Campbell Biology Chapter 10
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
photosynthesis
process of harnessing light energy to build carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water molecules
photosynthesis (equation)
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6 O2
autotroph
organism that CAN capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food (producer)

heterotroph
organism that CANNOT produce its own food and therefore obtains it by consuming other living things (consumer)

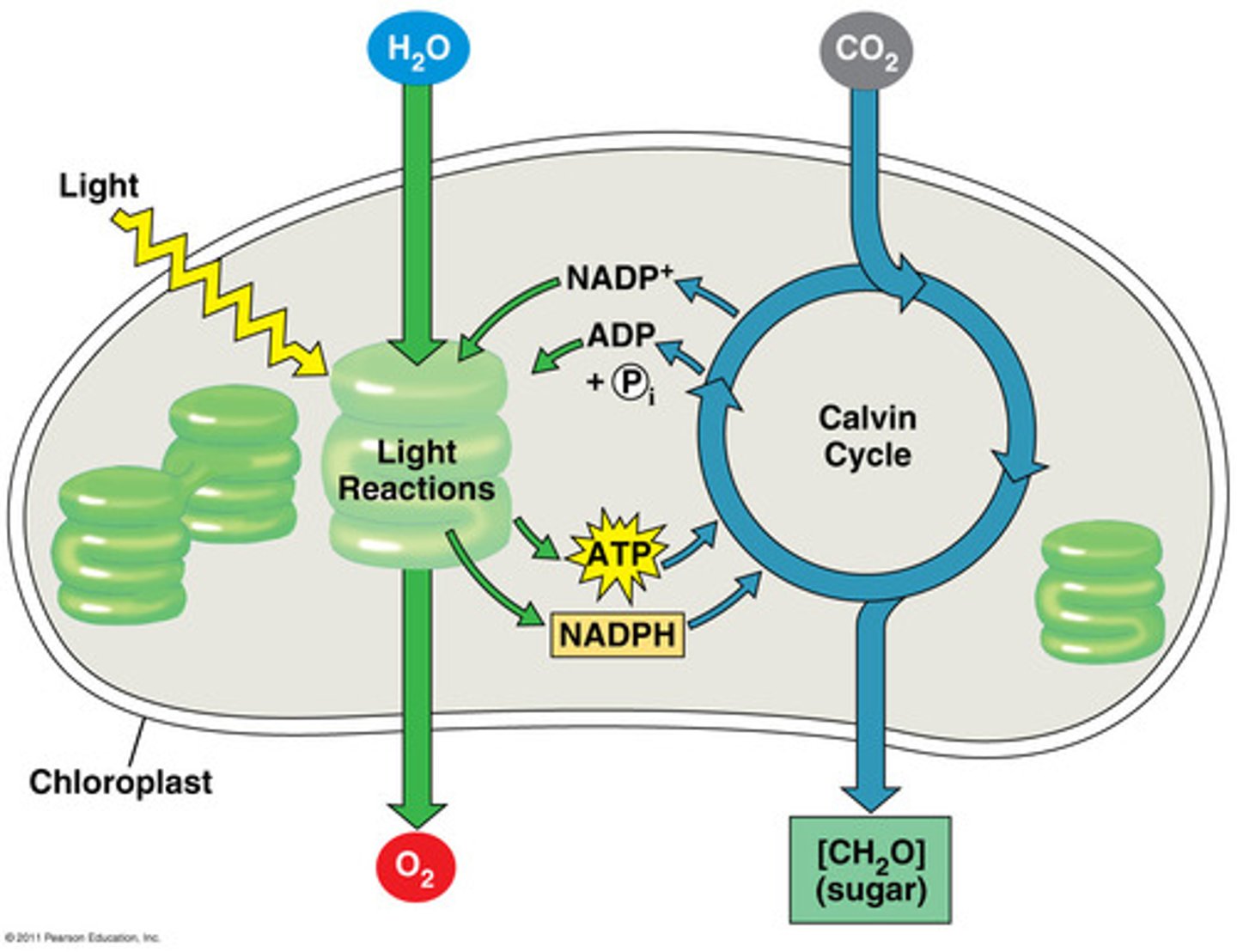
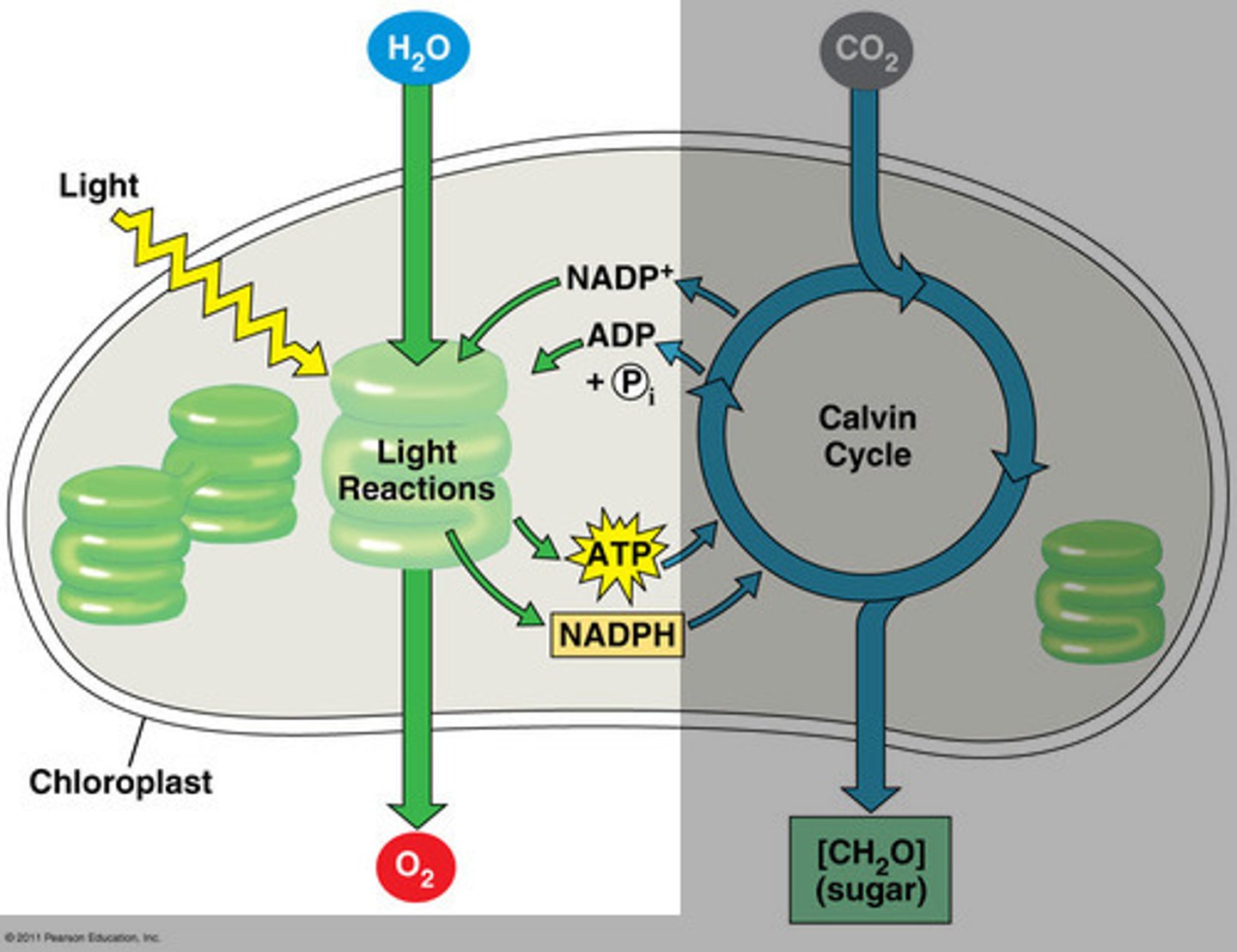
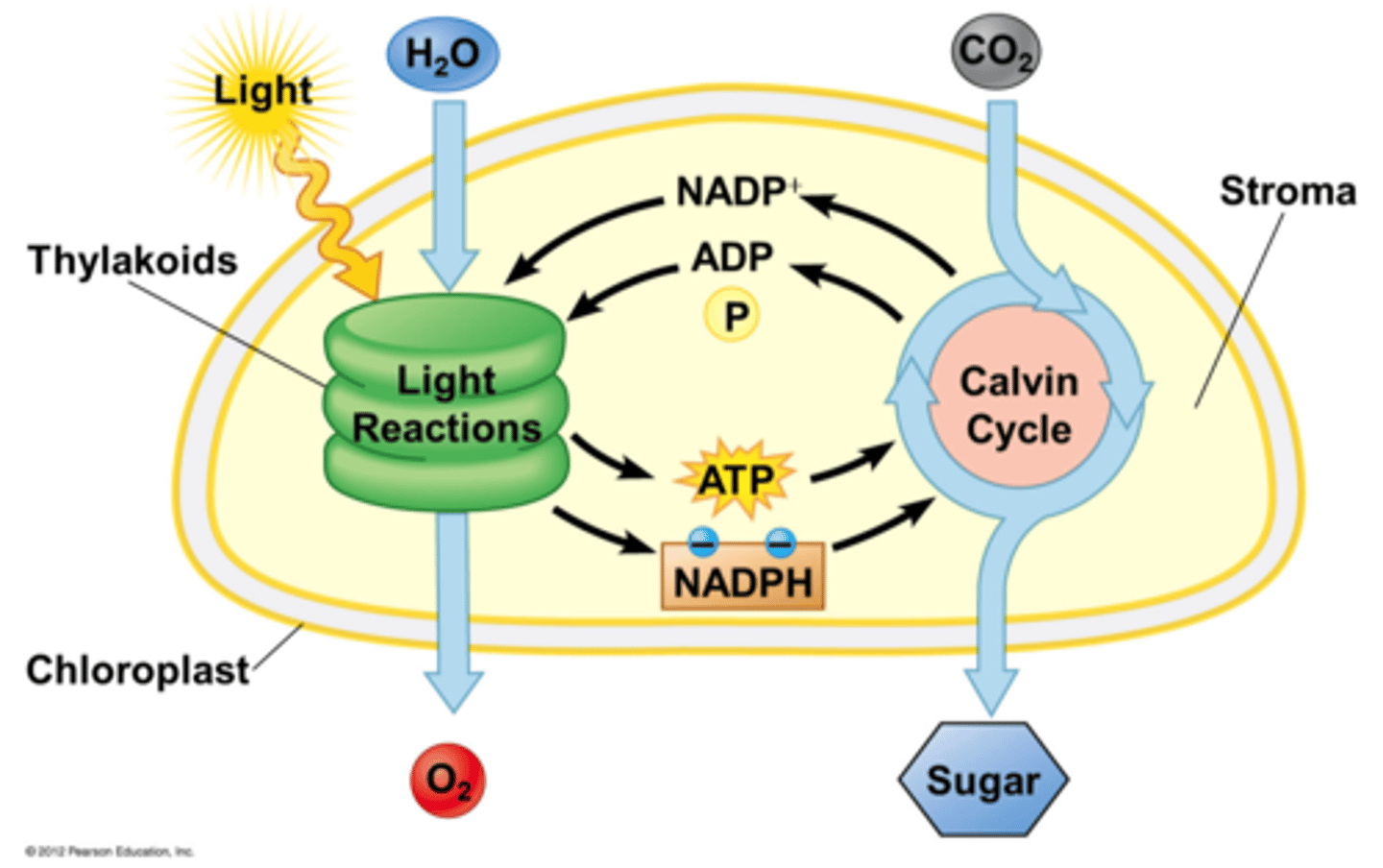
light-dependent reactions
1st step of photosynthesis during which light energy is captured and used to synthesize ATP and NADPH
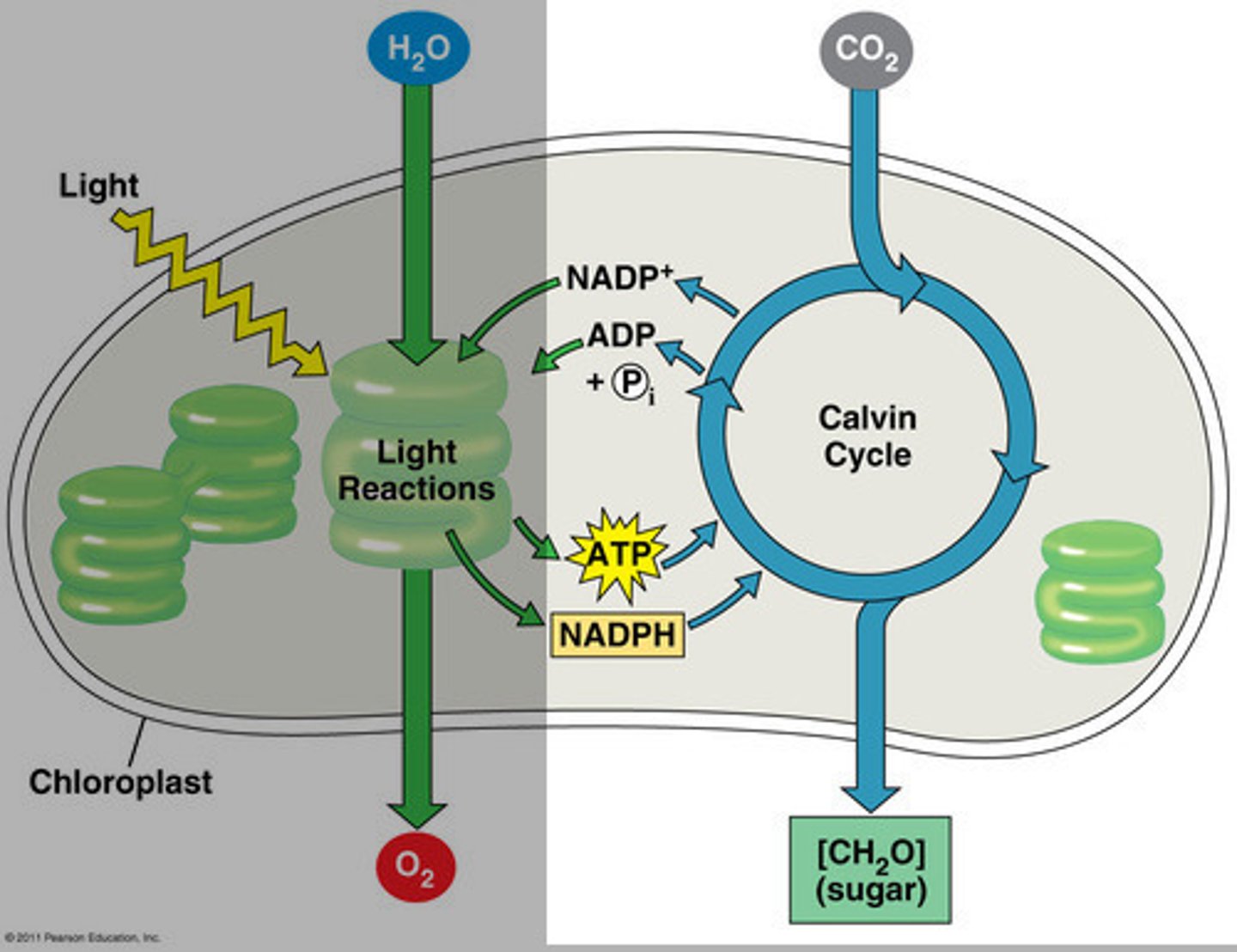
light-independent reactions
2nd step of photosynthesis during which CO2 is incorporated into a sugar molecule using ATP and NADPH produced during the first step
