefficient of coincidence
the formula for coefficient of coincidence (COC) is _______
observed DCO/expected DCO
true or false: Haldane assumed cross-over regions will always be predicted, and that they’re the same for each generation
false. Haldane assumed cross-over regions will always be random, and that they’re never the same for each generation
the formula for calculating the distance between outer genes (1-3) is
(SCO1 + SCO2 + DCO(2))/total length of the gene
_______ is when some recombinants occur while favoring “parental” types (NRCs)
partial linkage
a _______ shows loci of genes based on novel phenotypes, whereas a _______ shows genes as a segment of nucleotides on a single strand of DNA
recombination map, physical map
an _______ is a drawing of a chromosome, whereas a _______ is Giesma-stained bands of chomosomes, which are simialr between homologs
ideogram, karyotype
the _______ is the gene locaiton on a chromosome
locus/loci
the centromere has _______, where kinetochores form
satellite DNA
_______ is the p-arm’s telomore, where as _______ is the q-arm’s telomere
p-ter, q-ter
loci are number from _______ (small numbers) to _______ (bign numbers) in either direction
centromere, telomeres
the adjusted distance adds the total DCOs twice, which is calculated by
(SCO1 + SCO1 + SCO2 +SCO2 + (2(DCO1 + DCO2))/total)100 or (gene 1-2 sum or % + gene 2 and 3 sum or %/total)100
true or false: greater number of ecombinants mean the gene pair is farthest apart from one another
true
_______ are alleles that have opposite genes (AbC vs aBc)
reciprocals
true or false: SCO in region 1 results in recombinants with 1 new allele and 2 originals
false. SCO in region 1 results in recombinants with 2 new alleles and 1 original
true or false: SCO in region 2 results in recombinants with 2 new alleles and 1 original
false. SCO in region 2 results in recombinants with 1 new allele and 2 originals