Chemistry - Unit 11: Kinetics and Equilibrium
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
kinetics
study of how fast a chemical reaction is occurring and describes the rate of change in the concentrations of the reactants and products over time in chemical rxn
collision theory
reaction is most likely to occur if the reactant particles collide with sufficient energy and proper orientation
Factor that affect rate of reaction:
Temperature
temp increases, rate of chemical rxn increases
higher temps=particles collisions more frequently and with more energy
Factor that affect rate of reaction:
Surface Area
surface area increase=rate of rxn increase
Factor that affect rate of reaction:
Concentration
concentration increase= rate of rxn increase
Factor that affect rate of reaction:
Pressure (gas only)
pressure increase=rate of rxn increase and more effective collisions
Factor that affect rate of reaction:
Presence of a catalyst
catalyst presence=rate of rxn increase
gives an alternate reaction pathway which requires less energy than the normal
Factor that affect rate of reaction:
Nature of Reactants
Ions in water = fast
gases are FASTER than solids and liquids
ions FASTER than molecules
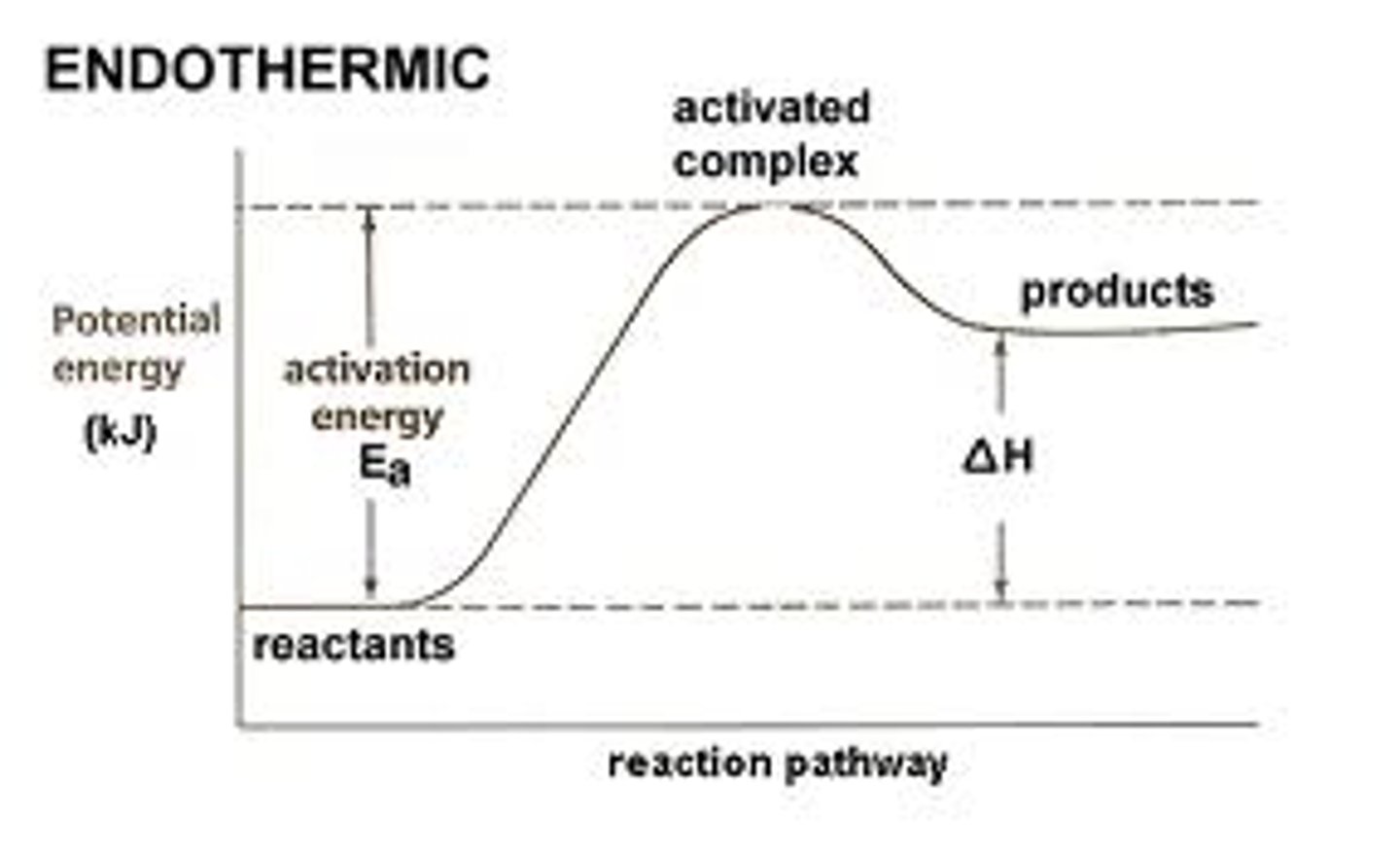
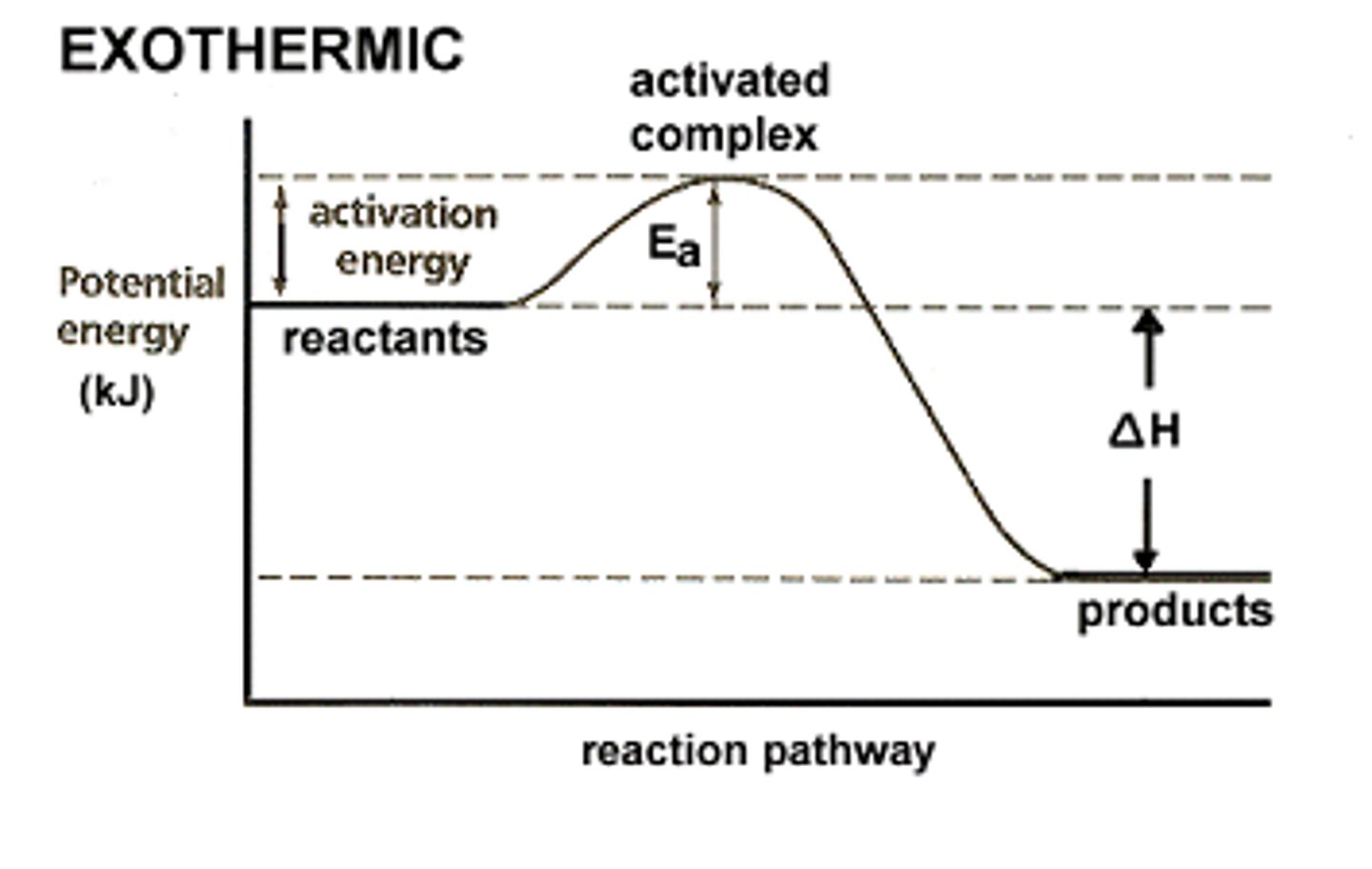
Catalyst & alternate reaction pathway
lower activation energy
endothermic chemical reaction
exothermic chemical reaction
Heat of Reaction
- change in enthalpy
△H = PE products - PE reactants
-△H=exothermic
+△H=endothermic
Reaction Mechanisms
series of rxn steps that have to occur for a rxn to go to completion that are determined by experimentation
intermediates
species produced in one step that become reactants in a subsequent step
Reaction Rate Laws
rate = k [A][B]
k (specific rate constant)
depends on the size, speed, and kind of molecule at a given temperature
rate law experssion
rate of chemical rxn is proportional to the product of the [ ] of reactants raised to the power of the coefficents