thylakoid membranes
location of light-dependent reactions
stroma
location of light-independent reactions
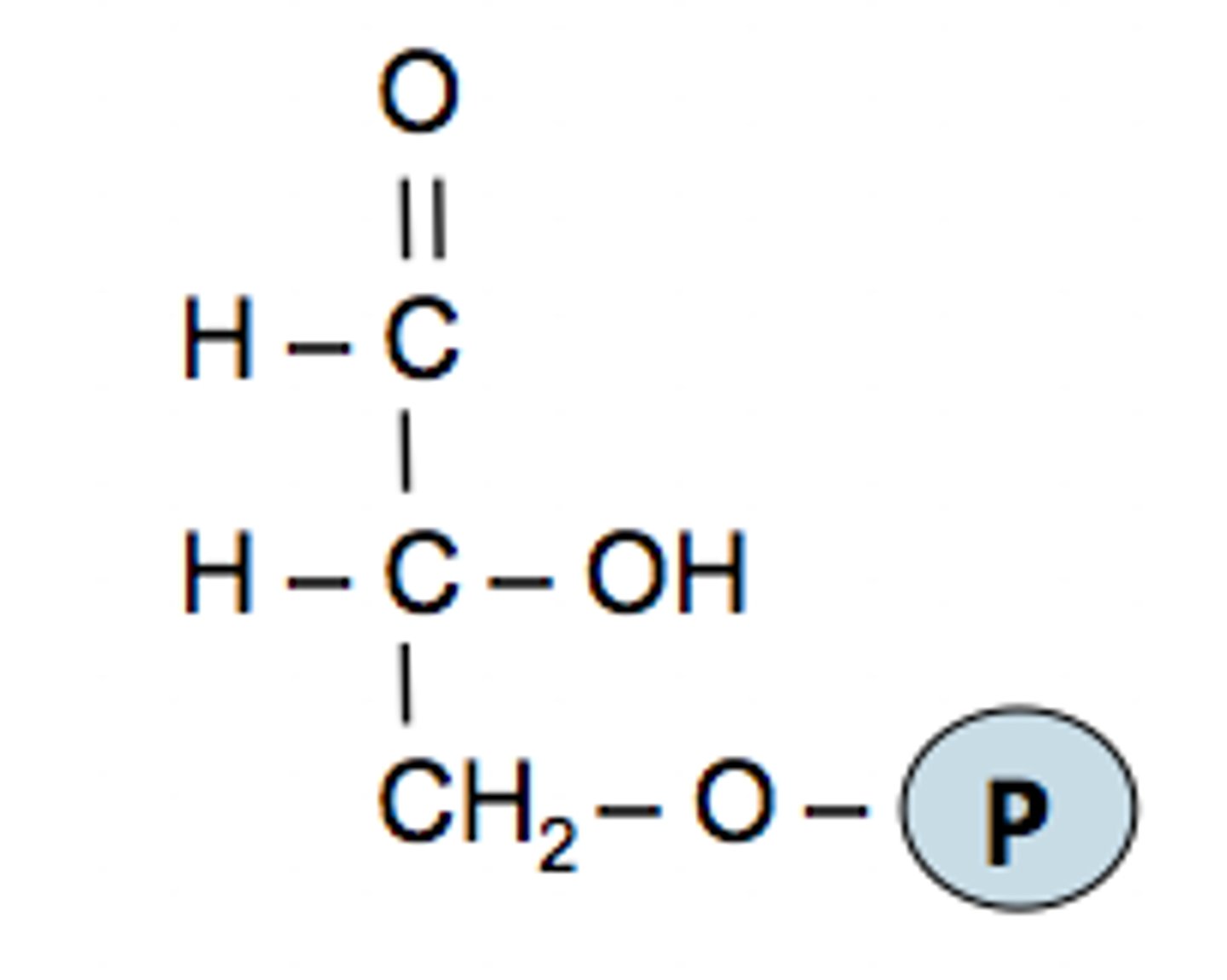
G3P
carbon product of the light-independent reactions, which used to form glucose sugar
blue, violet and red
Which wavelengths of the visible light spectrum do chlorophylls ABSORB?
green
Which wavelengths of the visible light spectrum do chlorophylls REFLECT?
