A&P 1 (Unit 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology)
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
B) Anatomy
Human ___________________ is the study of the structure of the human body.
A) Physiology
B) Anatomy
C) Pathology
D) Neurology
C) Anatomy
What is the study of the structure of the human body called?
A) Physiology
B) Pathology
C) Anatomy
D) Kinesiology
B) Physiology
Human _______________________ is the study of the body's functions.
A) Anatomy
B) Physiology
C) Pathology
D) Neurology
B) Physiology
What is the study of the body's functions called?
A) Anatomy
B) Physiology
C) Pathology
D) Biology
B) basic
The cell is the ___________ unit of life.
A) biggest
B) basic
C) fastest
D) loudest
C) Cell
What is the basic unit of life?
A) Tissue
B) Organ
C) Cell
D) Organism
A) smallest
Cells are the ________________ unit that can carry out the functions of life.
A) smallest
B) largest
C) weakest
D) strongest
B) Cell
What is the smallest unit that can carry out the functions of life?
A) Atom
B) Cell
C) Tissue
D) Organ
C) cells
All organisms are composed of _____________.
A) atoms
B) tissues
C) cells
D) organs
C) Cells
What are all organisms composed of?
A) Atoms
B) Organs
C) Cells
D) Bones
D) pre-existing
All cells come from _______________________ cells.
A) new
B) dead
C) random
D) pre-existing
C) Pre-existing cells
What do all cells come from?
A) Water
B) Atoms
C) Pre-existing cells
D) Energy
C) chemical
All living things rely on __________________ processes.
A) mechanical
B) electrical
C) chemical
D) artificial
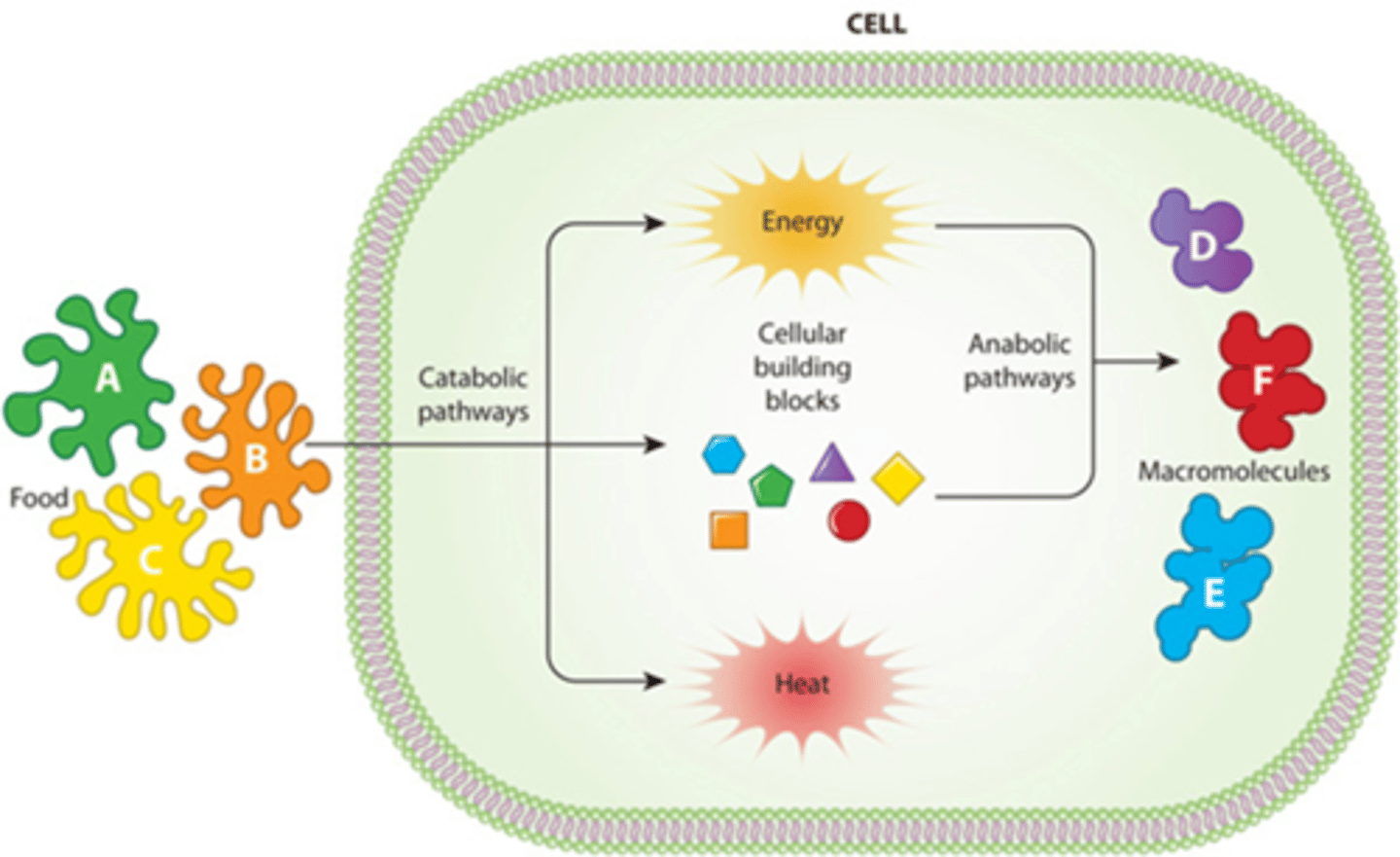
C) All living things relying on chemical processes
What is metabolism?
A) The study of cells
B) Movement of muscles
C) All living things relying on chemical processes
D) The structure of the body
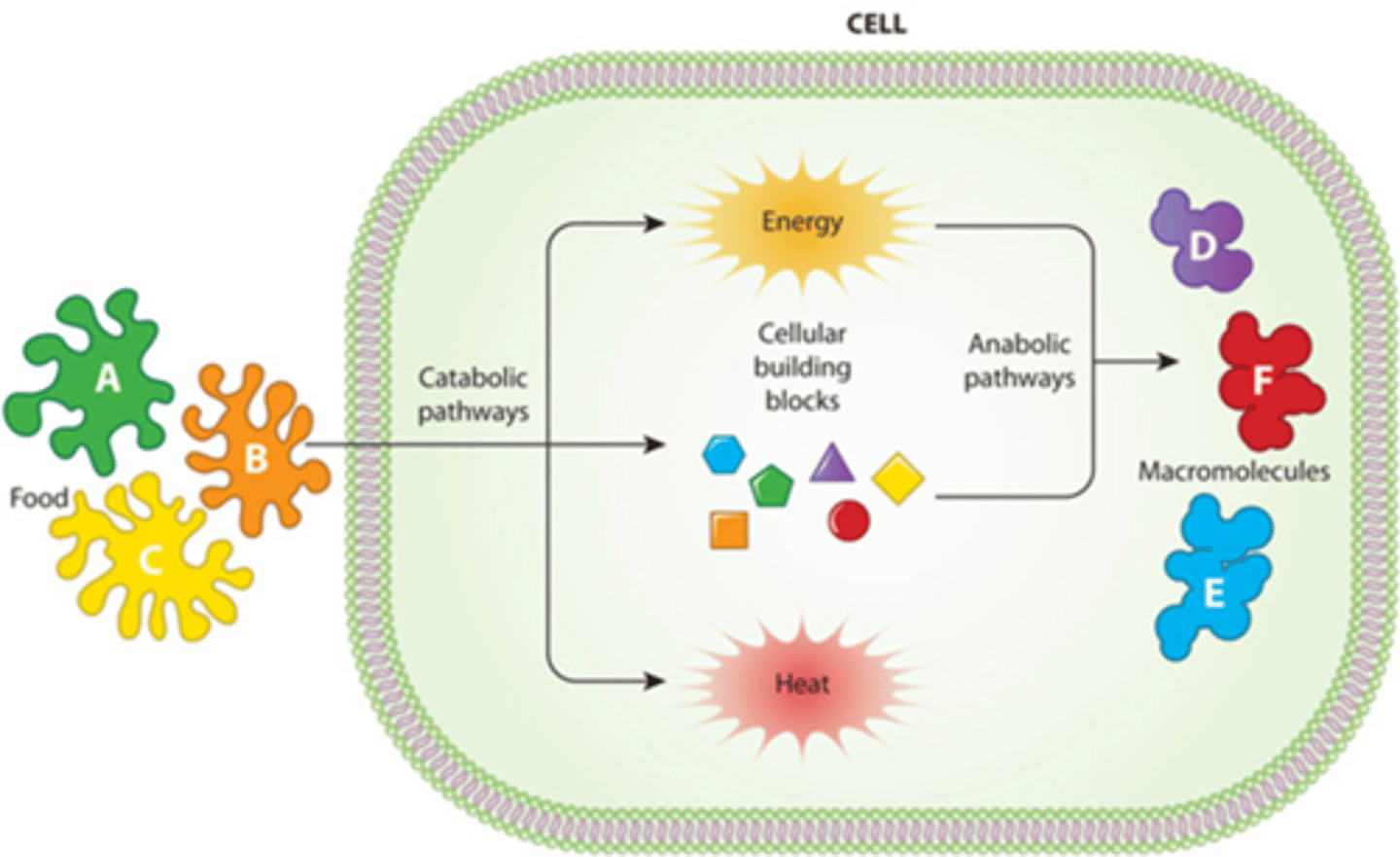
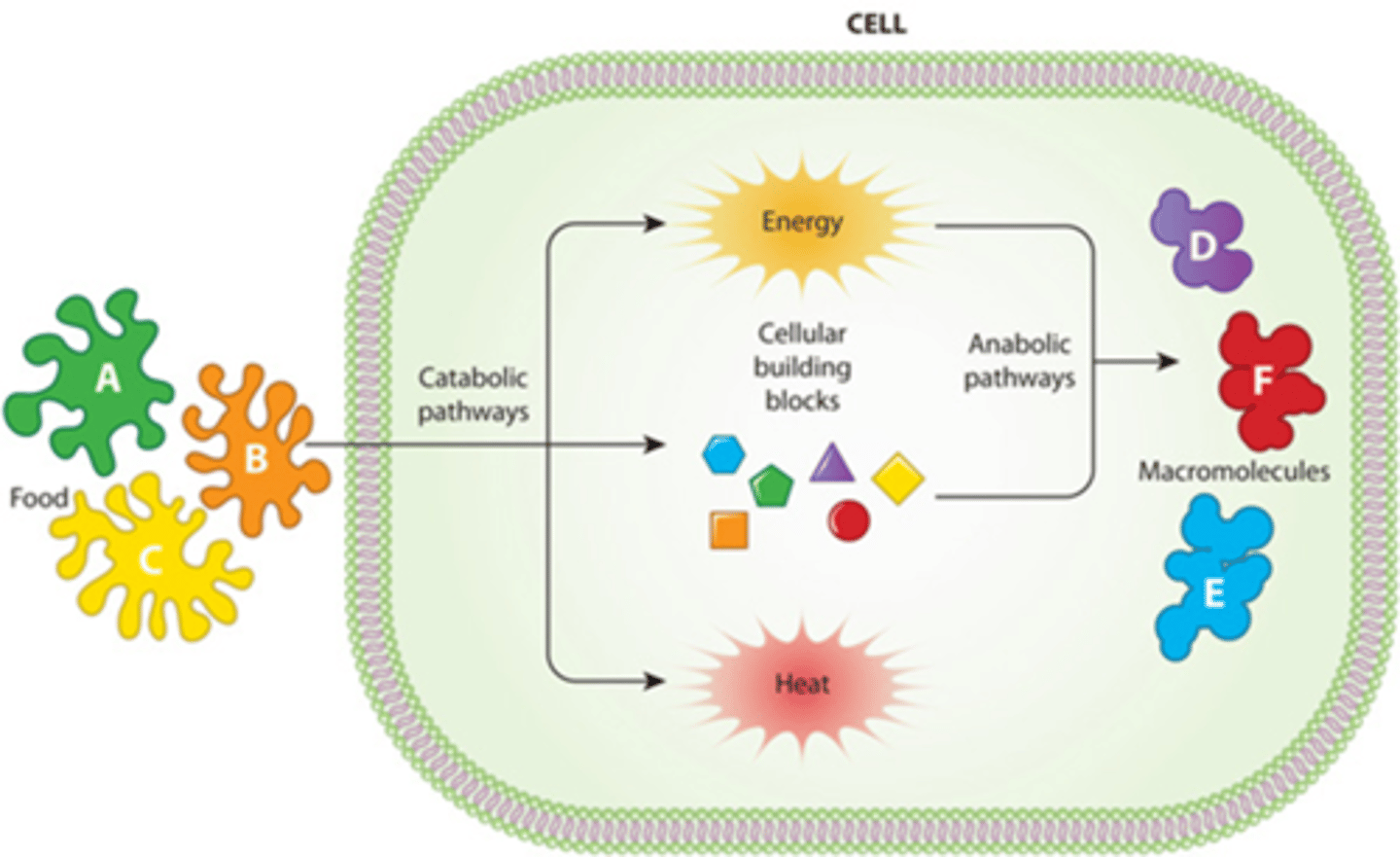
B) Anabolism
_________________________: chemical reactions that build molecules.
A) Catabolism
B) Anabolism
C) Metabolism
D) Digestion
B) Chemical reactions that build molecules
What is anabolism?
A) Chemical reactions that break down molecules
B) Chemical reactions that build molecules
C) Movement of muscles
D) The process of breathing
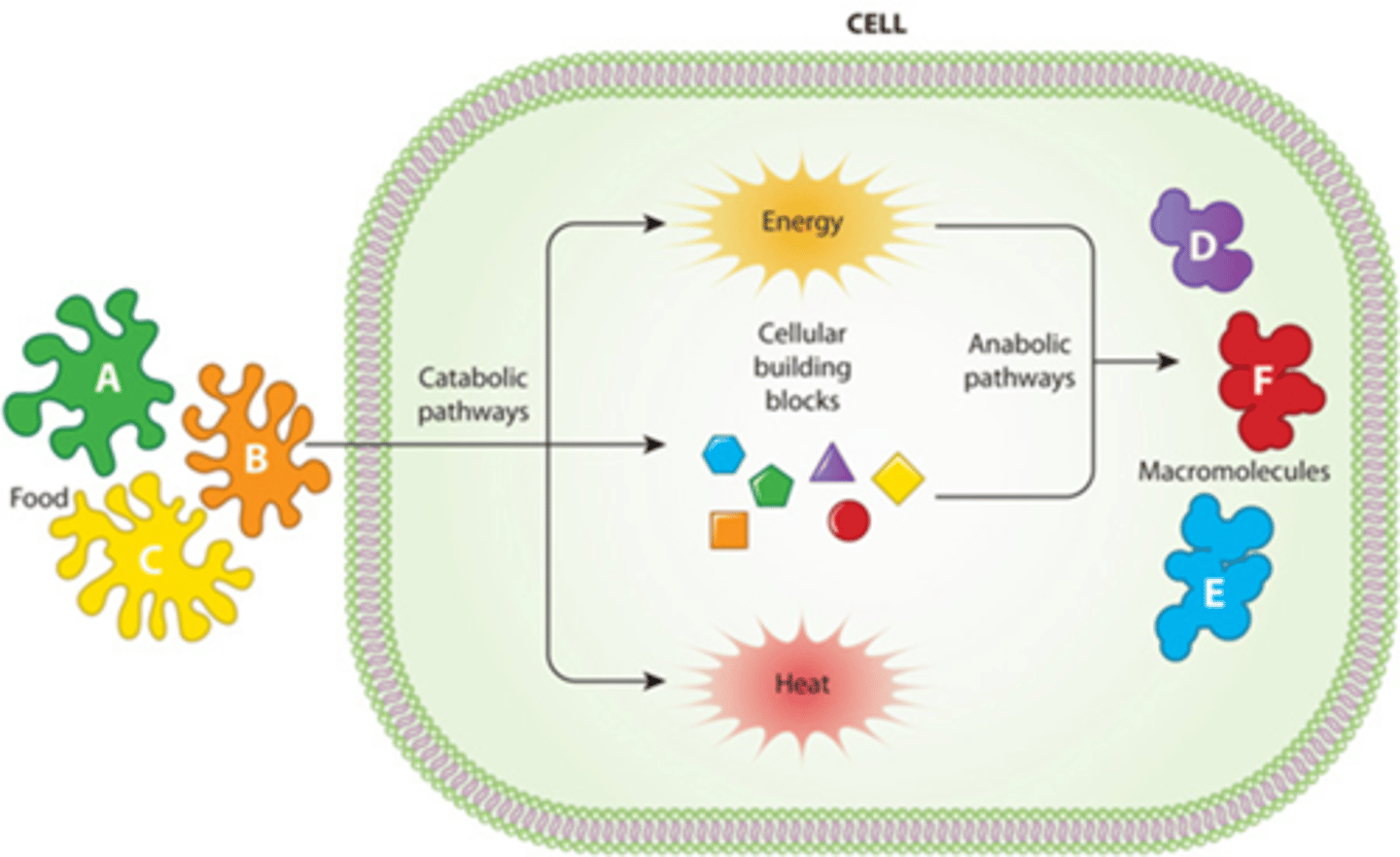
B) Catabolism
_______________________: Chemical reactions that break down molecules.
A) Anabolism
B) Catabolism
C) Metabolism
D) Photosynthesis
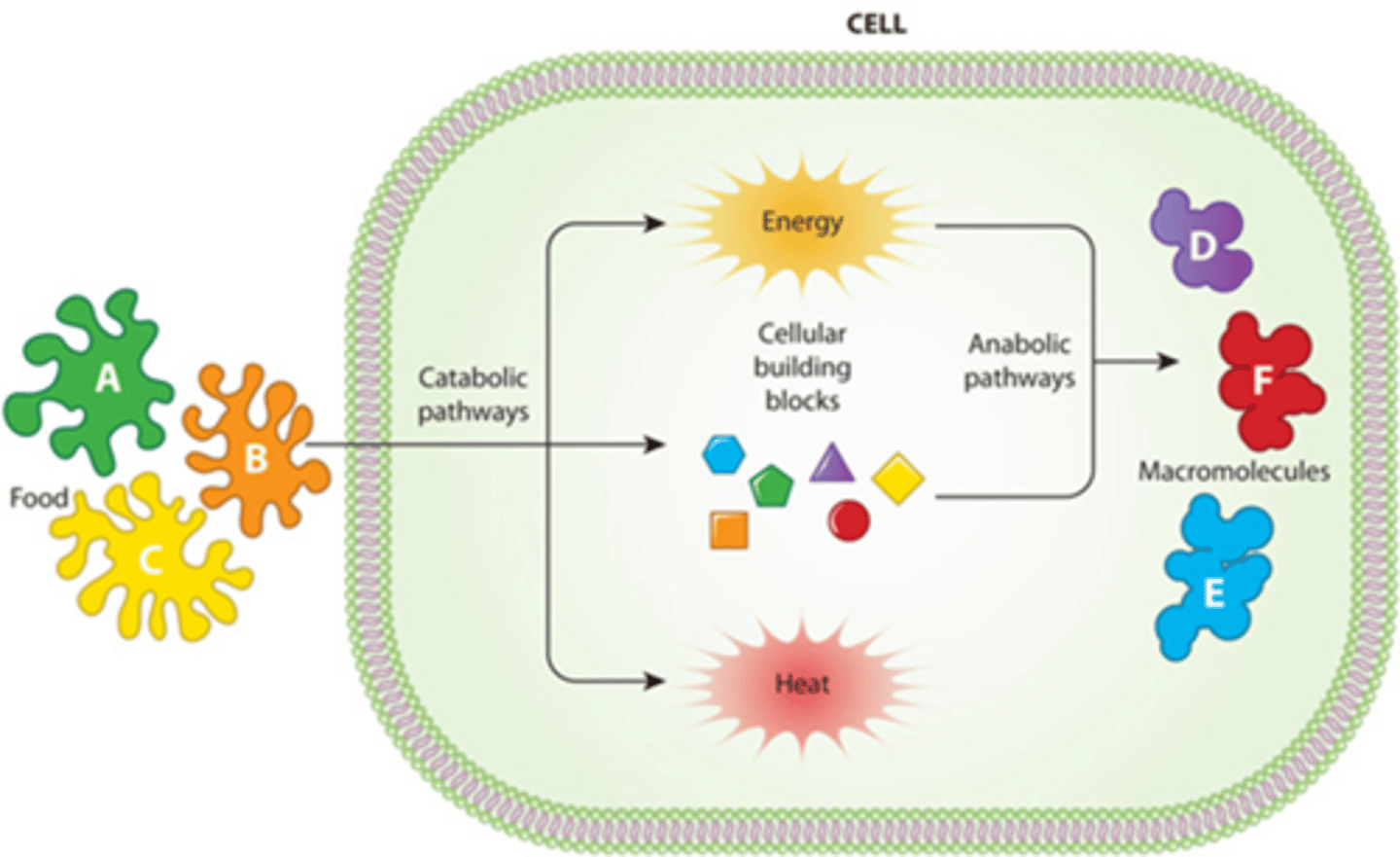
B) Chemical reactions that break down molecules
What is catabolism?
A) Chemical reactions that build molecules
B) Chemical reactions that break down molecules
C) The study of cells
D) The process of digestion
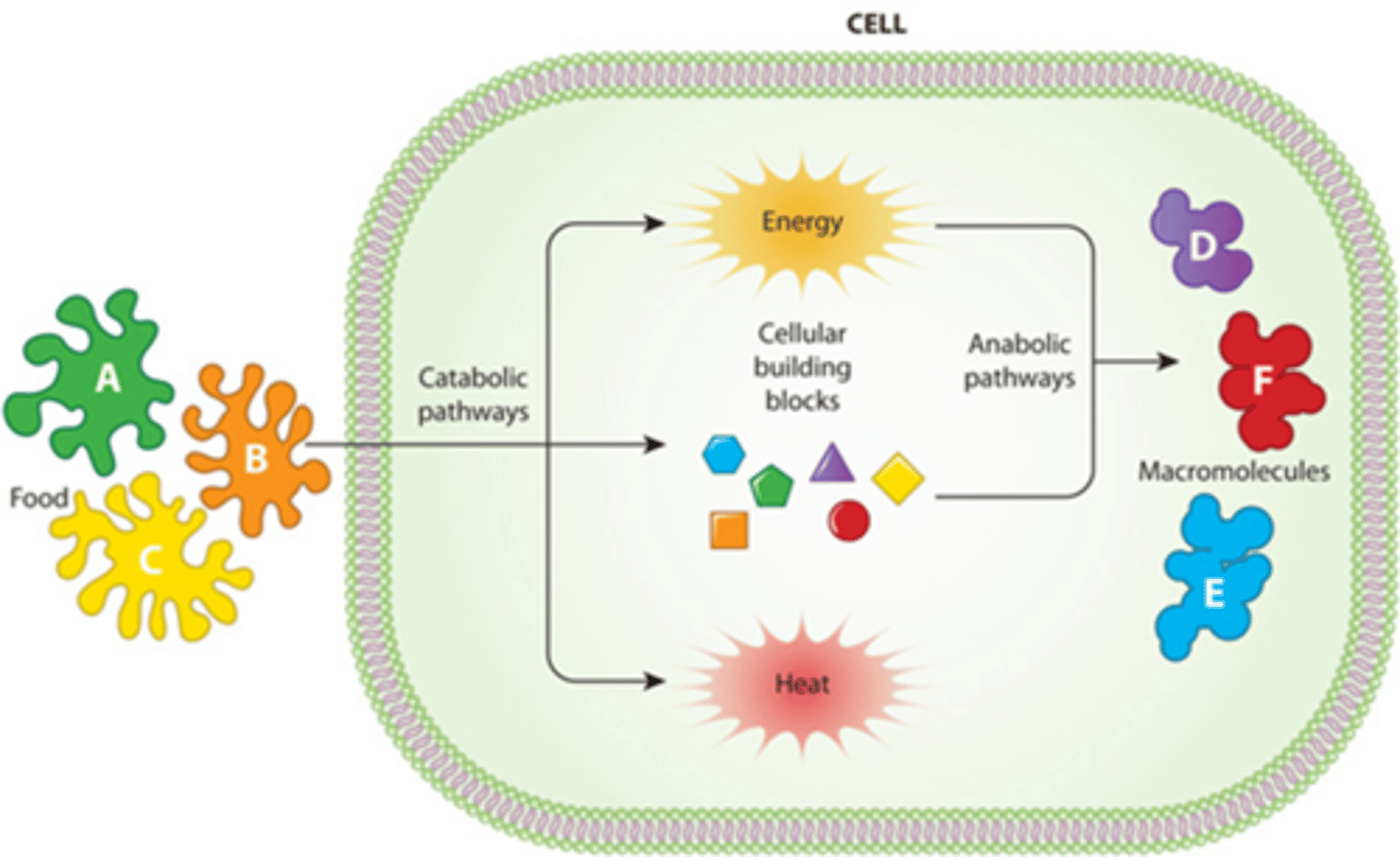
C) physical
During growth, anabolism outweighs catabolism. Growth may lead to an increase in the _____________ size of a cell.
A) emotional
B) chemical
C) physical
D) digital
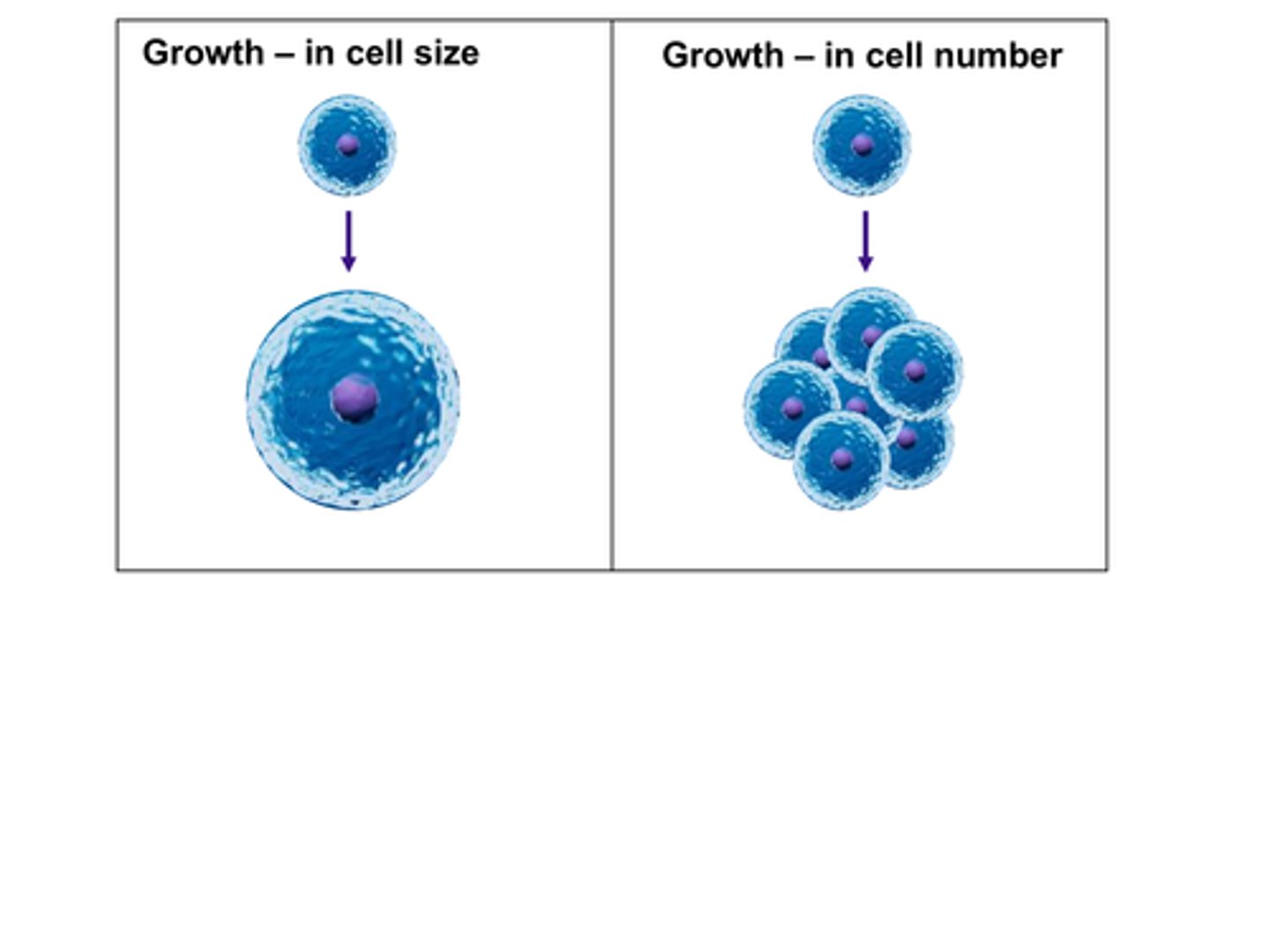
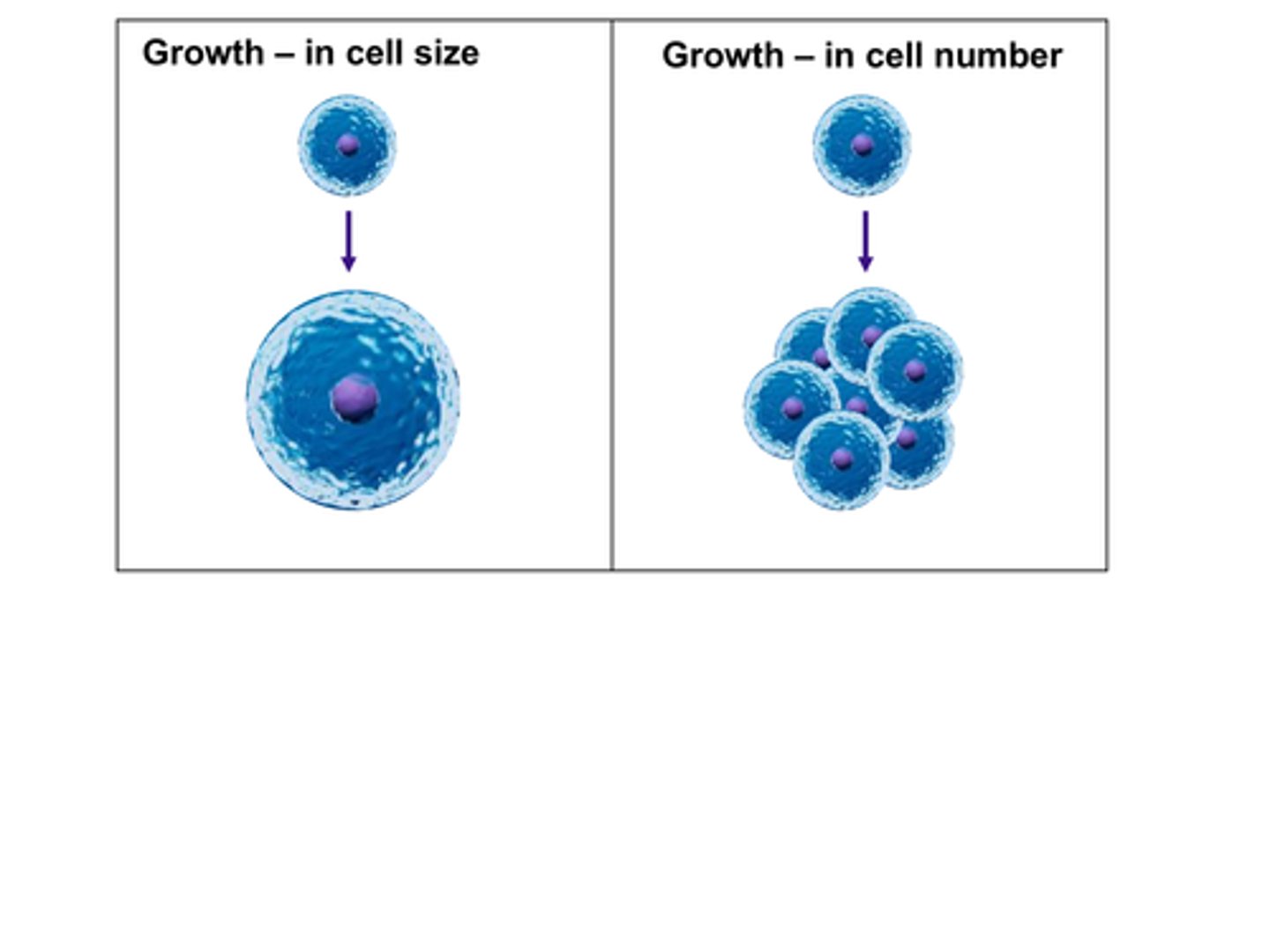
C) number
During growth, anabolism outweighs catabolism. Growth may lead to an increase in the ___________ of cells, especially in multicellular organisms.
