Abdominal Anatomy
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Rectus abdominis muscle
1

Inguinal Ligament
2
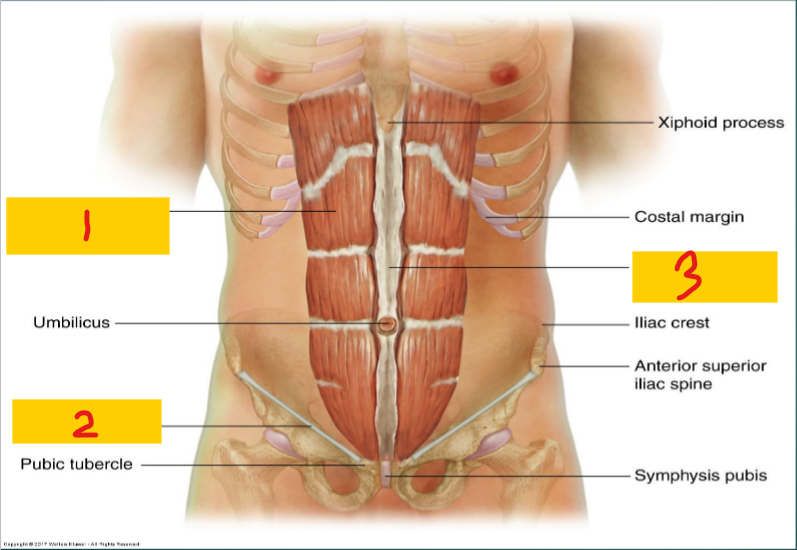
Linea alba
3
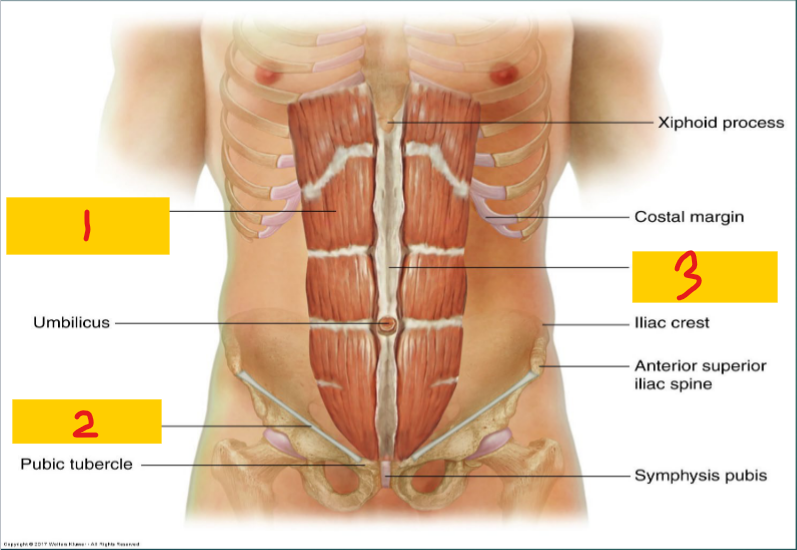
Diaphragm
Superior Boundary of the abdomen
Pelvic inlet
Deep inferior boundary of the abdomen
Superficial Inferior Boundary
Superior margin of lower limbs/inguinal ligament make up this boundary of the abdomen
5 lumbar vertebrae and pelvis
What makes up the posterior boundary of the abdomen
Abdominal muscles
What makes up the anterior boundary of the abdomen
abdominal cavity
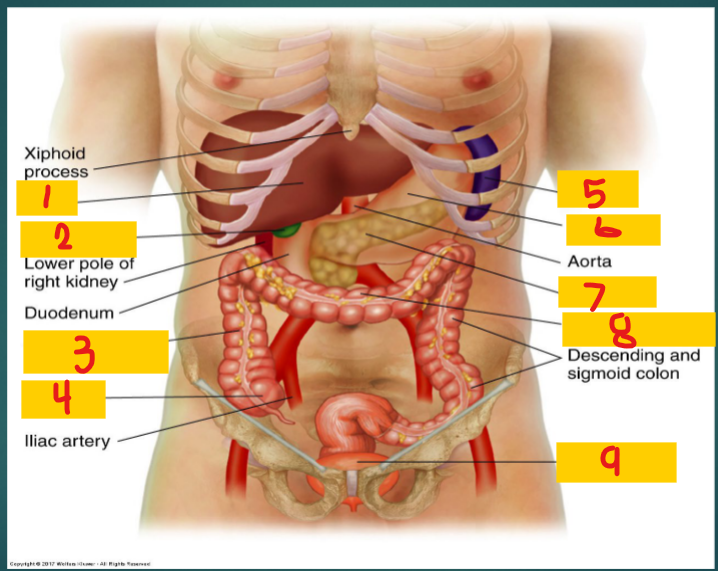
1

Costovertebral Angle (CVA)
Formed by the lower border of the 12th rib and transverse processes of the upper lumbar vertebrae
Liver
1

Gallbladder
2
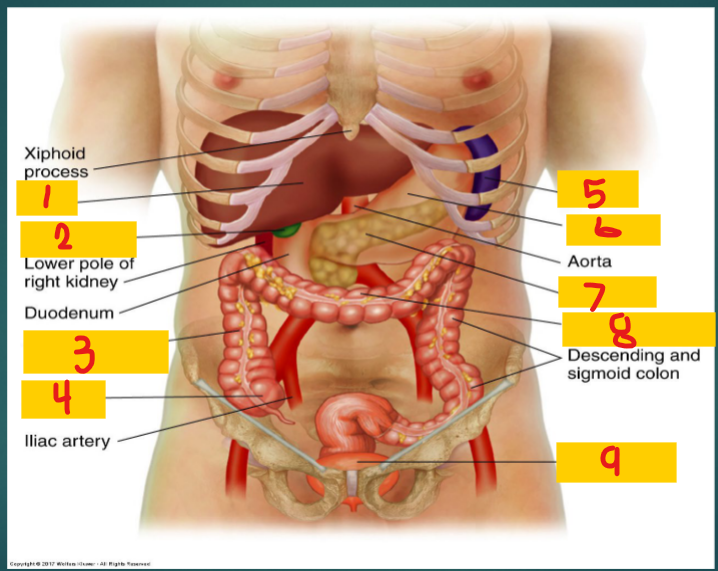
Ascending Colon
3

Cecum
4
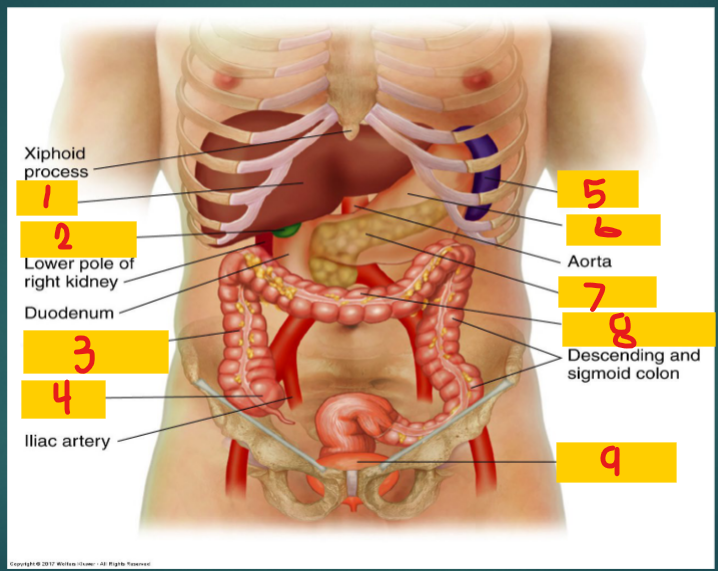
spleen
5
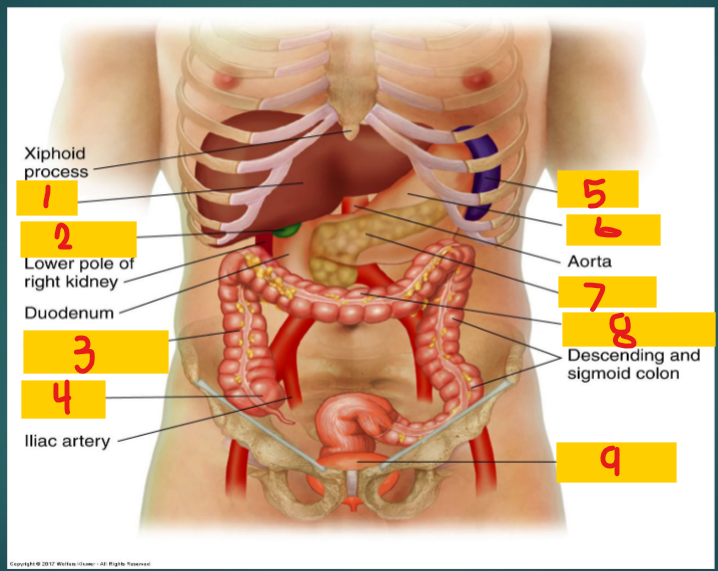
stomach
6