carotenoids
accessory pigments in chloroplasts that broaden the spectrum of colors used in photosynthesis (absorb green/blue but reflect red/yellow/orange)
photosystem II (PS II)
1st of two light harvesting units in thylakoid membrane that passes excited electrons to reaction-center chlorophyll
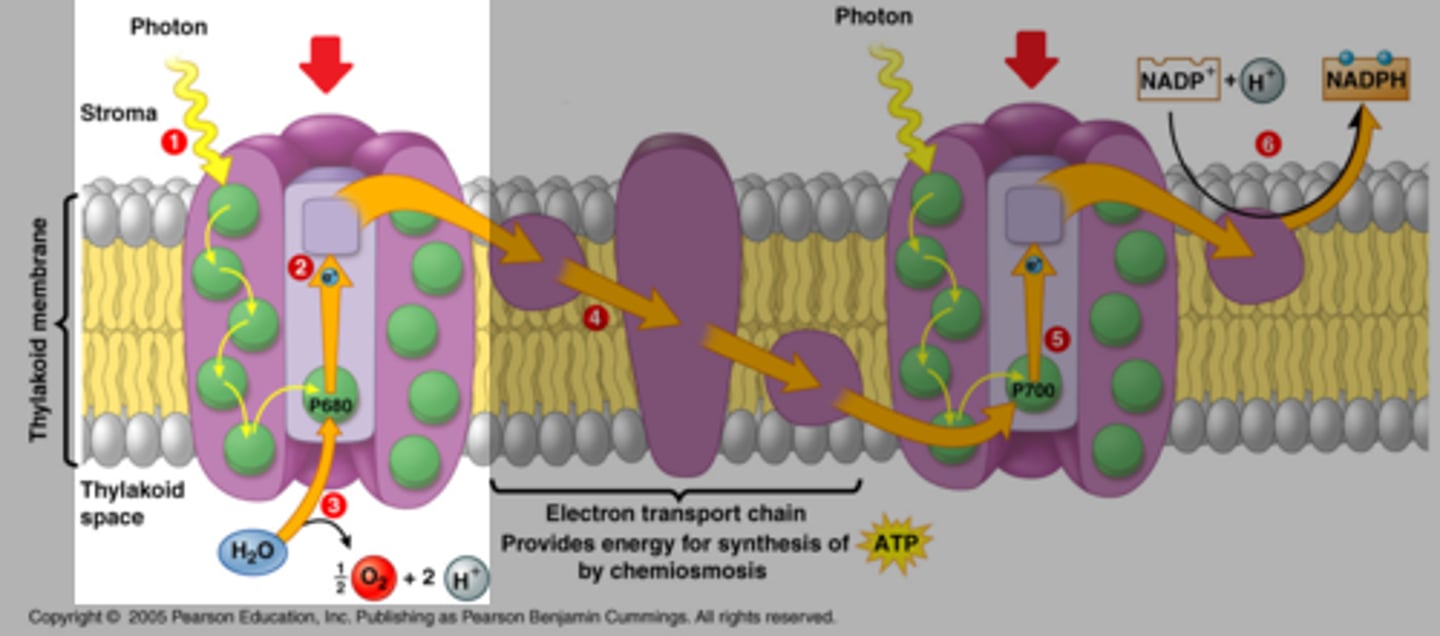
water