A) weight
B) color
C) number
D) shape
B) Excretion
Which life process involves the removal of toxic waste produced by metabolism?
A) Respiration
B) Excretion
C) Growth
D) Reproduction

C) Elimination
What is the process of removing potentially harmful (toxic) waste from the body?
A) Digestion
B) Circulation
C) Elimination
D) Absorption

Excretion
metabolism results in waste. (going to the bathroom)

B) Mobility
Entire organism movement is called ____________, which is the ability to move itself.
A) Circulation
B) Mobility
C) Respiration
D) Excretion

A) cells
Individual ___________ within an organism.
A) cells
B) organs
C) muscles
D) systems

B) Materials
__________________ within or between cells of an organism.
A) Energy
B) Materials
C) Communication
D) Movement

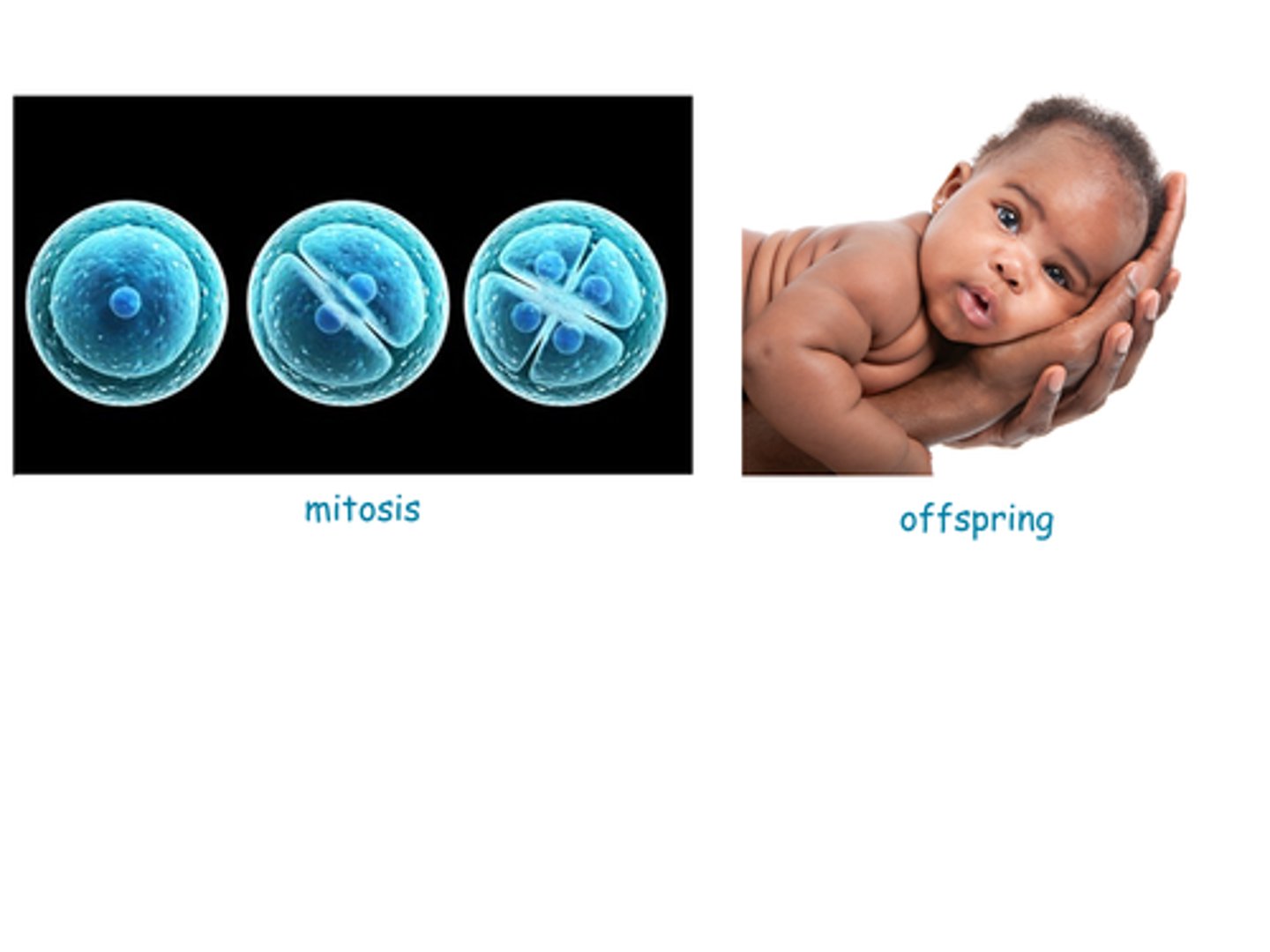
B) Mitosis
Individual cells reproduce through ___________ during growth and to replace damaged or old cells.
A) Meiosis
B) Mitosis
C) Fertilization
D) Germination
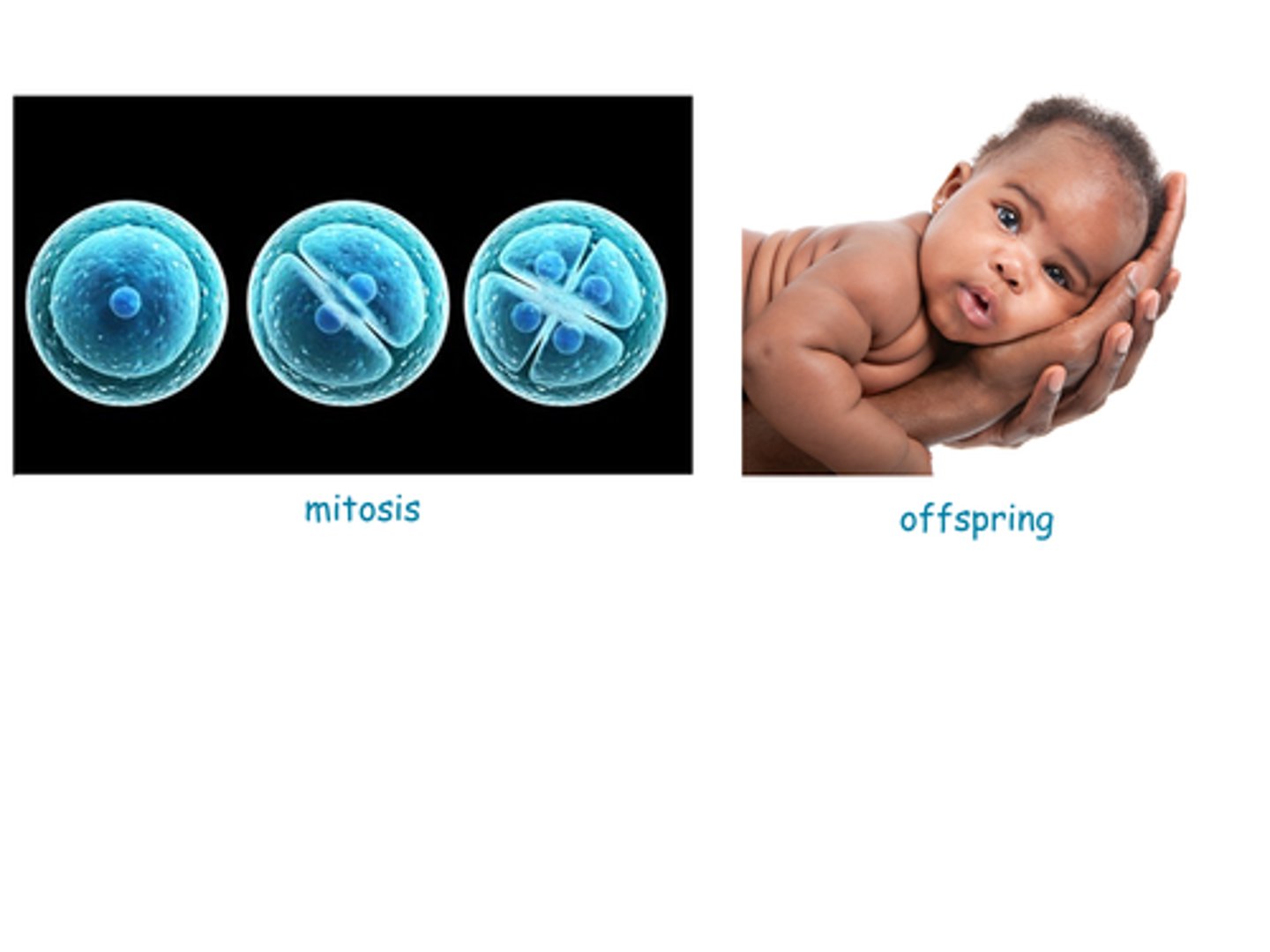
offspring
Organism itself reproduces; yields similar _______
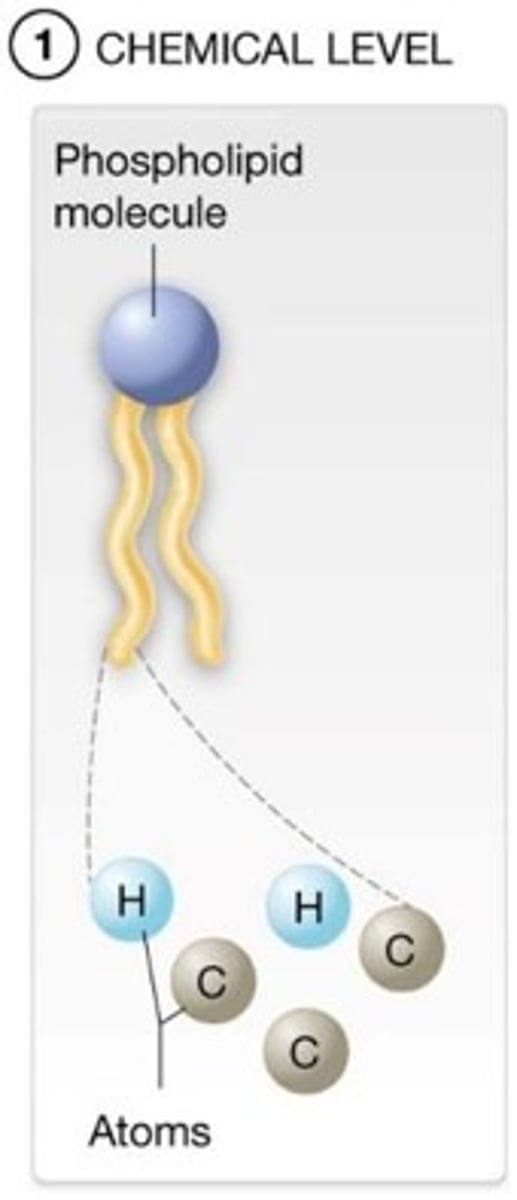
A) atoms; molecules
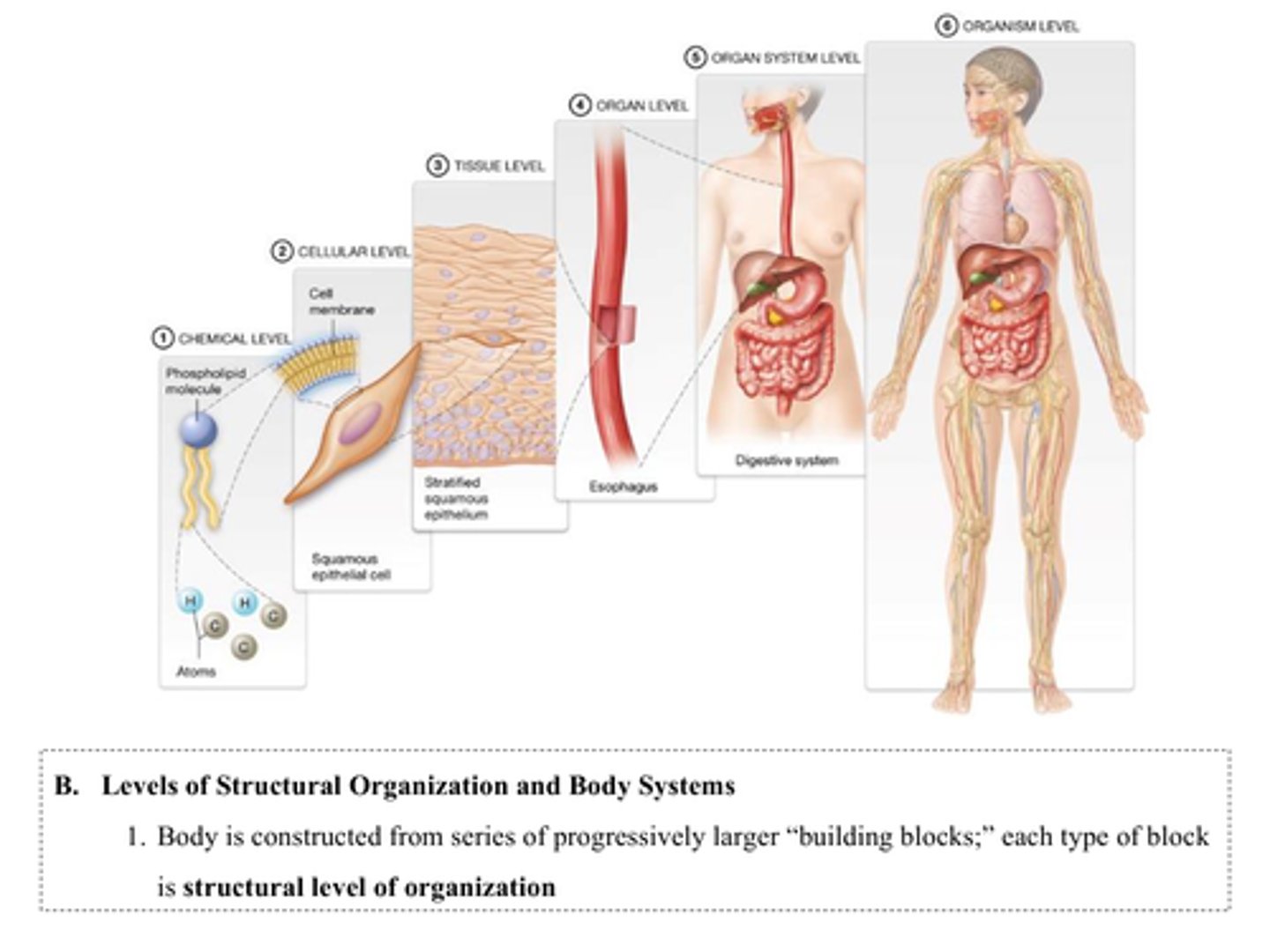
At the chemical level of organization, groups of many ____________ combine to form ___________________.
A) atoms; molecules
B) molecules; cells
C) cells; tissues
D) tissues; organs
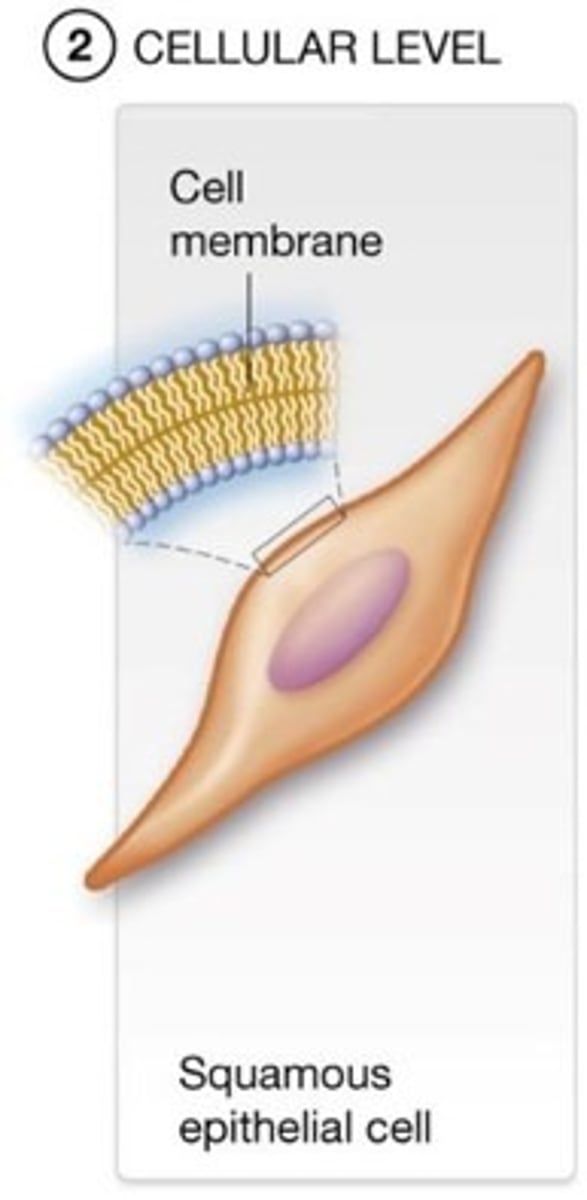
A) cellular
Groups of many different types of molecules combine in specific ways to form ____________ structures.
A) cellular
B) atomic
C) molecular
D) atomic-molecular
C) cell
The ____________ is the basic unit of life. Single-celled organisms are the smallest forms of life.
