Marine Productivity
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
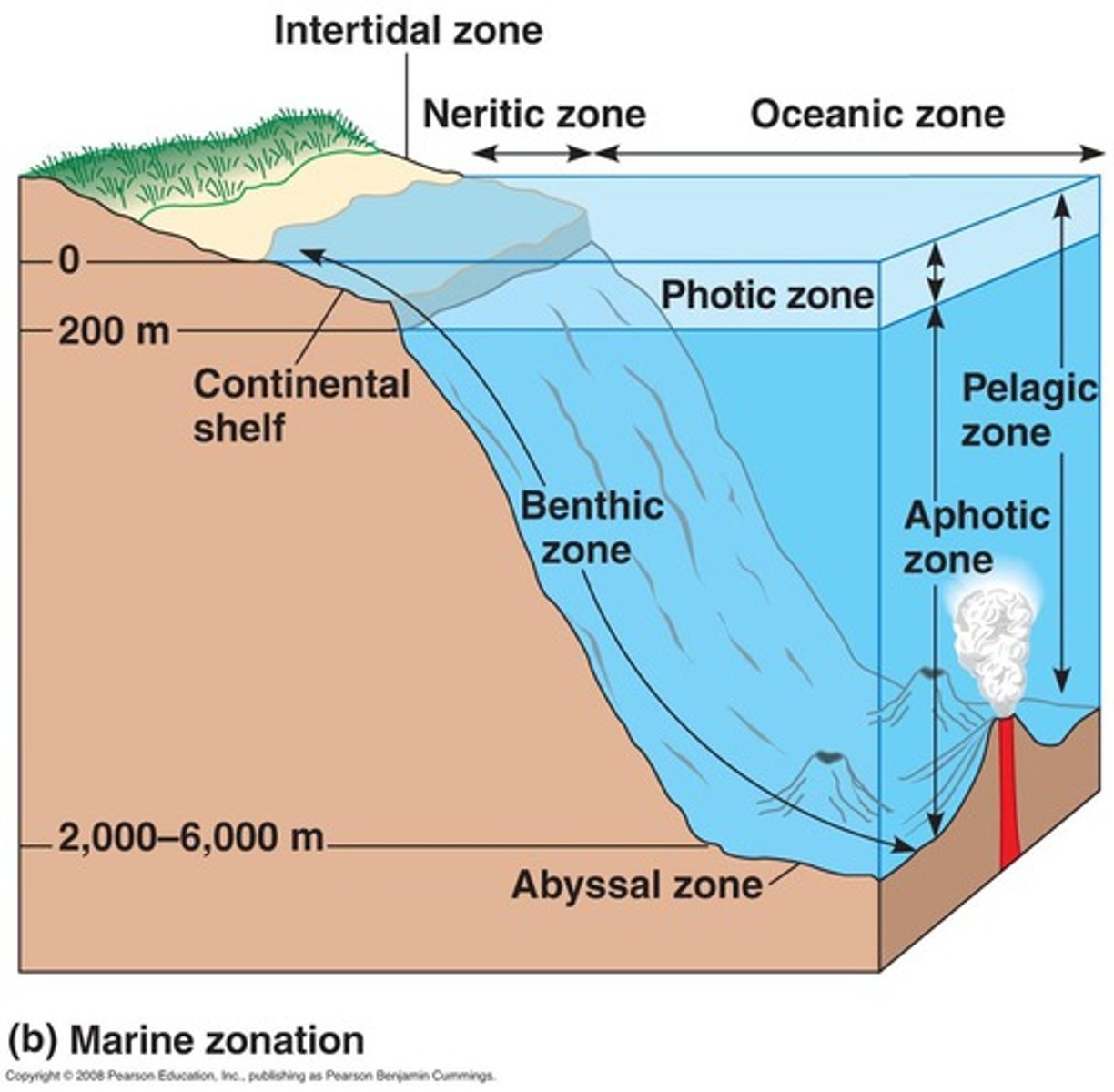
Photic zone
The water layer into which light can penetrate.
