Bones of the Orbit – Week 1 Vocabulary
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key anatomical terms, bones, walls, and openings of the orbit as introduced in Week 1 of HMO104.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Orbit (3)
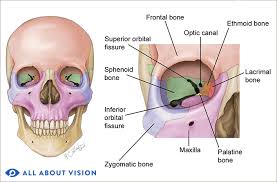
A conical (pyramidal) bony cavity ≈40 mm in each dimension that houses the eye and its supporting structures.
Cranium
The 8-bone portion of the skull enclosing the brain; joins facial bones at sutures.
Facial Bones
Fourteen bones that attach to the cranium and form the face (e.g., maxilla, zygomatic, nasal).
Suture
Immovable fibrous joint that unites the bones of the skull.
Frontal Bone
Cranial bone forming the forehead, roof of the orbits, and part of the supraorbital margin.
Parietal Bone
Paired cranial bone forming the sides and roof of the skull.
Occipital Bone
Posterior cranial bone containing the foramen magnum.
Temporal Bone
Paired cranial bone housing the ear structures; forms part of the skull base.
Sphenoid Bone
Butterfly-shaped cranial bone; its greater and lesser wings help form the orbit and contain the optic canal.
Ethmoid Bone
Light, perforated cranial bone forming part of the medial orbital wall and nasal septum.
Maxillary Bone
Facial bone forming upper jaw, part of orbital floor, and walls of maxillary sinus.
Zygomatic Bone
Cheekbone; contributes to the lateral wall and floor of the orbit.
Lacrimal Bone
Small facial bone in the medial orbital wall containing the lacrimal fossa/groove for tear drainage.
Palatine Bone
Facial bone forming posterior palate and a small portion of the orbital floor.
Supraorbital Margin
Superior rim of the orbit formed by the frontal bone and containing the supraorbital notch/foramen.
Infraorbital Margin
Inferior orbital rim formed laterally by zygomatic bone and medially by maxilla.
Lateral Orbital Margin
Strong outer edge of the orbit formed by the zygomatic process of frontal bone and frontal process of zygomatic bone.
Medial Orbital Margin
Inner orbital rim formed by the maxillary process of frontal bone and frontal process of maxilla.
Roof of Orbit
Superior wall composed of frontal bone and lesser wing of sphenoid; houses the optic canal.
Floor of Orbit
Inferior wall made of maxilla, zygomatic, and palatine bones; separates orbit from maxillary sinus.
Medial Wall of Orbit
Thin wall formed by ethmoid, lacrimal, body of sphenoid, frontal, and maxillary bones.
Lateral Wall of Orbit
Thickest orbital wall, built by the greater wing of sphenoid and zygomatic bone for protection.
Optic Canal
Opening in the lesser wing of sphenoid transmitting the optic nerve (CN II) and ophthalmic artery.
Superior Orbital Fissure
Gap between lesser and greater wings of sphenoid conveying most nerves and vessels entering the orbit.
Inferior Orbital Fissure
Opening between greater wing of sphenoid and maxilla; carries inferior ophthalmic vein and maxillary nerve (V2).
Ethmoidal Foramina
Anterior and posterior openings in the medial wall transmitting ethmoidal nerves and arteries.
Whitnall’s Tubercle
Small lateral orbital tubercle that serves as an attachment point for the lateral canthal tendon and ligaments.
Lacrimal Fossa
Depression in frontal bone (orbital roof) accommodating the lacrimal gland.
Trochlear Fossa
Medial orbital roof depression for the pulley (trochlea) of the superior oblique muscle.
Paranasal Sinuses
Air-filled cavities (frontal, maxillary, ethmoid, sphenoid) that lighten the skull and resonate the voice.
Frontal Sinus
Air cavity within the frontal bone located above the orbit.
Maxillary Sinus
Largest paranasal sinus situated within the maxilla beneath the orbital floor.
Ethmoid Sinus
Multiple small air cells within the ethmoid bone medial to the orbit.
Sphenoid Sinus
Midline sinus within the body of the sphenoid bone posterior to the orbit.
Orbital Fat
Connective tissue filling four-fifths of the orbital volume, cushioning and supporting the globe.
Extraocular Muscles
Six muscles (four recti, two obliques) plus levator palpebrae that move the eye and eyelid within the orbit.