A) organ
B) tissue
C) cell
D) molecule
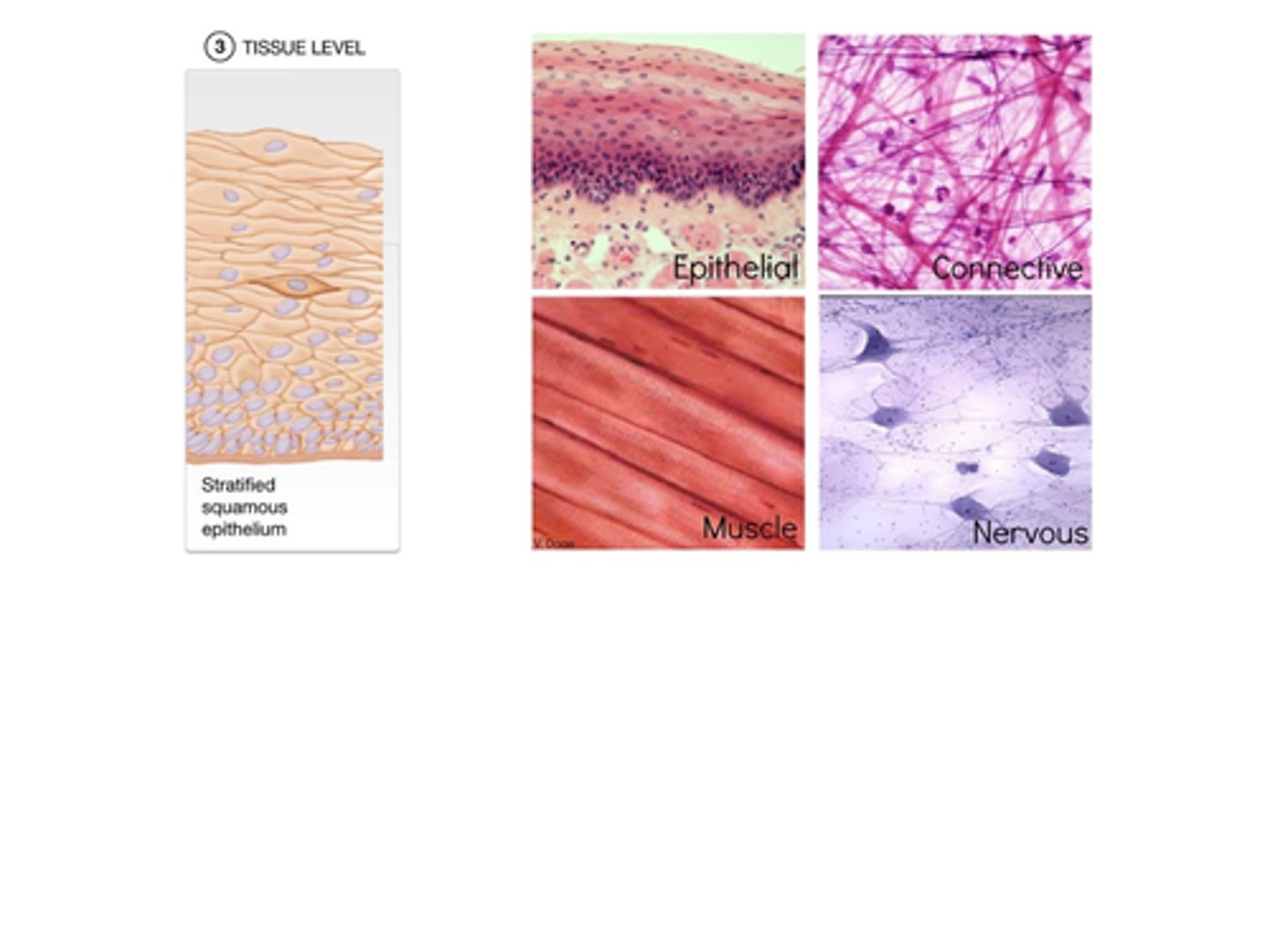
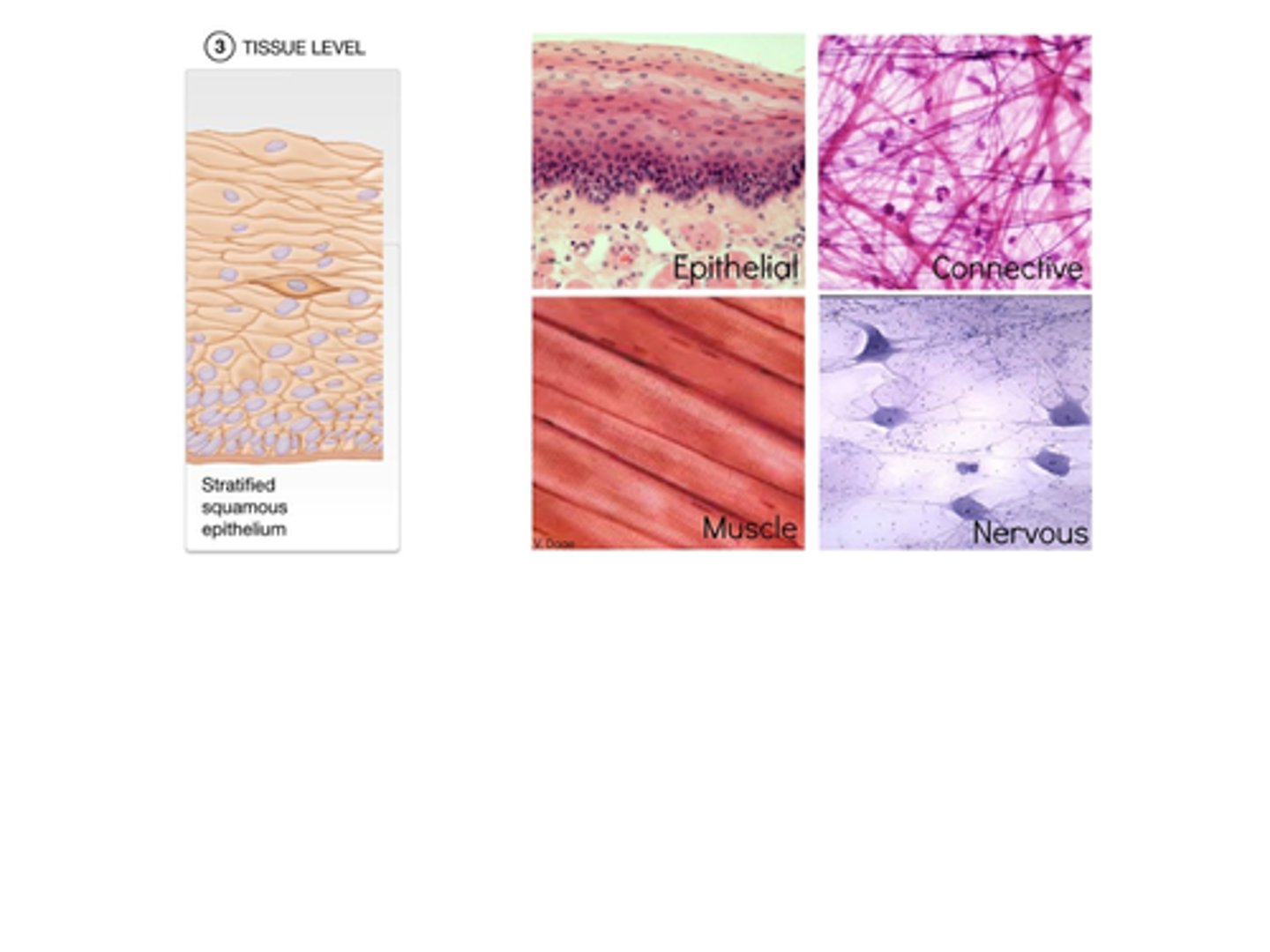
B) Tissues
_______________ consist of two components: cells and the surrounding extracellular matrix.
A) Organs
B) Tissues
C) Systems
D) Organoids
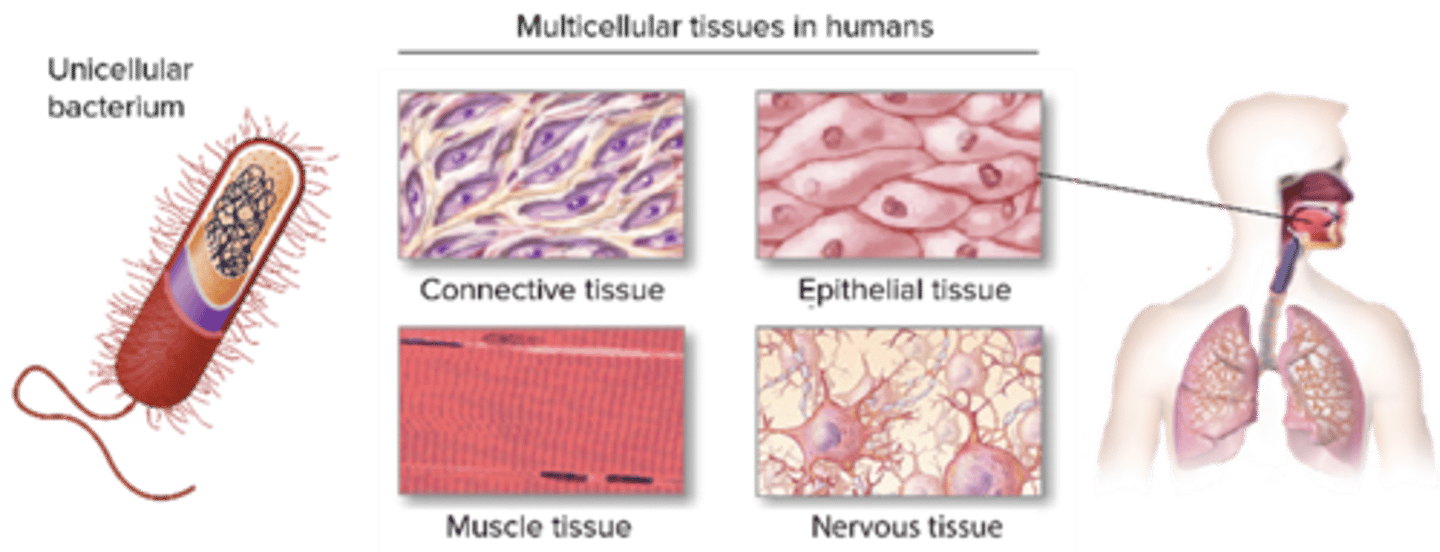
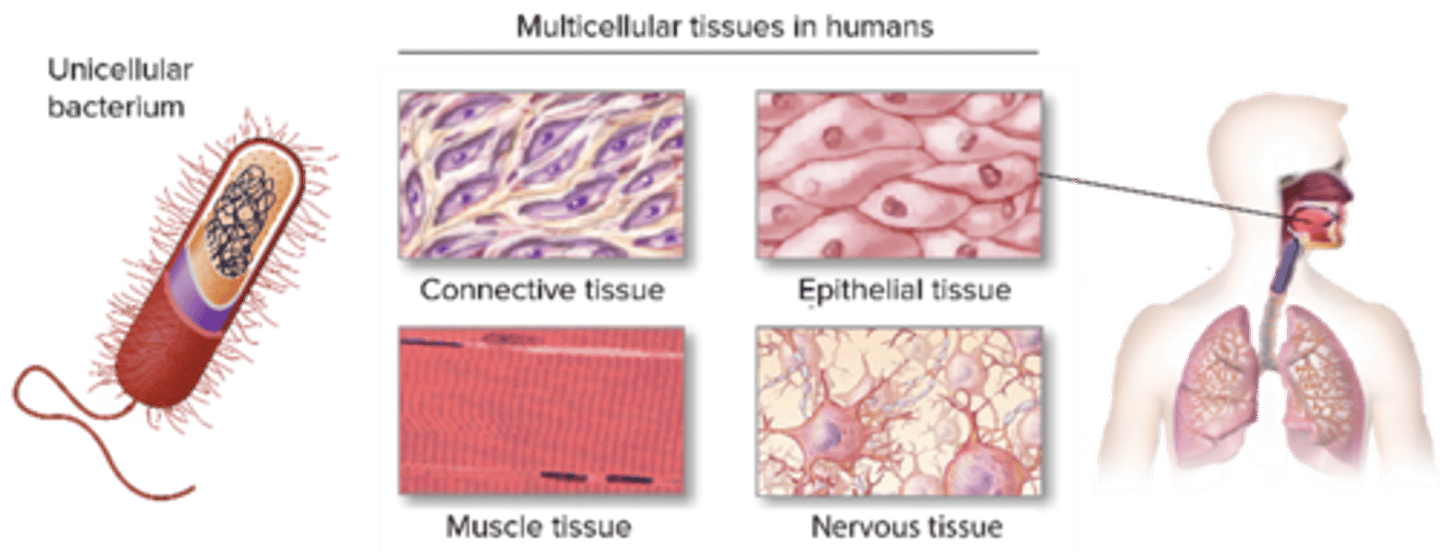
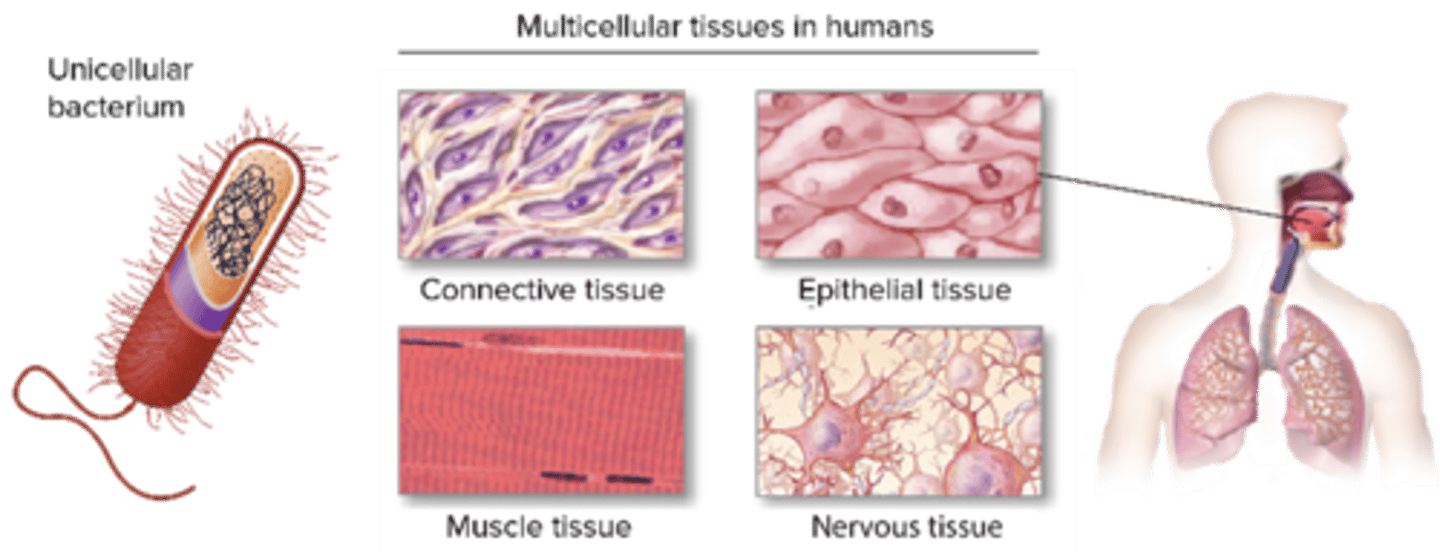
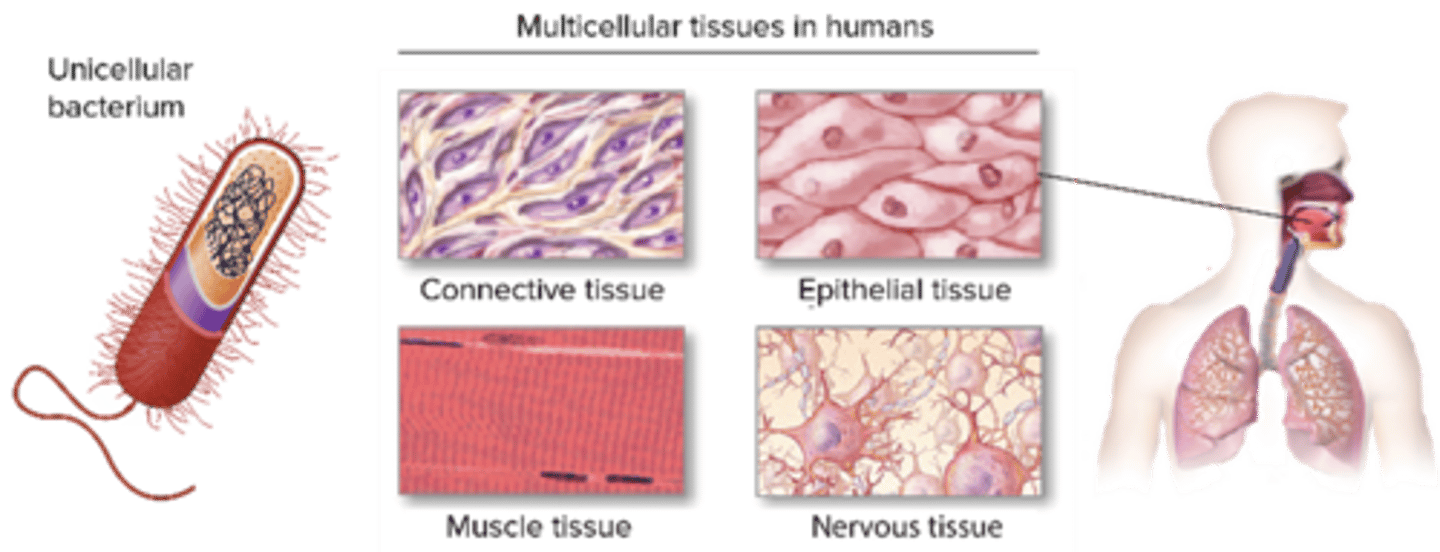
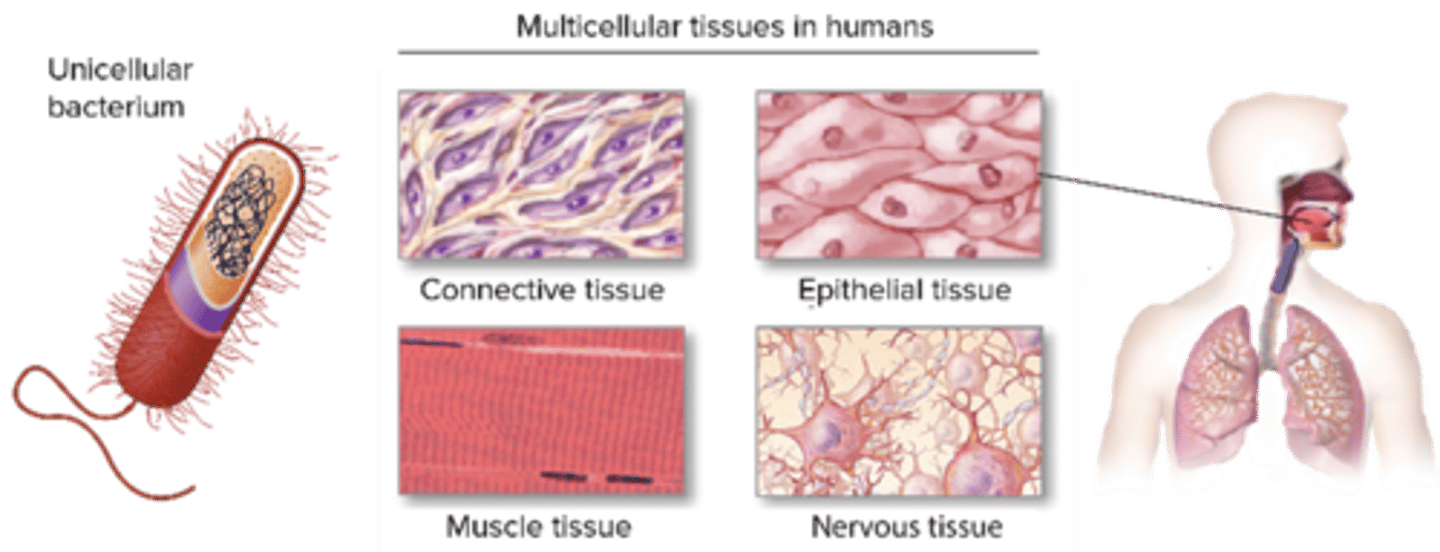
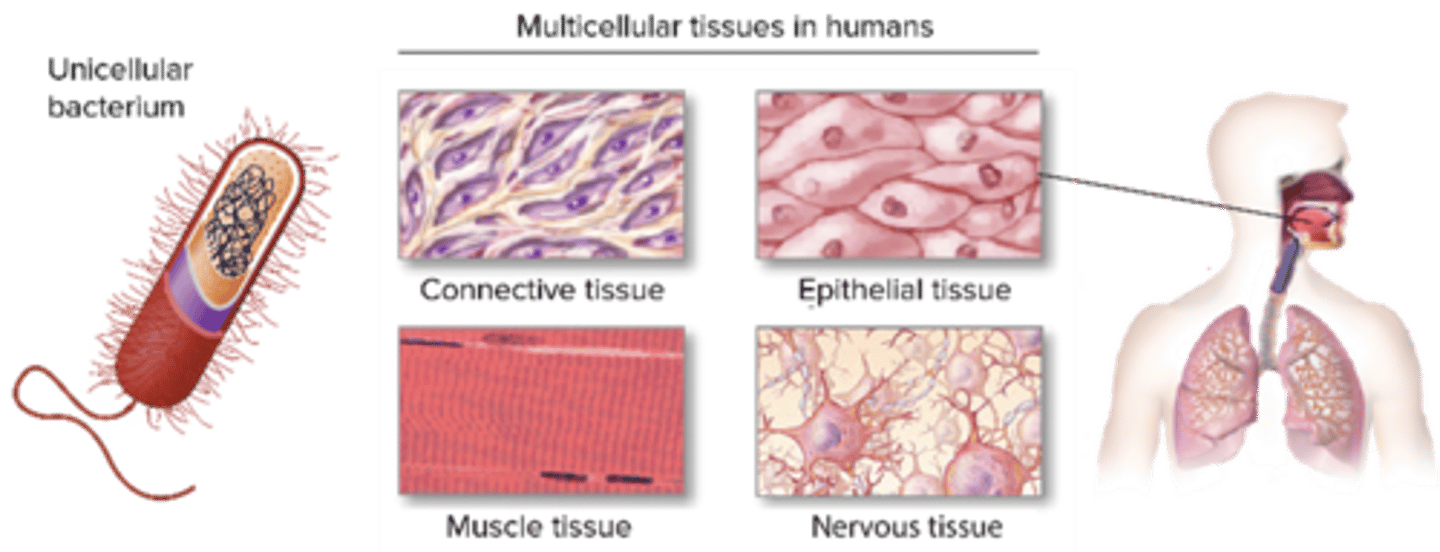
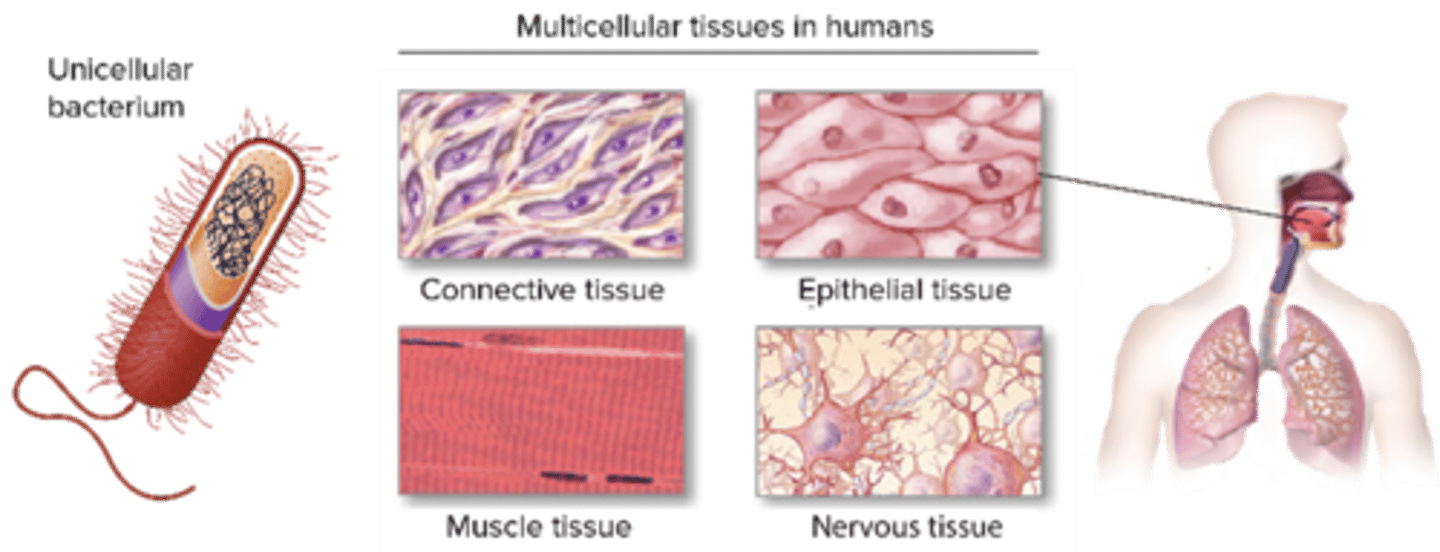
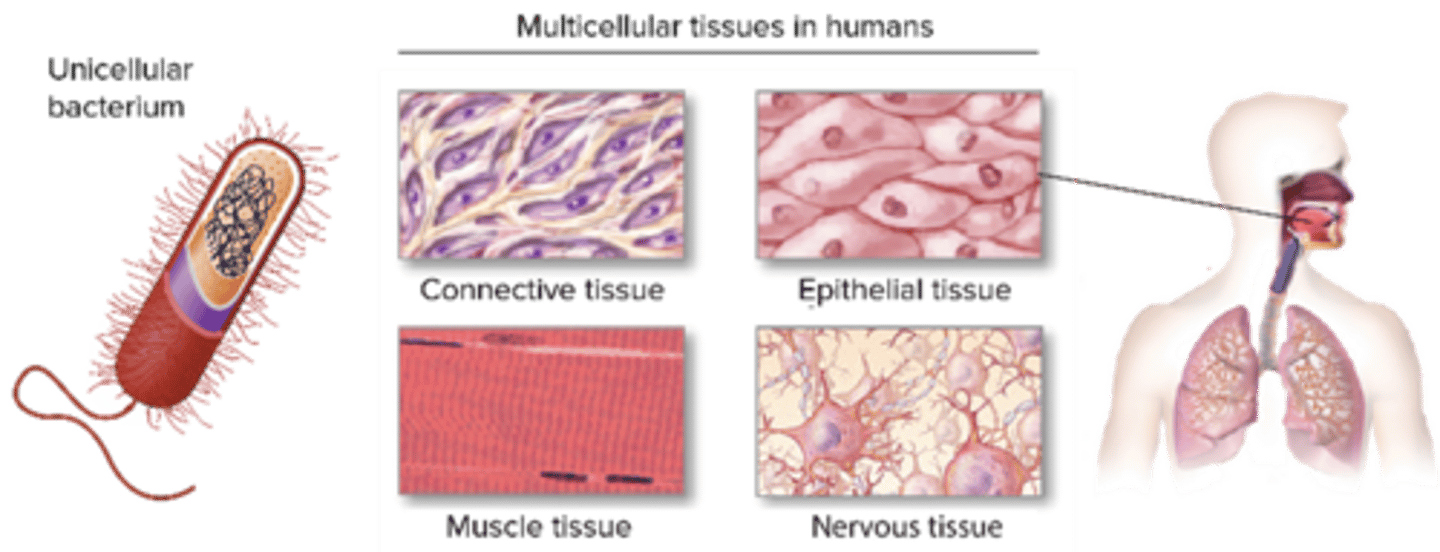
C) 4
How many primary tissue types are there in the human body?
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
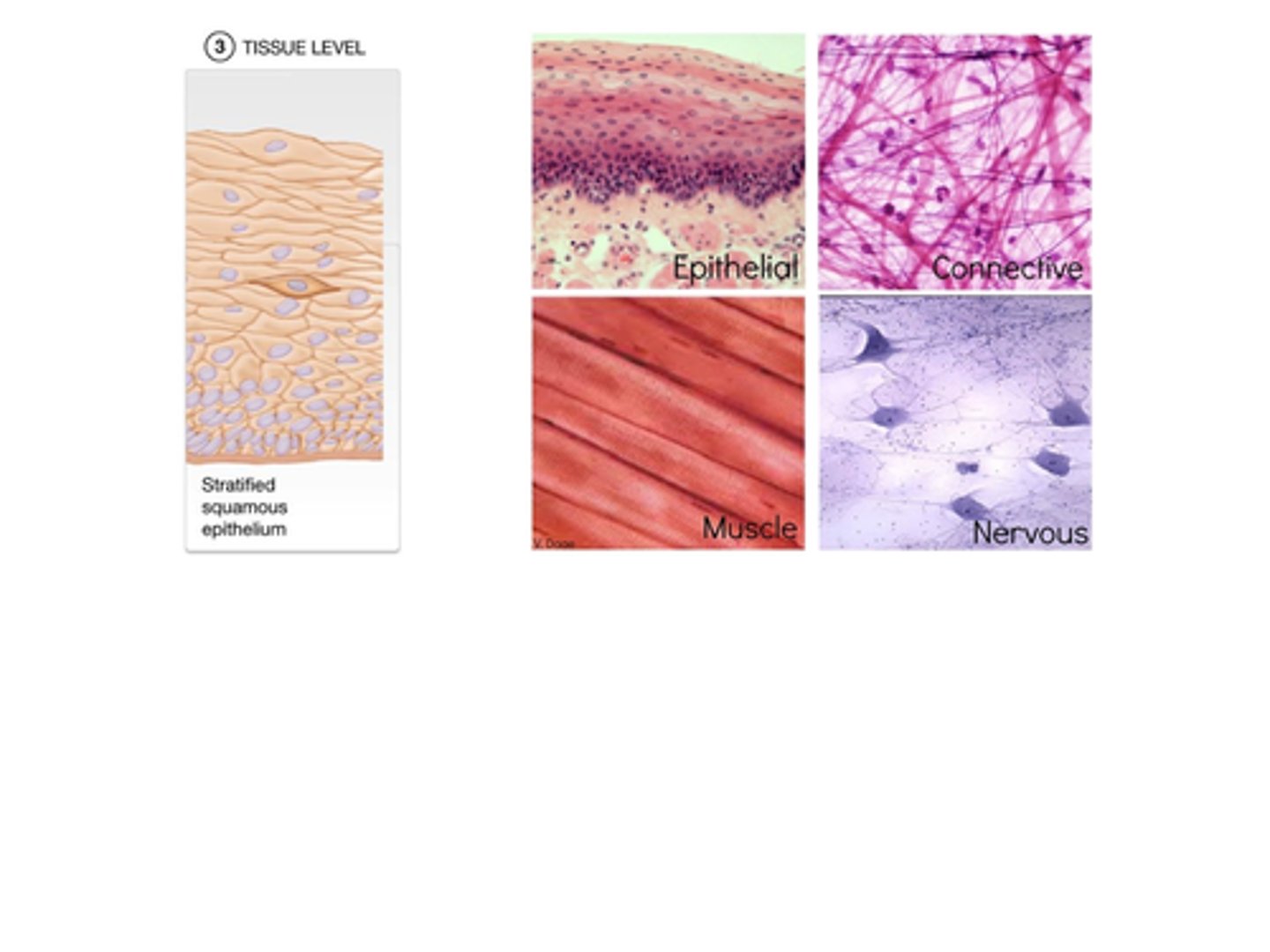
A) Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Nervous
Which of the following are the four primary tissue types in the human body?
A) Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Nervous
B) Epithelial, Cartilage, Bone, Nervous
C) Connective, Muscular, Bone, Blood
D) Muscular, Nervous, Fat, Skin
B) organs
At the organ level, two or more tissue types combine to form ______________.
A) cells
B) organs
C) systems
D) molecules
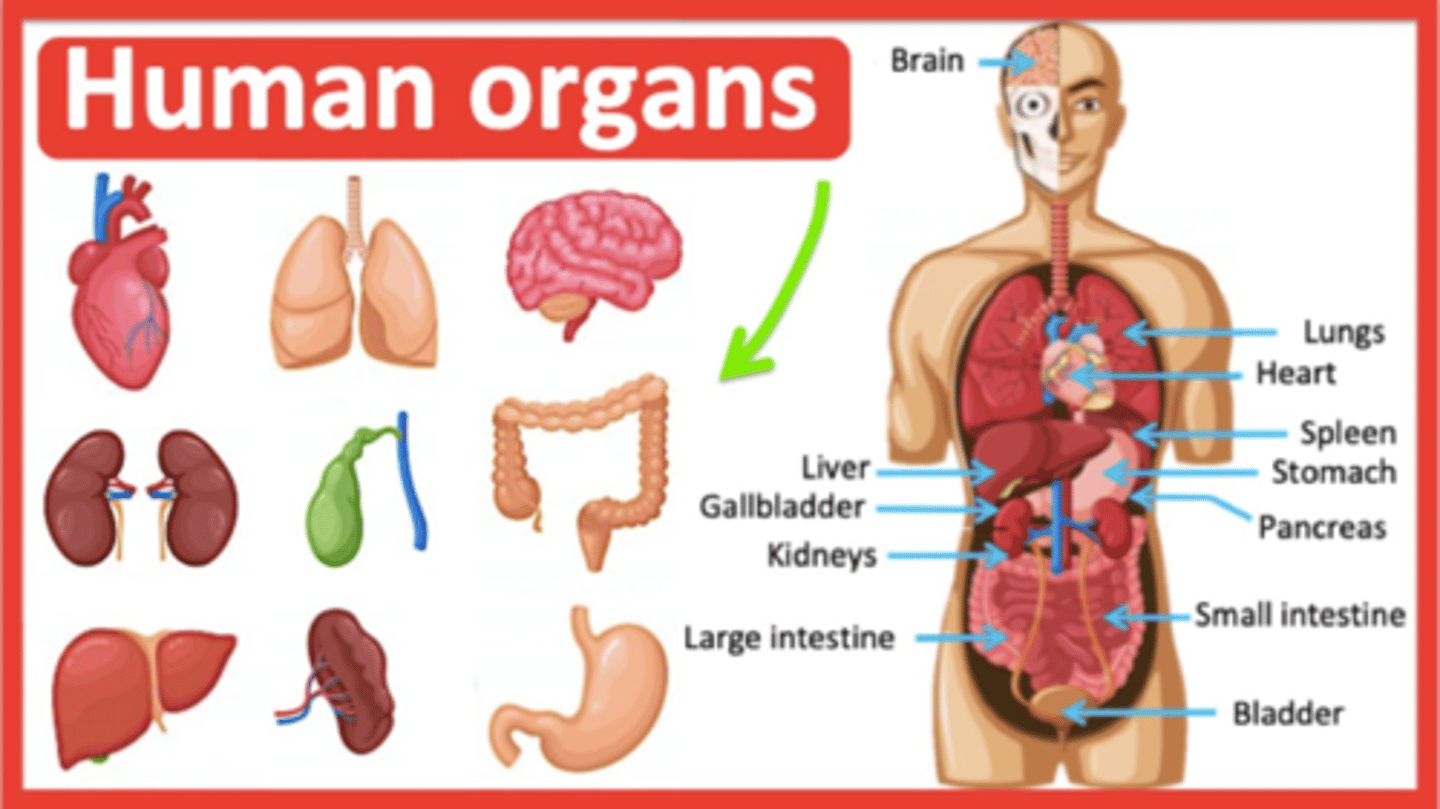
C) organ systems
At the organ system level, organs are grouped into _________________________.
A) tissues
B) cells
C) organ systems
D) molecules
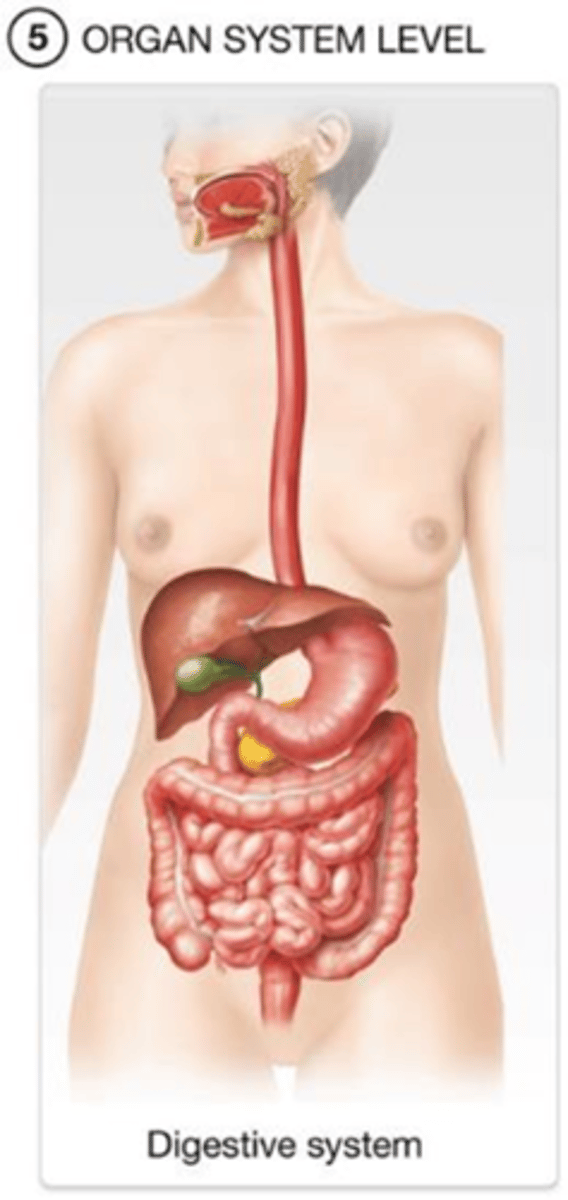
B) organism
Organs and organ systems work together to ensure the survival of the _______________.
A) cell
B) organism
C) tissue
D) organ
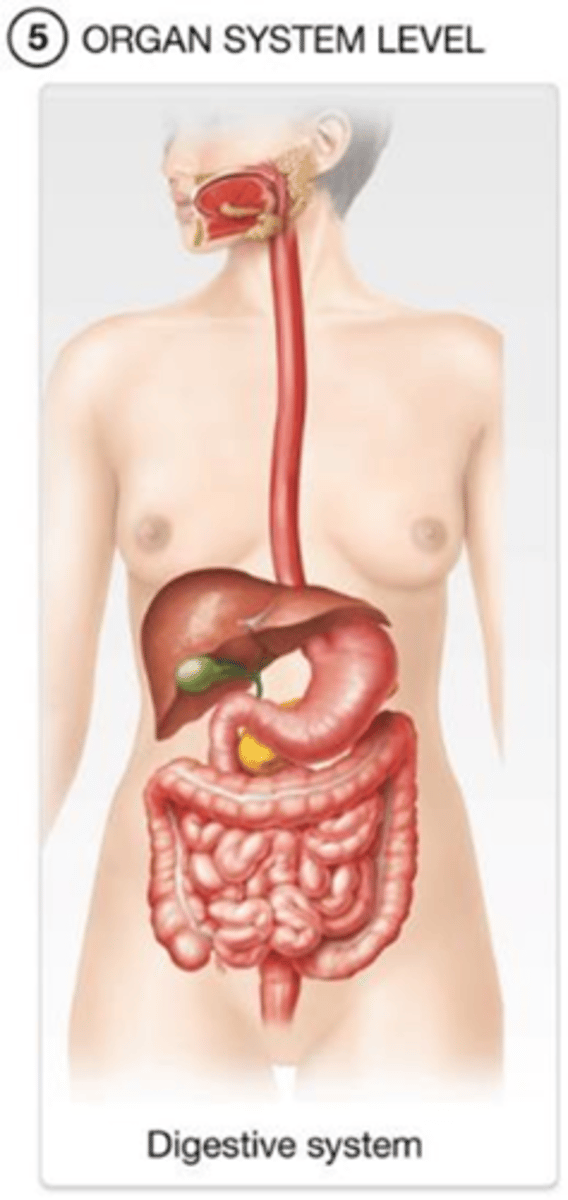
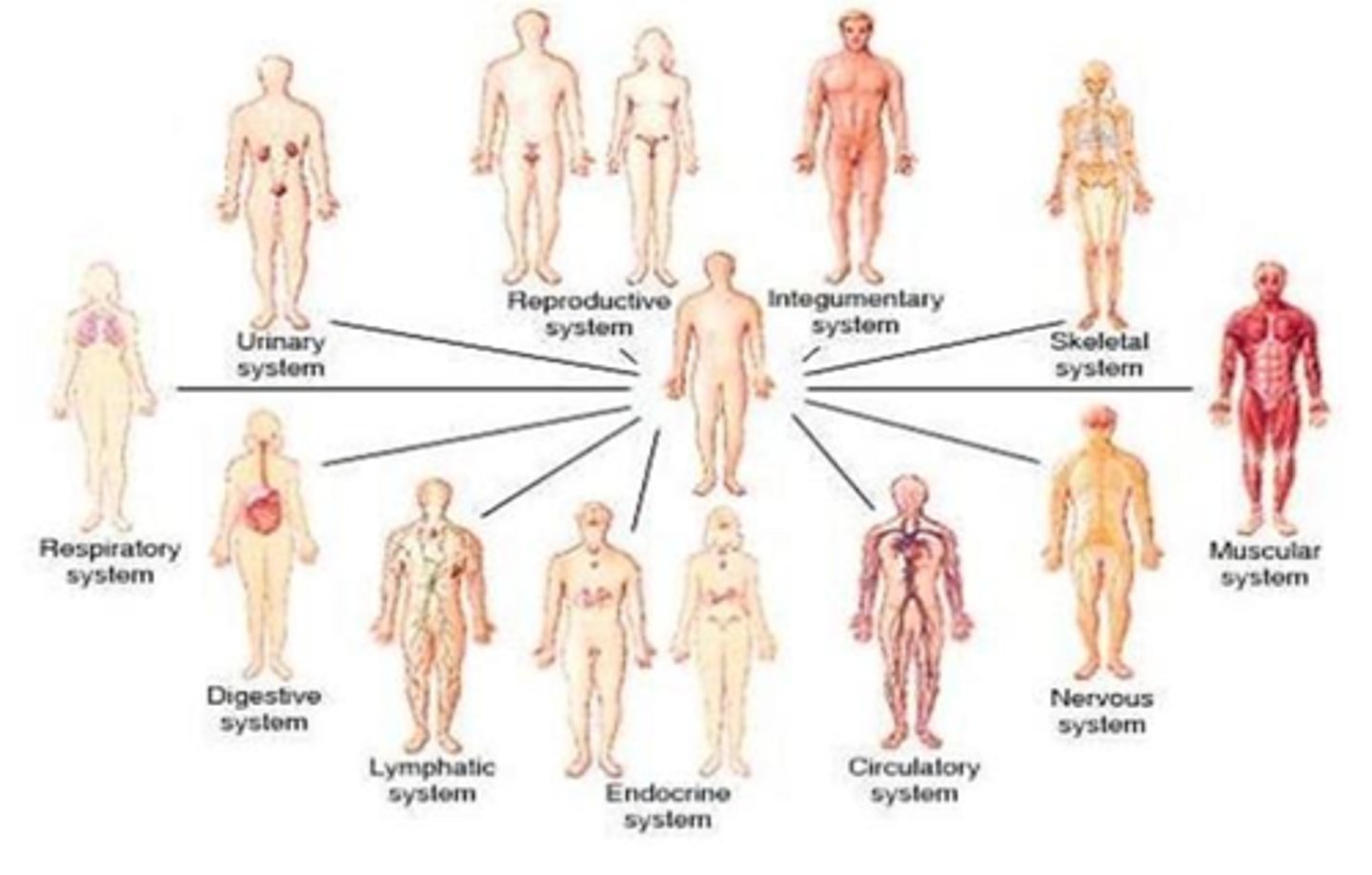
C) Integumentary system
Which body system protects the body from the external environment and helps maintain body temperature?
