neurobiology of hearing
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
peripheral auditory system
outer ear, middle ear, inner ear, cranial nerve viii
central auditory system
brainstem, brain
The outer ear
pinna > external auditory meatus (CANAL) > tympanic membrane (eardrum)
middle ear
tympanic membrane turns the acoustic energy into mechanical energy > ossicles > stapes (rocks in/out of oval window)
inner ear
mechanical energy changes to hydraulic energy > the waves disrupt the hair cells in the organ of corti > hydraulic energy changes to electrochemical energy.
three fluid filled areas?
scala vestibuli, scala media, scala tympani
scala vestibuli
where the hydraulic motion of the fluid starts. when it hits the round window at the end it displaces the reissner membrane
reissner membrane
inferior membrane that separates the scala vestibuli from the scala media; it can push down on the tectorial membrane (located in scala media)
basilar membrane
superior membrane that separates the scala tympani from the scala media.
where does the organ of corti sit?
on top of the basilar membrane
Inner hair cells are
bipolar
1 multiple choice option
outer hair cells are
unipolar
1 multiple choice option
perilymph fluid
high concentration of sodium, low concentration of potassium
(low mV)
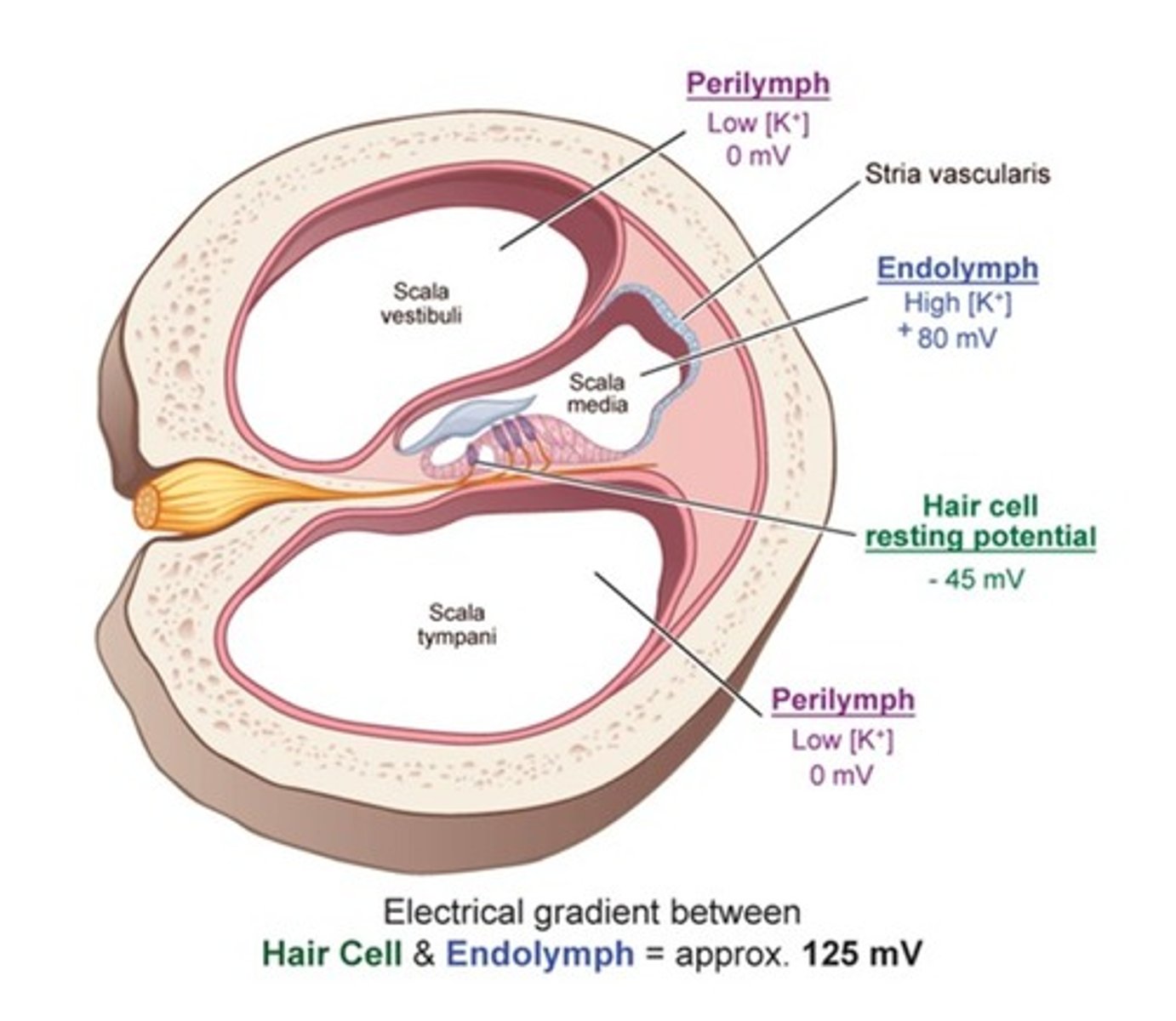
Endolymph fluid
high potassium concentration and low sodium
(high mV)
perilymph is located in the
scala vestibuli and the scala tympani
endolymph is located in the
scala media
what is maintained potential called?