Pancreas
7

Transverse Colon
8
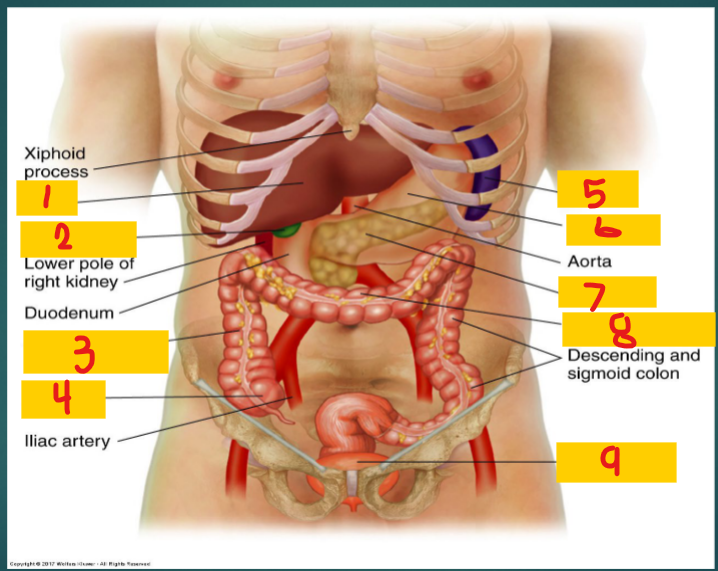
Full bladder
9
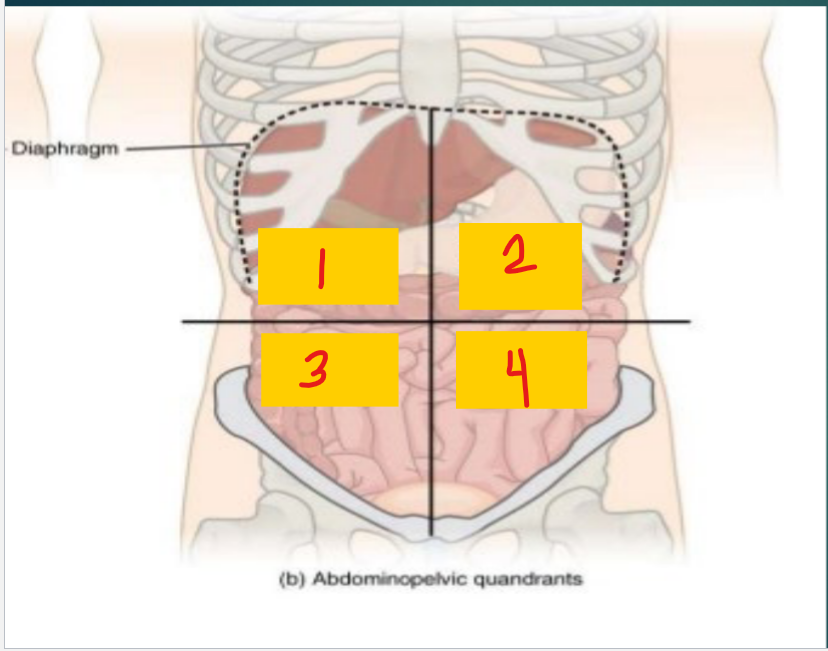
Right upper quadrant (RUQ)
1
Liver
Gallbladder
Pylorus (stomach)
Duodenum
Hepatic flexure (colon)
Head of pancreas
Part of transverse colon

Left upper quadrant (LUQ)
2
Spleen
Splenic flexure (colon)
Stomach
body/tail of pancreas
Part of transverse colon

right lower quadrant (RLQ)
3
Small intestine
cecum
appendix
ascending colon
right ovary
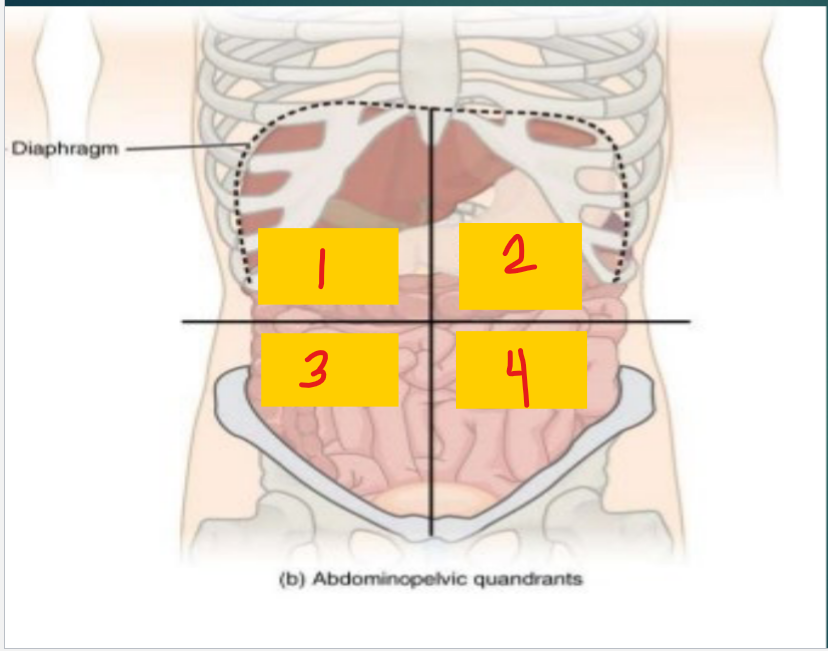
Left lower quadrant (LLQ)
4
Descending colon
Sigmoid colon
left ovary
Small intestine
Right hypochondriac region
1
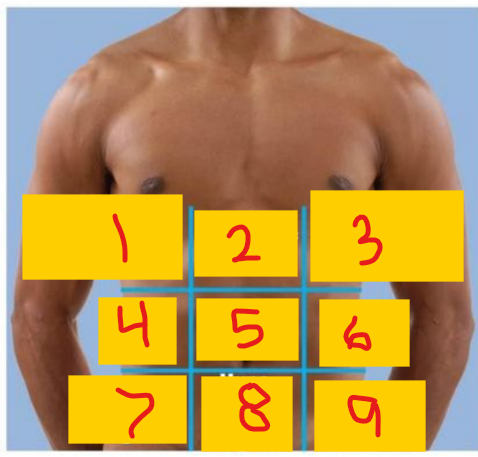
Epigastric region
2