A) Respiratory system
B) Nervous system
C) Integumentary system
D) Endocrine system
B) Skeletal system
Which body system supports the body, protects internal organs, provides leverage for movement, produces blood cells, and stores calcium salts?
A) Muscular system
B) Skeletal system
C) Nervous system
D) Circulatory system
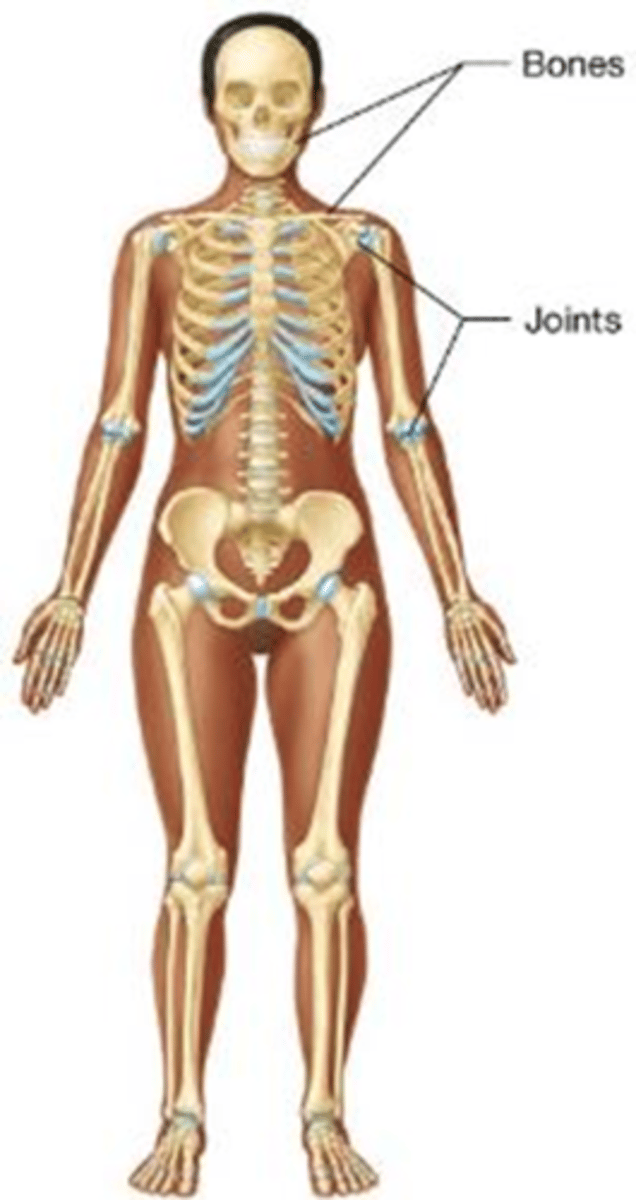
C) Muscular system
Which body system produces movement, controls body openings, and generates heat?
A) Nervous system
B) Endocrine system
C) Muscular system
D) Skeletal system
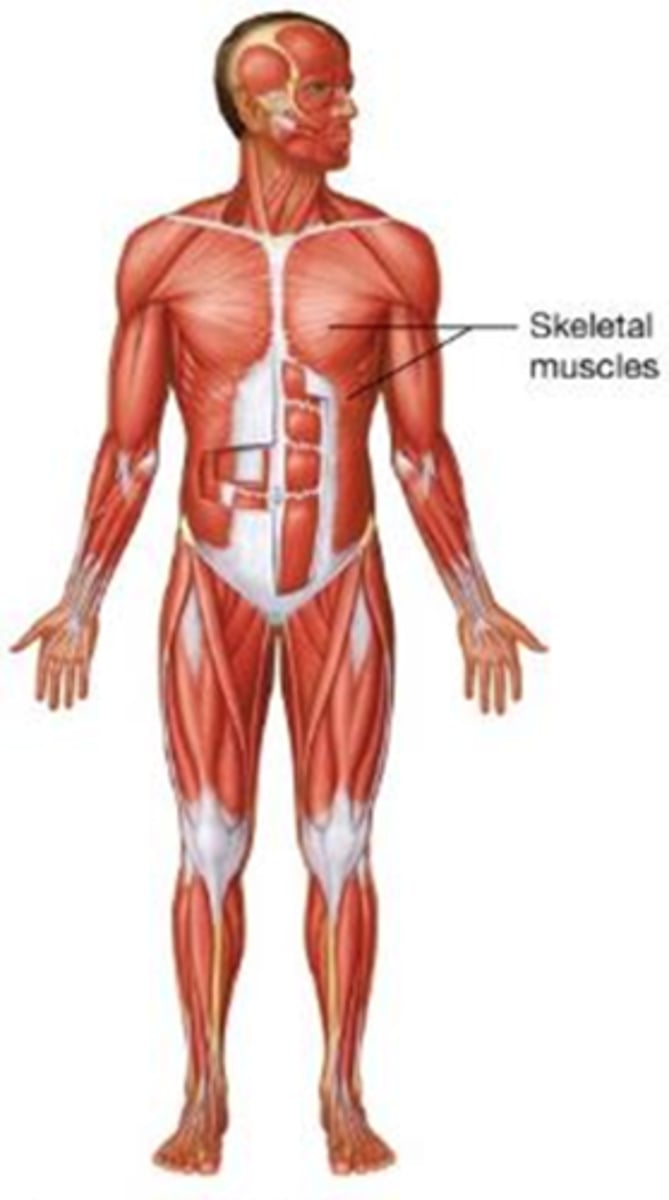
B) Nervous system
Which body system regulates body functions and provides sensation, movement, automatic functions, and mental functions?
A) Endocrine system
B) Nervous system
C) Muscular system
D) Respiratory system
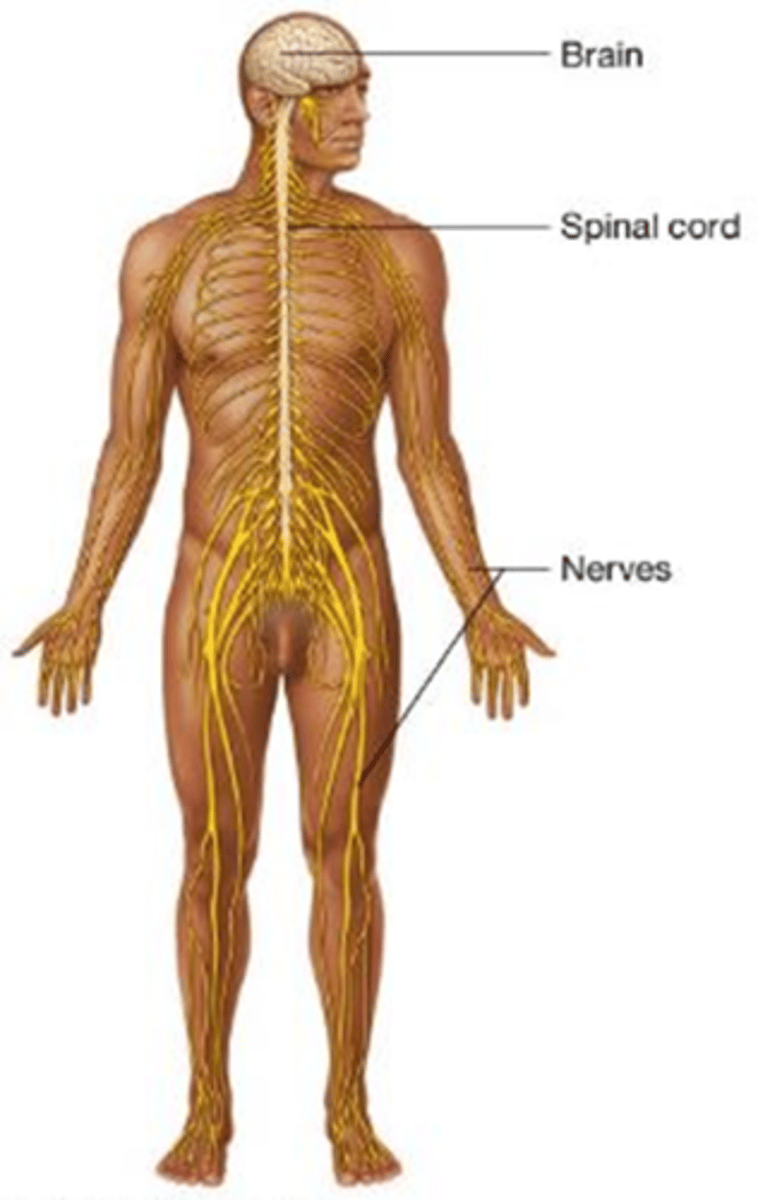
C) Endocrine system
Which body system regulates body functions and the functions of muscles, glands, and tissues using hormones?
A) Nervous system
B) Muscular system
C) Endocrine system
D) Circulatory system
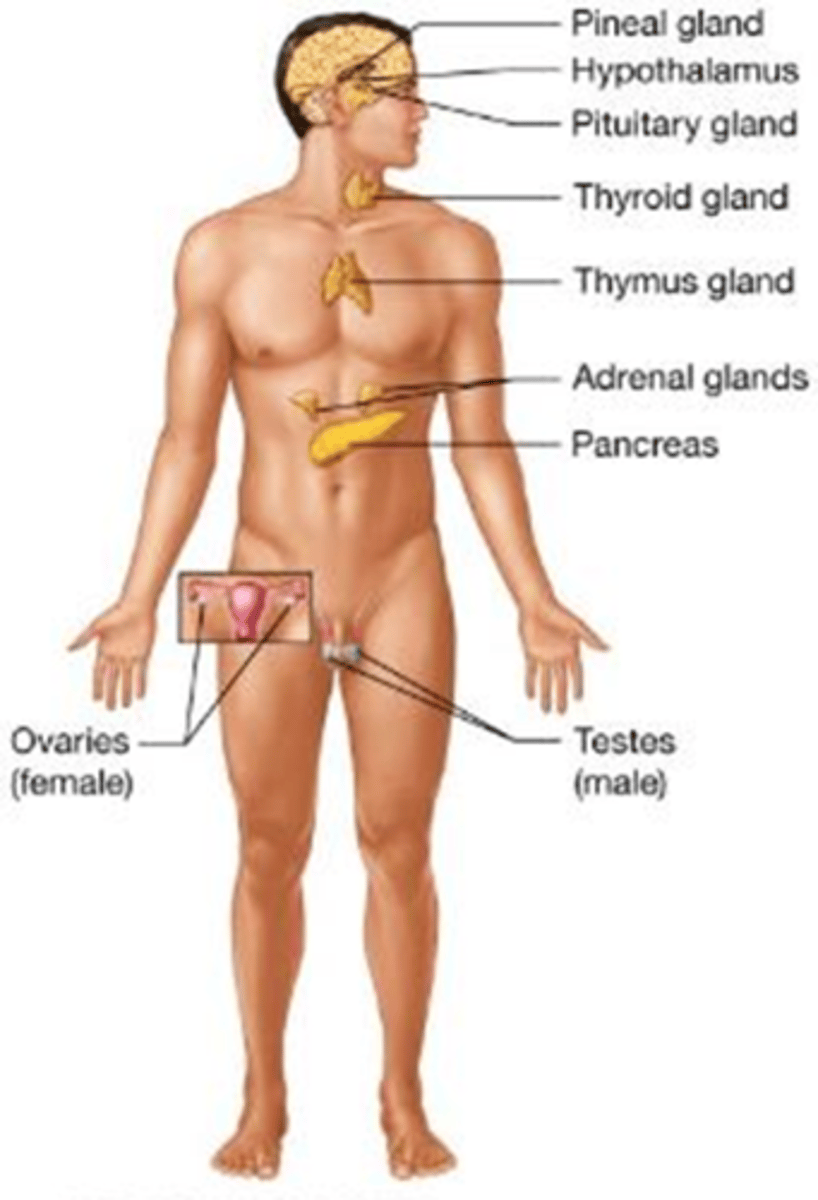
C) Cardiovascular system
Which body system pumps and delivers blood that carries oxygen, nutrients, waste, and other substances?
A) Respiratory system
B) Digestive system
C) Cardiovascular system
D) Lymphatic system
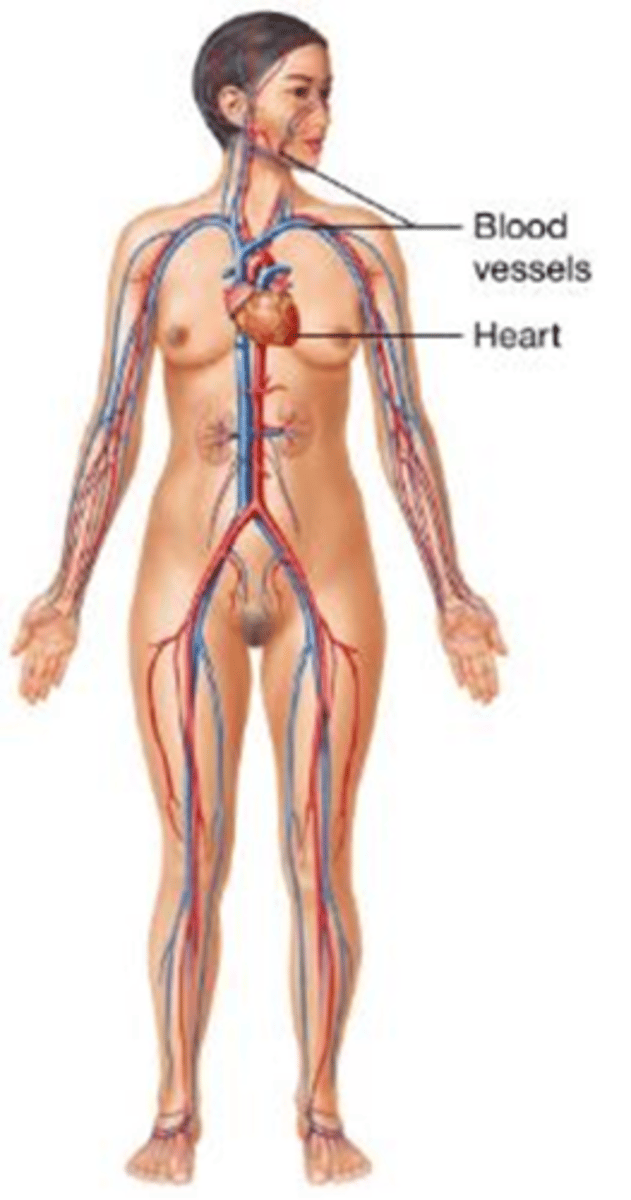
C) Lymphatic system
Which body system returns excess tissue fluid to the cardiovascular system and provides immunity?
A) Urinary system
B) Integumentary system
C) Lymphatic system
D) Endocrine system
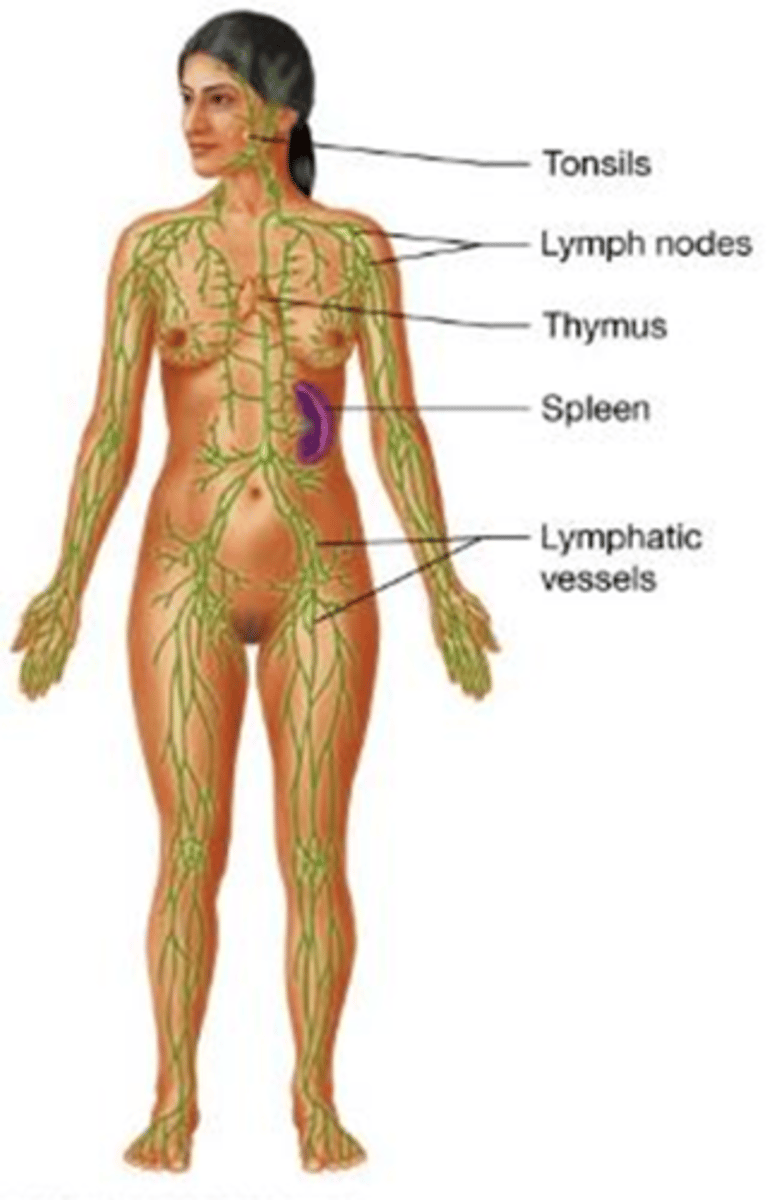
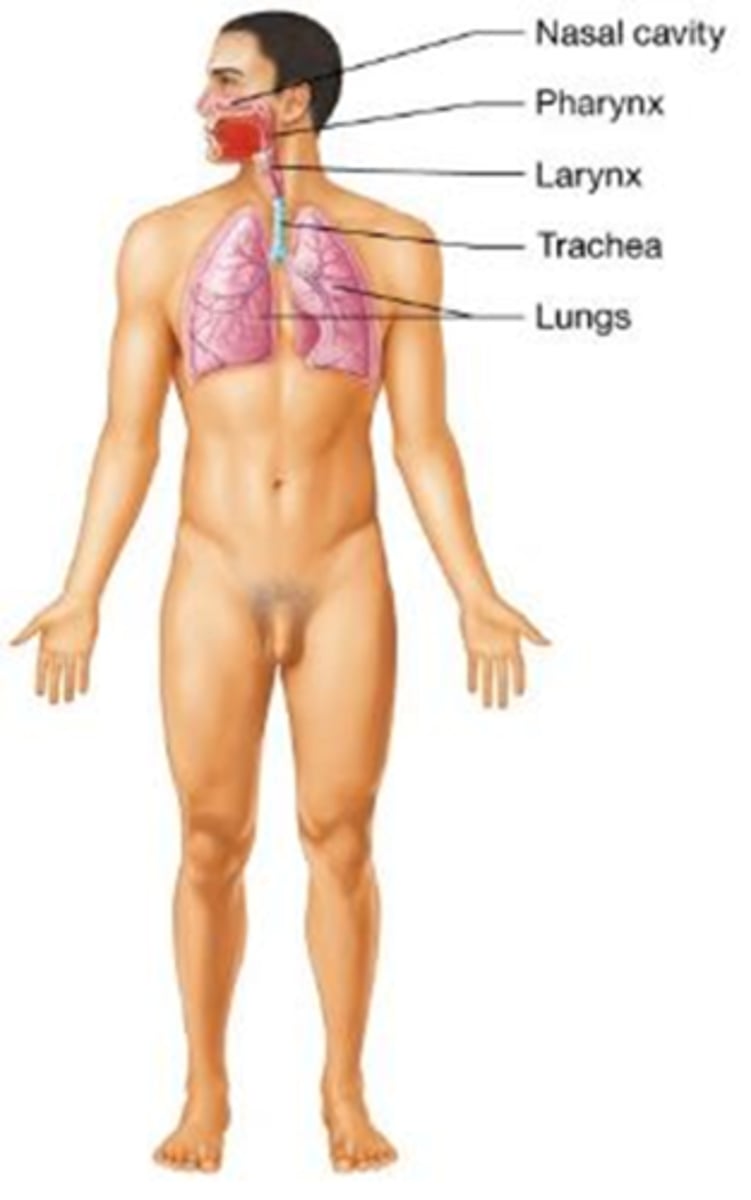
C) Respiratory system
Which body system delivers oxygen to the blood, removes carbon dioxide, and helps maintain the acid/base (pH) balance in the blood?
A) Digestive system
B) Circulatory system
C) Respiratory system
D) Nervous system
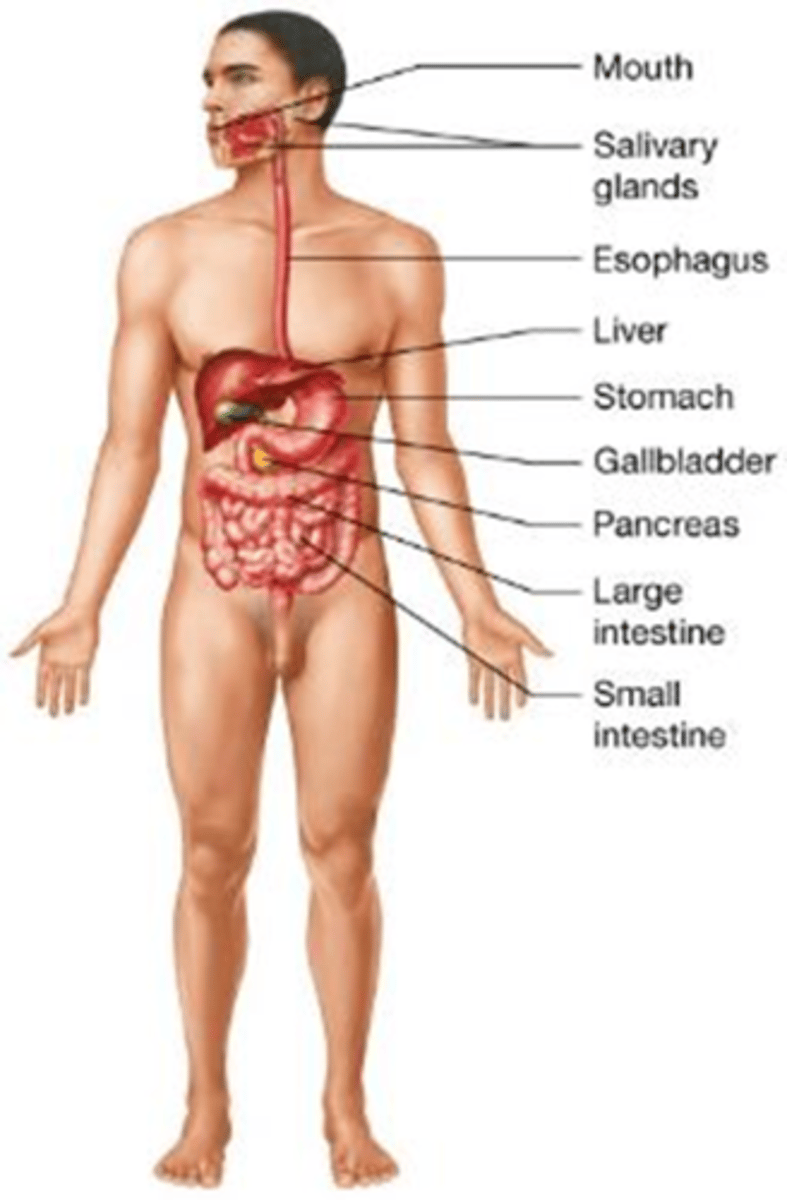
B) Digestive system
Which body system digests food, absorbs nutrients into the blood, removes food waste, and regulates fluid, electrolyte, and pH balance?
A) Urinary system
B) Digestive system
C) Lymphatic system
D) Endocrine system
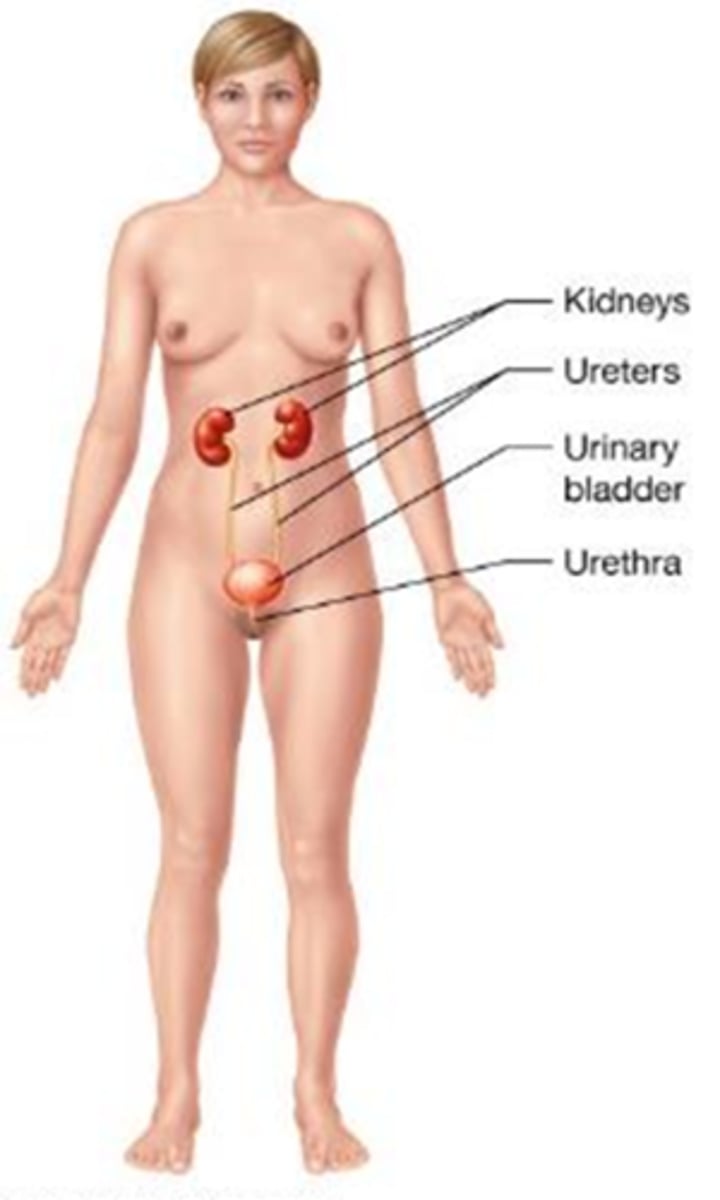
B) Urinary system
Which body system removes metabolic wastes from the blood, regulates fluid, electrolytes, and pH balance, and stimulates blood cell production?
