BCS 111 Unit 6.4
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Episodic vs. Semantic memory
-
Episodic memory
Personal experience from previous events
Encoding specificity:
remember something
with related context/events/surroundingsState-dependent and
mood-dependent
Semantic memory
General knowledge
One major difference from episodic memory: “timestamp” of events is not needed in semantic memory but is associated with episodic memory
Procedural vs. Declarative memory
-
Declarative memory
things that can be described (may include both episodic and semantic memory)
Procedural memory
things that are hard to describe (e.g., actions)
Implicit vs. Explicit memory
-
Implicit memory
skills/knowledge acquired without being aware of the rules/patterns; or unconsciously processed input
Equivalent to Procedural memory
Explicit memory
things that can be consciously recollected
Equivalent to Declarative memory
Long-term memory encoding – levels of processing
Why rote learning (i.e. memorization w/o deep understanding) not always helpful?
Shallow vs. deep processing = encoding of word form vs. encoding of meaning
Long-term memory encoding – shallow vs. deep processing
Craik & Tulving (1975): word learning and level of processing
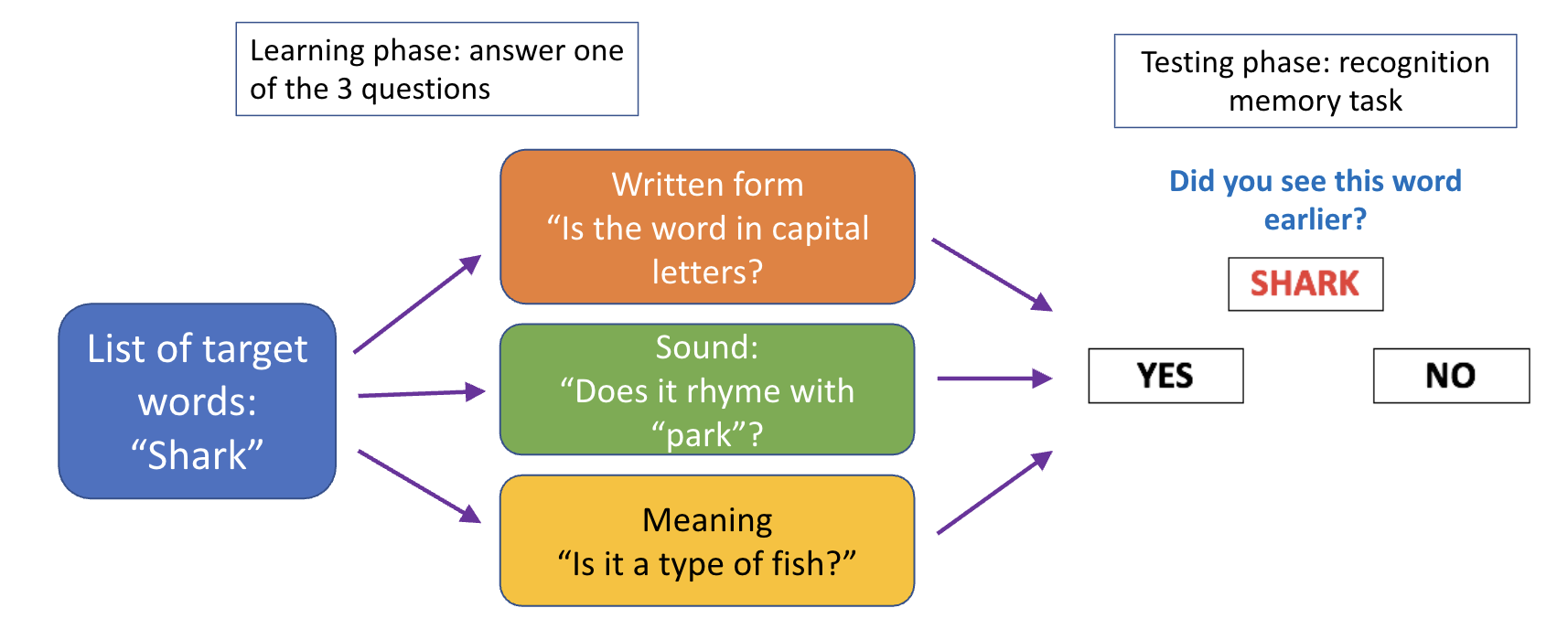
(cont)
Target word: shark
• Learning phase: Three types of attention focus:
Written form: Is the word in capital letters? → SHALLOW processing
Sound: does it rhyme with park? → Less shallow
Category (meaning): Is it a type of fish? → DEEP processing
Learn by meaning most helpful → effect of deep processing
Meaning-based learning (category) much more efficient than form-based method (spellings)
Sound-based learning not as good as meaning based, but still better than form-based
Why and how does mnemonics help us store and recall better?