splitting this molecule replaces electrons which are excited and passed to primary electron acceptor in PSII
O2
released as a byproduct of splitting water
photosystem I (PS I)
2nd of two light-capturing units in thylakoid membranes that replaces its electrons by those from the 1st complex and results in production of NADPH
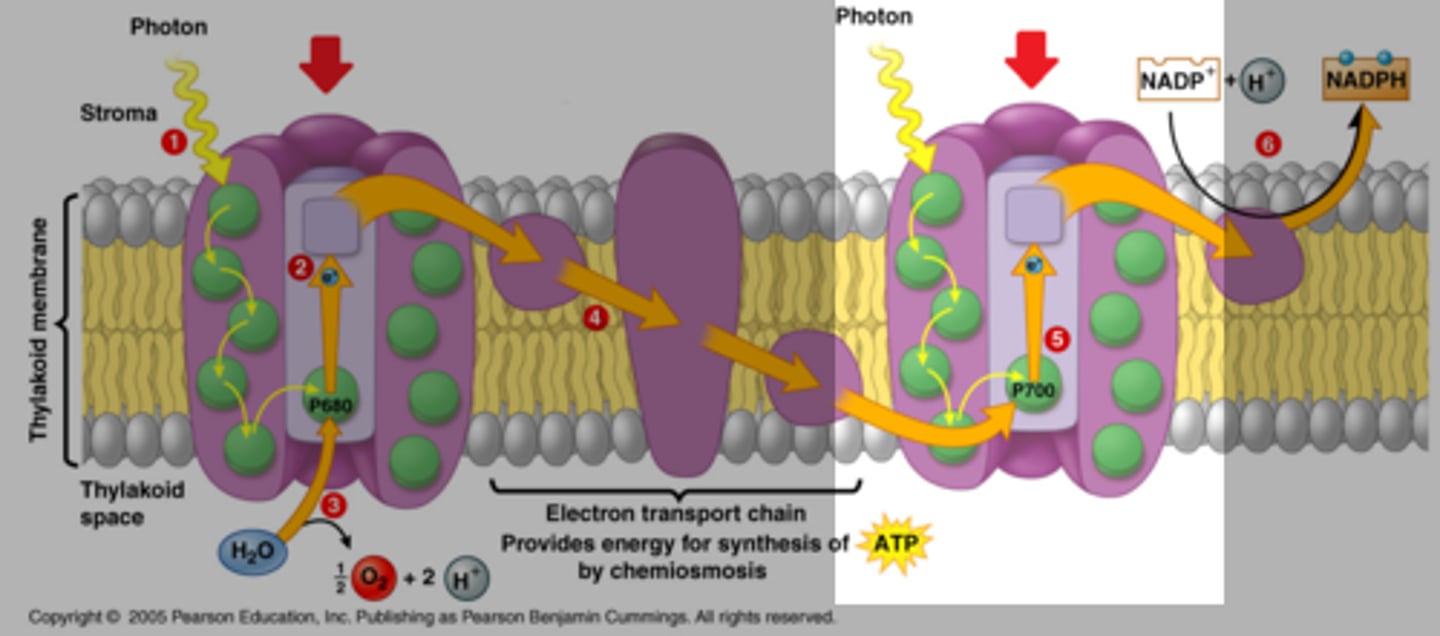
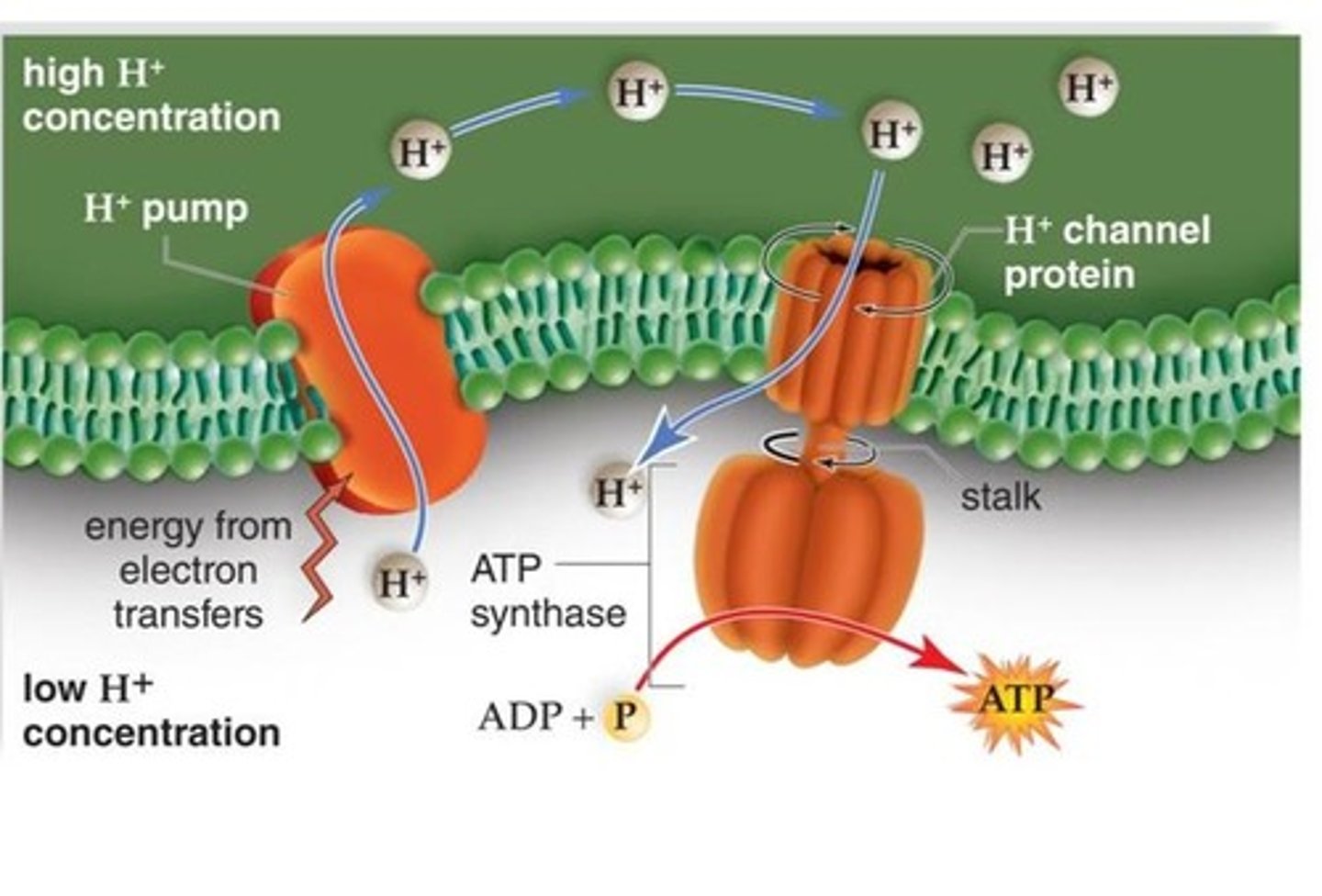