Left hypochondriac region
3
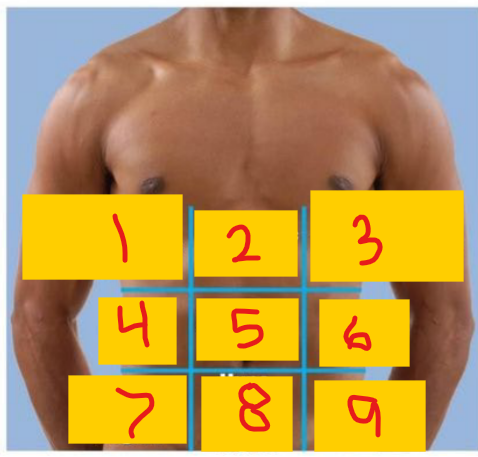
Right lumbar region
4
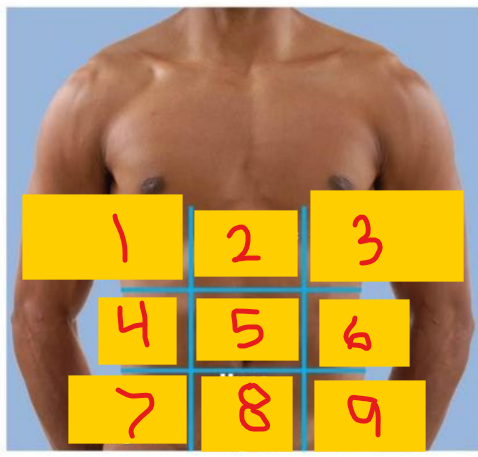
umbilical region
5
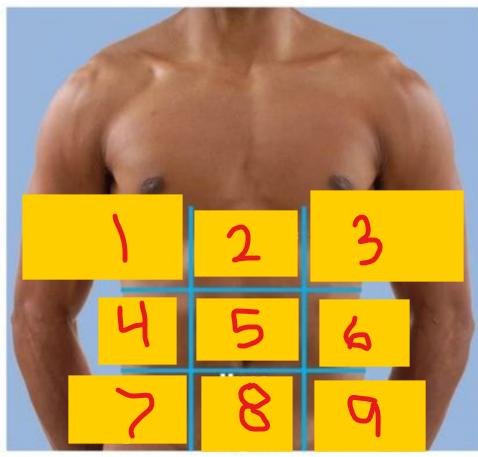
Left lumbar region
6
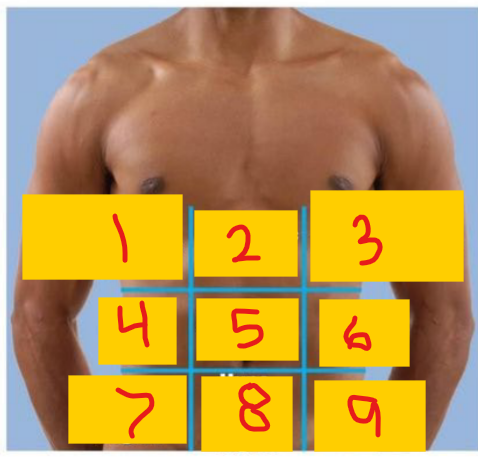
Right iliac (inguinal) region
7
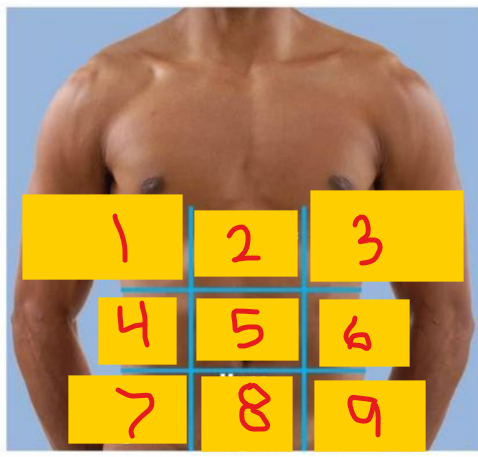
Hypogastric (pubic/suprapubic) region
8

Left iliac (inguinal) region
9

Transversus abdominis
1 - one of the flat muscles of the abdomen

Internal oblique
2 - one of the flat muscles of the abdomen
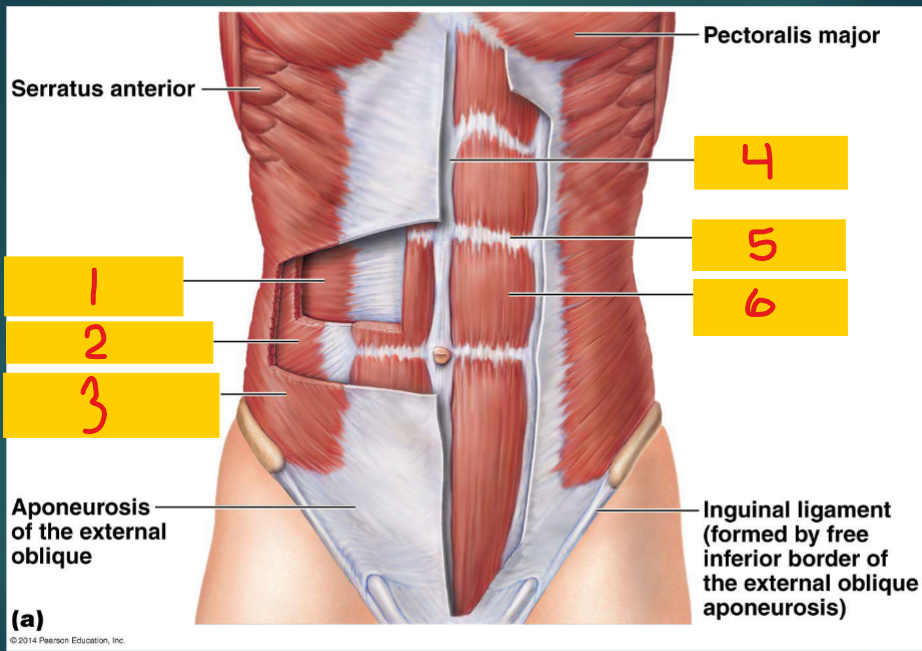
external oblique
3 - one of the flat muscles of the abdomen

Linea alba
4
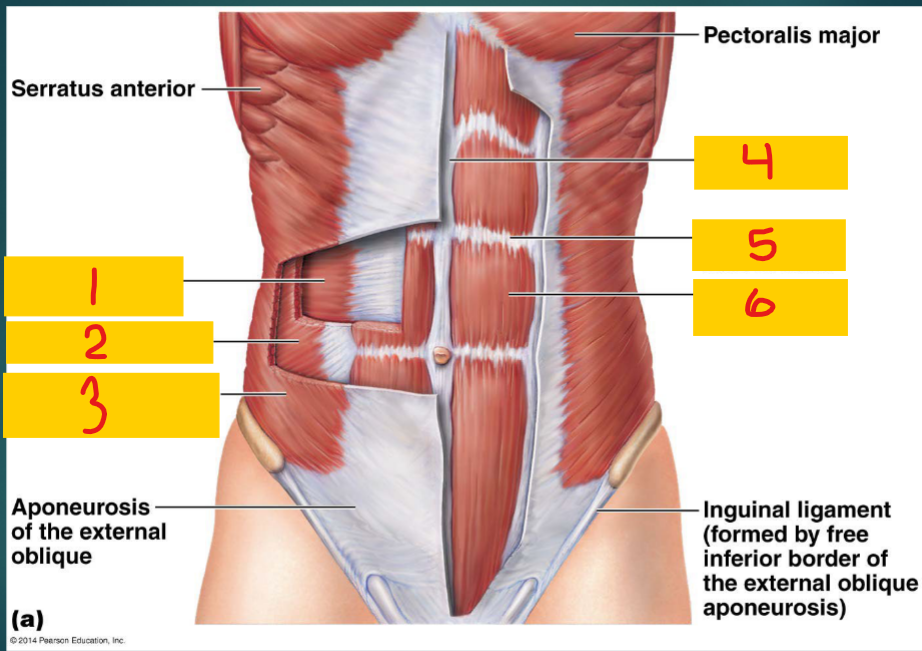
Tendinous intersection
5
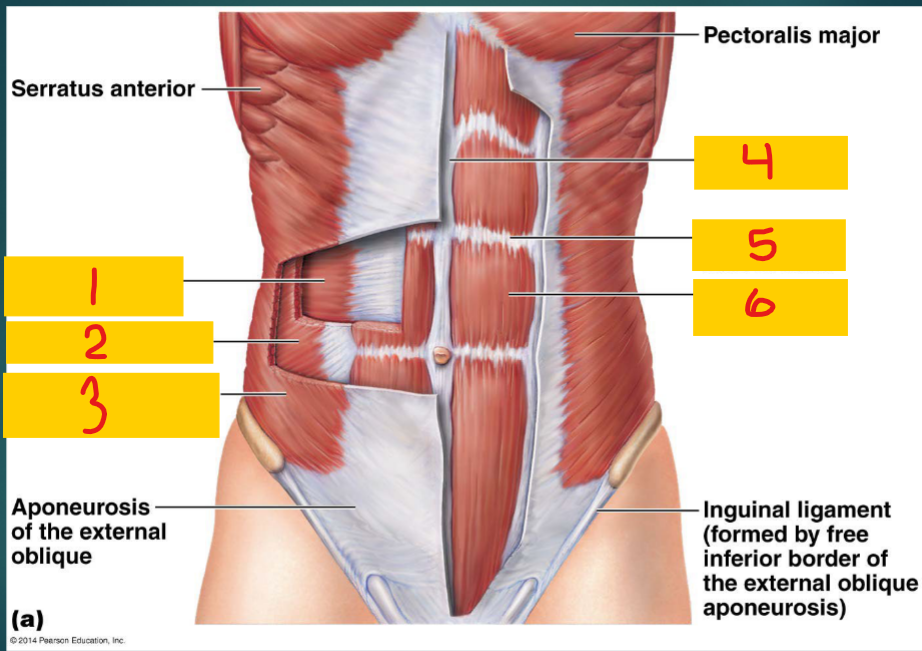
Rectus abdominis
6 - one of the vertical muscles of the abdomen