Recoding
Scattered pieces of info (e.g., 9
planets) → meaningful unit (e.g., a
sentence)
Involvement of working memory?
Of course!
What components of working
memory are involved?Central executive and phonological loop
Long-term memory encoding and retrieval
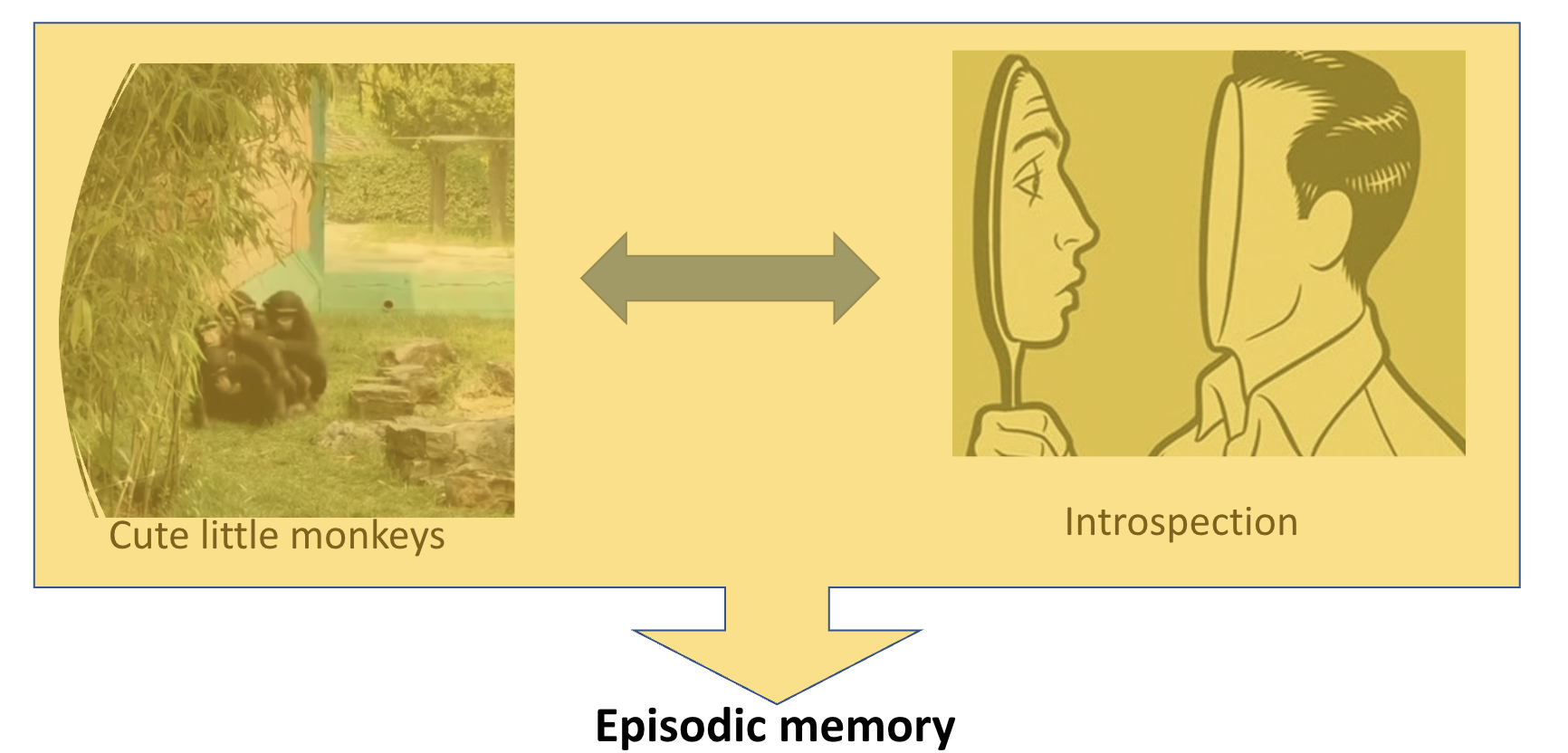
After 5-10 years, if you still remember the concept about “introspection”

When the cue and the retrieved info have a close relation in meaning….