endocochlear potential
(125 mV)
striata vascularis
contains the ion pumps that remove sodium and discharges potassium into the endolymph
(ensures we are pulling in new potassium and removing anything that should not be in there.
rows: inner hair cell
a single row nearest to central axis of the cochlear spiral
rows: outer hair cell
three parallel rows in the region closest to the stria vascularis
hair cells do not produce an ______ potential, but they do produce a _______ potential
action, receptor
1 multiple choice option
parts of a hair cell include
stereocilia, kinocilium, and tip links
kinocilium
the taller one
stereocilia
the shorter one
stereocilia of the outer hair cells are located where?
embedded into the tectorial membrane, forming a connection between the organ of corti and the tectorial membrane
stereocilia of the inner hair cell location
floating in the endolymph underneath the tectorial membrane
what do the tip links do?
connect the stereocilia and the kinocilium.
hyperpolarization
when the kinocilium moves towards the stereocilium
(off signal)
- CLOSES MECHANICAL CHANNELS
depolarization
when the stereocilia moves towards the kinocilium
(on signal)
- OPENS MECHANICAL CHANNELS FOR K+
when the hair cells depolarize potassium rushes in and changes the hair cell from _______ to _________
negative, positive
1 multiple choice option
when the positive signal moves down the hair cell, what happens?
calcium channels open, stimulating the release of neurotransmitters (glutamate)
what do the neurotransmitters do>
stimulate nerve endings that connect to bottom of hair cells (CN VIII)
the ______ is mostly responsible for transducing acoustic inputs
IHC
1 multiple choice option
the hair cells secrete what onto the auditory nerve?
neurotransmitters (glutamate)
frequency responses to the auditory nerve are based on what
the tonotopic distribution on the basilar membrane
CN VIII is what type of neuron
1st-order neuron
what is the order of the central auditory process?
1. cochlea
2. cochlear nucleus
3. superior olivary complex
4. inferior colliculus
5. medial geniculate body
6. A1
The cochlear nucleus is....
Relay station 1, it breaks down the frequency into spectral cues (frequency, intensity, timing)
the superior olivary complex is....
relay station 2, with the medial and the lateral parts.
SOUND LOCALIZATION
the medial superior olivary complex
specializes in low-frequency hearing (which direction its coming from = how long to get there)
the lateral superior olivary complex
specializes in higher-frequency hearing
high frequencies show what?
the difference in intensity between the two ears
low frequencies show what?
differences in time delay of the signal reaching each ear.
stapedius reflex
involuntary contraction of the stapedius muscle in the middle ear to loud sounds
what is in charge of the stapedius muscle?
superior olivary nucleus
inferior colliculi
relay station 3.
- BINAURAL HEARING AND LOCALIZATION (3D)
medial geniculate body of the thalamus
relay station 4.
- relays auditory tracts to the auditory parts of the cerebral cortex
- where the 2nd order neuron meets the 3rd order neuron
auditory cortex (heschl's gyrus)
located on the surface of the superior temporal gyrus and divided into the primary auditory cortex, secondary auditory cortex, and auditory association cortices.
primary auditory cortex (A1)
highly response to pure tones.
- sensation
secondary auditory cortex (A2)
highly responsive to complex tones
- perception.
outer hair cells send what type of signals
efferent ones
sensorineural hearing loss
an inner ear hearing loss usually due to damage to the organ of corti hair cells
auditory processing disorder
difficulty processing and interpreting symbols; a dyslexia of the ears
auditory brainstem response
non-invasive electrophysiological evoked response method used routinely by clinical audiologists to objectively assess cochlear function and neural function without need for active participation by the subject
if you turn to the right, which way will the endolymph spin?
it will move in the opposite direction so it will turn left
what are the receptor potential steps in order
neurotransmitter is released
CN VIII fibers fire
K+ enters the hair cell
kinocilium is triggered
kinocilium is triggered, K+ enters the hair cell, neurotransmitter is released, CN VIII fibers fire