SKELETAL SYSTEM
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Skeletal System
The skeletal system is the body system made up of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints.
An adult human has 206 bones.
This system provides structure, protection, movement, and performs important metabolic functions.
Support
The skeleton forms the structural framework of the body. It supports body weight and maintains posture, allowing the body to stand upright.
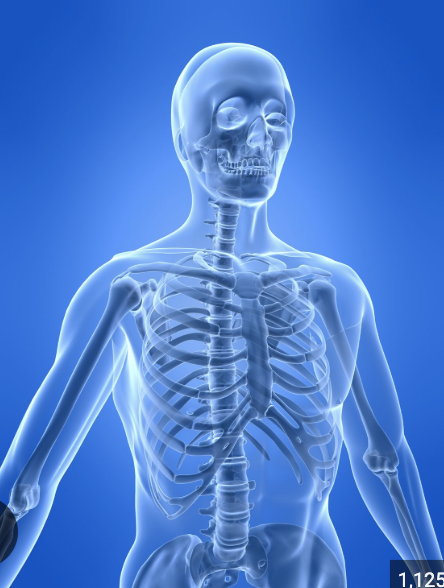
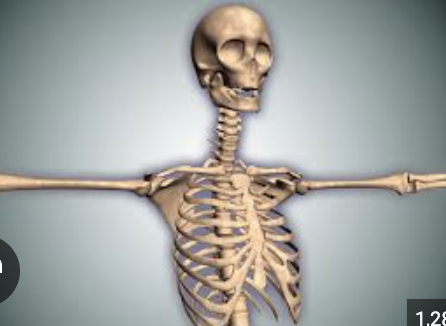
Protection
Bones protect vital organs:
The skull protects the brain
The vertebral column protects the spinal cord
The rib cage protects the heart and lungs
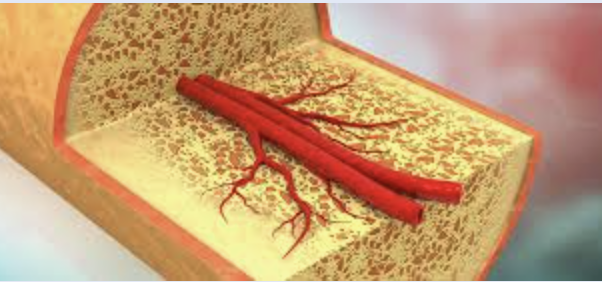
Mineral Storage
Bones store minerals, mainly calcium and phosphorus.
These minerals can be released into the bloodstream when needed to maintain normal body functions.
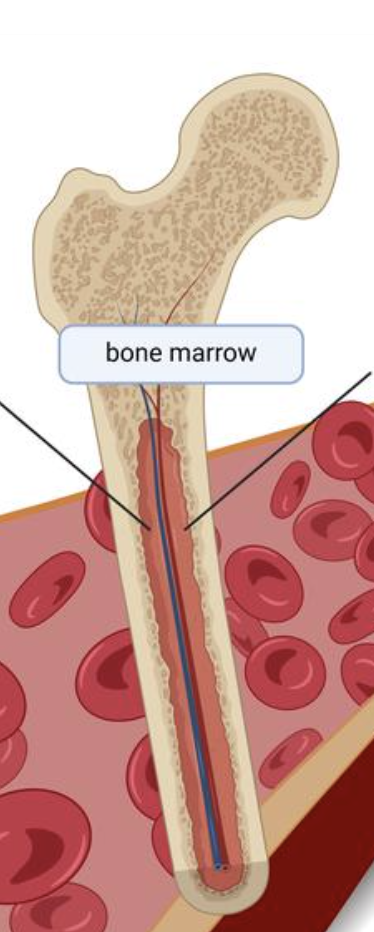
Blood Cell Production (Hematopoiesis)
Blood cells are produced in red bone marrow. This includes:
Red blood cells
White blood cells
Platelets
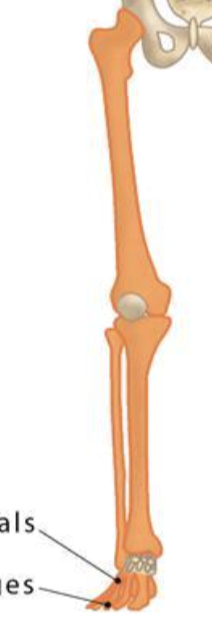
LONG BONES