Paired-associate task: tests connective
processes (association) in LTM
Clear relation in meaning between two words/concepts/events → semantic memory
Opaque relation in meaning between two words/concepts/events (Cute little monkeys vs. Introspection) → episodic memory
Long-term memory retrieval
Bousfield (1953): free recall
Recall a list of 60 words
Ss recall words in clusters
Similar to foraging (as discussed in Ecological Approach)
Ecological approach to the study of LTM retrieval
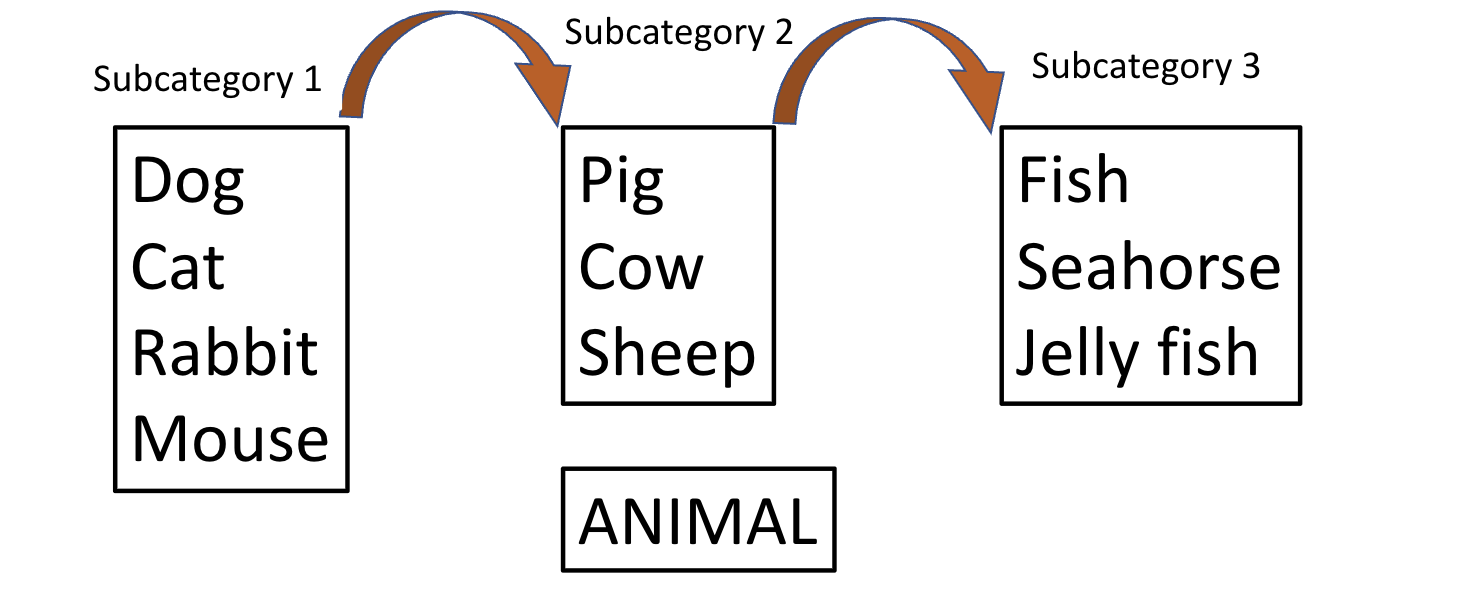
Memory search: verbal fluency task: recall as many words as possible in a given category
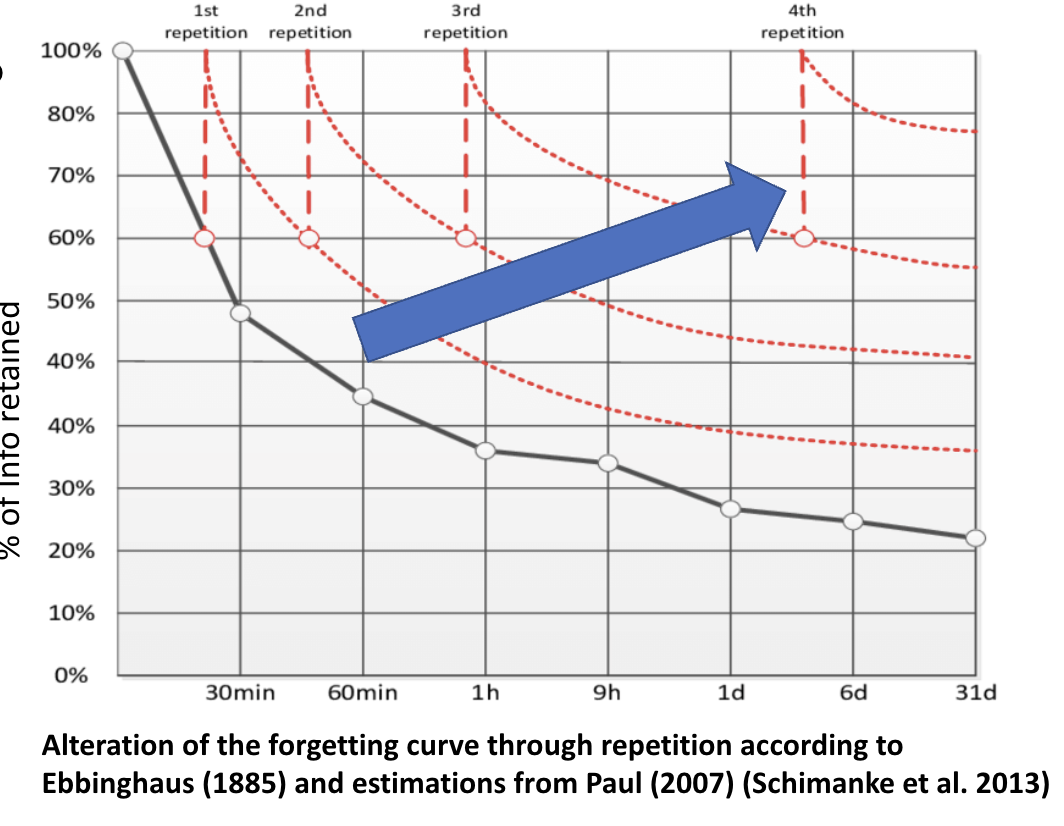
Long-term memory - forgetting
How do you ”flatten the curve”?
Study, study and study!
Mechanisms underlying forgetting?
Interference vs. decay (as in STM)
Long term memory – Forgetting (cont)
Use paired-associates task to test forgetting
Pair the same cue word with a different target word
Proactive interference: old pairing interferes new
(old pairing) Science – cat
(new pairing) Science – rain
Task: Recall the new pair: Science – cat
(cont)
Use paired-associates task to test forgetting
Retroactive interference: new replaces old
(old pairing) Science – cat
(new pairing) Science – rain
Q: Recall the old pair?
A: Science - rain
Summary of LTM
-
3 classification schemes
Episodic vs. Semantic; Declarative vs. Procedural; Implicit vs. explicit
We have limited processing capacity but theoretically unlimited LTM storage capacity
Encoding and retrieval
Deep vs. shallow processing = meaning-based vs. form-based processing
How does recoding help us remember things better?
LTM Free recall vs. cued recall: free recall is like foraging
Forgetting
Paired associate learning: Proactive vs. retroactive interference