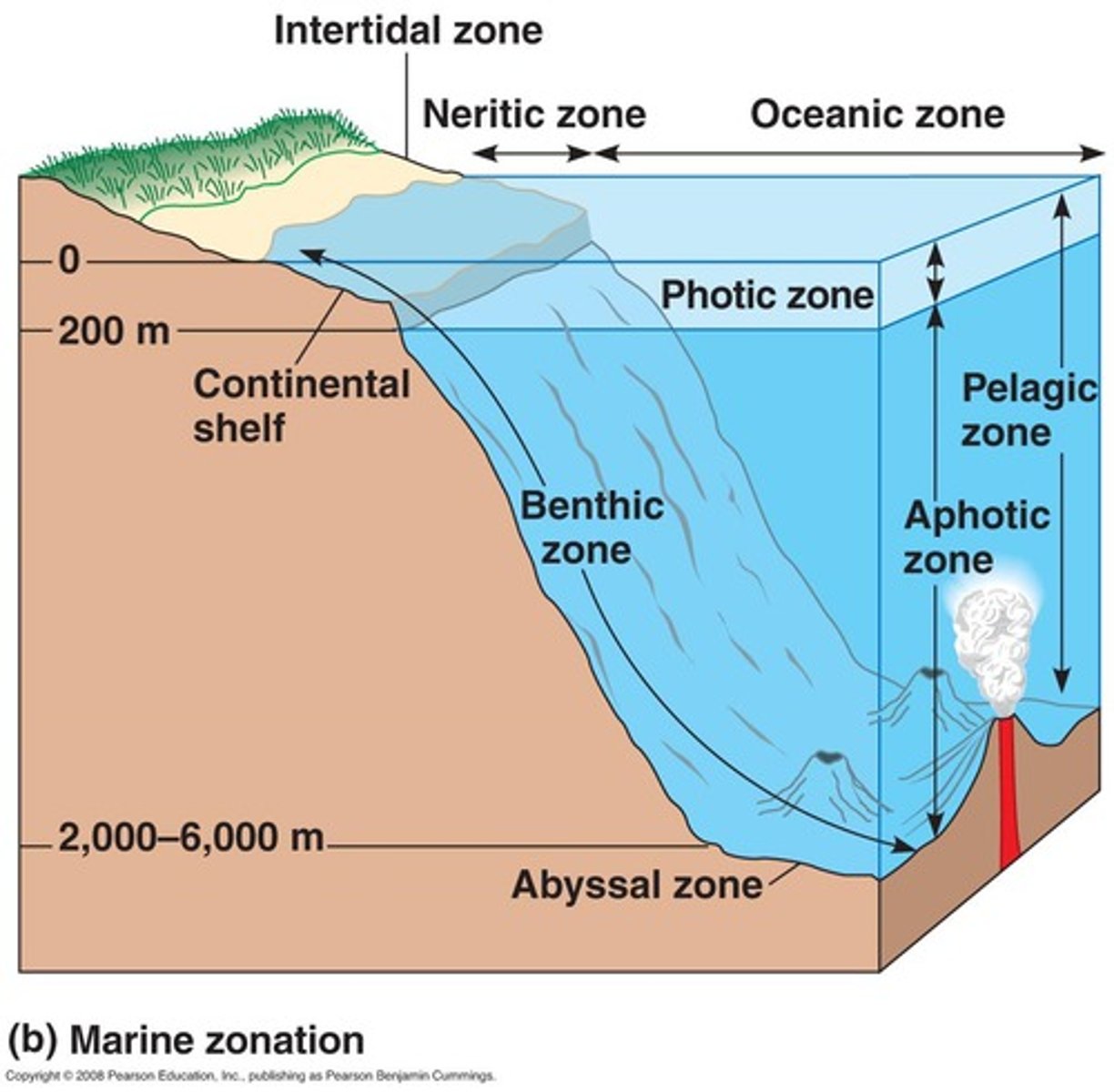
Aphotic zone
Deeper layers of water that receive no sunlight because they are absorbed by shallower layers.
What do most life at greater depths (in the aphotic zone) rely on?
They rely on:
- food produced near the surface (like planktonic algae) to be carried down by water currents.
- the bodies of dead organisms that sink.

How do algae get nutrients?
Algae absorb nutrients directly from the water because there is no soil and they don't have roots.