rate of multi-step rxns
product of the [ ] of the reactants in the slowest step
equilibrium
- rates of forward = rate of reverse
- concentrations of reactants and products stay CONSTANT
Solution Equilibrium
when a solution is saturated
Phase equilibrium
rate of condensation/melting = rate of evaporation/freezing
chemical equilibrium
concetration of reactants and products remain constant
rates of forward and reverse are equal
equilibrium expression
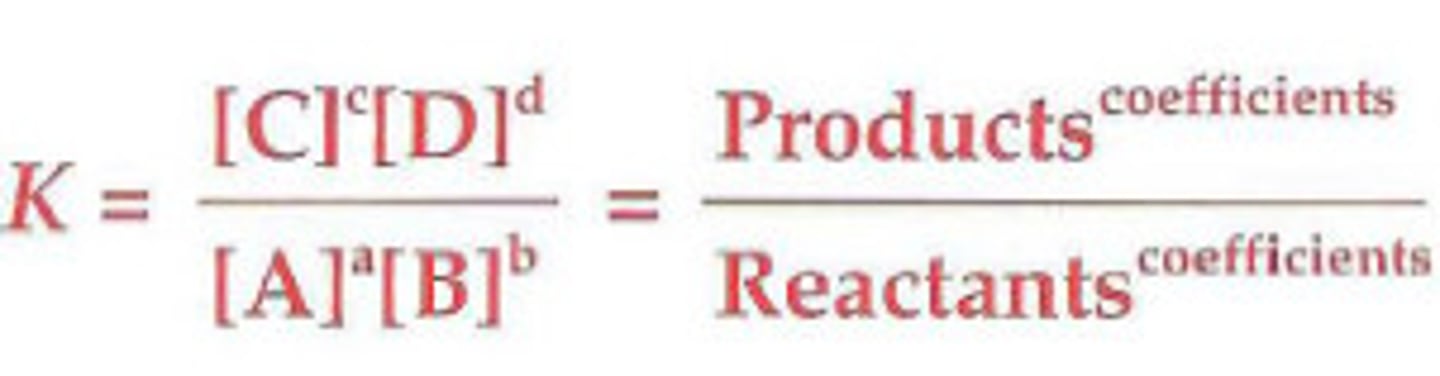
Keq
shows the extent to which the reactants are converted to products
AT EQUILIBRIUM
RATES of opposing rxns are EQUAL
solubility product constant
Ksp
values are always SMALL
Le Chatelier's Principle
if stress to a system at equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift to reduce of alleviate the stress
Stressors of system @ equilibrium
- concentration
- temperature
- pressure (only gases)
Describe the shift given that reactants are on the left and products are on the right:
add reactant
right
the other reactants DECREASE as products INCREASE
trying to balance the products by making more so shifts right
Describe the shift given that reactants are on the left and products are on the right:
add product
left
the other reactants INCREASE as products DECREASE
trying to balance the reactants side by making more so shifts left
Describe the shift given that reactants are on the left and products are on the right:
remove reactant
left
the product DECREASES as the reactants INCREASE
trying to balance the reactants side since there isnt enough reactant to make the product
Describe the shift given that reactants are on the left and products are on the right:
remove product
right
the product INCREASES as the reactants DECREASE
trying to balance products side to make more products
TRICK FOR LE CHATELIER with concentration stressors and temperature
DISCLAIMER: IF YOU DO NOT UNDERSTAND THIS RIGHT AWAY, PLEASE SKIP. I DON'T WANT TO CONFUSE ANYONE AND THEN GET BLAMED FOR IT lol
