APC 3- The body systems
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all the body systems ,how they work ,blood vessels
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Describe the function of the digestive system?
functions of the digestive systems:
•Functions: Ingestion (taking in food), Mixing (stomach), Secretion (stomach e g. Digestive enzymes ) , Digestion, Absorption (small intestine), Elimination (Anus)
What doe the digestive system consist of?
-the alimentary GI Tract 9m long
-continuous lumen for an external environment
It has the same 3 layers throughout: Mucosa (epithelial cells lining the mucous glands),Muscle (contracts) and connective tissue (serosa, protects)
-mucous -helps to lubricate as food goes through the system
-the small intestine is not smooth
-squeeze food in different directions
-connective tissue - keeps us warm and protects
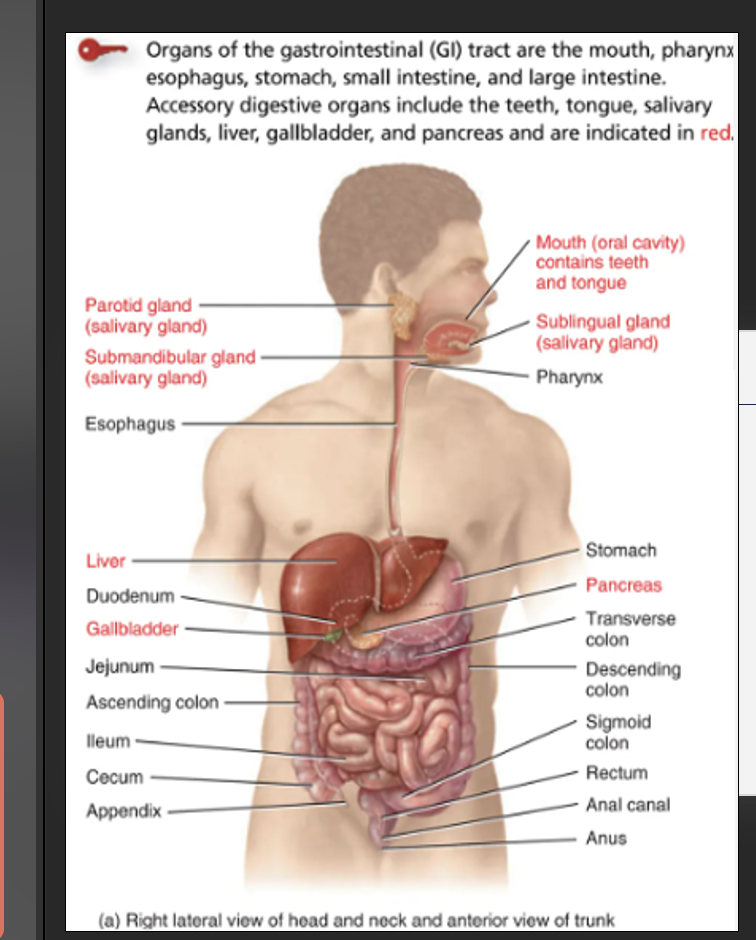
What is a GI Tract ?
Gastrointestinal tract - long tube that extends from the mouth to the anus ,transporting food etc ..
Describe the structure of the upper Gi Tract?
Oral cavity:
•Accessory organs: teeth, tongue, salivary glands ( not part of Gi but aid digestion)
•Buccal (between cheeks and teeth)
•Sublingual/Translingual (under/on tongue)
•Mucosa has rich blood supply for absorption
Oesophagus:
•Muscular contractions – controlled by nervous system (peristalsis- squeezing food down to stomach )
•Inferior sphincter prevents stomach reflux
Stomach: Gastric pits-go down to crypts where there are cells that produce substances : Examples
•HCl: pH2; antimicrobial & denaturing
•Pepsin: hydrolyses peptide bonds in protein
•rich Blood supply – but limited absorption ,helps to prevent break down of drugs
Duodenum (~25 cm):
Site of bile and pancreatic juice entry to GI tract
Describe the structure of the lower GI Tract?