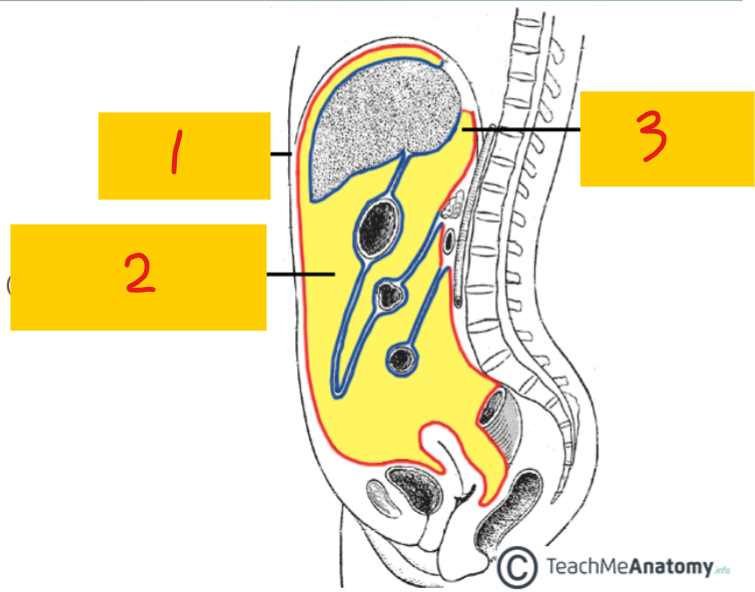
Visceral peritoneum
3 - lines the organs (blue); poorly localized pain (referred pain)
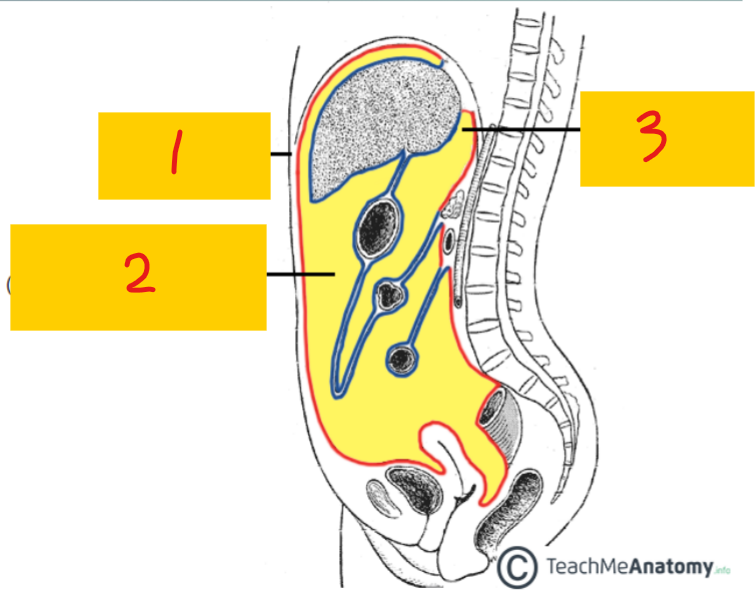
parietal peritoneum
1 - lines inner abdominal wall (red); localized pain

peritoneal cavity
2
intraperitoneal
suspended in the peritoneal cavity; completely covered by peritoneum
retroperitoneal
not suspended in the cavity; only partially covered by peritoneum
stomach, small intestine (jejunum, ileum, some of the superior part of the duodenum), spleen, liver, gallbladder, cecum, appendix, transverse colon, sigmoid colon
Examples of intraperitoneal organs
kidneys, ureters, suprarenal glands, uterine cervix, duodenum (descending, horizontal, and ascending), pancreas, ascending and descending colon, cecum, rectum (upper 2/3)
Examples of retroperitoneal organs
Pylorus
1

Cardia
2
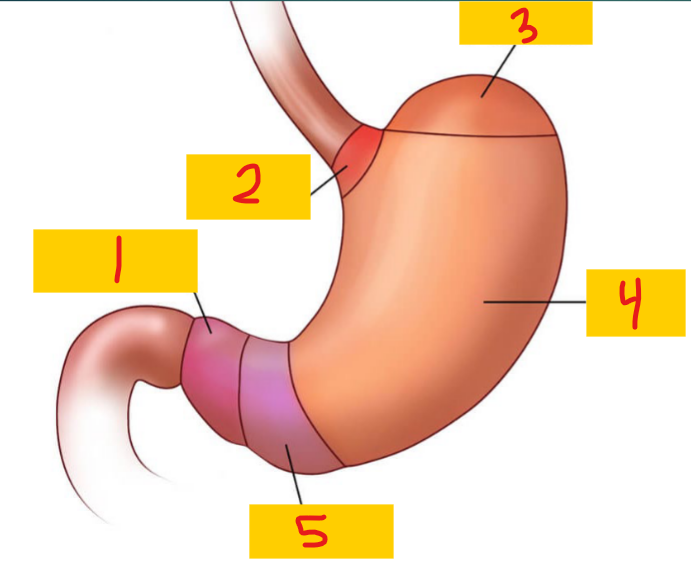
Fundus
3

Body
4

Antrum
5
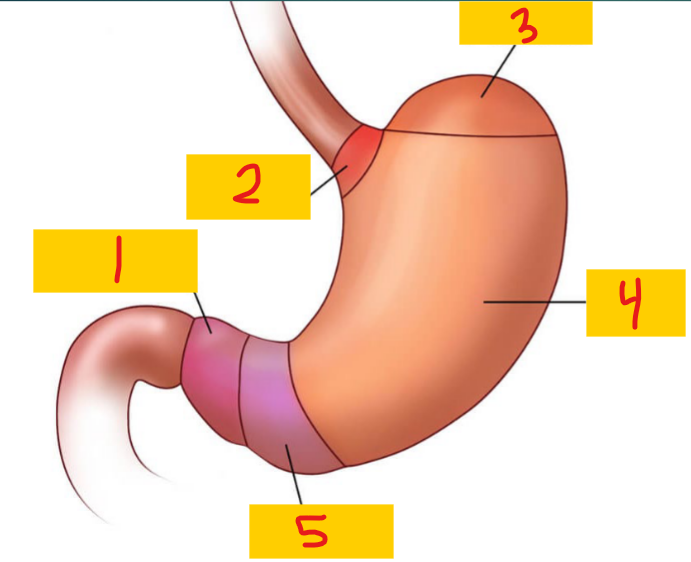
Stomach
Secretes acid and enzymes to help digest food
small intestine
does most of the digestion and absorption of food/nutrients
Small intestine
1, 2, 3