Nutrient availability
Some nutrients are readily available (CO₂).
Others are often the limiting factor on biological productivity when they are not sufficiently abundant (phosphates).
Why are phosphates often not available in the ocean?
Phosphate has a low solubility.
The ocean is deficient in phosphates except where there are processes that cause phosphates to be added
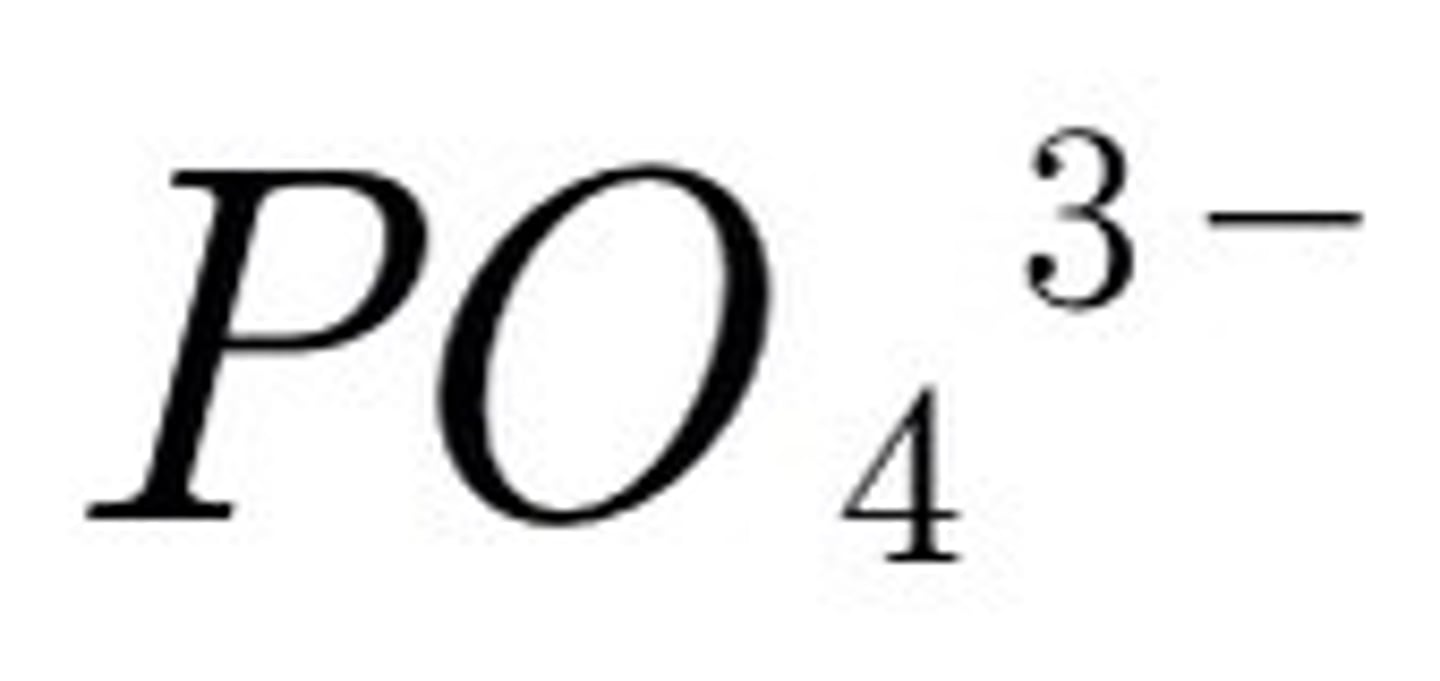
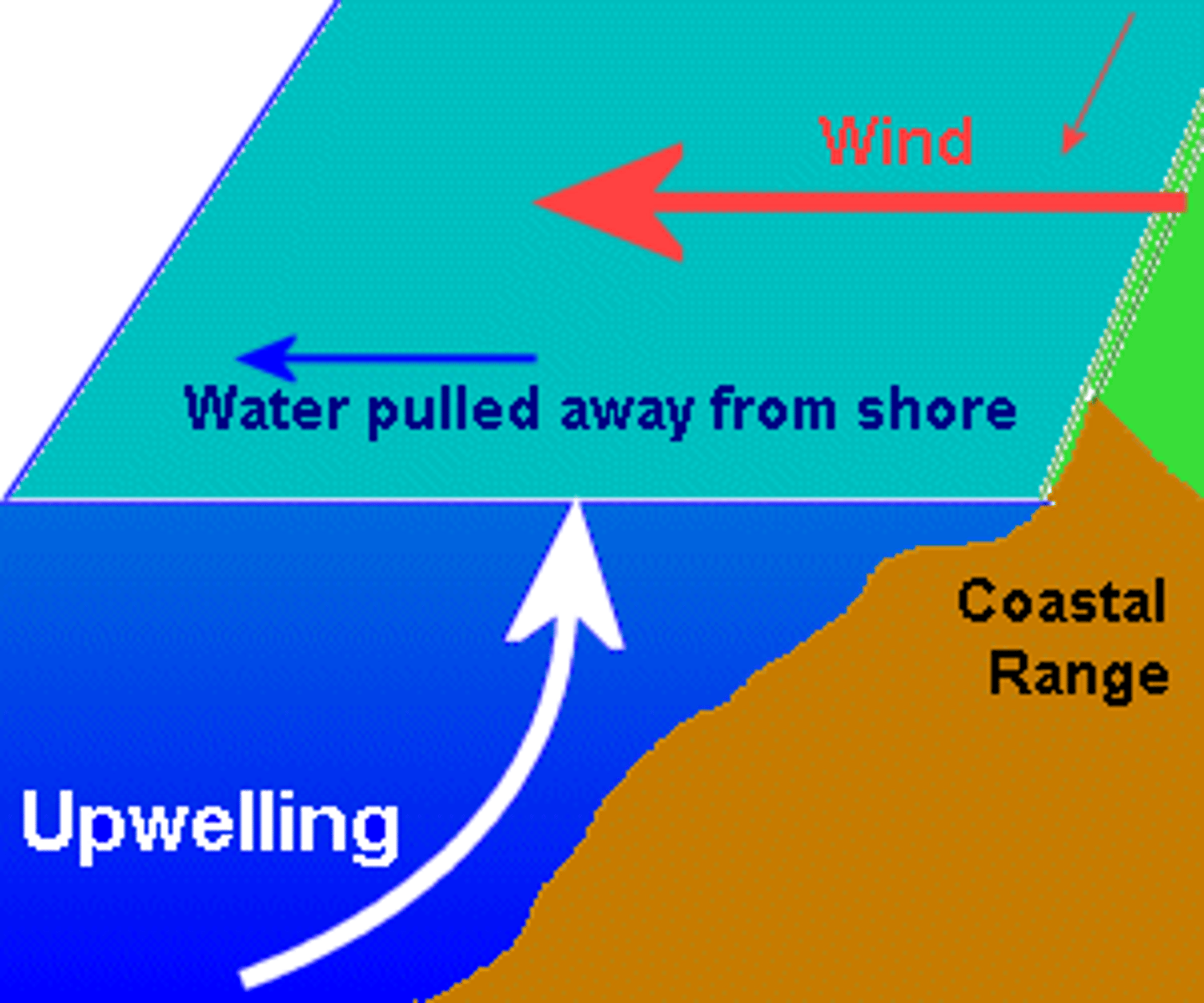
Why are there higher phosphate levels in the photic zone?
Phosphate levels are increased by runoff from rivers which carry phosphates from weathered rocks, and also in areas with upwelling (deep ocean currents bring nutrient-rich water, including phosphates, from the seafloor back to the surface, where it becomes available to marine life.)
Are there high phosphate levels in open areas of the ocean?
No
What happens in open areas of the ocean?
When planktonic organisms die, the nutrients contained are carried to the seafloor.
This may reduce nutrient availability in the surface photic layer, so future biological productivity is reduced.

What is freshwater?
Water without salt

Freshwater productivity
Water bodies on land are often very productive, as they receive nutrient runoff from the land, and receive high light levels because they are relatively shallow.
What is total freshwater productivity limited by?
The small total area of rivers and lakes