A) Respiratory system
B) Urinary system
C) Digestive system
D) Endocrine system
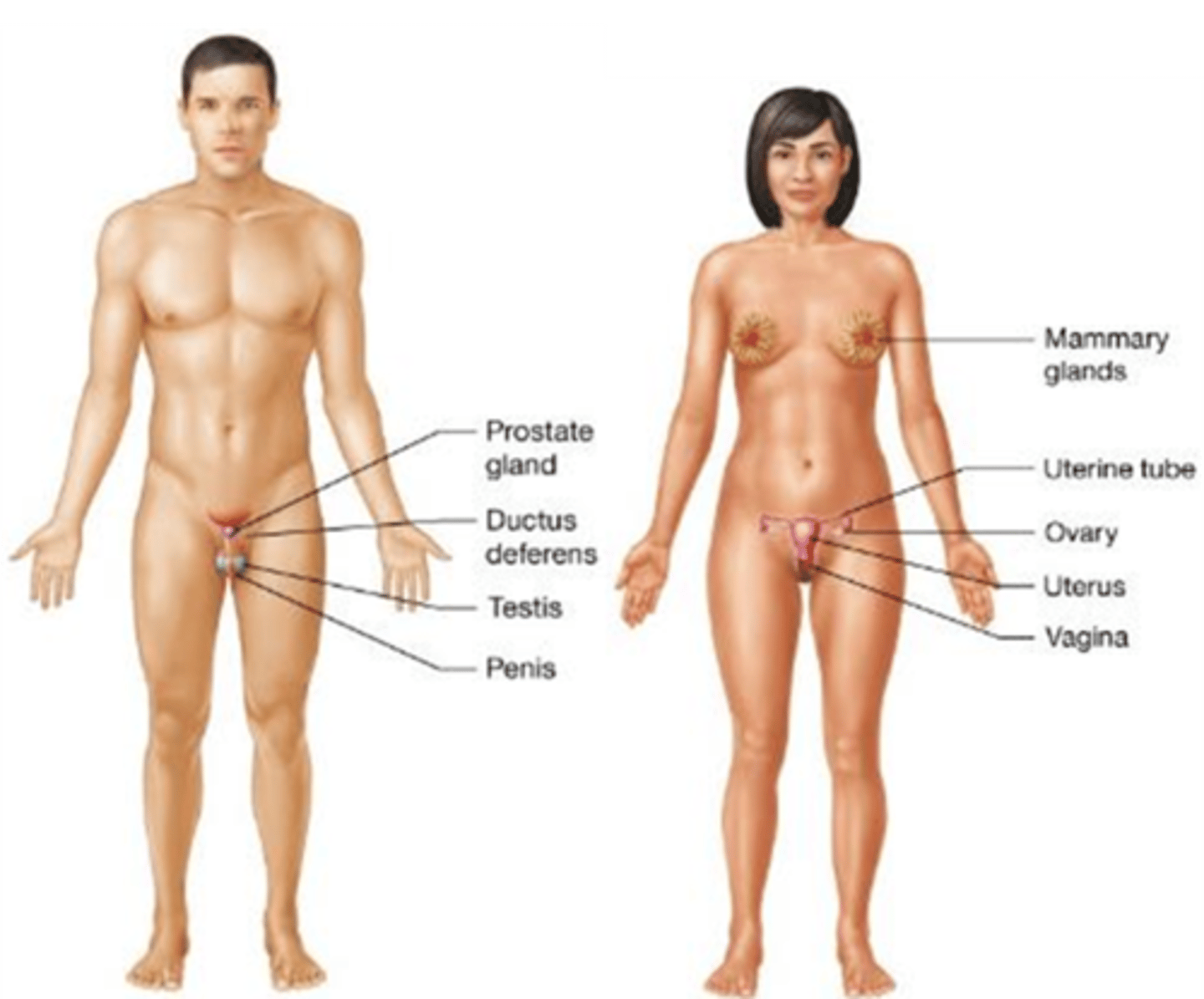
C) Reproductive system
Which body system is used for sexual reproduction, with males producing and transporting sperm and females producing and transporting oocytes, secreting hormones, and supporting fetal development and lactation?
A) Urinary system
B) Endocrine system
C) Reproductive system
D) Nervous system
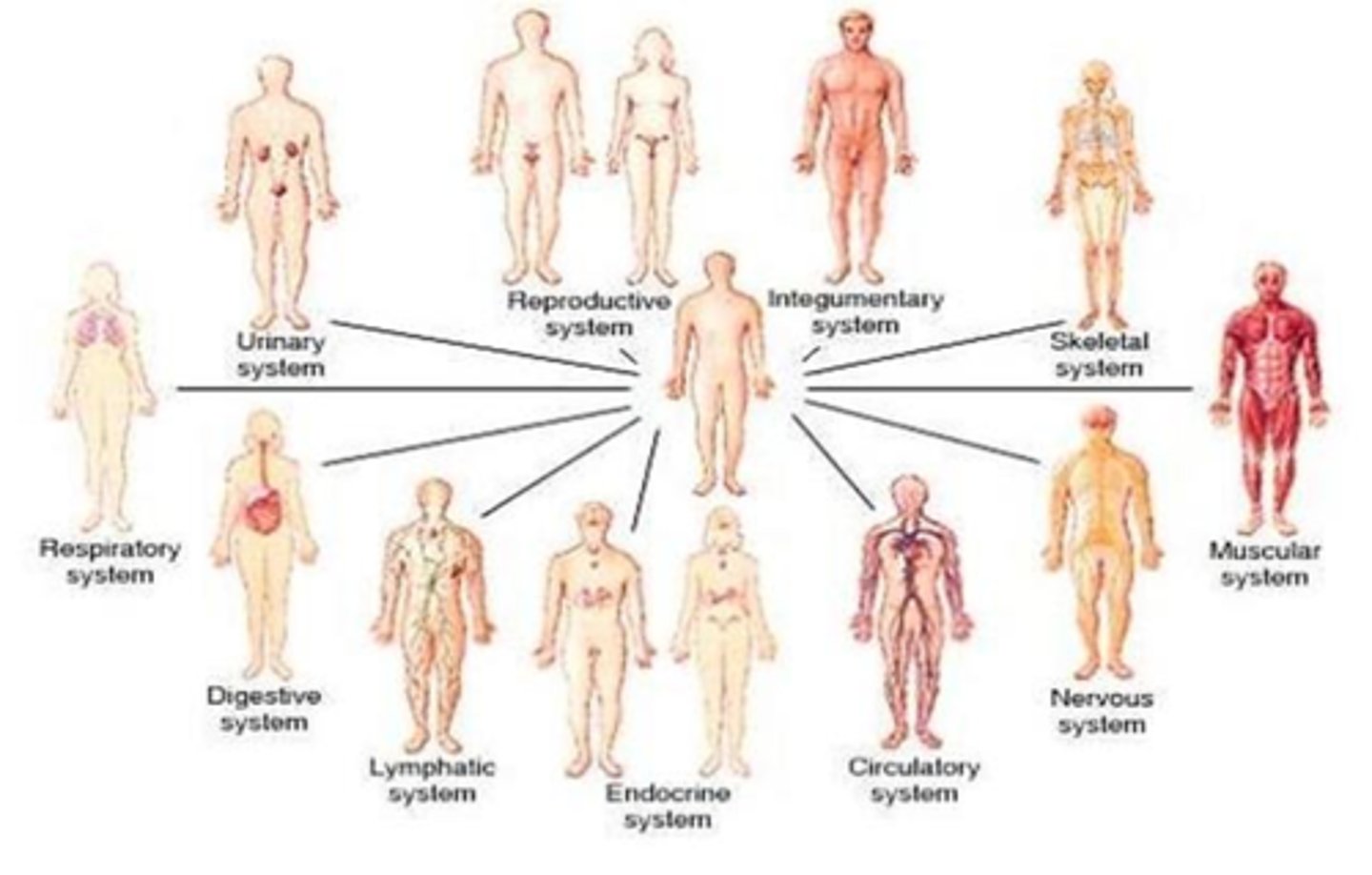
B) Systemic
_____________________ anatomy is the study of the body system by system (our approach).
A) Regional
B) Systemic
C) Surface
D) Microscopic
C) Systemic anatomy
What type of anatomy studies the body system by system, as in our approach?
A) Regional anatomy
B) Surface anatomy
C) Systemic anatomy
D) Microscopic anatomy
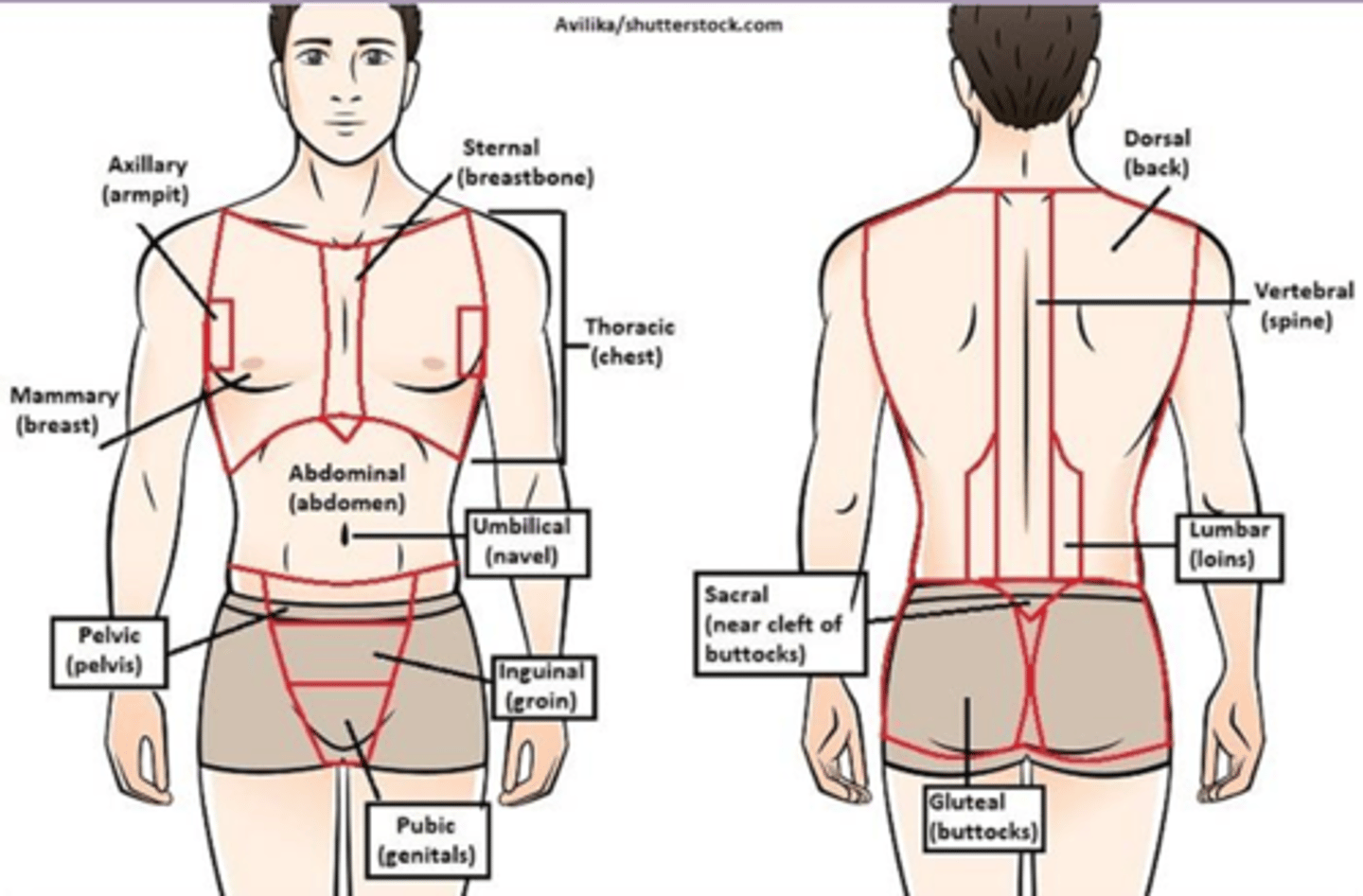
C) Regional
____________________ anatomy divides the body into regions of study.
A) Systemic
B) Surface
C) Regional
D) Microscopic
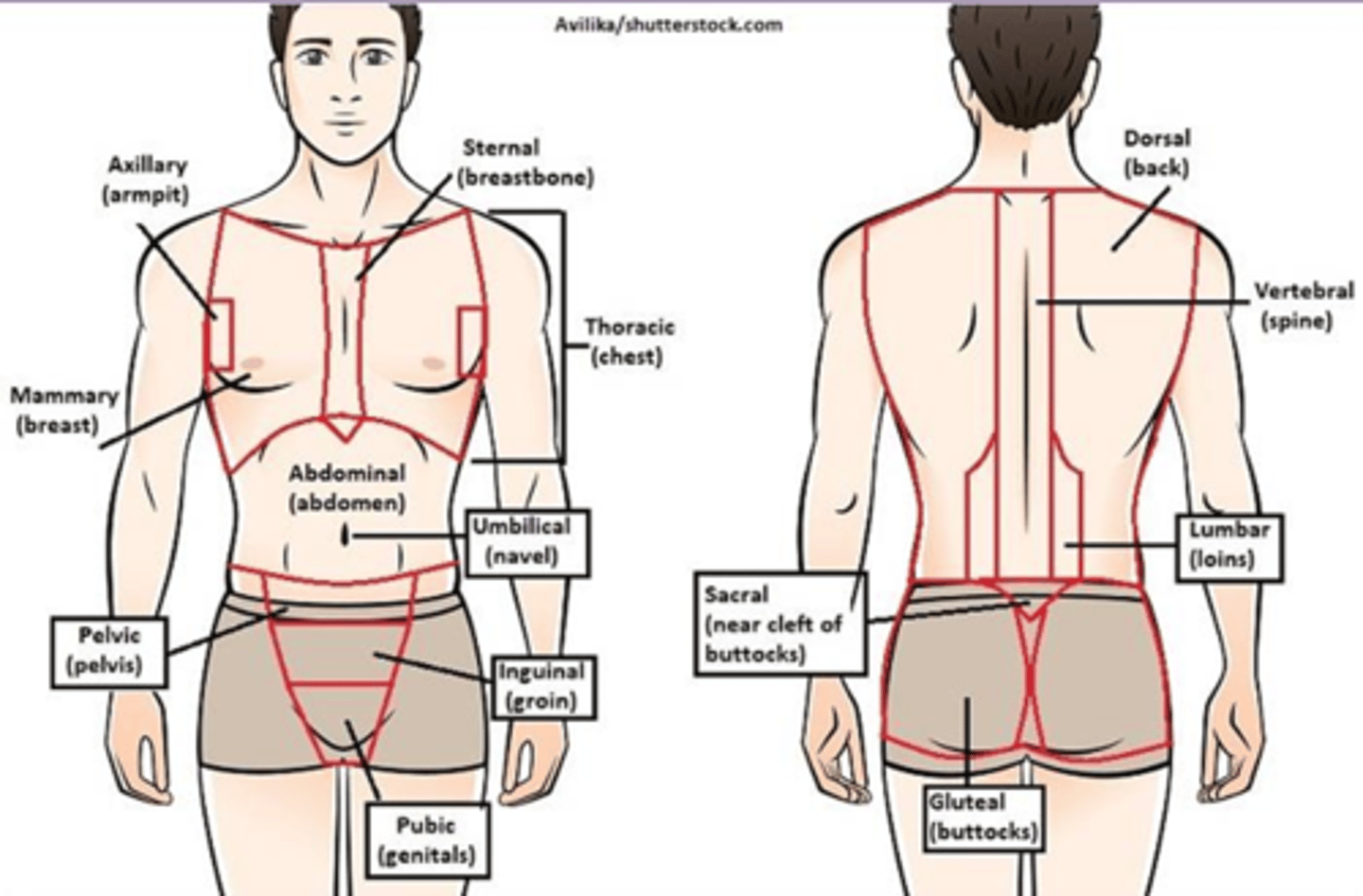
B) Regional anatomy
Which type of anatomy divides the body into regions of study?
A) Systemic anatomy
B) Regional anatomy
C) Surface anatomy
D) Microscopic anatomy
C) Gross
_________________ anatomy examines structures that can be seen with the unaided eye.
A) Microscopic
B) Developmental
C) Gross
D) Histology
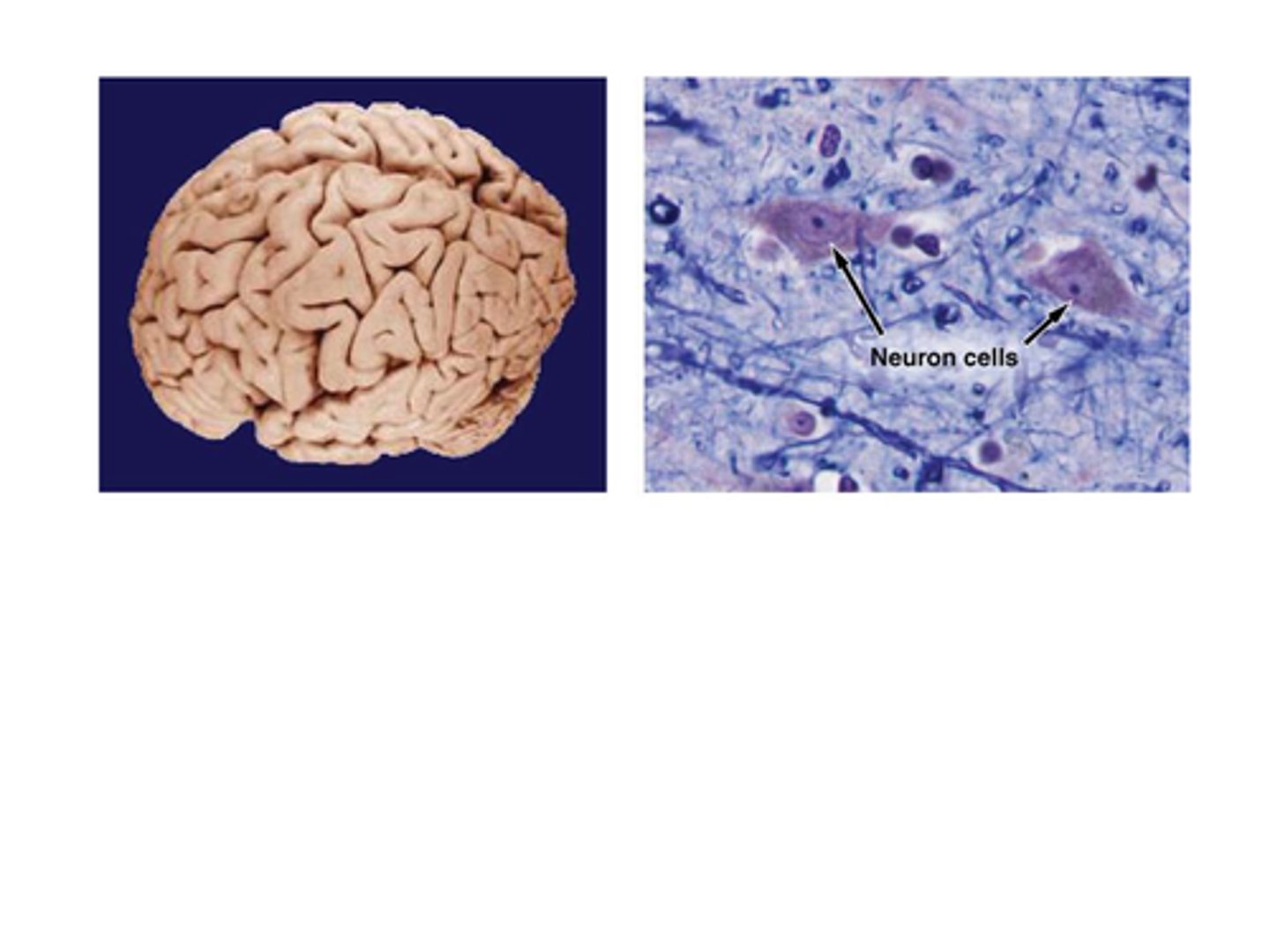
B) Gross anatomy
Which type of anatomy examines structures that can be seen with the unaided eye?
A) Microscopic anatomy
B) Gross anatomy
C) Histology
D) Cytology
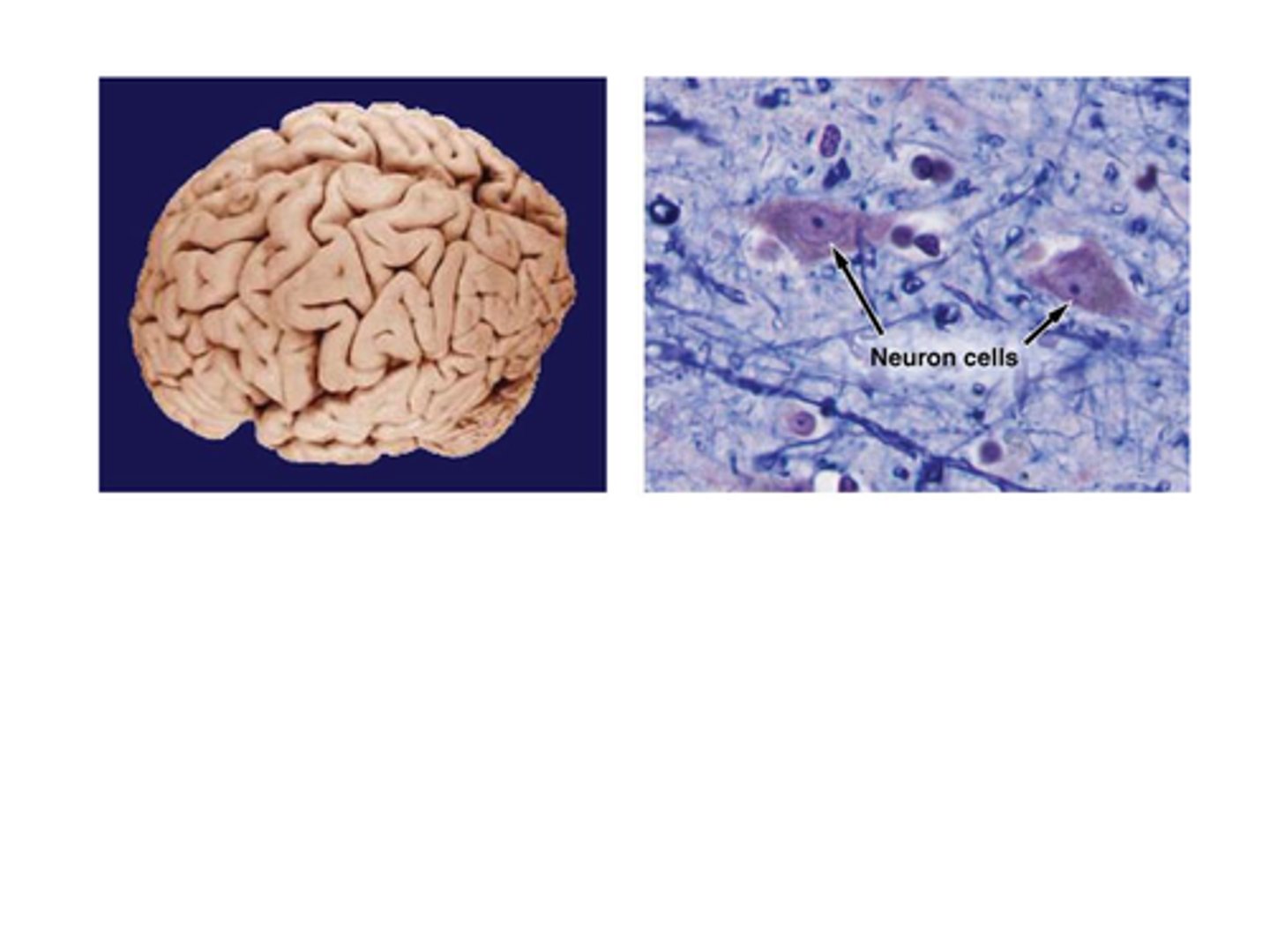
B) Histology
____________________ is the study of tissues.
A) Cytology
B) Histology
C) Anatomy
D) Physiology
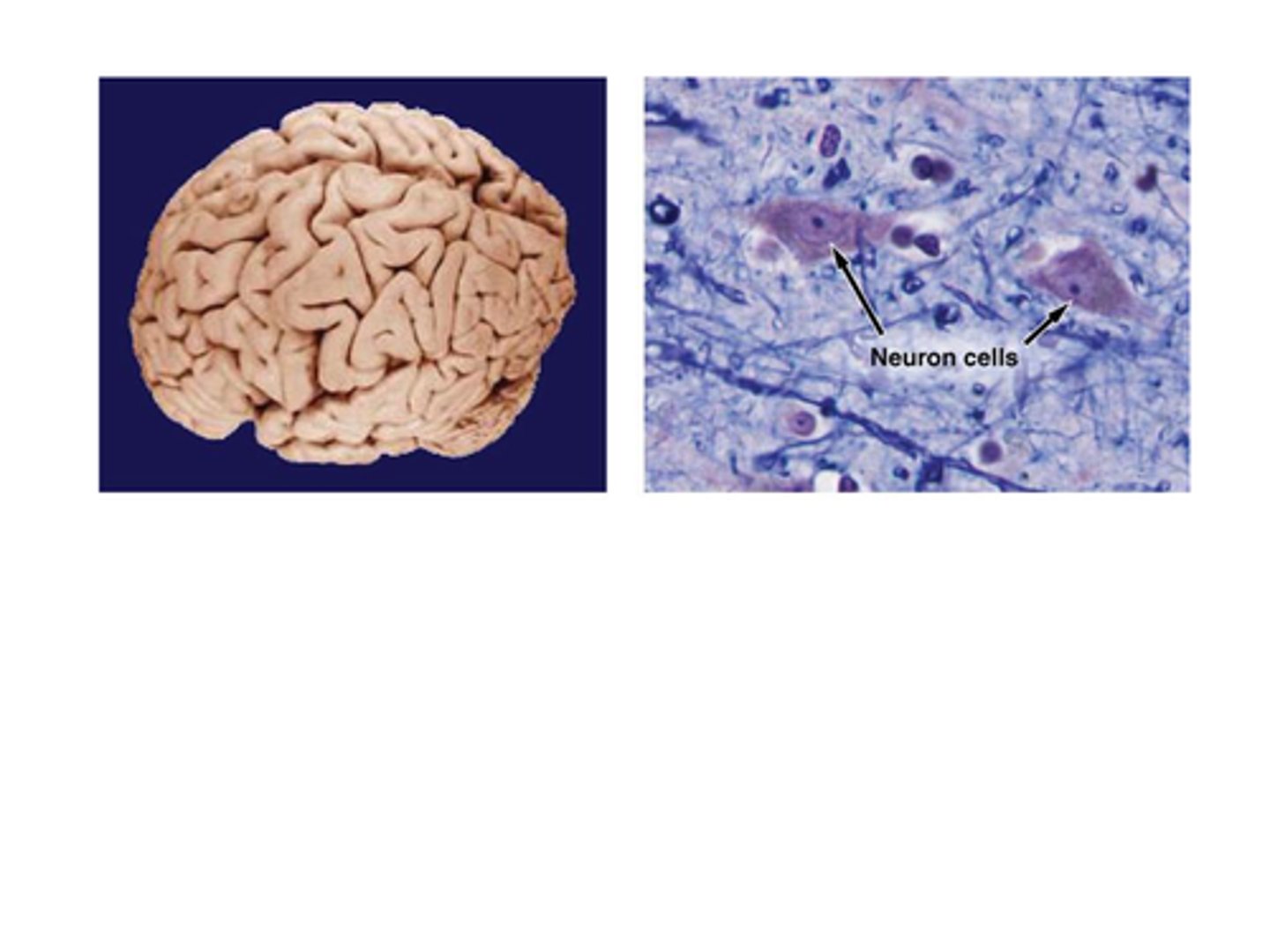
B) Tissues
What is histology the study of?
