3.4 MT - HAEMOGLOBIN
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
WHAT DOES BLOOD PLASMA TRANSPORT?
CO2: organs —> lungs.
Soluble digestion products: small intestine —> other organs.
Urea: liver —> kidneys.
WHAT ARE PLATELETS?
Small fragments of cells.
No nucleus.
HOW LONG DO RBC LAST?
WHERE ARE THEY OFTEN DESTROYED?
120 Days.
Membranes become more and more fragile until destroyed.
In the spleen.
HOW IS THE STRUCTURE OF THE RBC UNUSUAL?
(HOW IS IT ADAPTED FOR OXYGEN TRANSPORT?
VERY SMALL:
Means that every haemoglobin molecule is near to the cell’s plasma membrane.
Short pathway for oxygen.
Large SA:V.
BICONCAVE DISC:
SA:V.
Dent also provides short path,
NO ORGANELLES:
No nucleus, mitochondria, or ER.
(:: No protein synthesis, cell division, or AT.)
PURPOSE OF TISSUE FLUID?
Bathes cells.
Site of the efficient exchange of metabolites.
Fresh TF has high [oxygen, glucose, and mineral ions] that cells need. They diffuse into cells.
Waste products diffuse out of cells into tissue fluid and then into capillaries along with water at the venule end.
HOW IS TISSUE FORMED AND RETUNED TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM?
Ventricular contraction creates the high pressure.

ROLE OF HEART IN FORMATION OF TISSUE FLUID?

HOW IS THE OXYGEN CARRYING CAPACITY OF THE BLOOD INCREASED?
WHY DOES IT NEED TO BE INCREASED?
Increased by blood pigments.
Solubility of oxygen in water is relatively low.
WHAT IS THE AMOUNT OF OXYGEN CARRIED BY HAEMOGLOBIN REFERRED TO AS?
WHAT RANGE OF VALUES CAN THIS TAKE?
WHAT IS PARTIAL PRESSURE?
Percentage maximum that can be carried - known as the percentage saturation.
Can be 0-99%.
Oxygen concentration.
WHY DOES THE OXYGEN DISSOCIATION CURVE HAVE A SIGMOIDAL SHAPE?
Co-operative binding.
The binding of the first haem group changes the 3* structure and shape, uncovering the second haem group ::: making it more accessible and increasing the affinity.
Carries on.
WHAT DOES THE SIGMOIDAL CURVE DISPLAY?
The percentage saturation of haemoglobin at varying partial pressures.
FACTORS AFFECTING THE DISSOCIATION CURVE?
Temperature.
pH —> will alter 3* structure of haemoglobin to have a lower affinity.
[CO2].
Higher metabolic rate can shift curve to the right.
EFFECT OF INCREASING [CO2] ON THE DISSASOCIATION OF OXYHAEMOGLOBIN?
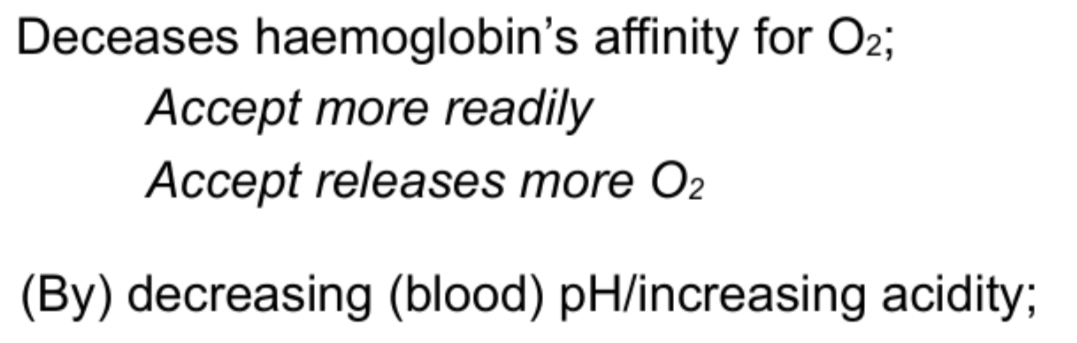
WHAT IS THE BOHR EFFECT?
WHICH FACTORS CAN BRING IT ABOUT?
WHAT IS THE SIGNIFICANCE?
Shift to the right, high pCO2.
Lower saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen at any given partial pressure.
ADVANTAGE OF BOHR EFFECT?
Increased disassociation.
More respiration at cells.
FIND REAL ANSWER PPQ
WHAT CAN CAUSE AN ORGANISM TO HAVE A DIFFERENT FORM OF HAEMOGLOBIN?
ENVIRONMENT: Where they live, e.g. altitude, temperature, oxygen levels.
STAGE OF LIFE: Enable these developmental stages to maximise their oxygen uptake.
DESCRIBE THE ROLE OF HAEMOGLIBIN IN THE LOADING, TRANSPORT, AND UNLOADING OF OXYGEN.