proton-motive force
created by pumping hydrogen ions from stroma to thylakoid space during electron transport chain between PS II and PS I
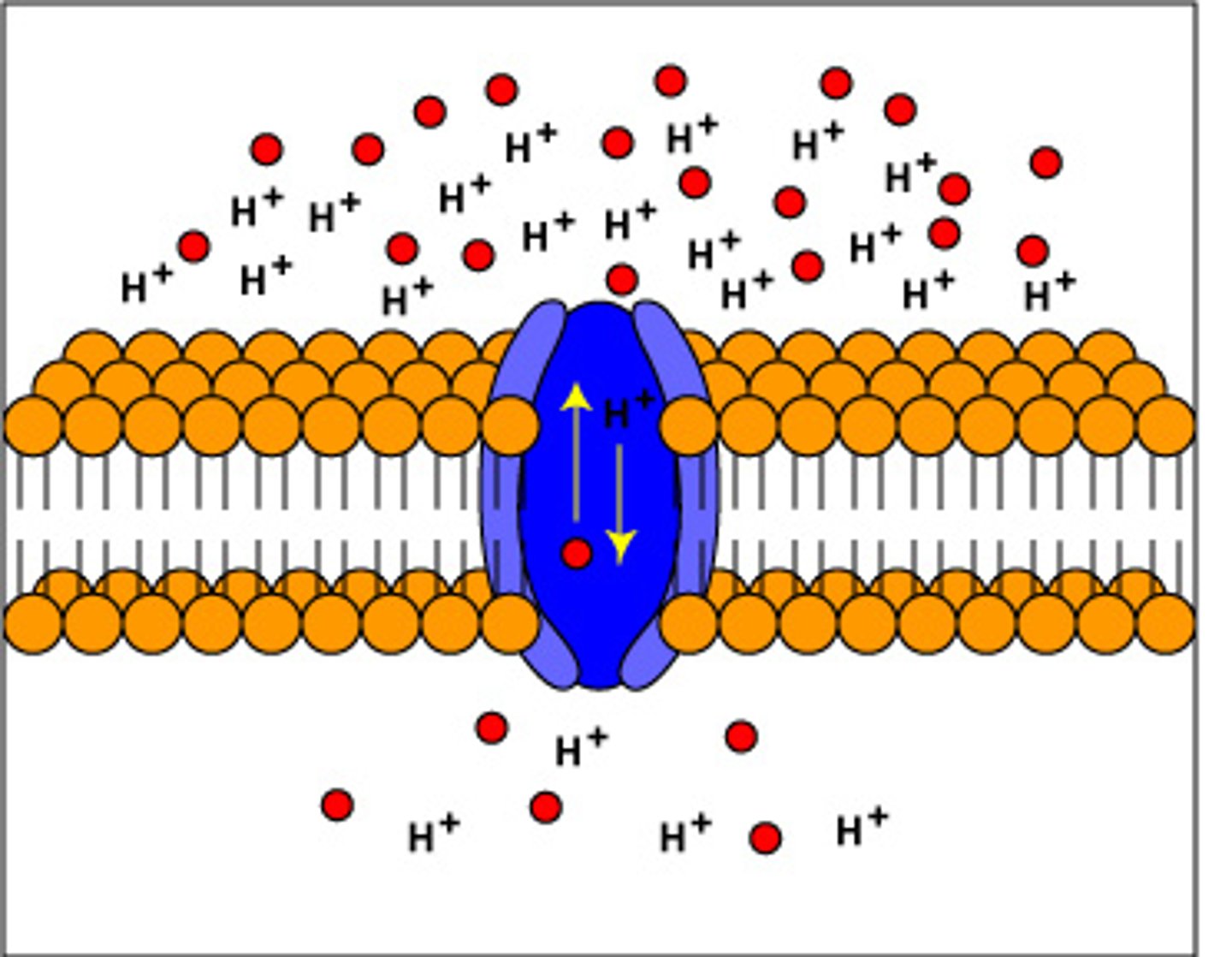
ATP synthase
enzyme that synthesies ATP by utilizing a proton-motive force
Calvin cycle
other names for light independent reactions include dark reactions, carbon fixation or _______
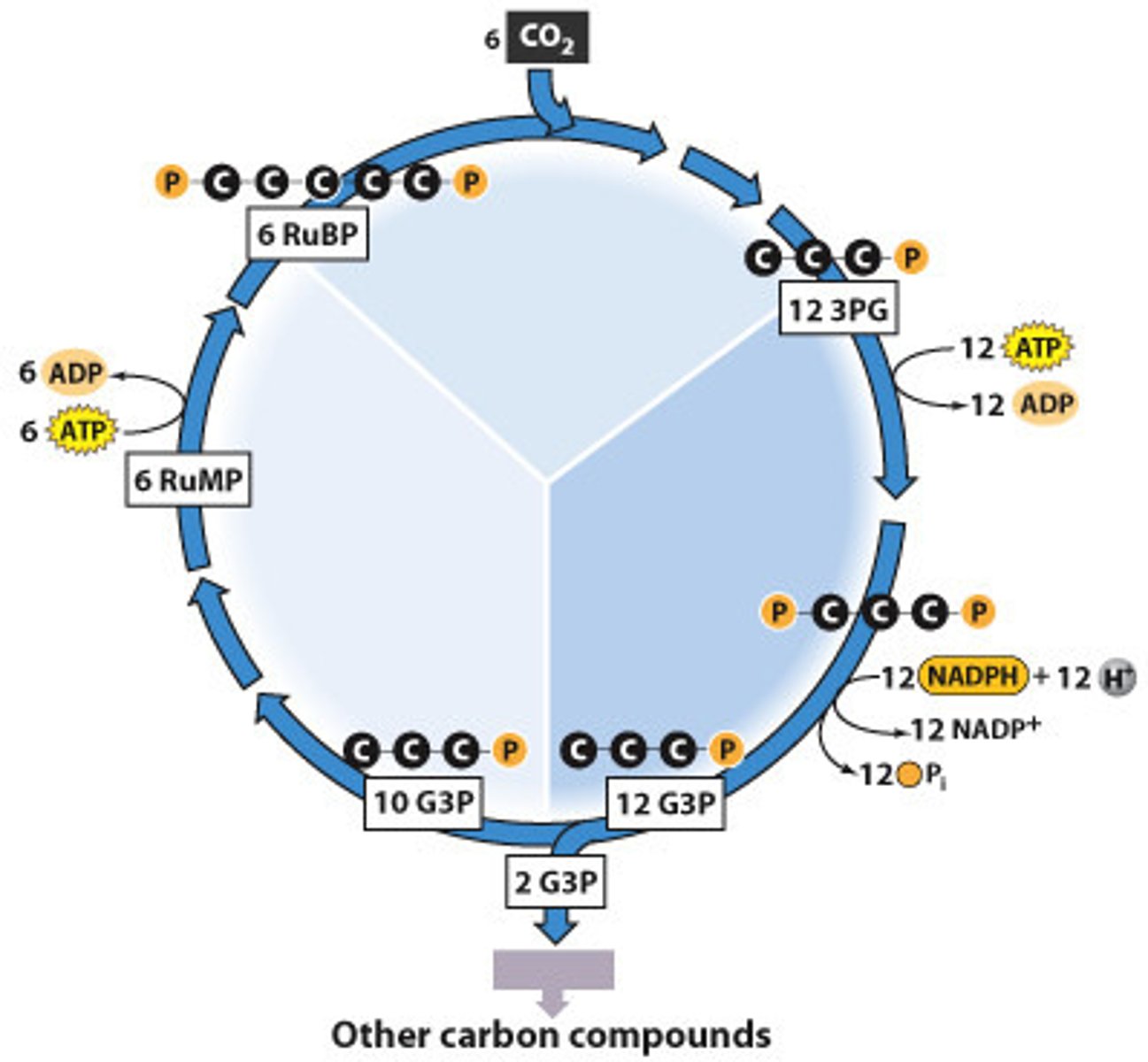
