Cervical Spine Lab Manual
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
most superior cervical vertebra that supports head
atlas
second cervical vertbra with unique dens
axis
how much of the rotation that occurs in the c-spine happens at C1-C2?
50%
the _____ pivots around the ______ of the ______ to allow cervical rotation
atla, dens, axis
defining features of the axis (C2)
odtontoid process (dens), large and palpable spinous process
defining features of the atlas (C1)
doesn’t contain vertebral body or spinous process
is there and IV foramen or disc b/w C1 and C2?
no
features of the typical cervical vertebrae (C3-C7)
transverse foramen, short bifid spinous processes, small vertebral bodies, triangular and large vertebral foramen, horizontally oriented articular facets
which typical cervical vertebra does not have a bifid spinous process? what are its defining features
C7- is especially long, prominent, and palpable at the lower neck
why are cervical vertebral bodies small?
they do not have to bear as much weight as the thoracic or lumbar vertbrae
what distinguishes thoracic vertebrae from cervical vertebrae?
thoracic vertebrae do not have transverse foramina or bifid spinous processes
what is the function of IV discs?
weight bearing and strength
outer layer of the disc that is composed of many fibrocartilage
laminae. This part of the IV disc is made up of dense regular connective tissue and contains collagen layers that are laid down in different directions to add strength to the disc
annulus fibrosus
the inner layer of the IV disc that is rich in hyaluronic acid, making it a gelatinous substance. It provides shock absorption for the disc
nucleus pulposus
articulations between the unci of the lower cervical vertebrae. This area is a frequent site of bone spurs that can contribute to cervical pain
uncovertebral joints
Adjacent vertebral arches are connected by synovial joints between the superior and inferior articular facets. These joints allow for gliding motions depending on their orientation
zygapophyseal joints (facets)
These joints are formed by the lateral masses of the Atlas and the occipital condyles of the cranium
atlanto-occipital joints
what motions occur at the AO joints?
flexion and extension, a small degree of lateral flexion
what motions occur at the AA joints?
rotation
Two lateral and one median joint that are located between the C1 and C2 vertebrae
atlanto-axial joints
joints represent the connection between the thoracic vertebrae and the ribs
costovertebral joints
connect the head of the ribs with the costal facets of the two adjacent vertebral bodies, one superior and one inferior
costocorporeal joints
what is the function of costocorporeal joints
allow the ribs to rotate ascend and descend during respiration
forms between the tubercle of the rib and transverse process of the corresponding vertebra
costotransverse joints
what is the potential consequence if there is a tear n the cruciate ligament of the c-spine?
C1 could translate forward on C2 possibly compromising the spinal cord
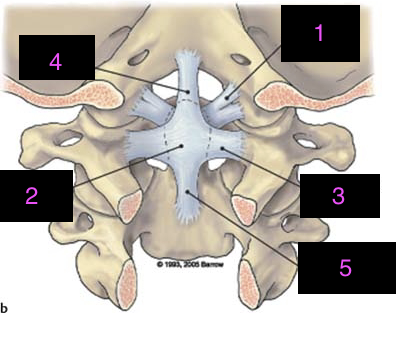
label the ligaments
alar , cruciate, transverse band of cruciate, ascending band, descending band
what muscles make up the sub occipital region
rectus capitus posterior major, rectus capitus posterior minor, obliquus capitus superior, obliquus capitus inferior
what muscles form the area called the suboccipital triangle
rectus capitus posterior major, obliquus capitus superior, obliquus capitus inferior
what is contained in the suboccipital triangle?
vertebral artery, posterior arch of C1, suboccipital nerve
where is the greater occipital nerve found?
inferior to the obliquus capitis inferior (not in the suboccipital riangle)
what muscles make up the suprahyoid group?
mylohyoid, geniohyoid, stylohyoid, digastric
what muscles make up the infrahyoid group?
sternohyoid, omohyoid, sternothyroid, thyrohyoid
Function of the suprahyoid muscles
elevate hyoid, assists with speaking and swallowing
function of the infrahyoid muscles
depress the hyoid