Whichever side has less stuff, that the side the equilibrium will shift.
for example,
N2 + 3H2 <-> 2NH3 + 22.0 kcal
if H2 is removed, theres less "stuff" on the reactant side so the shift would be left
if N2 is added, there is less "stuff" on the product side, so the shift is right
if temp increases, theres less stuff on the reactants side, so the shift would be left
Describe the shift given that reactants are on the left and products & temperature are on the right:
increase temperature
left
the reactants INCREASE and the products DECREASE
the endothermic process is favored
the more energy/temp there is, the more of the reactants side can be made
Describe the shift given that reactants are on the left and products & temperature are on the right:
decrease temperature
right
the reactants DECREASE and the products INCREASE
the exothermic process is favored
the less energy/temp there is, the less of the reactants side can be made so it tilts towards the products side
Describe the shift given that reactants are on the left and products & temperature are on the right:
increase pressure
right
only works for gases and favors LESS mols of gas
the reactants DECREASE and the products INCREASE
Describe the shift given that reactants are on the left and products & temperature are on the right:
decrease pressure
left
the reactants INCREASE and the products DECREASE
only works for gases and favors MORE moles of gas
entropy
measure of randomness represented by +/-△S
entropy increases or decreases:
solid -> liquid -> gas
increase
affect of synthesis
decrease in entropy
affect of decomposition
increase in entropy
affect of gas
the more moles of gas, the greater the entropy
Gibb's Free Energy

spontaneous reactions
HIGH entropy & LOW energy & exothermic
-△G = -△H - T * +△S
non-spontaneous reactions
+△G = +△H - T* -△S
spontaneous under low temp
-△G = -△H - T * -△S
spontaneous under high temp
-△G = +△H - T * +△S
to be spontaneous, the △G must be ...
negative