carbon dioxide
molecule used in Calvin cycle to produce sugar
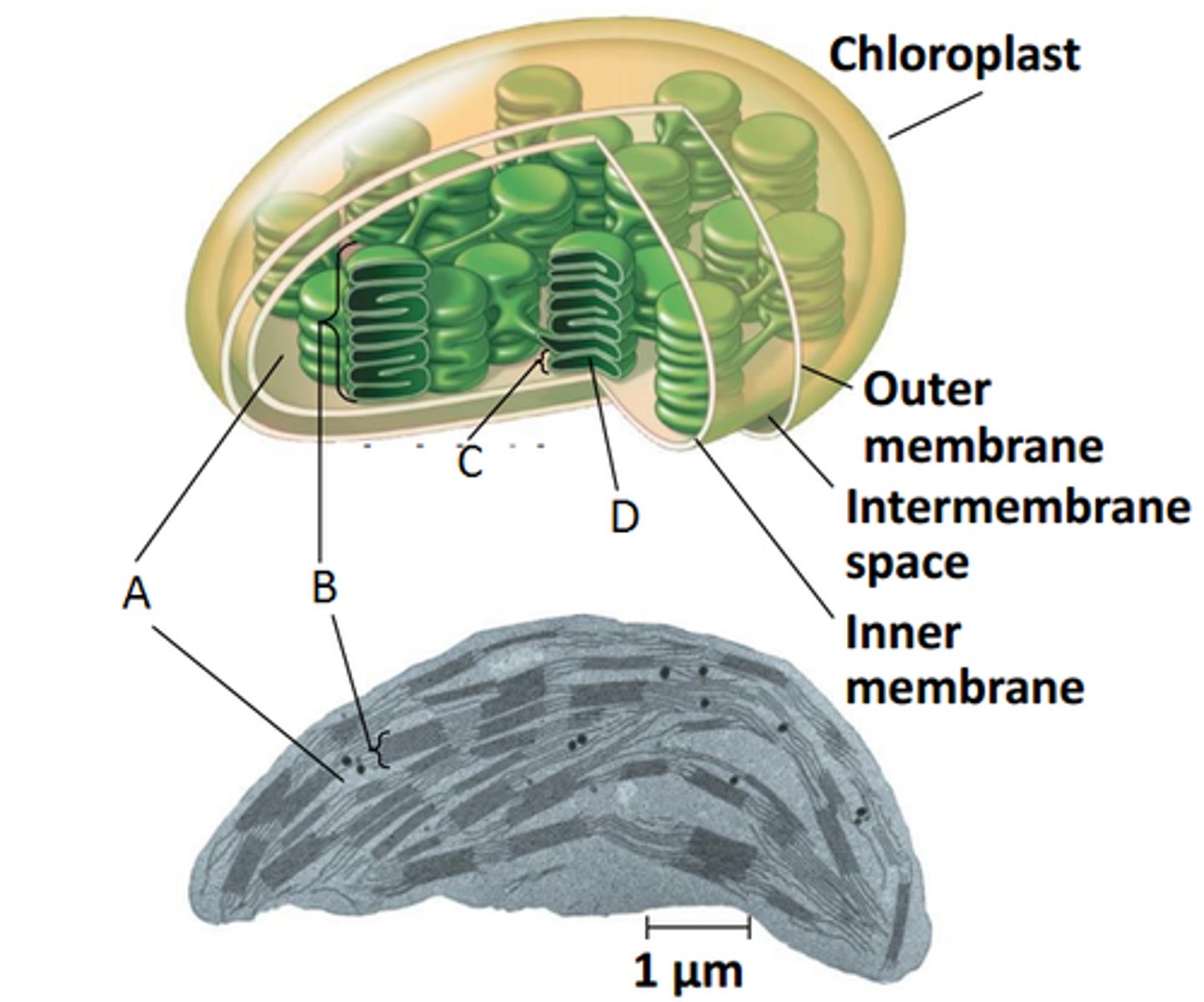
thylakoids
(C) flattened membranous sacs inside chloroplasts that contain systems which convert light energy to chemical energy
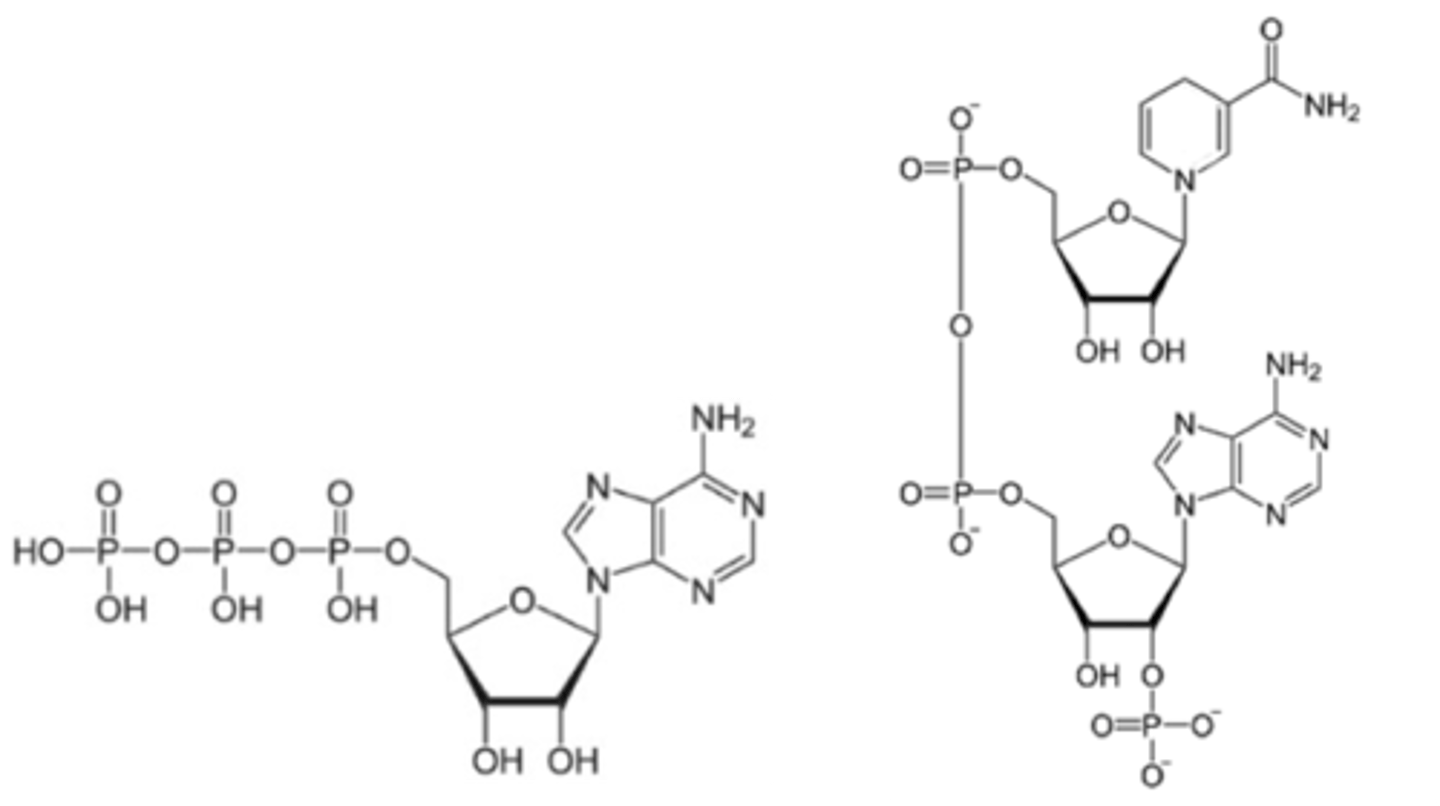
NADP+
high energy electron carrier(s ) before reduction in photosynthesis (after they drop off electrons for Calvin cycle)