Duodenum
1
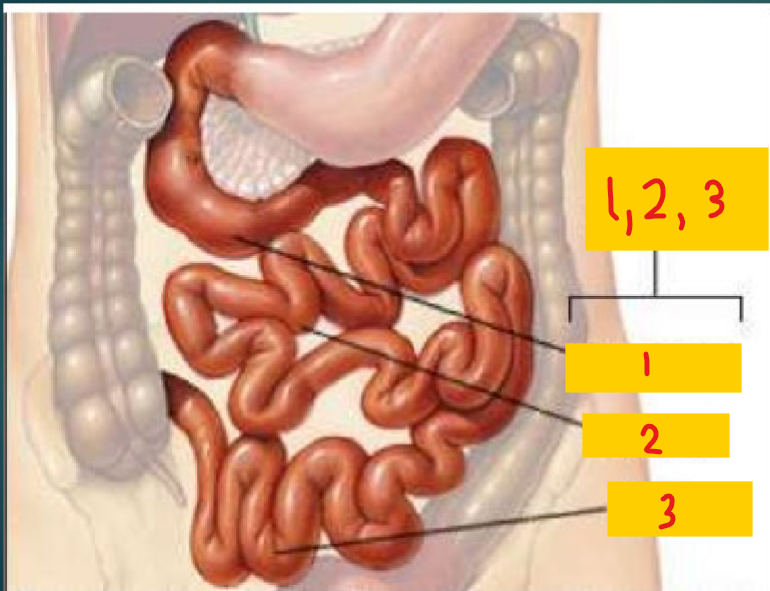
Jejunum
2
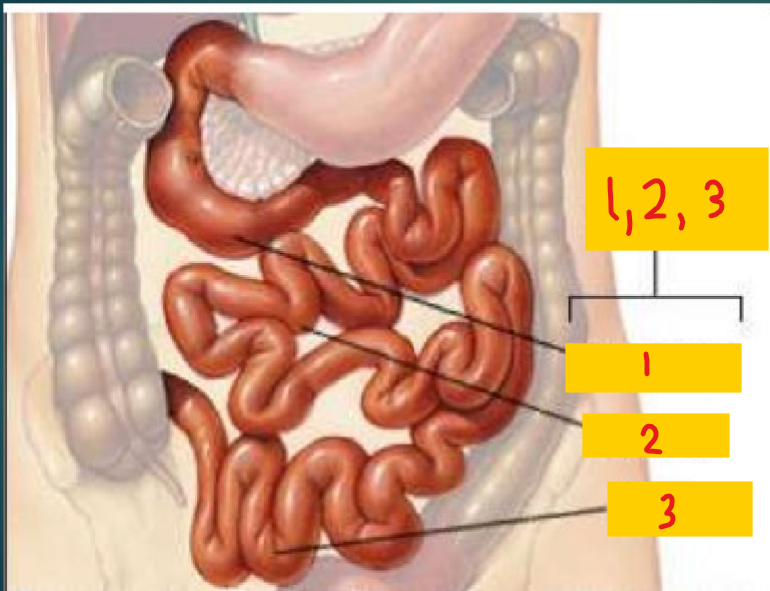
Illeum
3

Large intestine
Absorbs fluid and minerals from undigested food matter; forms feces
Transverse colon
1
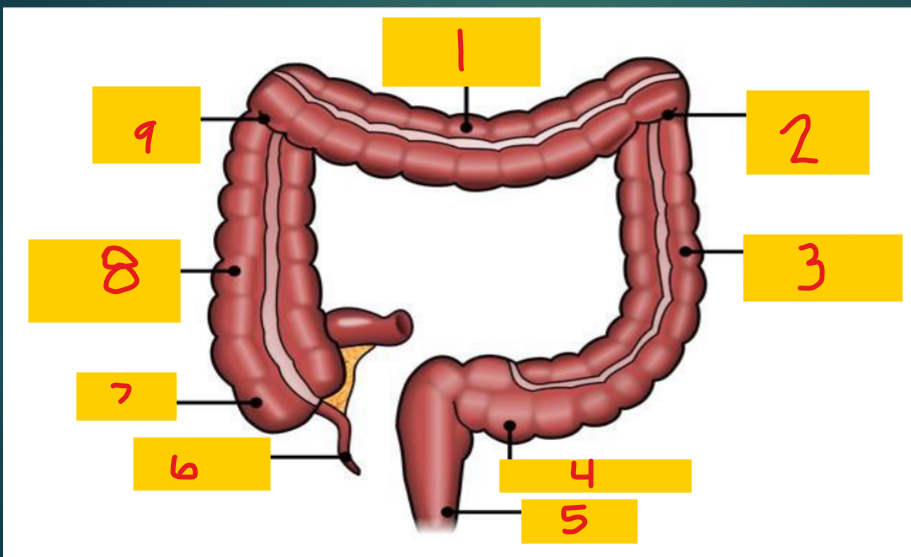
Splenic flexure
2
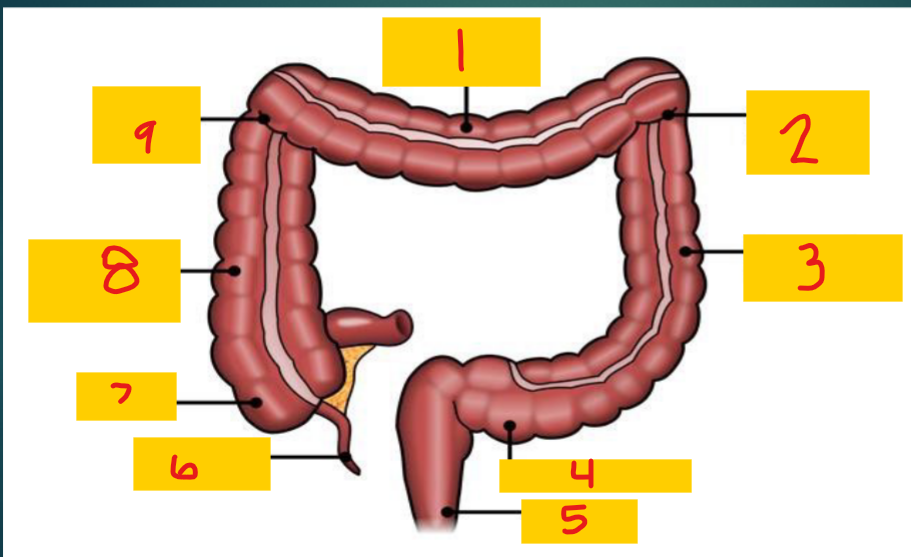
Descending colon
3
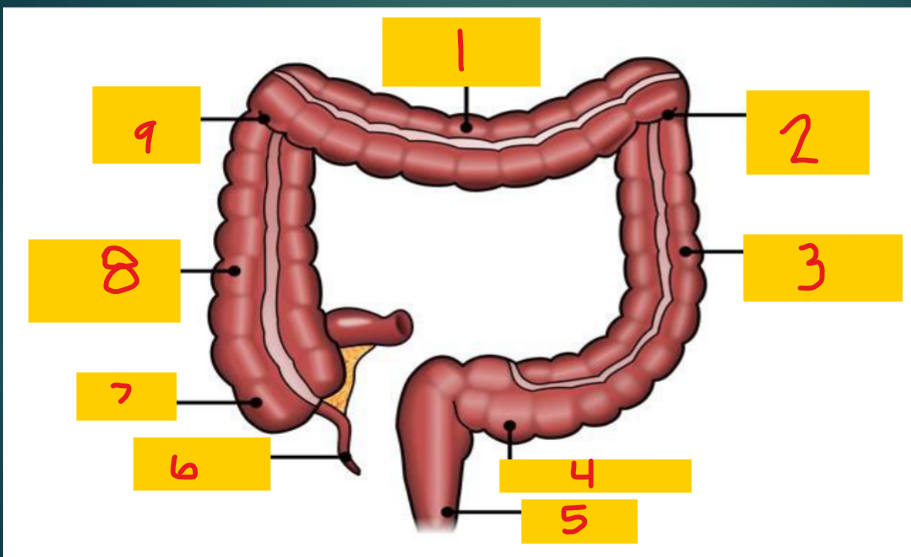
Sigmoid colon
4