A) Cells
B) Tissues
C) Organs
D) Systems
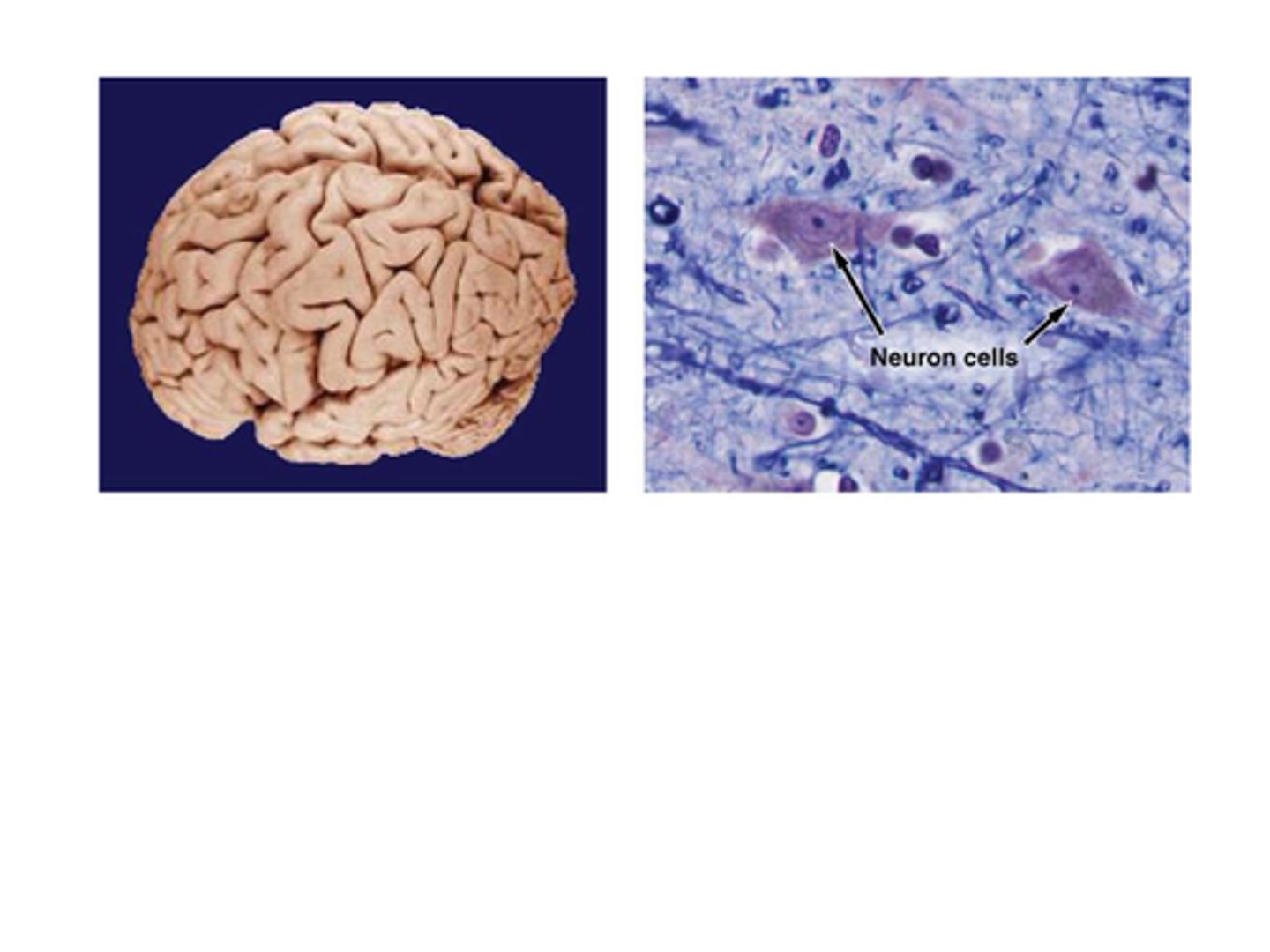
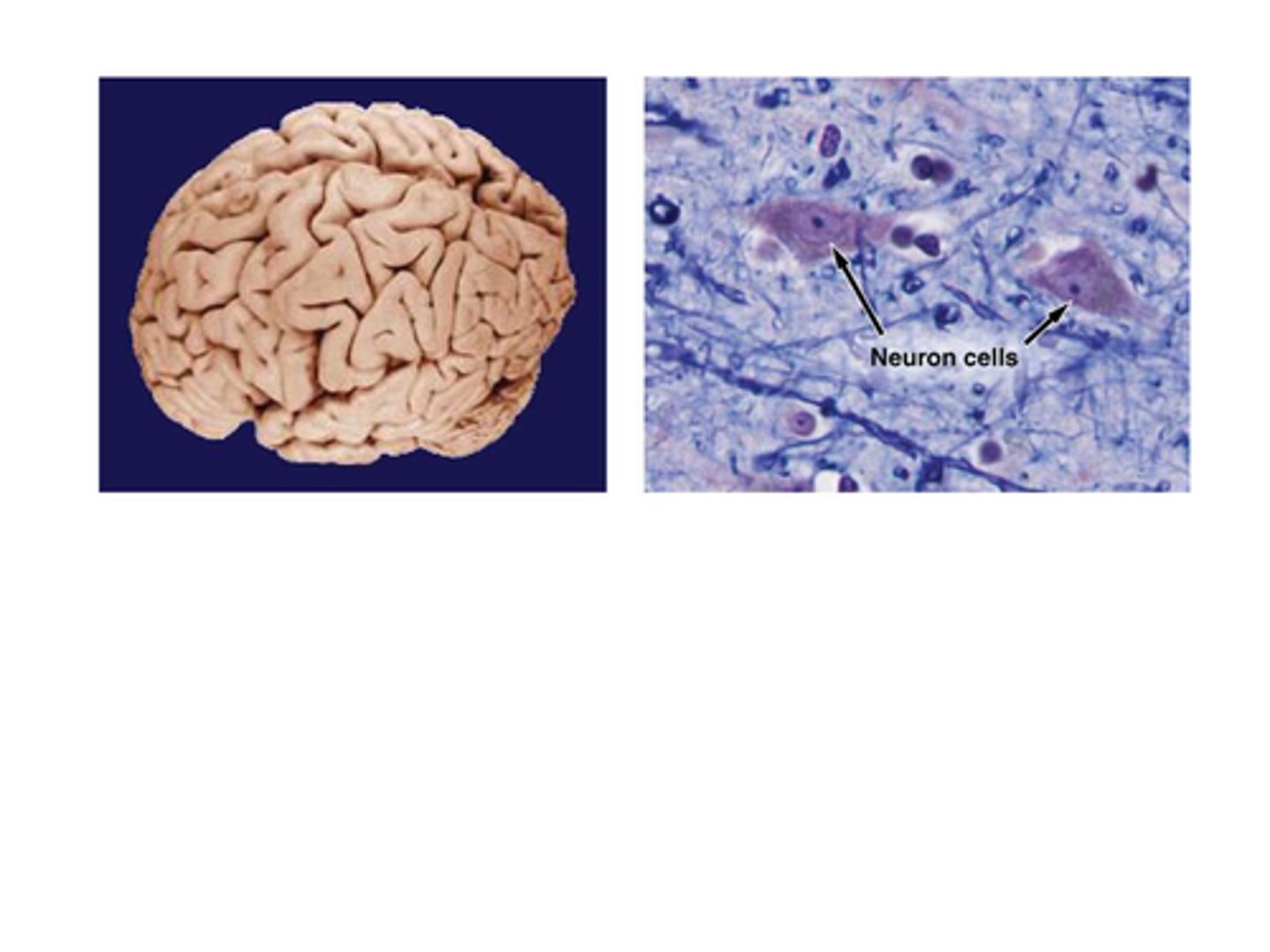
B) Cytology
___________________ is the study of cells.
A) Histology
B) Cytology
C) Anatomy
D) Physiology
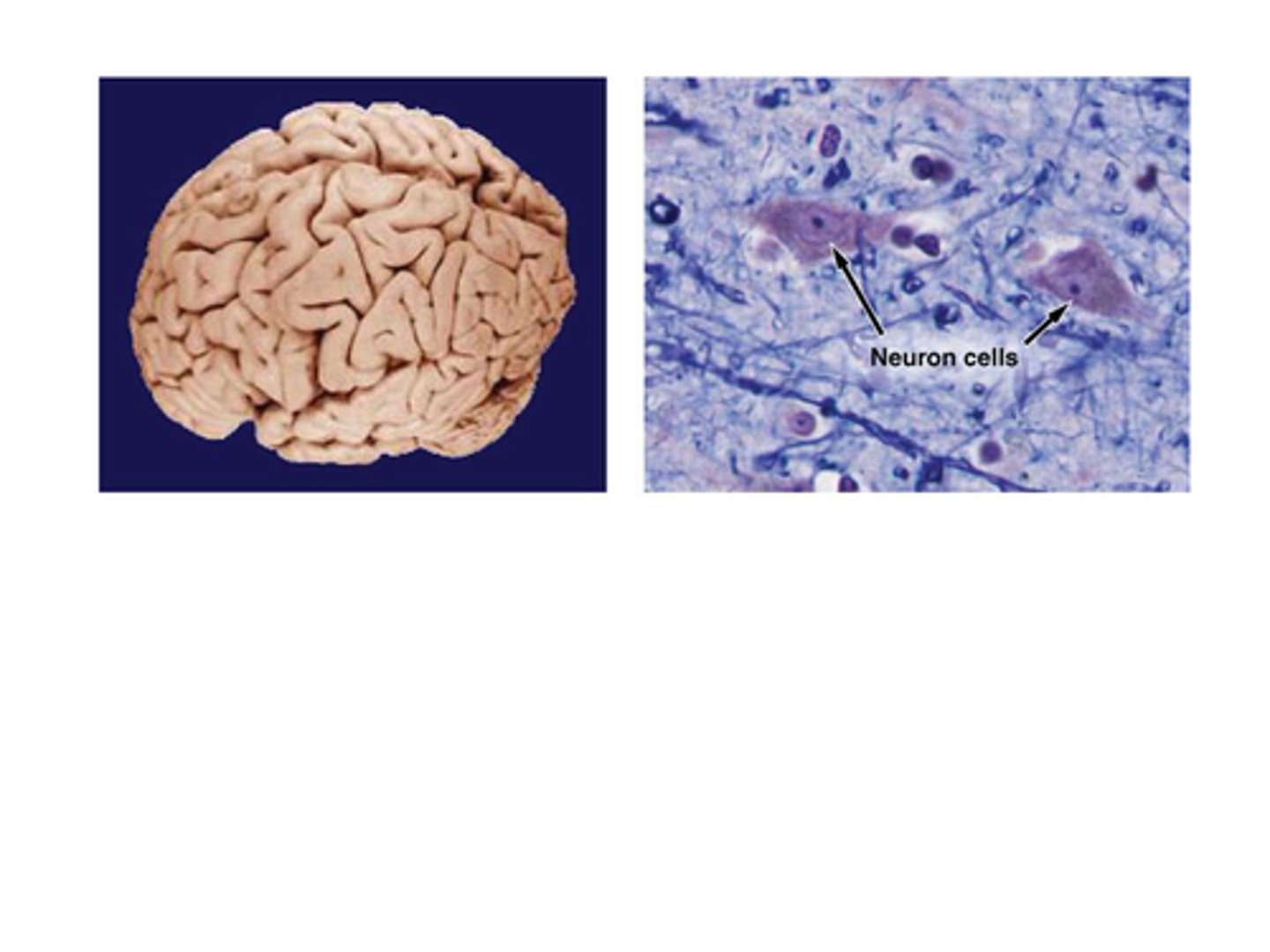
C) Cells
What is cytology the study of?
A) Tissues
B) Organs
C) Cells
D) Systems
B) Surface
____________________ anatomy (external gross anatomy) studies surface markings of the body.
A) Regional
B) Surface
C) Systemic
D) Microscopic
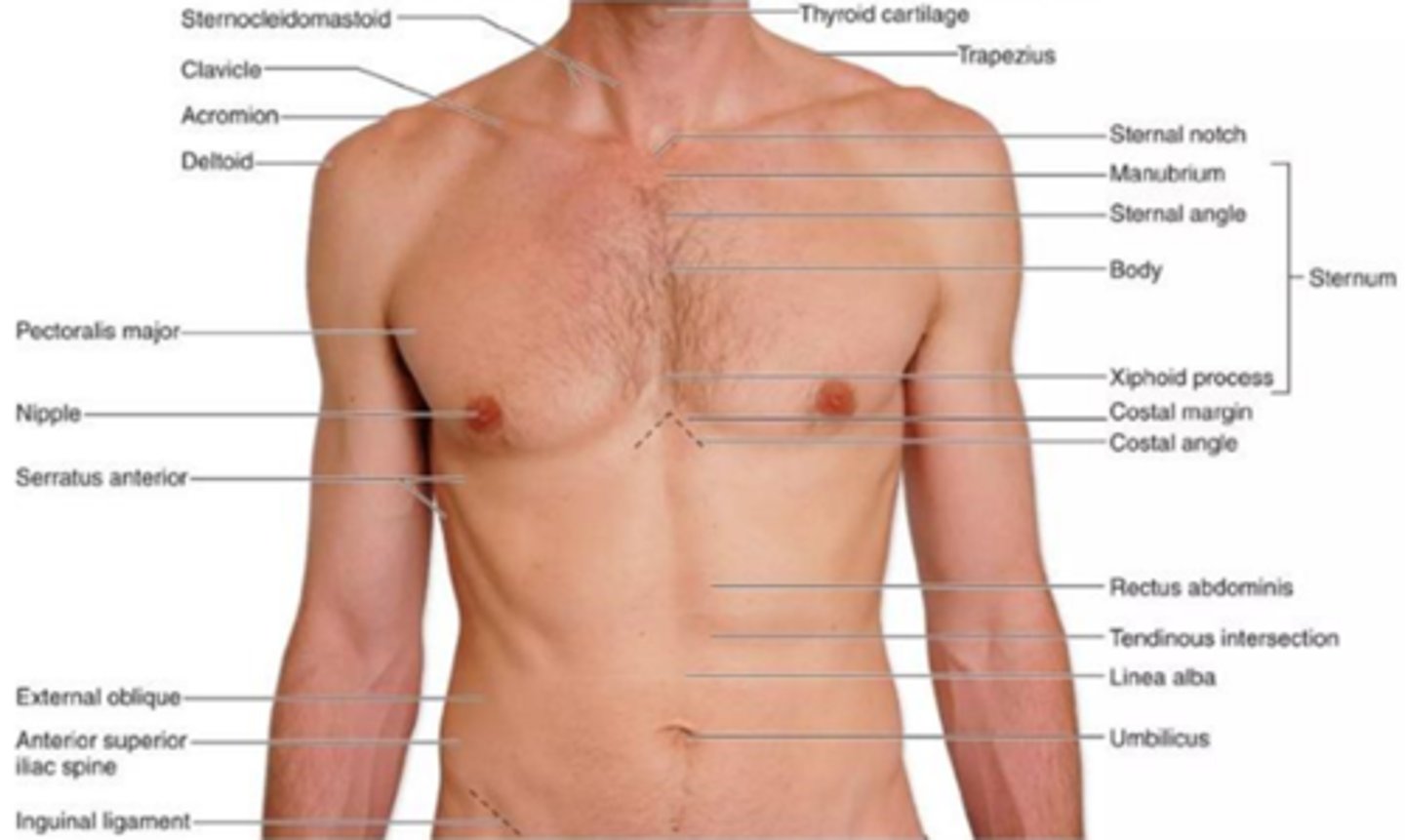
C) Surface anatomy
What type of anatomy studies surface markings of the body and is considered external gross anatomy?
A) Microscopic anatomy
B) Regional anatomy
C) Surface anatomy
D) Systemic anatomy
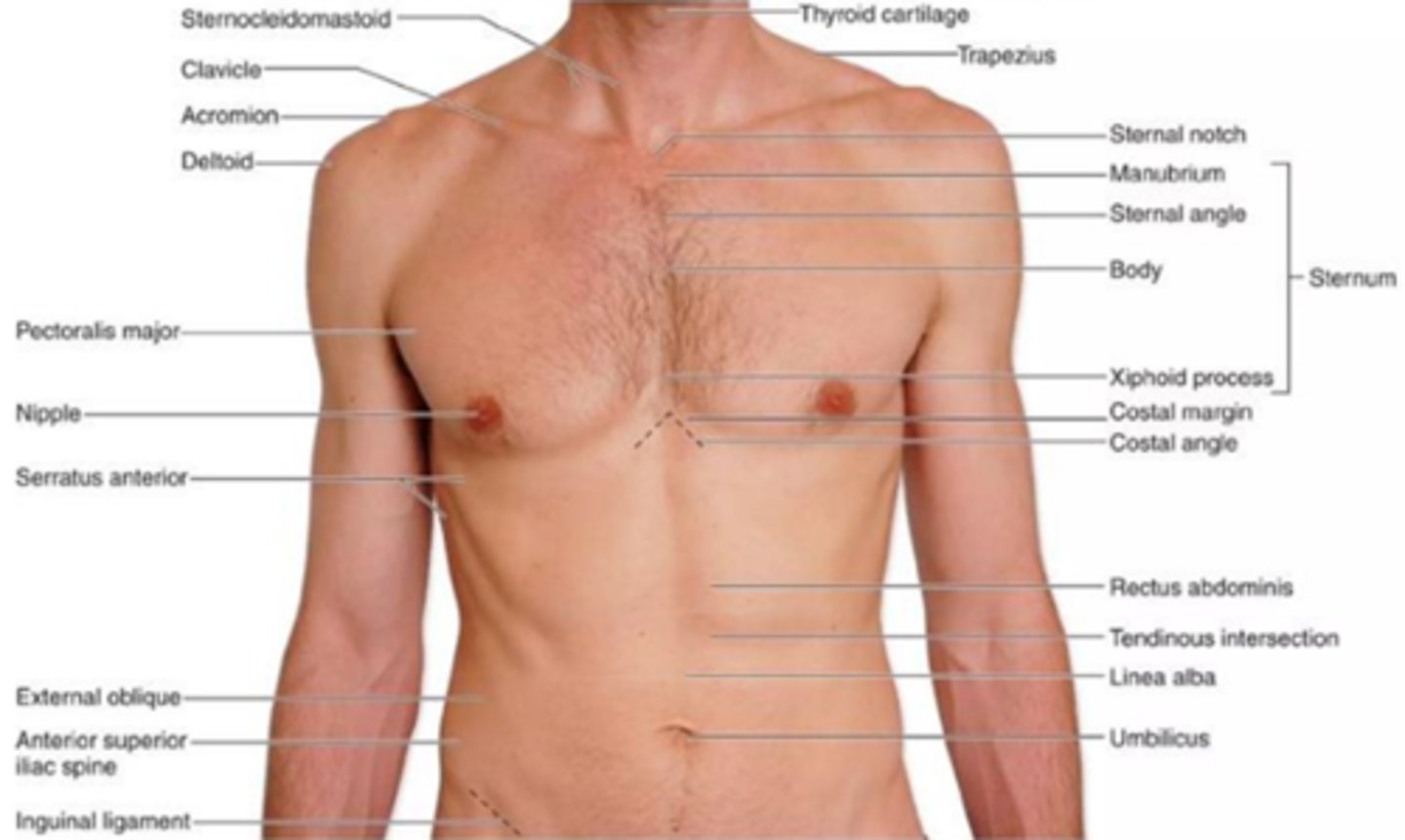

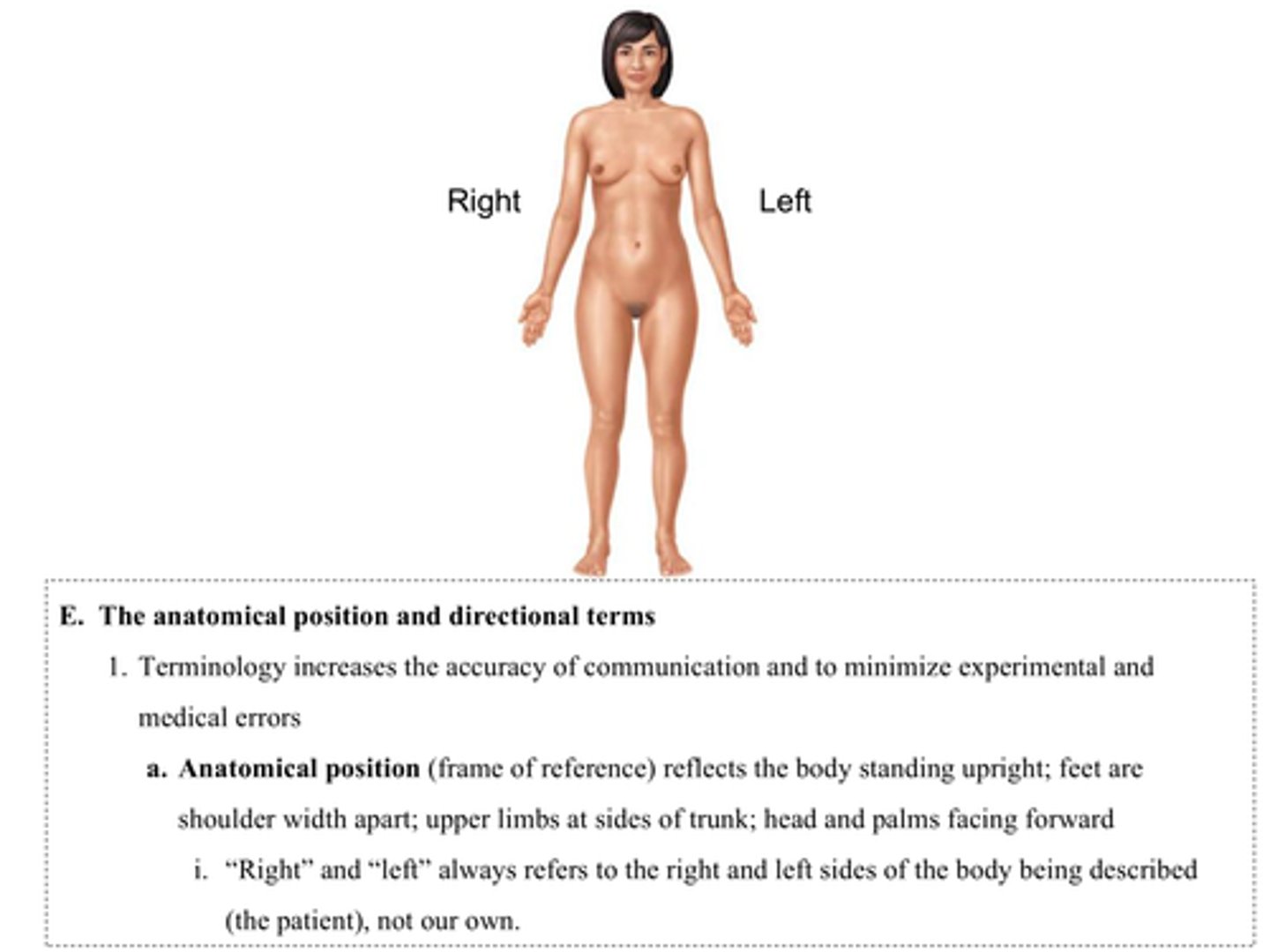
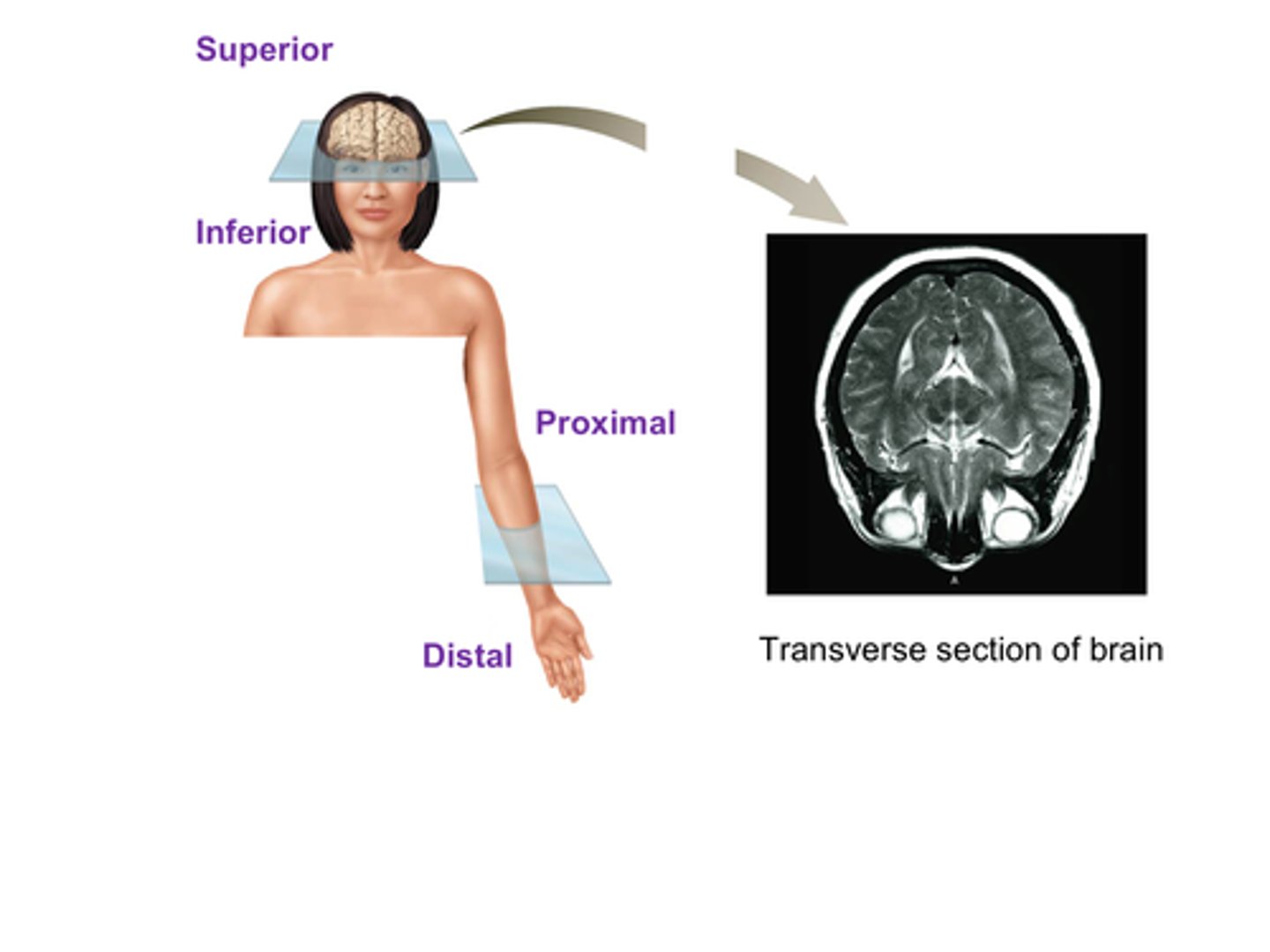
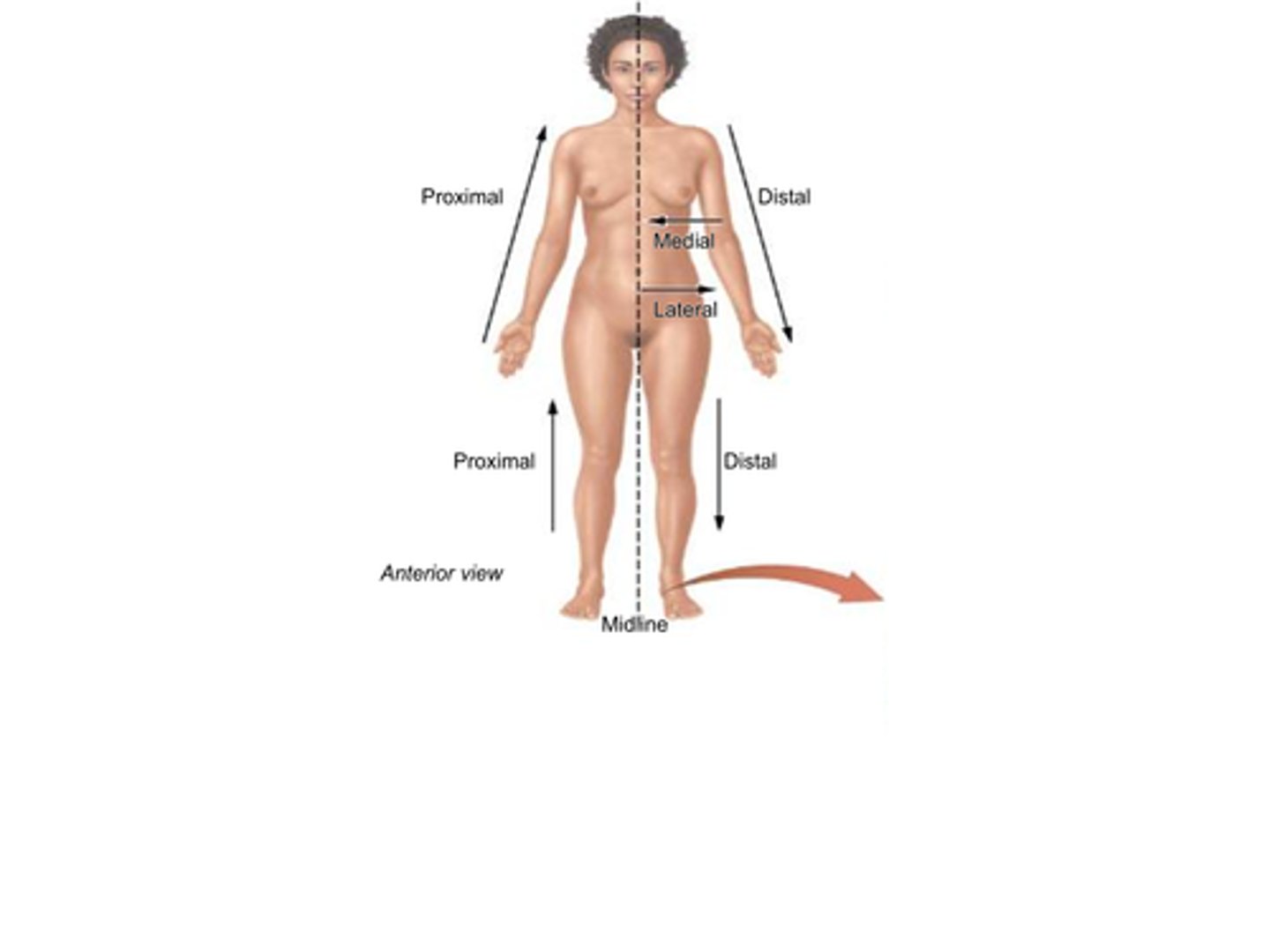
C) Anterior
Which anatomical term refers to the front (ventral) side of the human body?
A) Posterior
B) Dorsal
C) Anterior
D) Superior
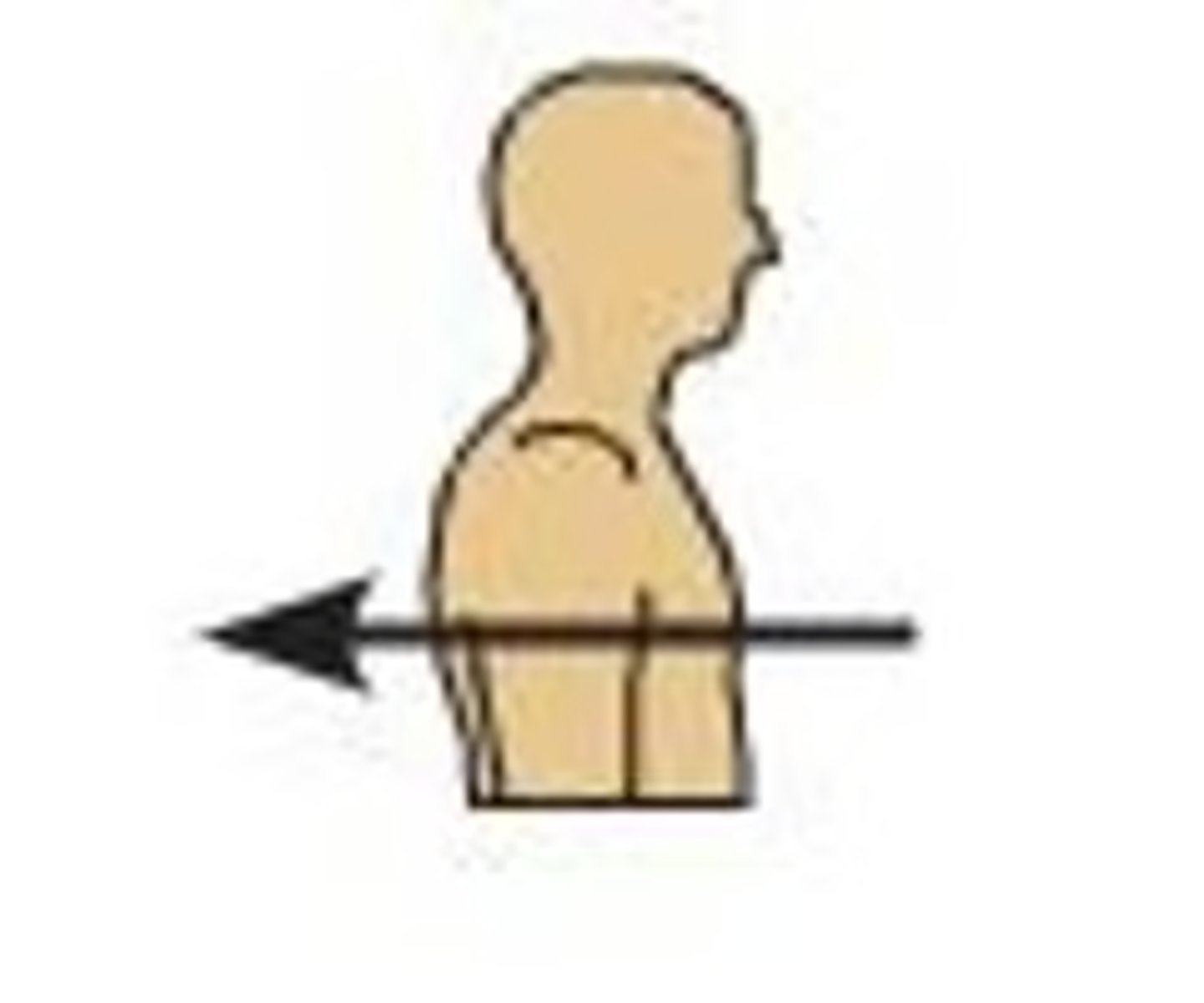
C) Posterior
Which anatomical term refers to the back (dorsal) side of the body?