Longer than they are wide; involved in movement
Examples: femur, humerus
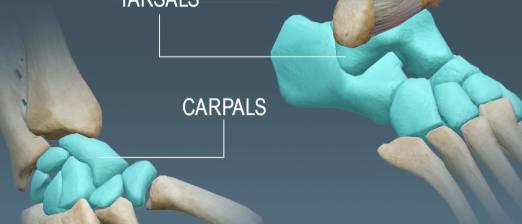
SHORT BONES
cube-shaped; provide stability
Examples: carpals (wrist), tarsals (ankle)
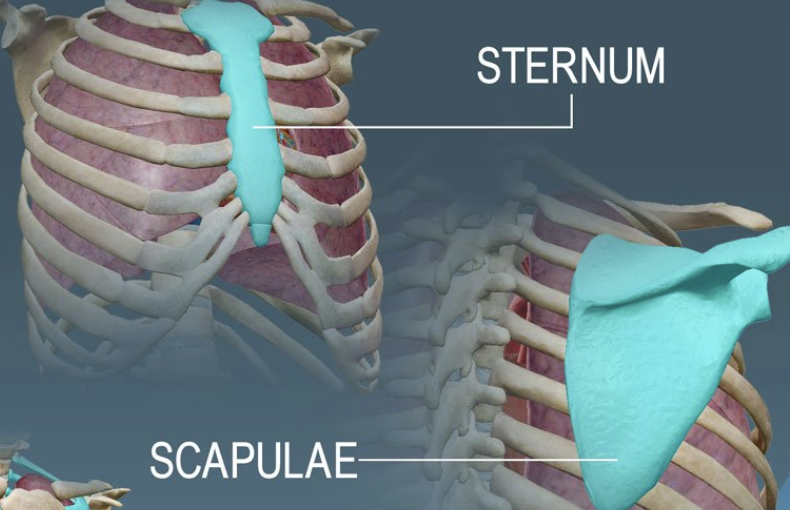
FLAT BONES
thin and flat; protect organs
Examples: skull, ribs, sternum
IRREGULAR BONES
complex shapes
Examples: vertebrae, facial bones
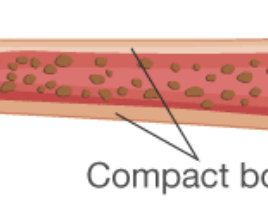
COMPACT BONE
Dense, hard outer layer that provides strength and protection.
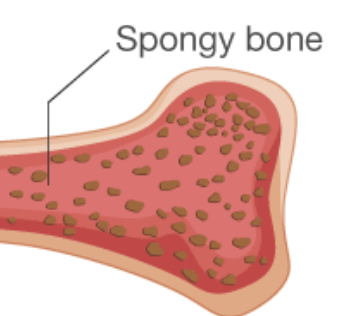
SPONGY BONE
Porous inner layer found mainly at the ends of long bones; contains red bone marrow.
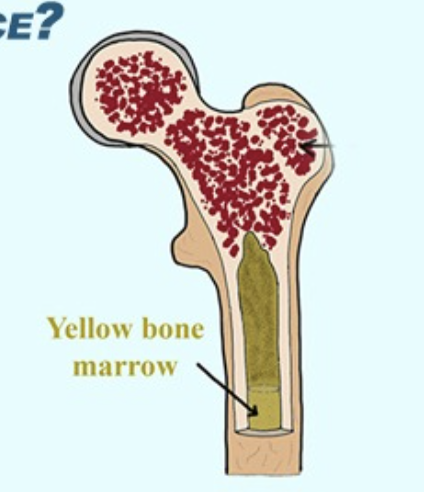
RED BONE MARROW
produces blood cells
YELLOW BONE MARROW
stores fat and can convert to red marrow if needed
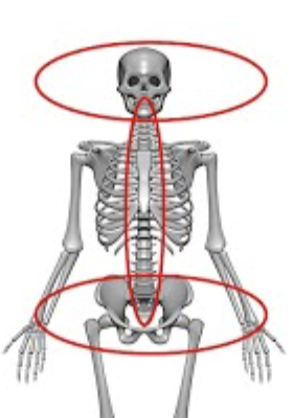
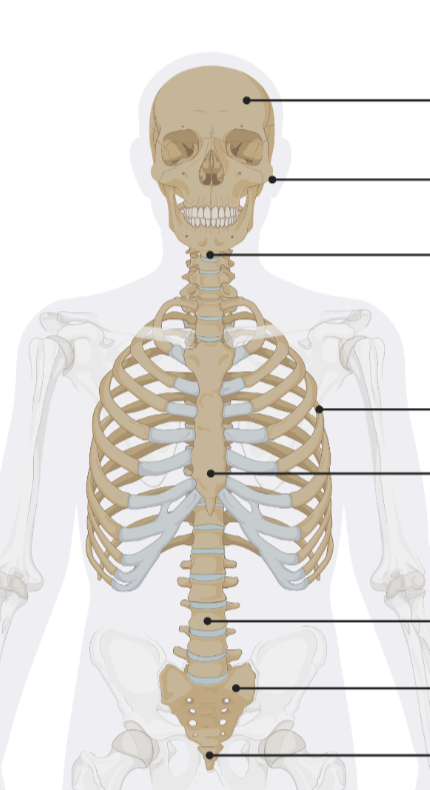
AXIAL SKELETON
Forms the central axis of the body and includes:
Skull
Vertebral column
Rib cage
Primary function: support and protection
APPENDICULAR SKELETON
Includes:
Upper limbs
Lower limbs
Shoulder girdle
Pelvic girdle
Primary function: movement
JOINTS
A joint is the point where two bones meet.