Jejunum (~2.5m) and Ileum (~3.5m)
•Mucosa adapted - villi and microvilli
•↑ ↑ surface area for absorption of nutrients/drugs* into blood
•*Fats/fat soluble drugs taken up first via lacteals (green) into lymphatic system
Large intestine (colon): 3 REGIONS
•Reabsorbs 90% of remaining (1.5L) water/day (dysfunction → diarrhoea)
•Limited absorption for drugs (no villi)
•Rectal route for drug absorption
•Microbiome – where bacteria lives – modifies (some) drugs
What is the main function of the liver ?
-produces bile
Where does the liver receive blood from?
Largest internal organ
•Receives blood from:
1. Hepatic artery (branch of aorta)
2. Hepatic portal vein - ( detoxifies blood) from GI tract, spleen, pancreas
•Produces bile
Describe the Metabolic functions of the liver
•Glycogenesis (glucose → glycogen)
•Gluconeogenesis (lactate/amino acids → glucose
•Amino acid breakdown
•Clotting factors and albumin synthesis
•First-pass metabolism of most oral drugs*
•*remember fat-soluble drugs absorbed into lacteals – do not end up in h.p.v.
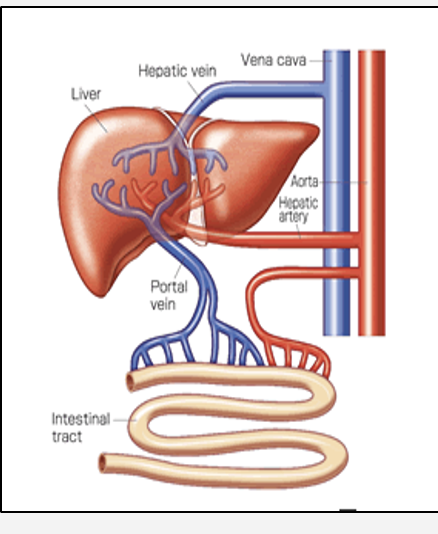
Why does the liver need a constant blood supply?
for respiration to nourish the cells as it is highly metabolic organ
What is the Function of the gall bladder ?
Stores bile made in liver
What does the bile contain ?
Bile:
•Contains bile salts, cholesterol, bilirubin (breakdown from r.b.c. turnover)
•Essential for fat emulsification (increase sa to form chylomicrons from micelles) and hence absorption of dietary fat, fat-soluble drugs and vitamins (A, D, E, K)
•Released via common bile duct into duodenum along with pancreatic juices
What is the Exocrine function of the pancreas?
Exocrine
• releases Pancreatic juice: containing Amylase, lipase, protease from acinar cells, and bicarbonate (neutralises* stomach acid)
•Released via pancreatic duct into duodenum
What is the endocrine function of the pancrease?
Endocrine
• reaeases Hormones: into bloodstream
•Insulin when blood glucose is ↑
•Glucagon when blood glucose is ↓
NOTE- *pH important for drug absorption
Structure of gall bladder and pancreas

What is the main function of the cardiovascular system ?
•: distribution (mass transport) of O₂/CO₂, nutrients, hormones, heat, clotting factors, drugs
What does the distribution rate depend on ?