A) Anterior
B) Superior
C) Posterior
D) Inferior
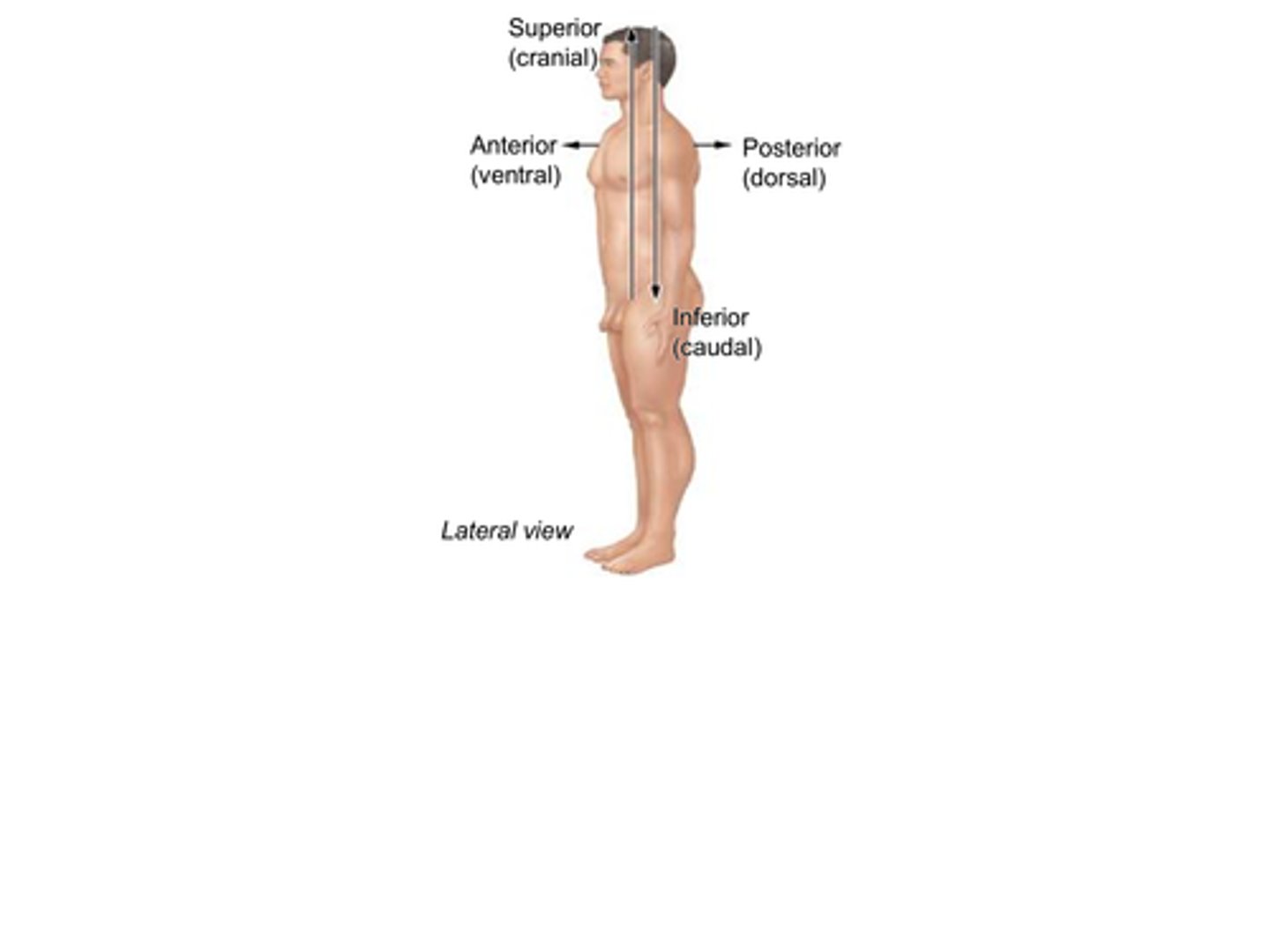
C) Superior
Which anatomical term means "toward the head" and is also known as cranial?
A) Inferior
B) Posterior
C) Superior
D) Anterior
C) Posterior
What anatomical term refers to the back side of the body and is also known as dorsal?
A) Superior
B) Anterior
C) Posterior
D) Inferior
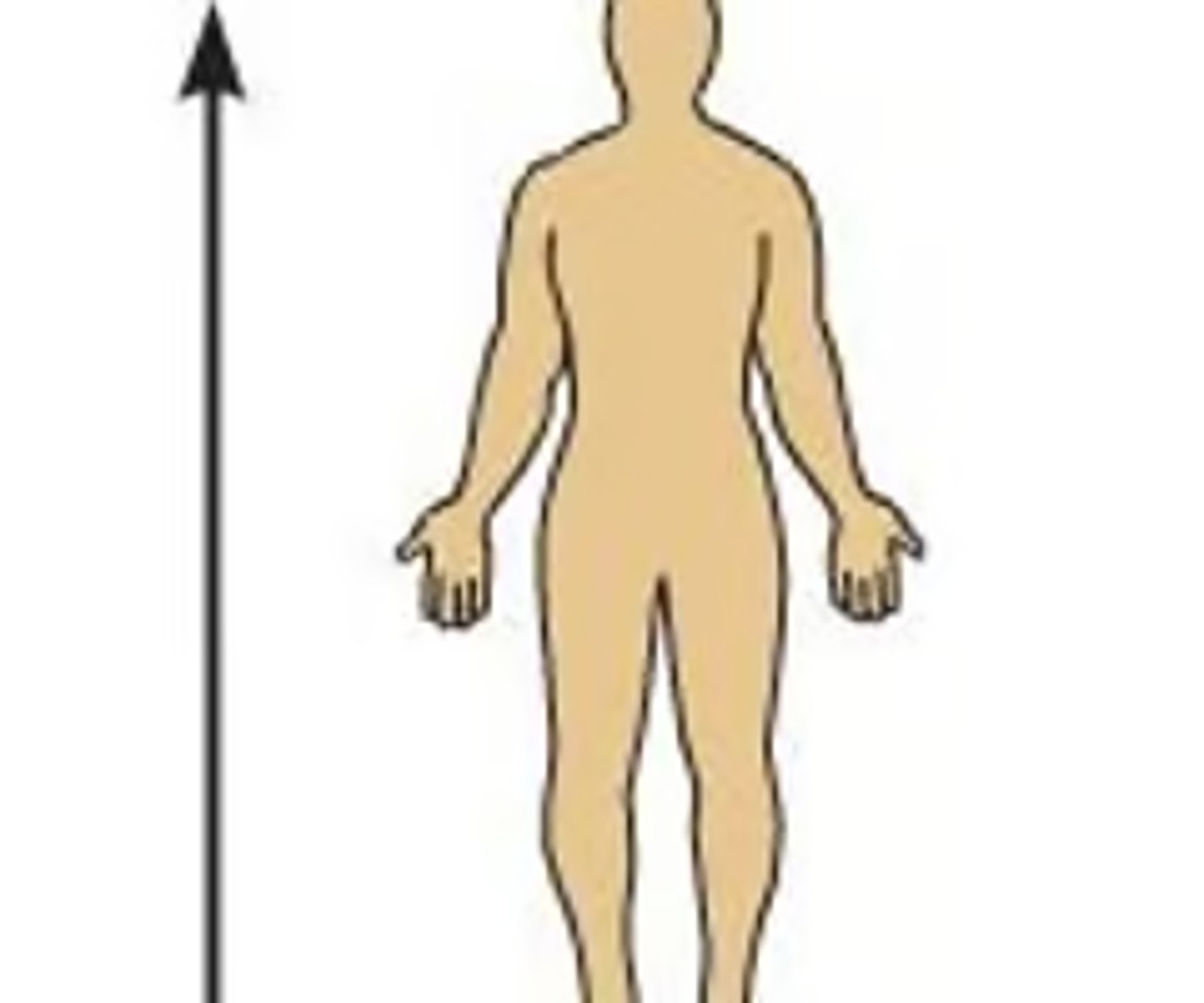
B) Toward the head
What does the anatomical term superior (cranial) mean?
A) Toward the feet
B) Toward the head
C) Toward the front
D) Toward the back
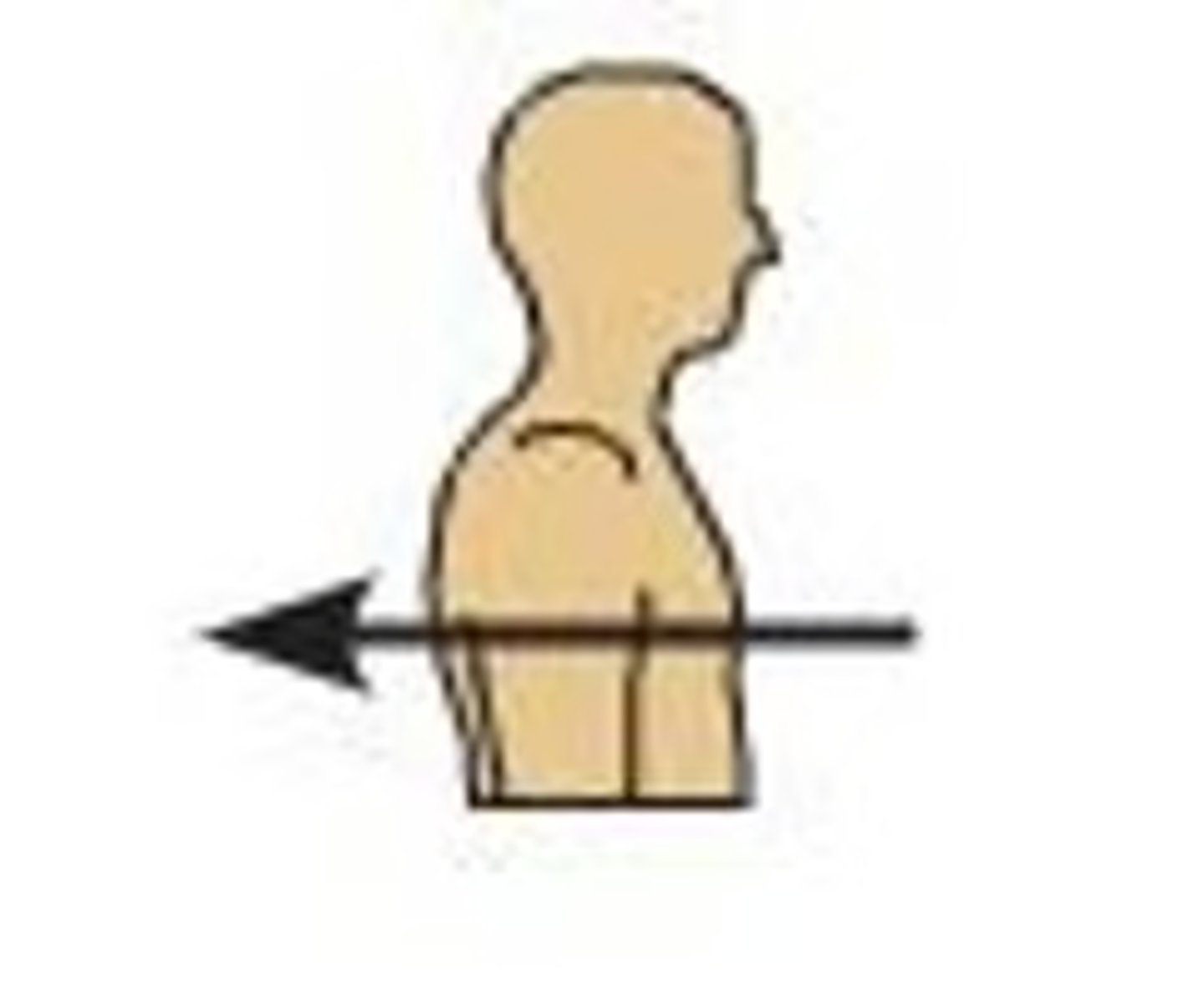
D) Inferior
Which anatomical term refers to "toward the tail" and is also known as caudal?
A) Superior
B) Anterior
C) Posterior
D) Inferior
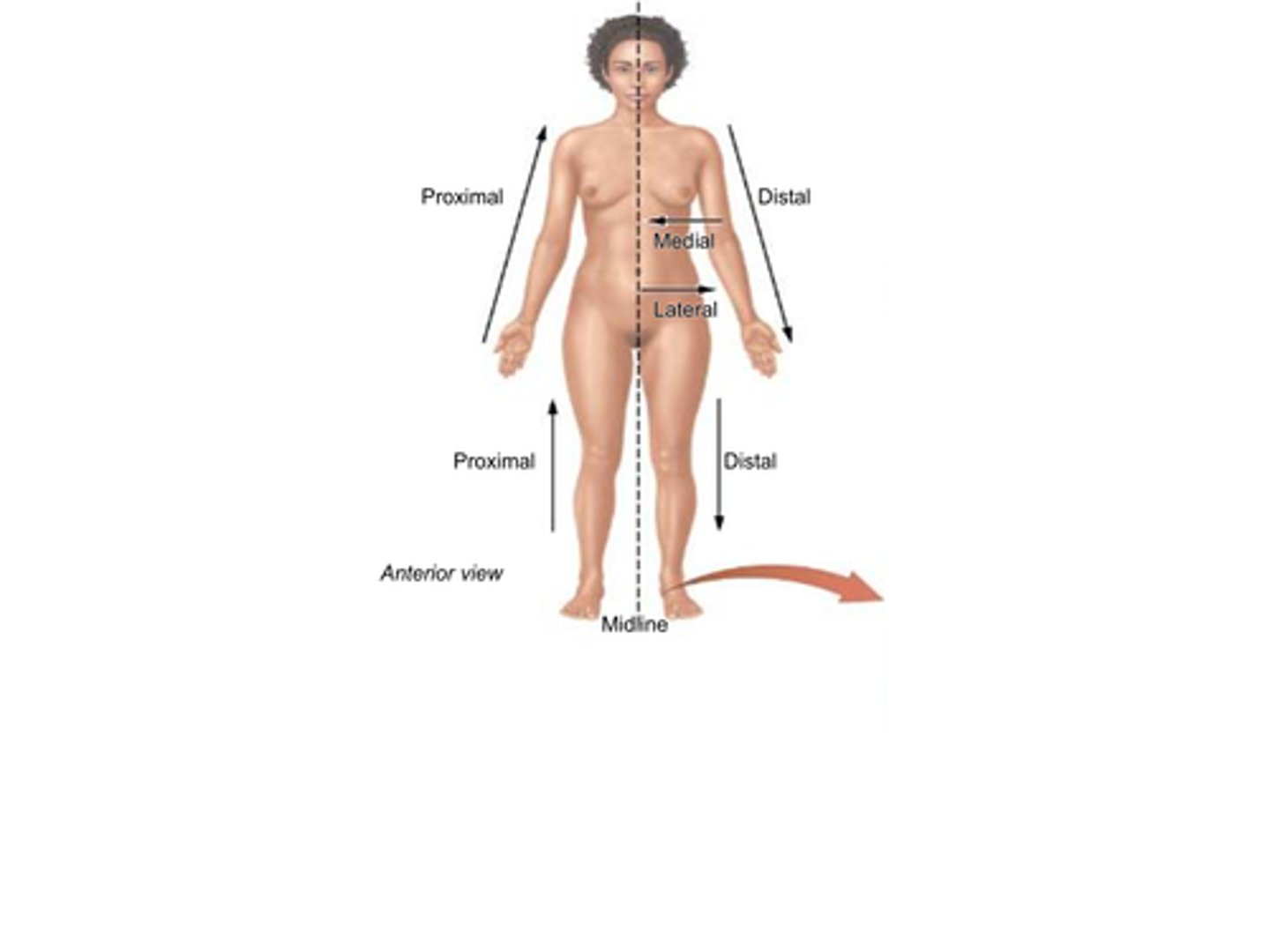
B) Proximal
Which term refers to something being closer to the point of origin?
A) Distal
B) Proximal
C) Superior
D) Lateral
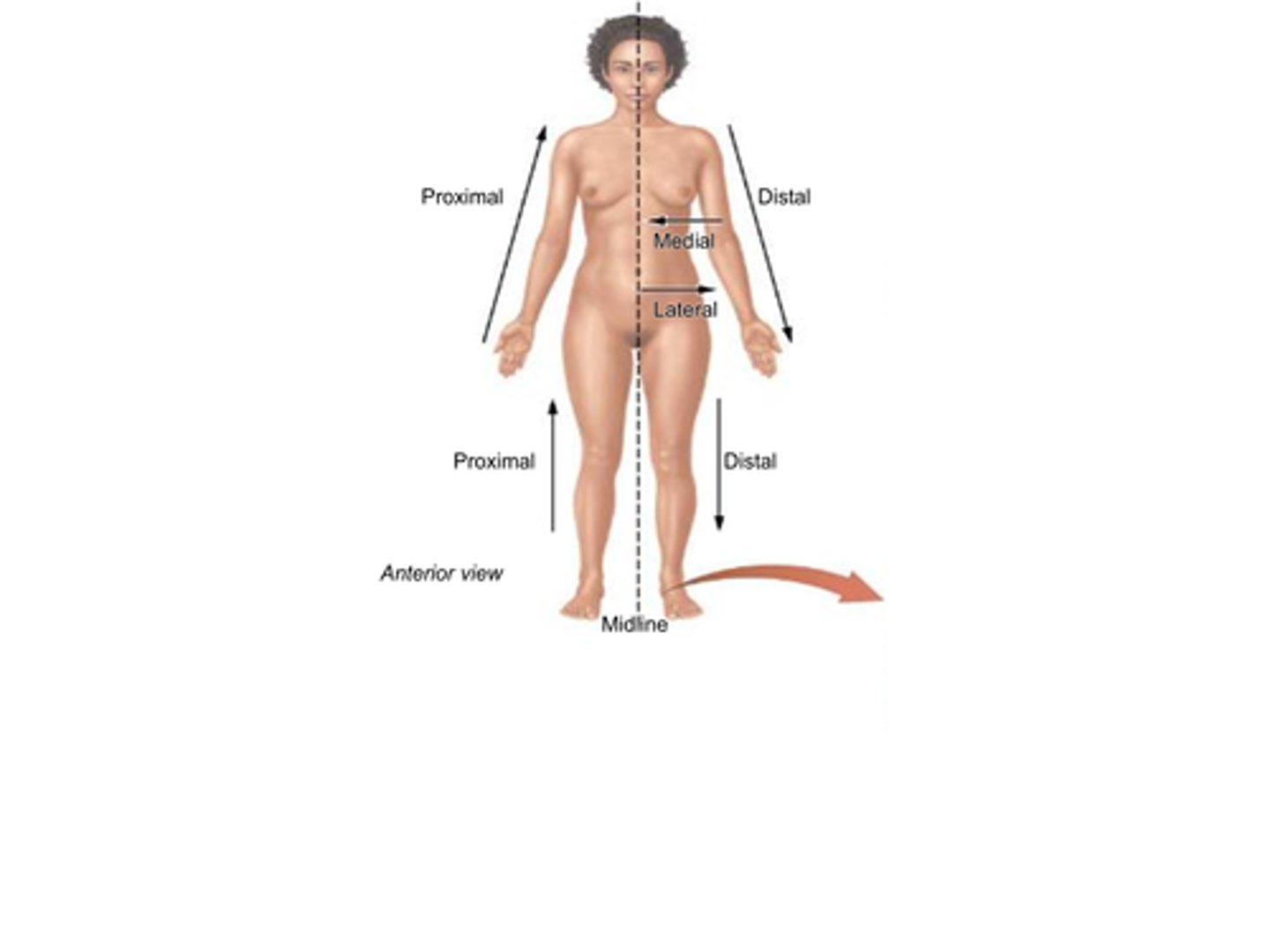
B) Closer to the point of origin
What does the term proximal mean?
A) Farther from the point of origin
B) Closer to the point of origin
C) Toward the front of the body
D) Toward the back of the body
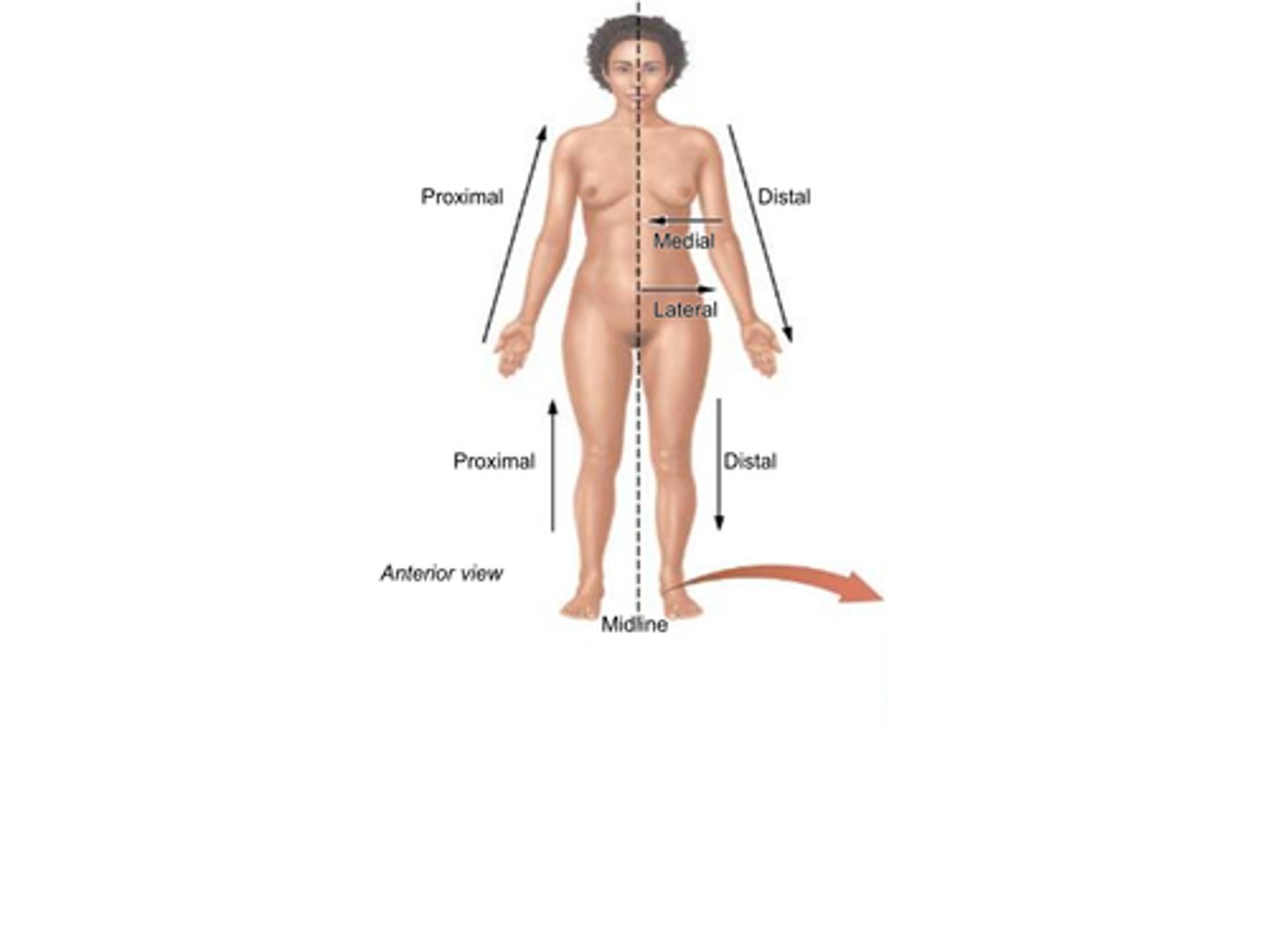
B) Distal
Which term refers to being further (distant) from the point of origin?
A) Proximal
B) Distal
C) Superior
D) Medial
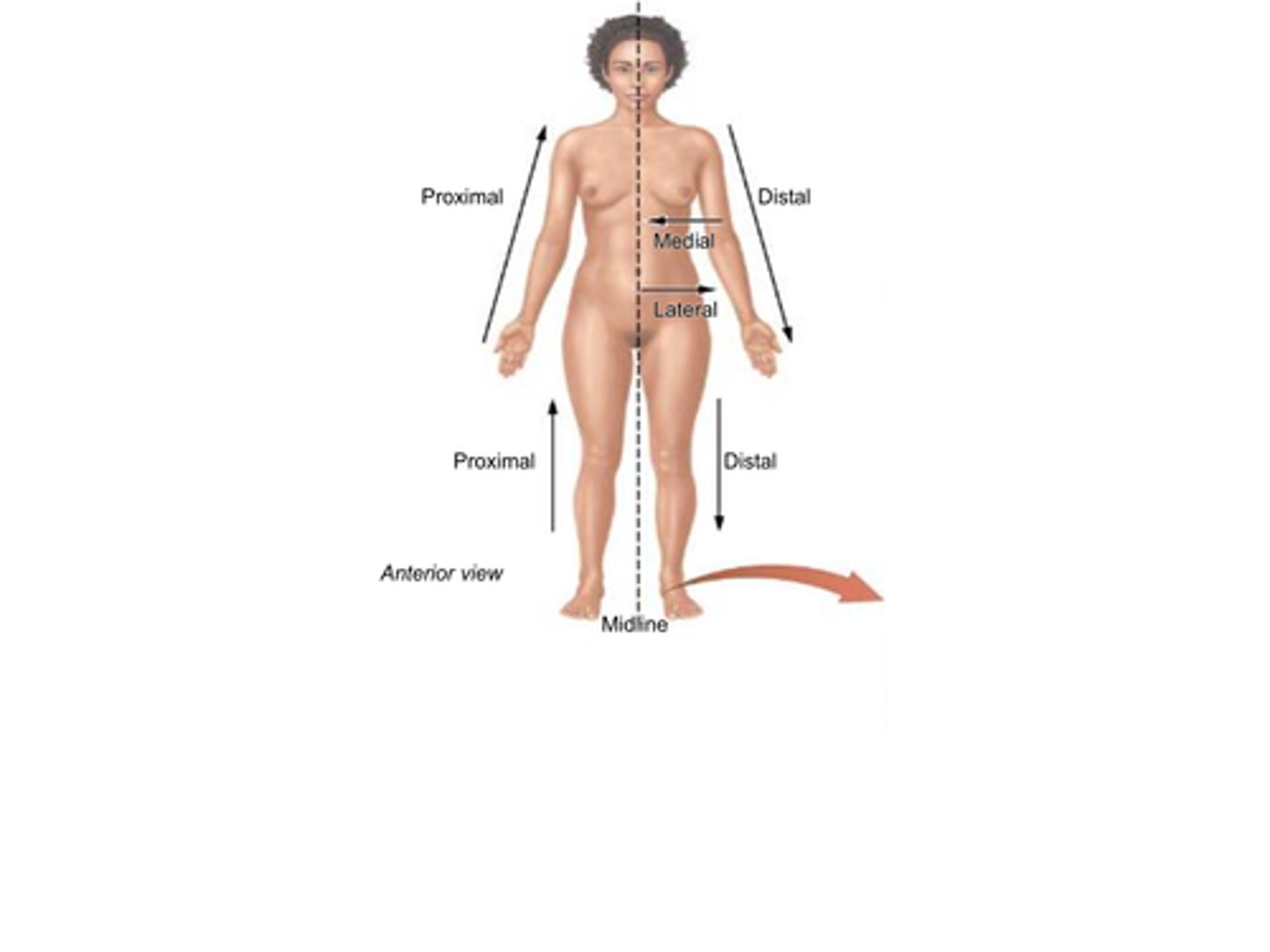
B) Further (distant) from the point of origin
What does the term distal mean?