Rectum
5
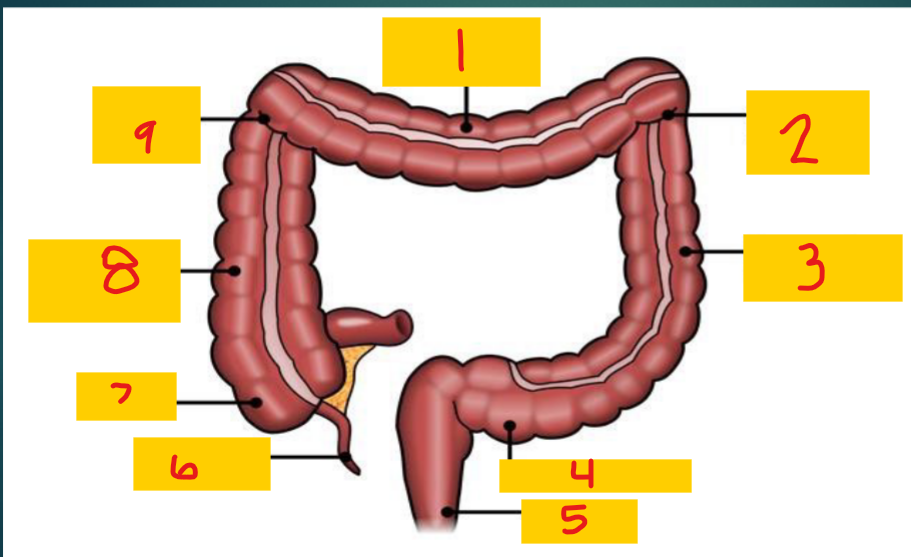
appendix
6

Cecum
7

Ascending colon
8
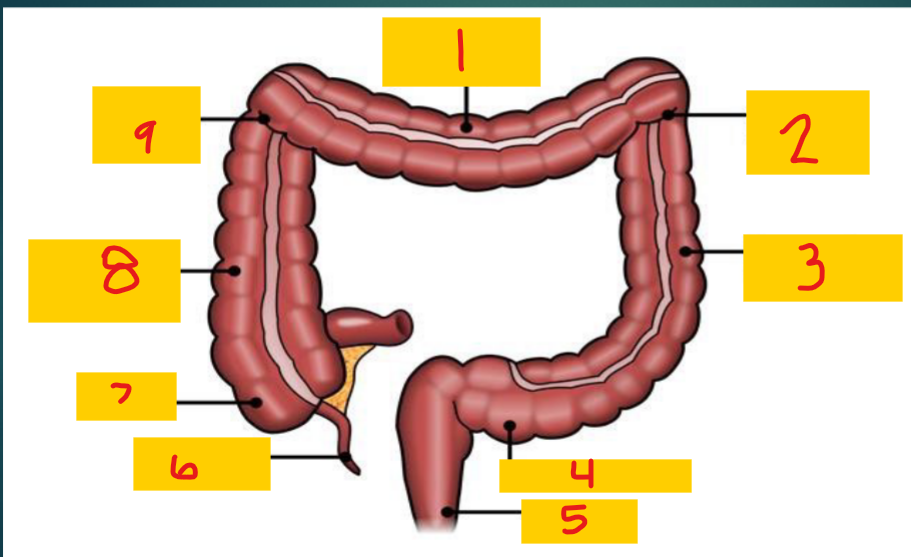
Hepatic flexure
9
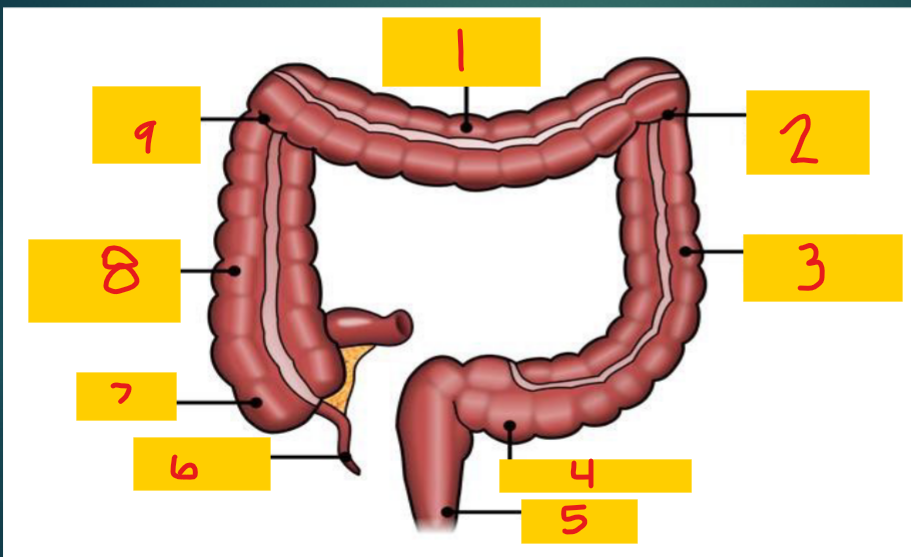
Liver
2 lobes; Filters blood coming from GI tract; detoxifies chemicals and metabolizes drugs; produces bile
Gallbladder
Lies under right lobe of liver; stores and concentrates bile
Liver
1

Spleen
2

pancreas
3

Gallbladder
4
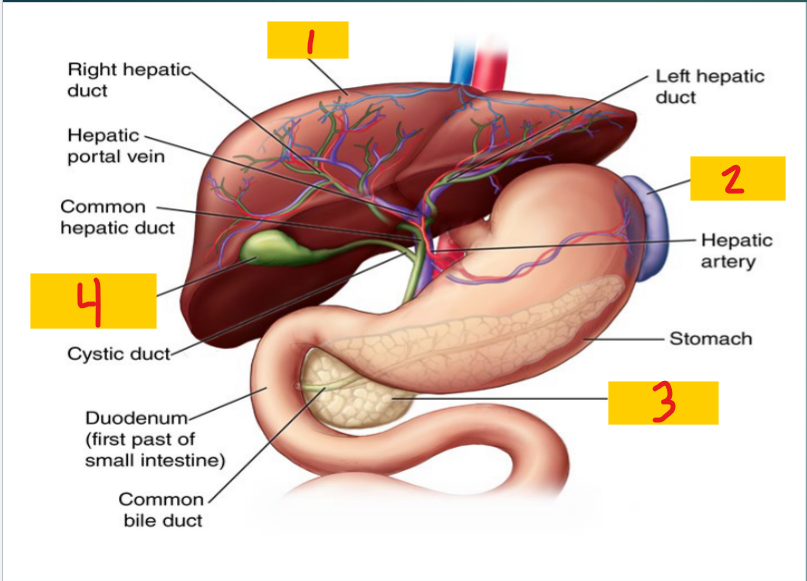
Pancreas
secretes enzymes to help digest food; helps regulate blood sugar
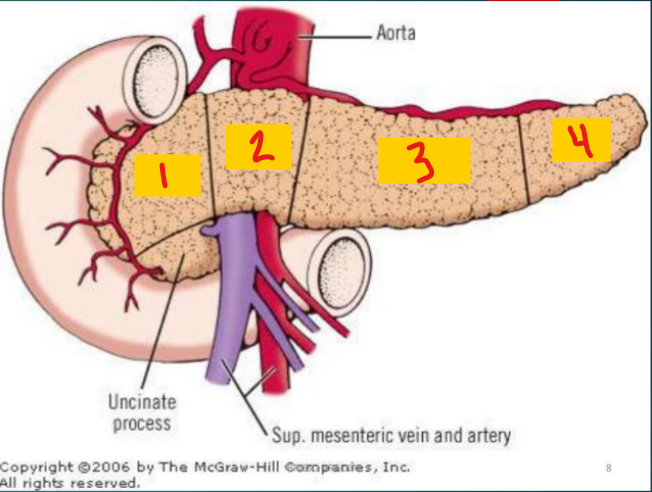
head of pancreas
1
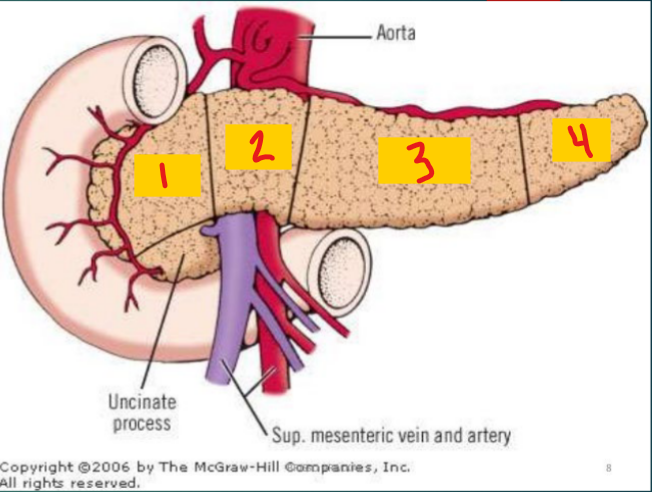
neck of pancreas
2