cardiac output (CO): amount of blood pumped out of the heart in one minute
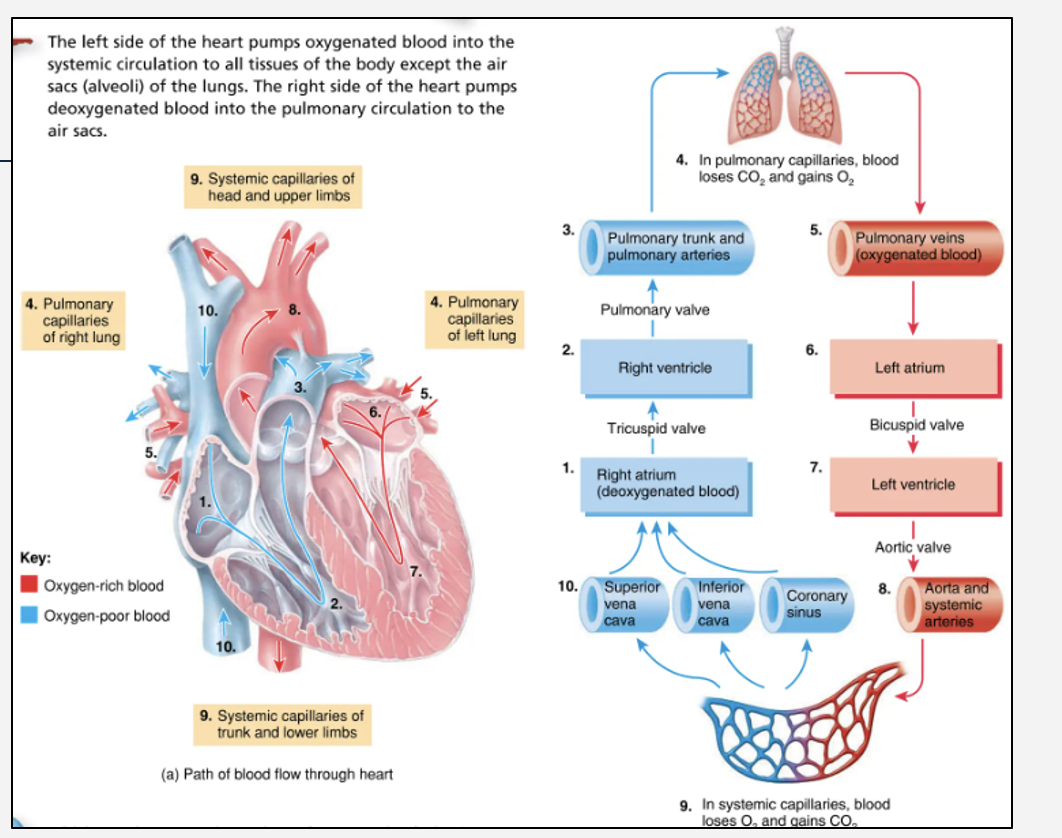
•1 min for blood to move round the whole system:
Aorta → systemic circulation → right heart → lungs →
left heart → Aorta
Describe the structure of the heart ?
4 chambers: R/L side separated by septum:
Right atrium (RA)
Right ventricle (RV)
Left atrium (LA)
Left Ventricle (LV)
4 valves prevent backflow:
Tricuspid- prevent right v to r a
Pulmonary semilunar prevent blood back form left v
Bicuspid (mitral)
Aortic semilunar
Coronary arteries branch off aorta – supply blood to heart tissue
Sinoatrial node initiates impulse for contraction
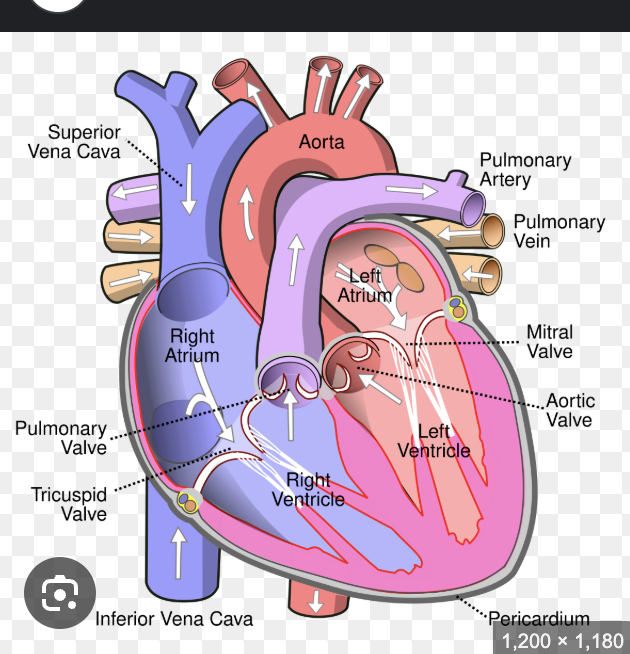
What is the the direction of blood flow in the heart ?