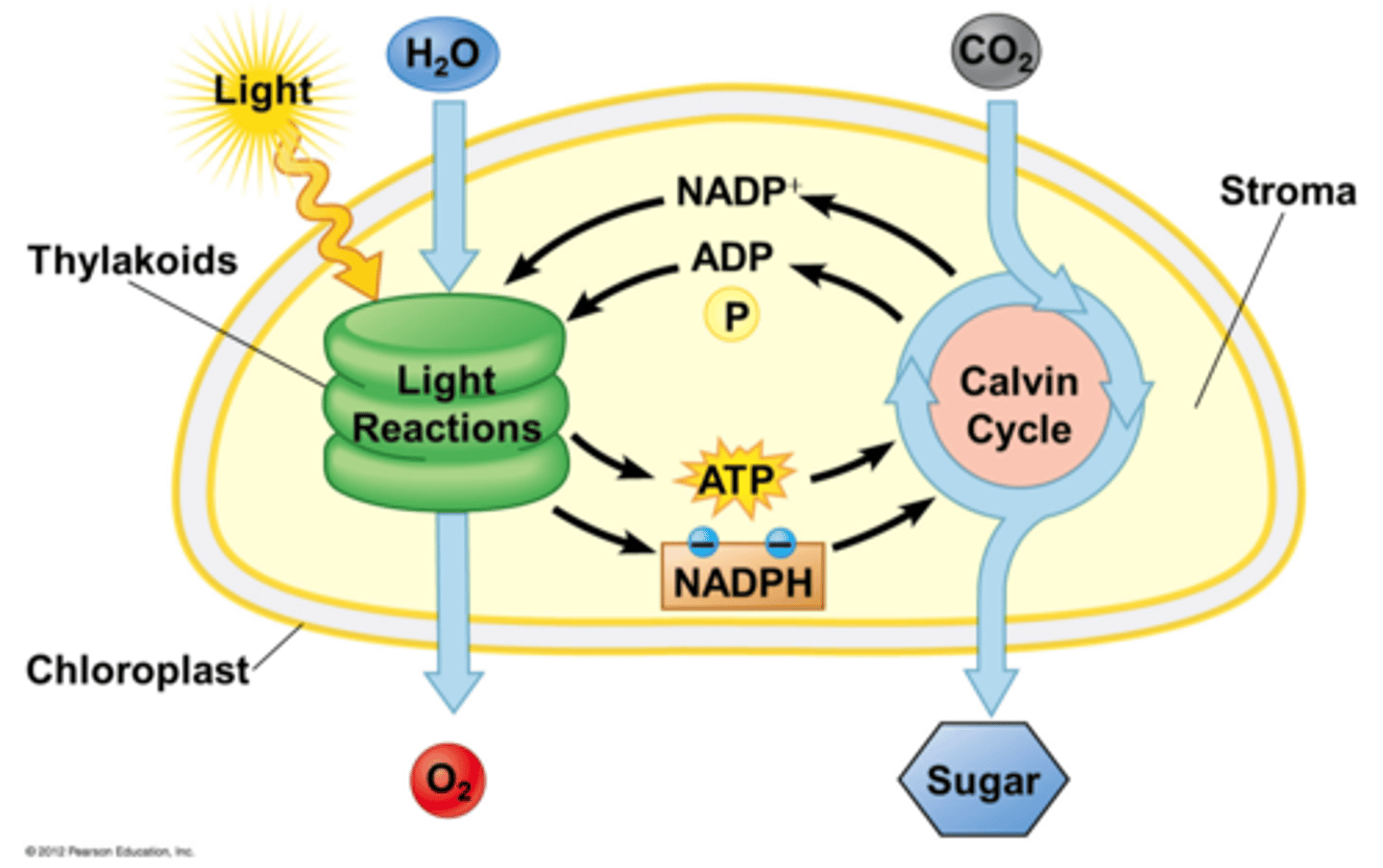
NADPH
high energy electron carrier(s ) after reduction in photosynthesis (after they pick up electrons from ETC)
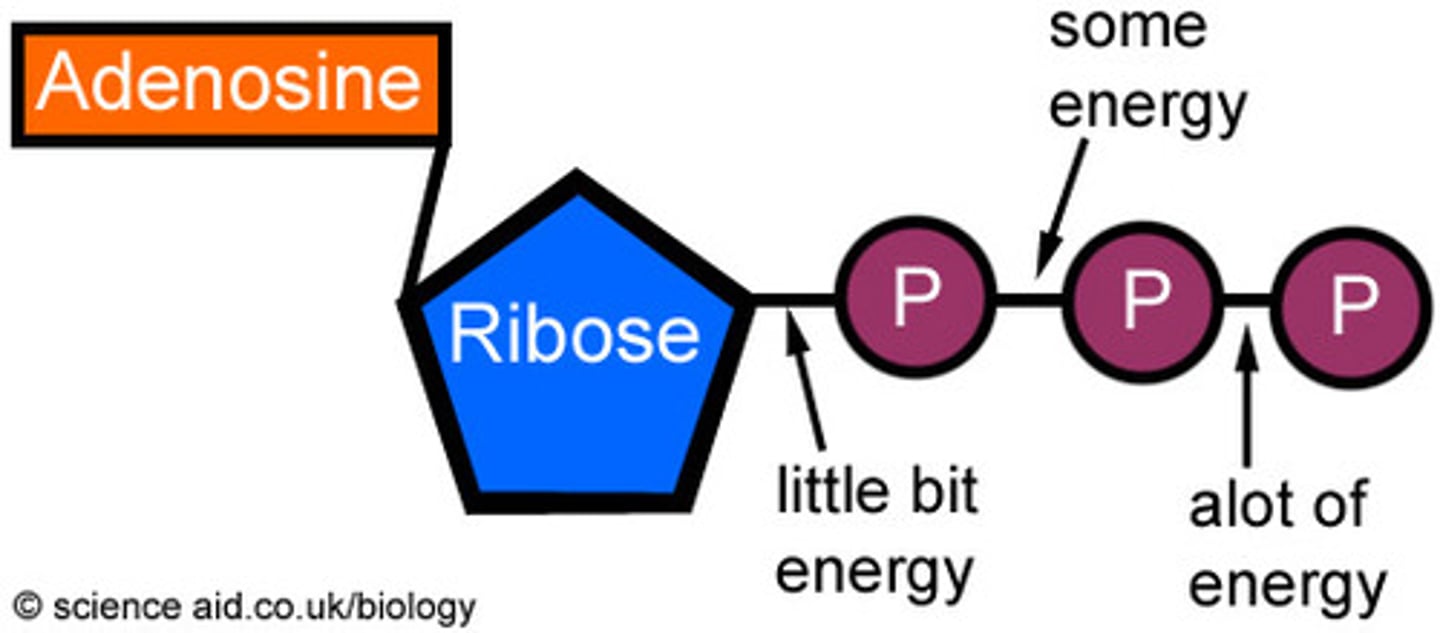
ATP
energy product(s) from ETC in cellular respiration
ATP and NADPH
product(s) from ETC in photosynthesis, which are required for the Calvin cycle