Body of pancreas
3

Tail of pancreas
4
Spleen
LUQ/left hypochondrium in the area of the 9th and 10th ribs; filters blood as part of the immune system; recycles RBCs; stores WBCs and platelets
Kidney
extracts waste from blood, balances body fluids, forms urine
right organ is lower than left
left organ is longer, slender, and closer to midline than right
extend from T12 to L3
Adrenal glands
located on top of kidneys
Produce hormones that help control blood sugar, burn protein and fat, react to stressors, and regulate BP
Adrenal gland
1

kidney
2
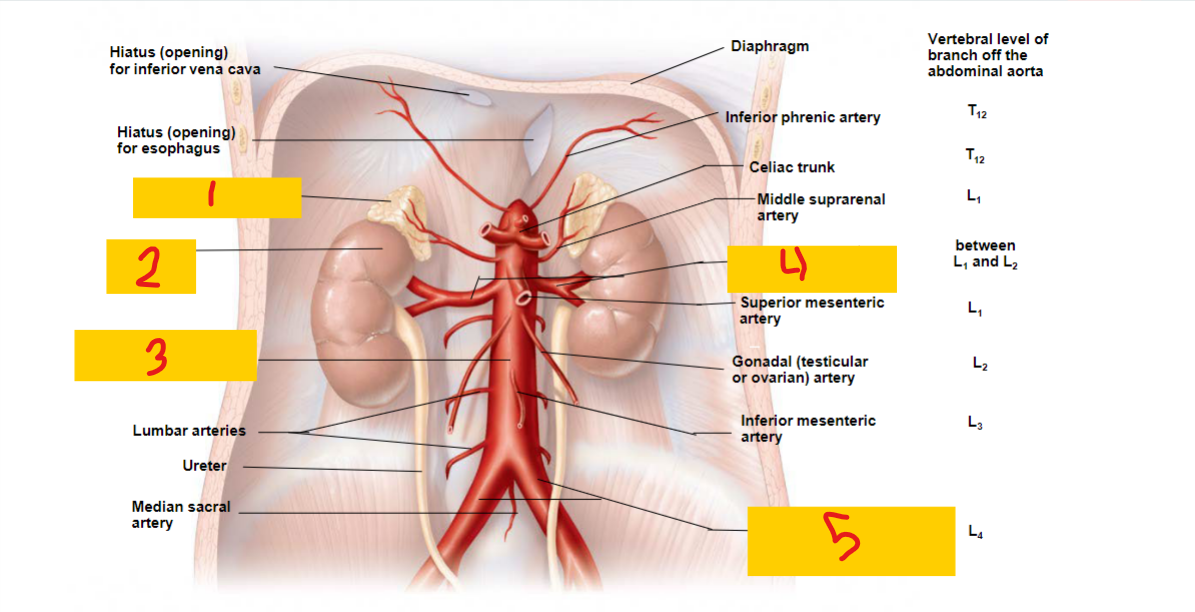
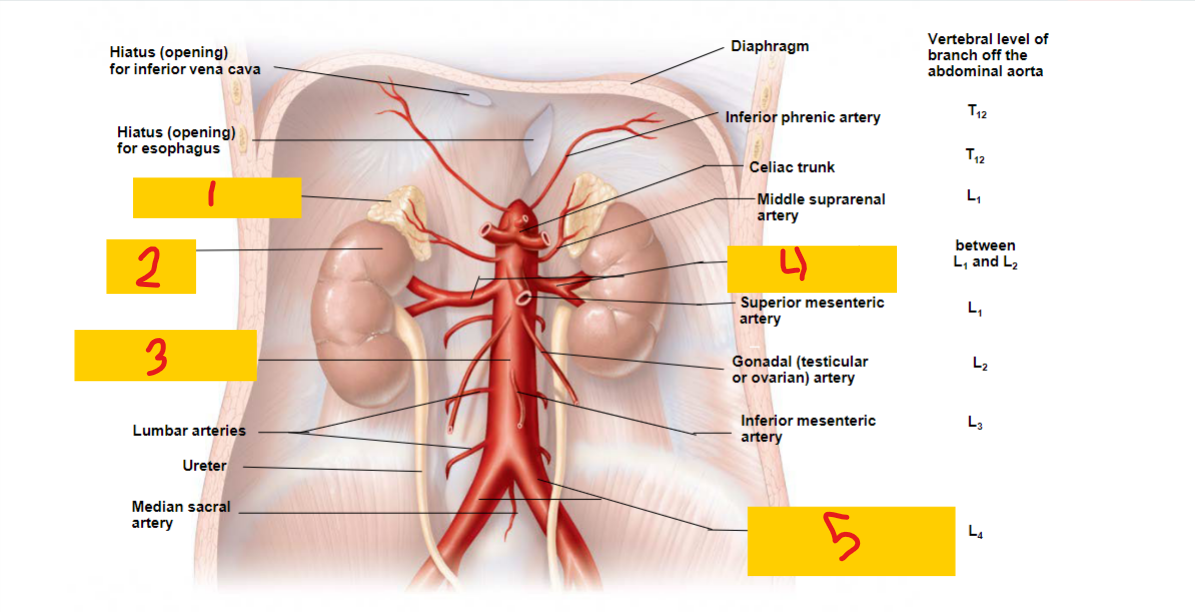
abdominal aorta
3
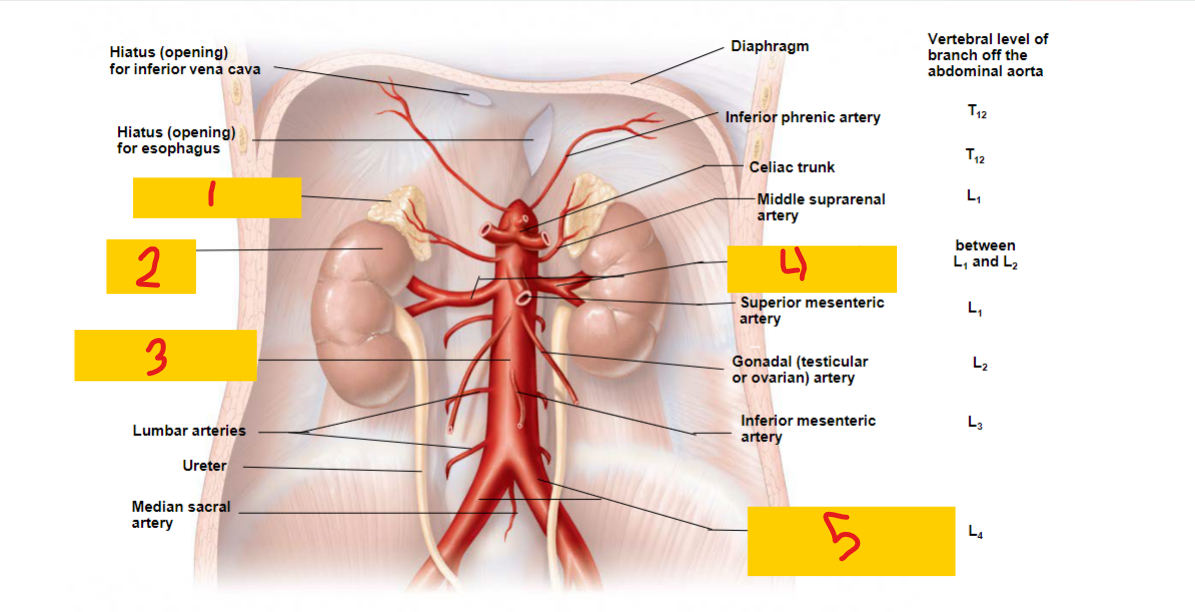
renal artery
4
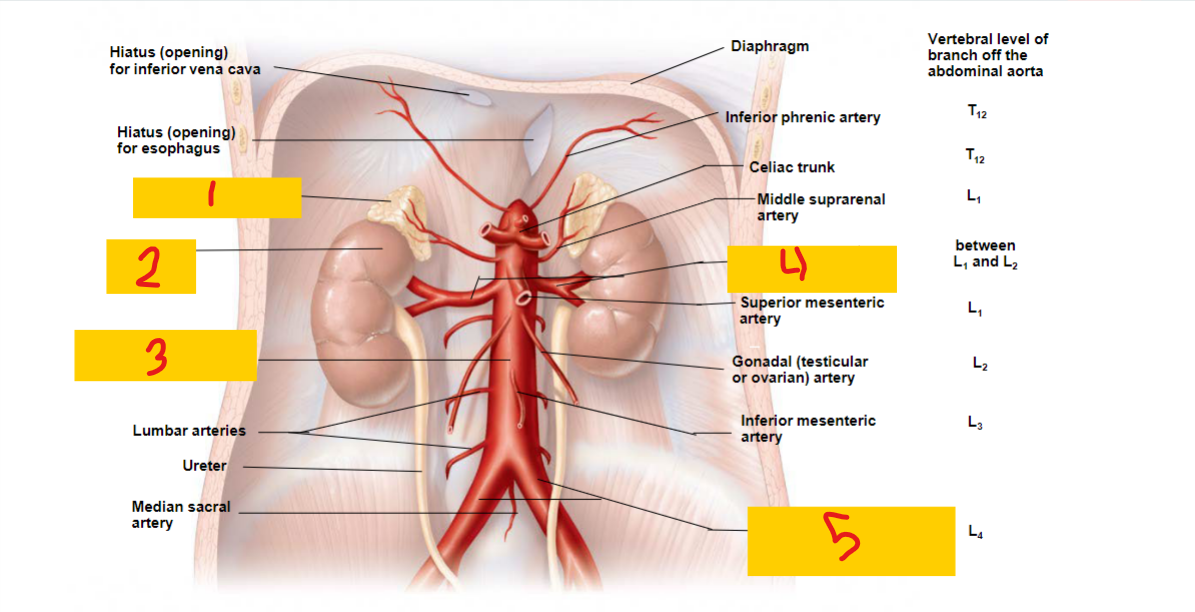
common iliac artery
5
Transversalis fascia
1