Direction of blood flow:
Body → RA → RV → Lungs → LA → LV → Body
What does blood consists of ?
Blood
Transport for O₂, CO₂, nutrients, hormones, drugs
Components: plasma (water, proteins, clotting factors, ions), red & white blood cells, platelets (thrombocytes)
What are the main Blood vessels ?
Blood Vessels – all lined by endothelial cells
•Arteries – thick muscular walls, blood under high pressure away from heart
•Arterioles - smaller arteries - muscular wall can constrict to increase blood pressure - how brain controls blood p ,and vasodilation …
•Veins – thinner muscle layer, valves prevent back flow, blood under low pressure back to heart
•Capillaries – thin walled (single layer of cells) fairly permeable, site of exchange (nutrients, gases, drugs),no muscular layer
What is tissue perfusion?
●the process of blood flowing through the blood vessels to deliver oxygen and nutrients to cells and remove carbon dioxide and waste products, can use oximeter
●Oxygen and substance are transported through water acts as a transport medium
●Osmotic p,< capillary p
●Gives extra fluid
Which is transported in lymph vessels
NOTE- Distribution rate will affect he amount of tissue perfusion( for nutrient ,gas, drugs)
What is the function of the lymphatic system?
Functions:
○Drains excess tissue fluid from tissues after capillary exchange and returns it to blood
○Absorb fats and fat/soluble drugs in chylomicrons (via lacteals)
○Immune system: circulation & activation of lymphocytes (type of WBC)
What is lymph and where does it go?
Fluid = lymph (similar to plasma, fewer proteins)
Enters the blood circulation via thoracic duct - left or right goes to right lymphatic duct
NOTE- ONLY GOE SIN ONE DIRECTION ALL TOWARDS THE HEART
Describe the structure of the respiratory tract?
Upper tract:
Nose, pharynx, larynx: filters, warms, humidifies air
Lower tract: trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli: conduct & exchange gases
Lining: ciliated epithelium and goblet cells (mucus + ciliary clearance)
Inhaled irritants/drugs can affect mucociliary clearance (e.g. smoking)
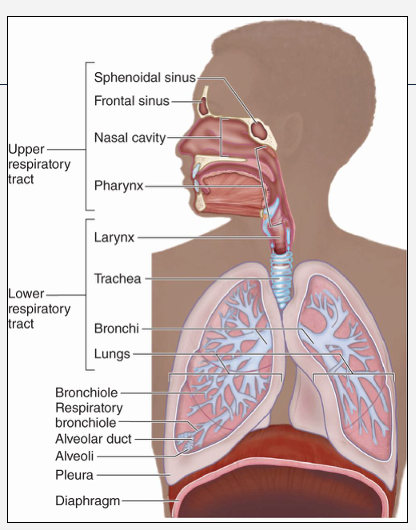
Where does gas exchange occur ?
•Occurs in alveoli (tiny air sacs, 300 million in lungs)
Thin respiratory membrane (alveolar epithelium and capillary endothelium
How does gas exchange occur ?
•Gases move by simple diffusion (from area of higher concentration to area of lower concentration
•O₂:from alveoli → blood
•CO₂: from blood → alveoli
•Inhaled drugs can reach the blood quickly
•Lungs also excrete volatile drugs e.g., anaesthetics, alcohol
NOTE- higher concentration of o2 in alveoli so it can diffuse into the blood
What are the functions of the renal system
•Filter blood to remove waste (urea, creatinine, drugs)
•Major site of drug excretion
•Maintain water & electrolyte balance (Na⁺, K⁺, Ca²⁺, Cl⁻)
•Regulate pH of blood (H⁺ secretion into blood, HCO₃⁻ reabsorption from blood)
•Control blood pressure (RAAS system)
•Produce the erythropoietin hormone - stimulates RBC production in bone marrow
•Location of final stage of vitamin D activation in calcitriol
What is the structure of the renal system ?
Organs- 2 kidneys,2 ureters ,bladder and urethra
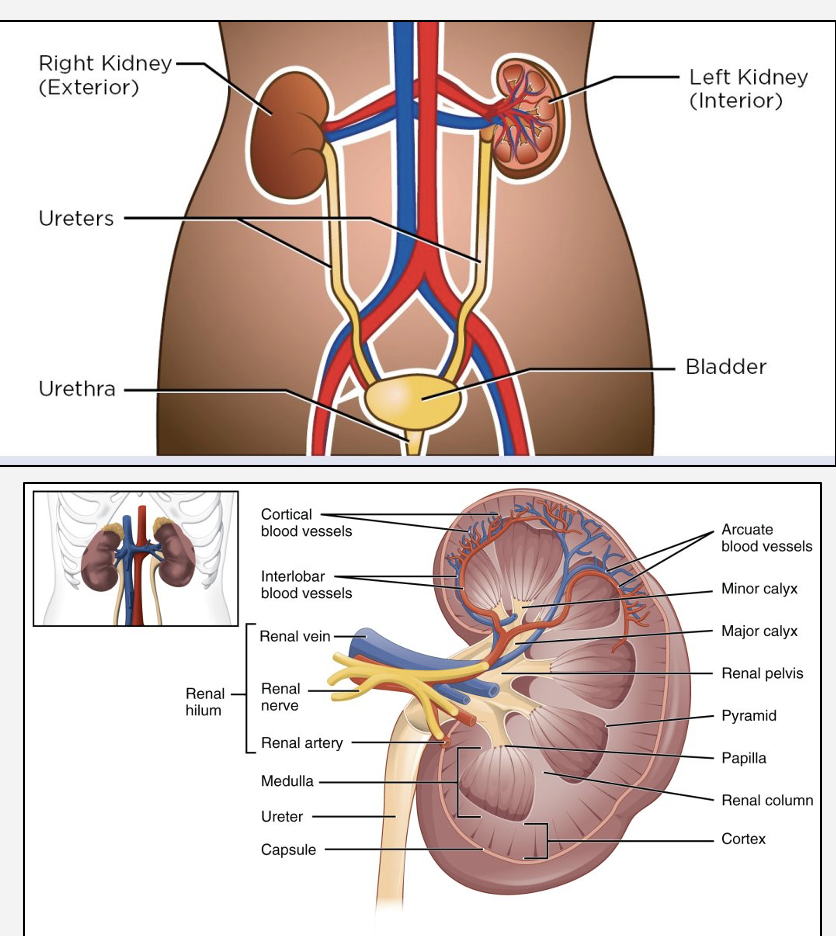
What is the Nephron?
Functional unit of a kidney -filter blood, remove waste products like urea, and regulate the balance of water, electrolytes, and acids in the body to form urine
Decribe the key structures and their roles in the nephron?
•Glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule: site of blood filtration, forms filtrate in nephron
•Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT): reabsorbs most Na⁺, water, glucose, amino acids
•Loop of Henle: concentrates urine (descending limb: water out, ascending limb: Na⁺ out)
•Distal tubule and Collecting duct: controls final Na⁺, K⁺, water in urine; regulated by Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from posterior pituitary gland and Aldosterone from the cortex (outer region) of adrenal gland
•Nephron = site of action of diuretics - decrease amount of water reabsorbed into blood: increase water output in urine
•Excretion = filtration – reabsorption + secretion
NOTE - DIURETIC DRUGS - prevent uptake of ions
What is the function of the nervous system ?
Main functions: control, coordination, communication within the body
What are the 2 major divisions?
MAJOR DIVISIONS
•Central Nervous System (CNS) – brain and spinal cord (integration, processing, higher functions)
•Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – cranial & spinal nerves (connect CNS ↔ body)
SUBDIVISIONS PNS:
•Somatic – voluntary, skeletal muscle control
•Autonomic (ANS) – involuntary, smooth muscle, glands, heart
•Sympathetic: fight or flight
•Parasympathetic: rest and digest