Deep inguinal ring
2
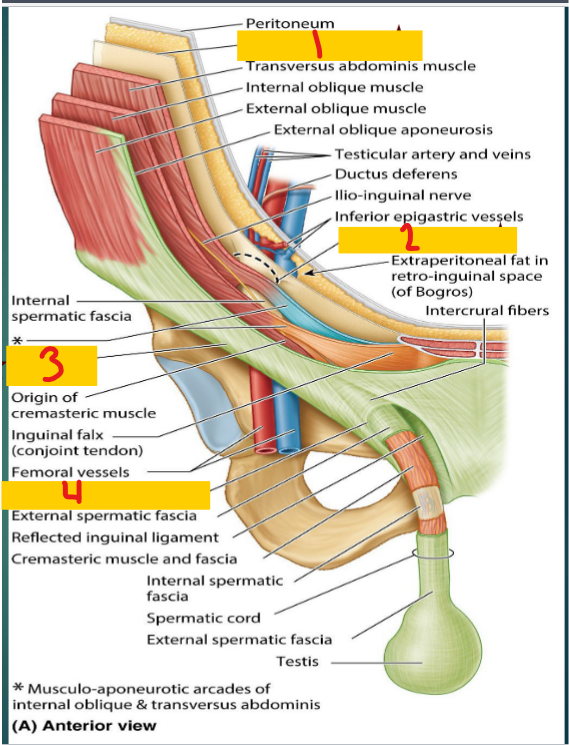
inguinal ligament
3
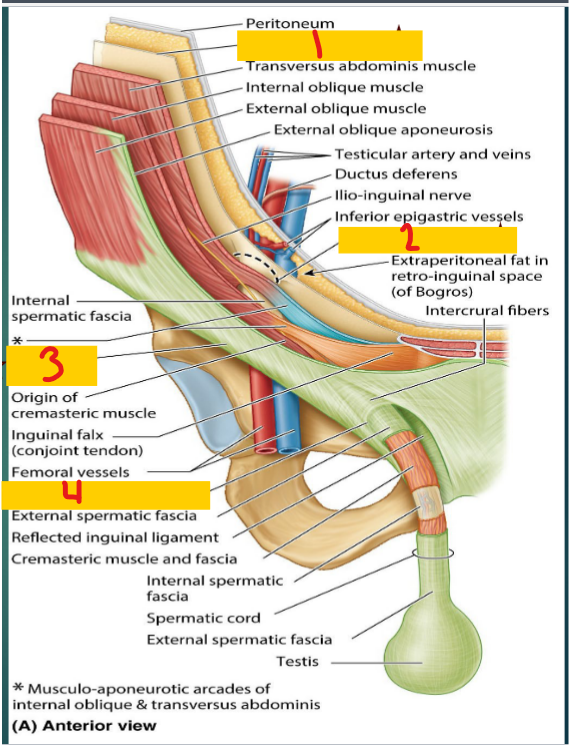
Superficial inguinal ring
4
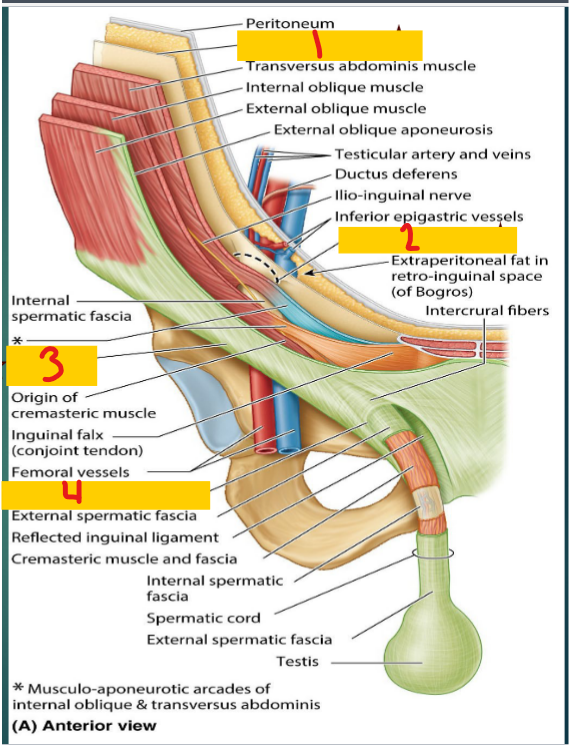
Anterior
The ______ wall of the inguinal canal
aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle
posterior
the ____ wall of the inguinal canal
transversalis fascia
Floor
the _____ of the inguinal canal
inguinal ligament
Roof
The ____ of the inguinal canal
Fibers of the transversus abdominis and internal oblique muscles