A) Closer to the point of origin
B) Further (distant) from the point of origin
C) Toward the front of the body
D) Toward the back of the body
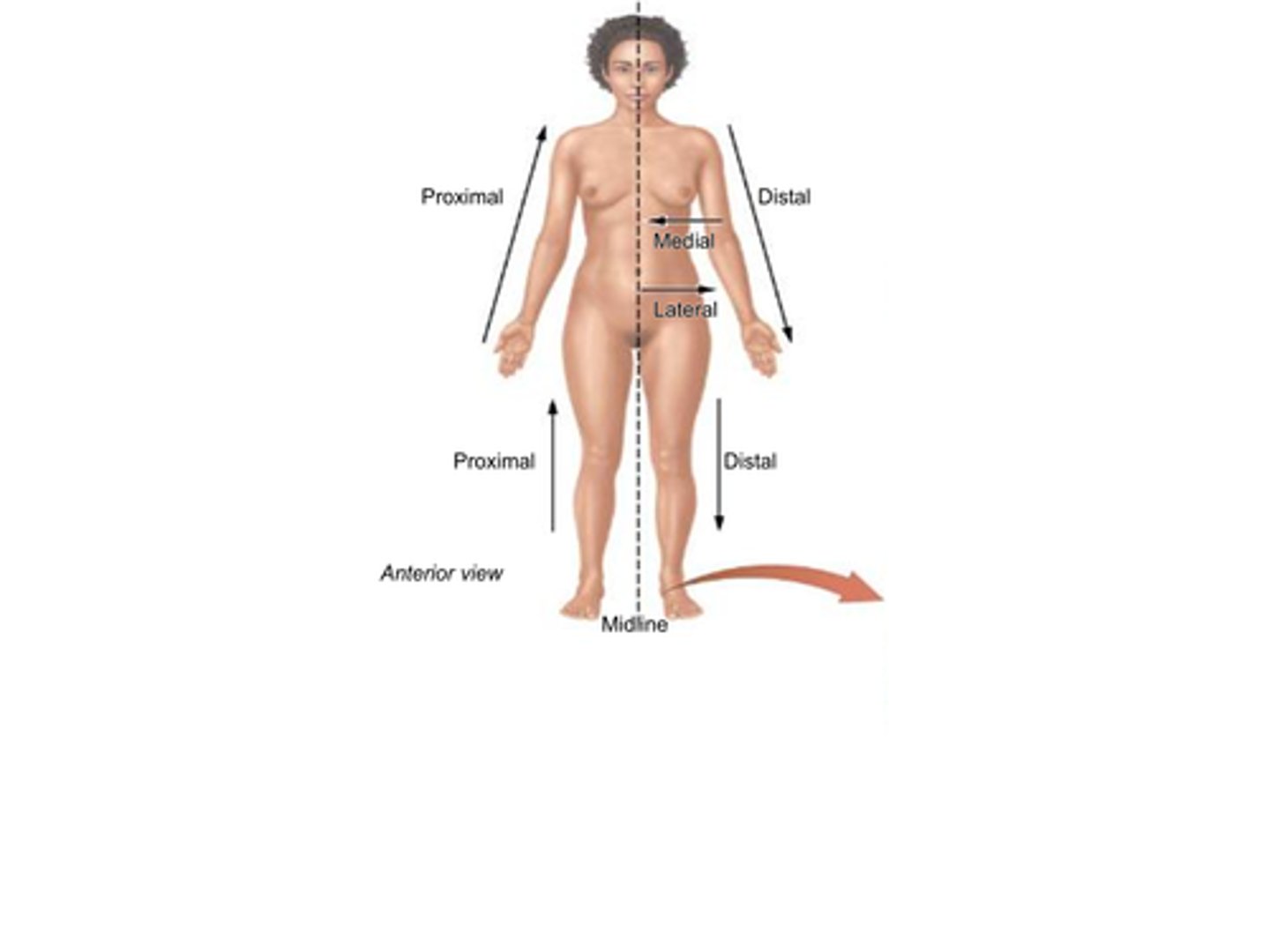
B) Medial
Which term refers to a position that is closer to the midline of the body?
A) Lateral
B) Medial
C) Proximal
D) Distal
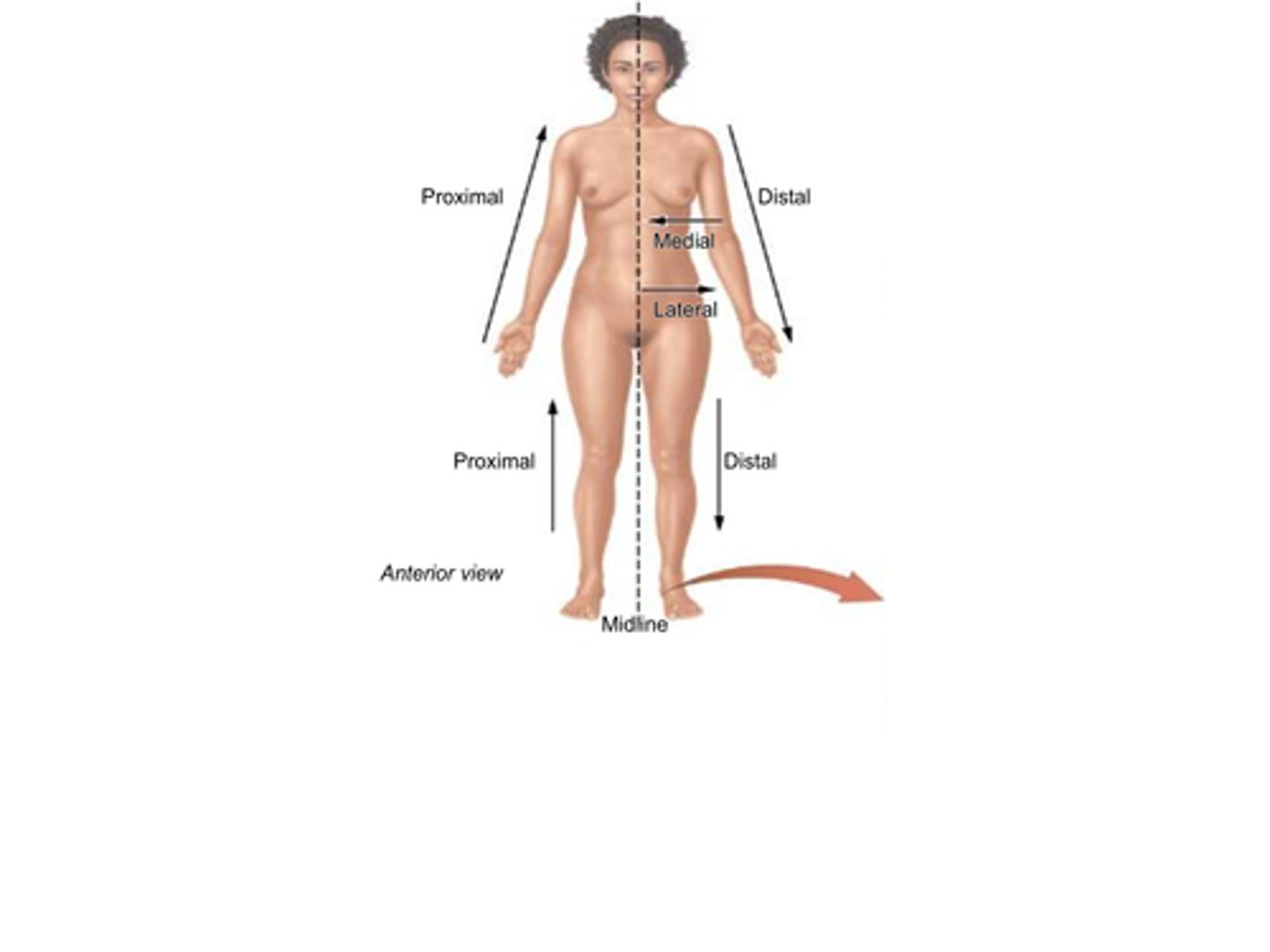
B) Closer to the midline
What does the term medial mean?
A) Farther from the midline
B) Closer to the midline
C) Toward the head
D) Toward the feet
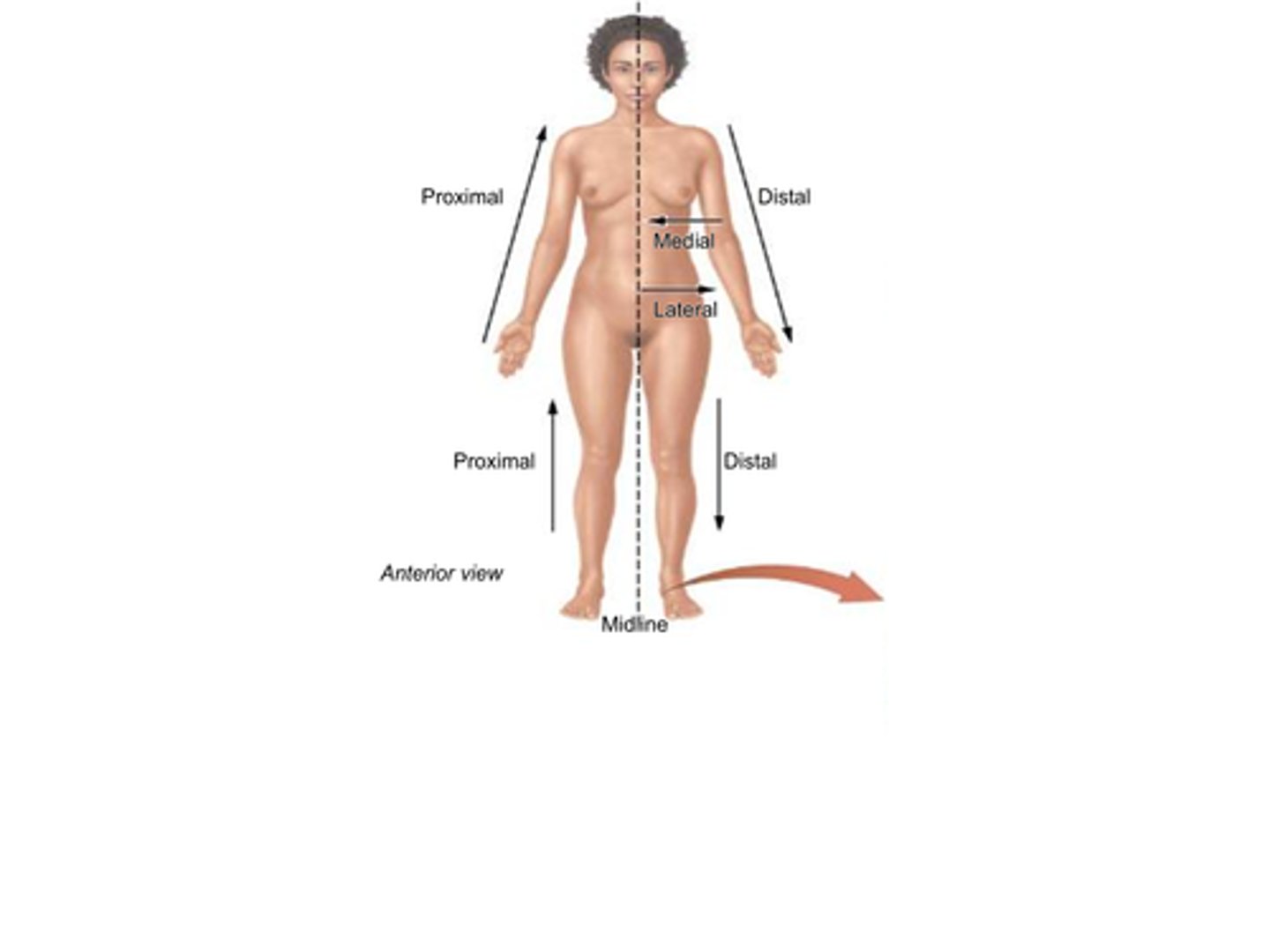
B) Lateral
Which term refers to a position that is further from the midline of the body?
A) Medial
B) Lateral
C) Proximal
D) Distal
B) Further from the midline
What does the term lateral mean?
A) Closer to the midline
B) Further from the midline
C) Toward the head
D) Toward the feet
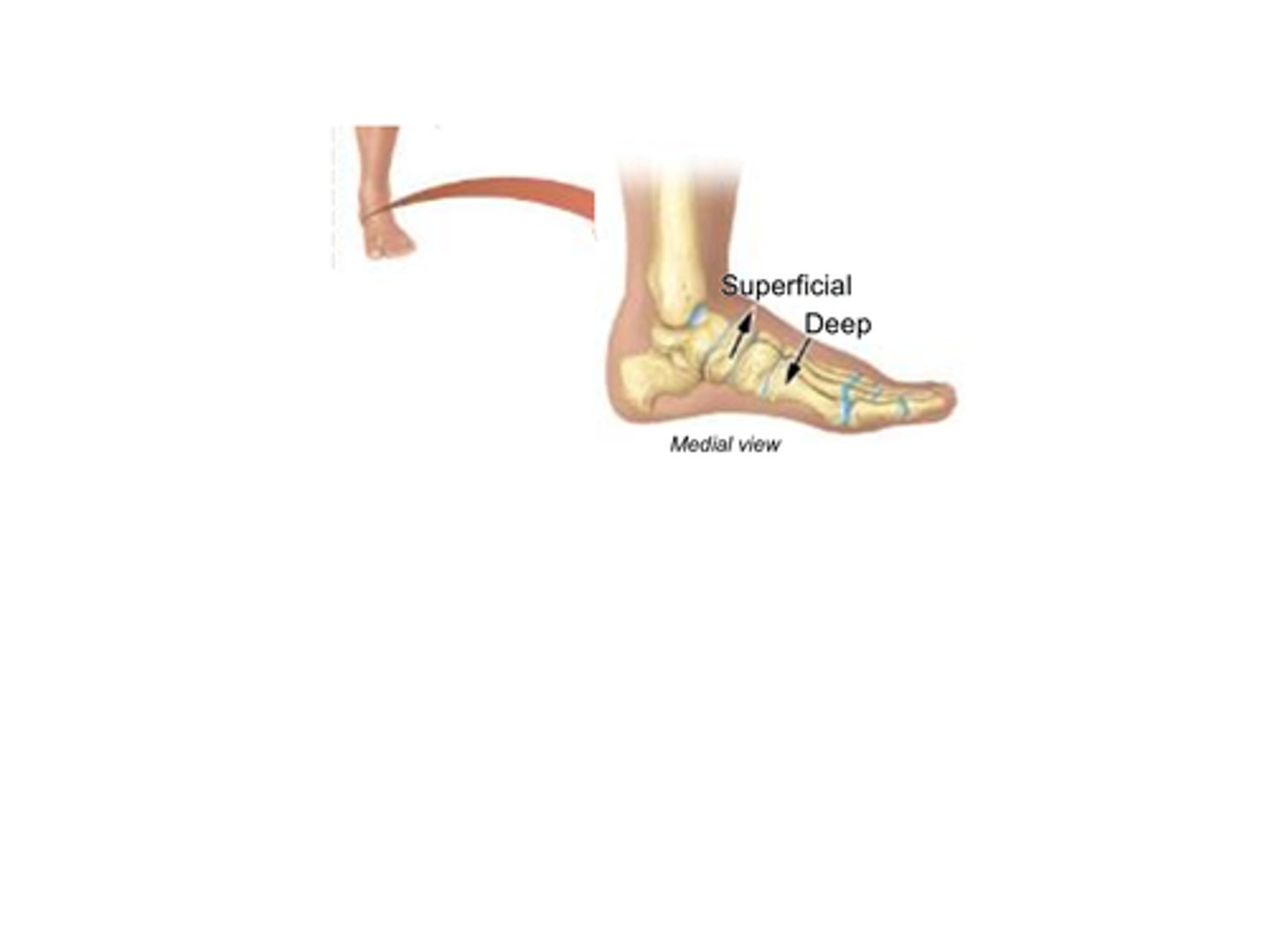
B) Superficial
Which term refers to structures that are closer to the surface of the body?
A) Deep
B) Superficial
C) Proximal
D) Distal
A) Closer to the surface of the body
What does the term superficial mean?
A) Closer to the surface of the body
B) Farther from the surface of the body
C) Toward the midline
D) Away from the midline
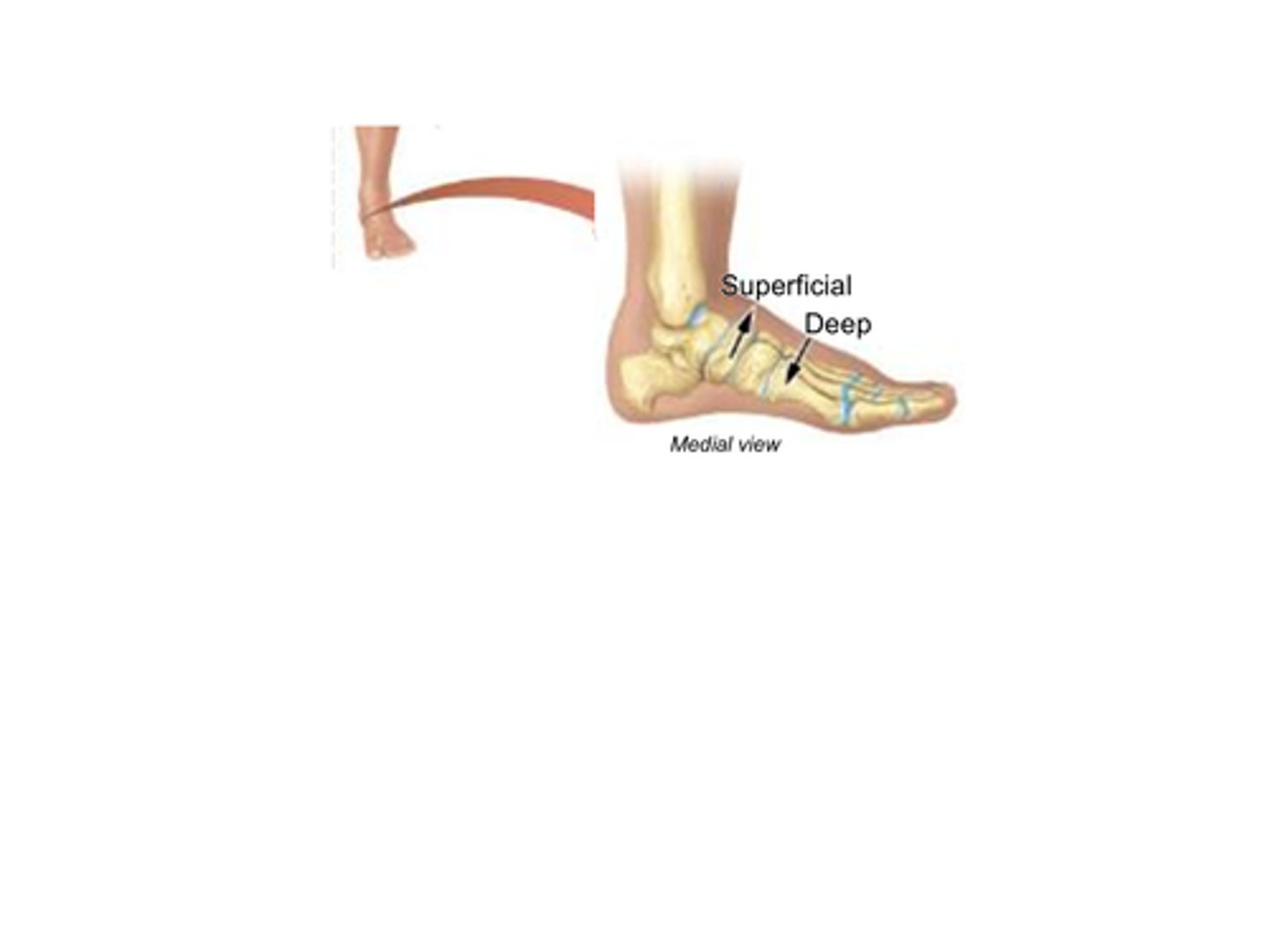
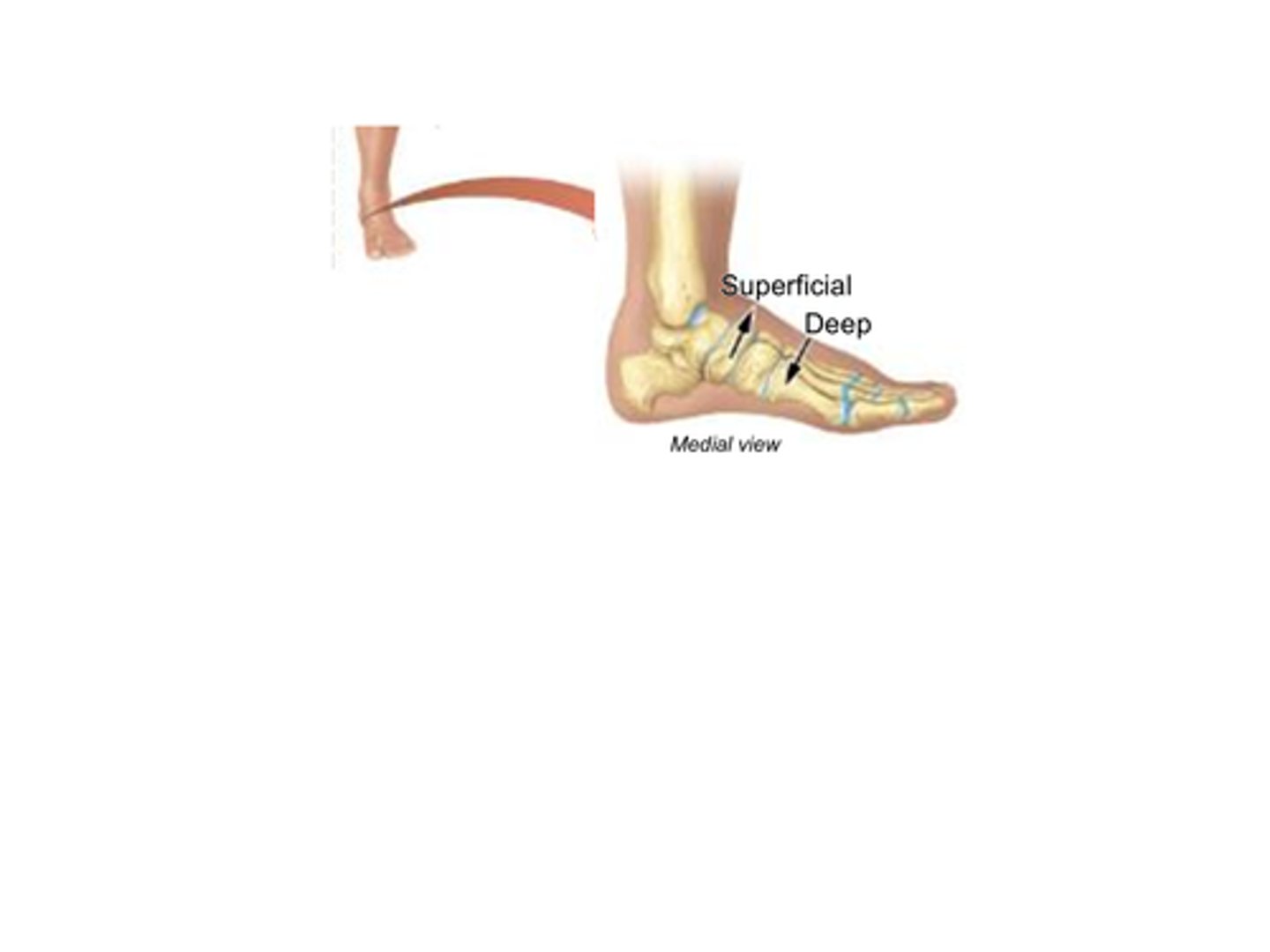
B) Deep
Which term refers to structures that are further away from the surface of the body?
A) Superficial
B) Deep
C) Proximal
D) Distal
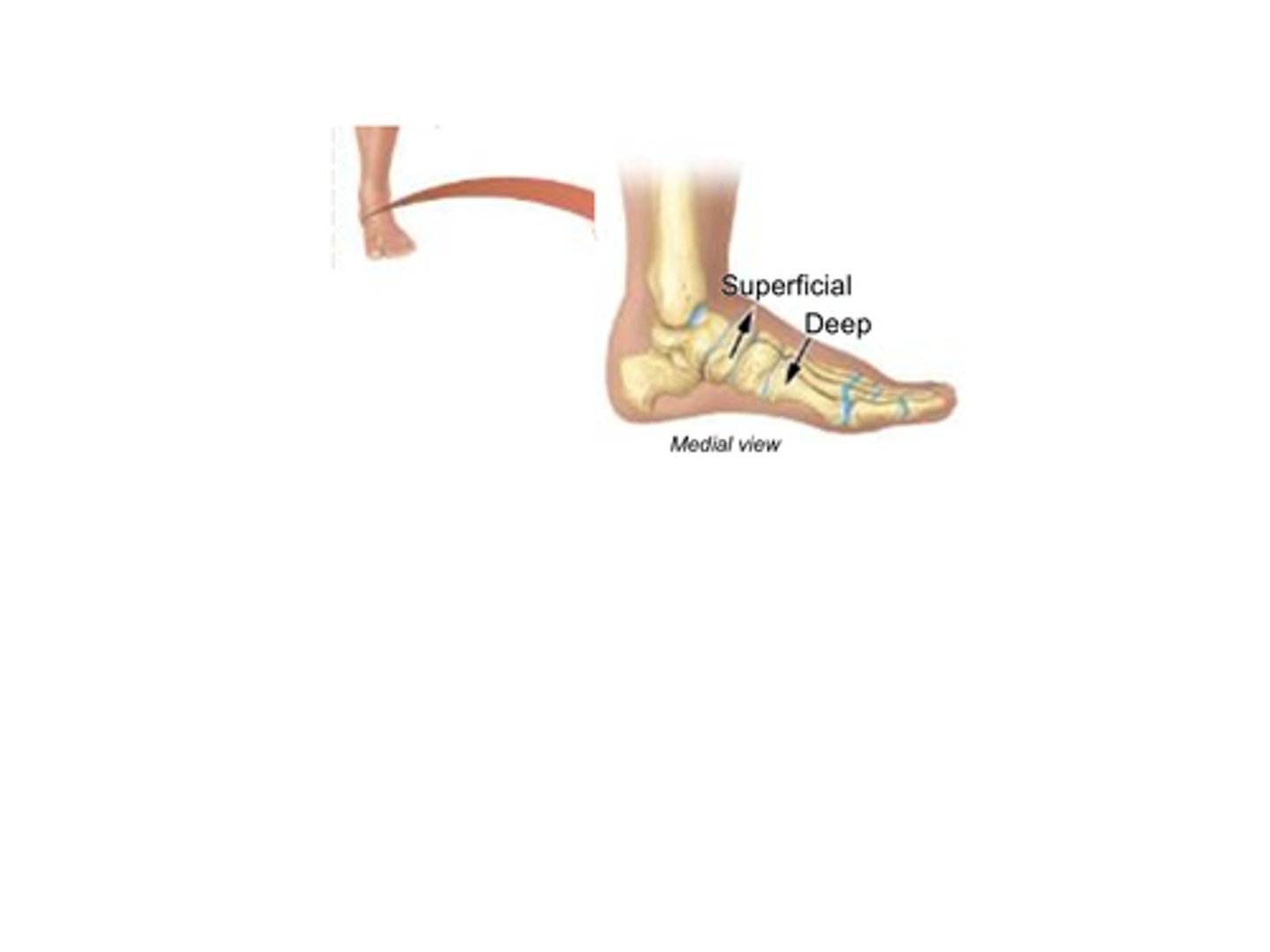
B) Further away from the surface of the body
What does the term deep mean?
A) Closer to the surface of the body
B) Further away from the surface of the body
C) Toward the midline
D) Away from the midline
A) Axial and Appendicular
The body can be divided into which two main regions?
A) Axial and Appendicular
B) Superior and Inferior
C) Medial and Lateral
D) Proximal and Distal
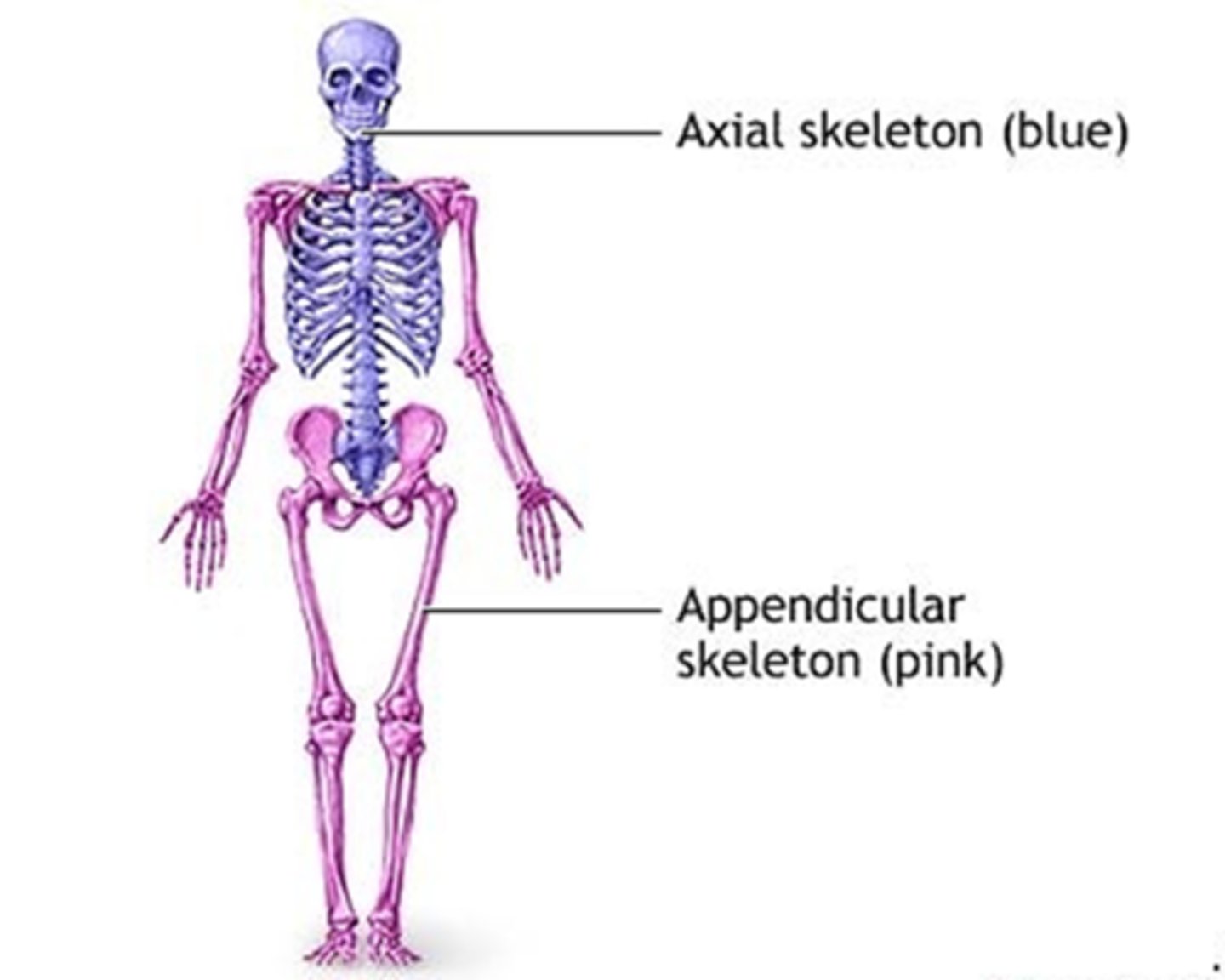
C) Axial region
Which region of the body includes the head, neck, and trunk?
A) Appendicular region
B) Medial region
C) Axial region
D) Lateral region
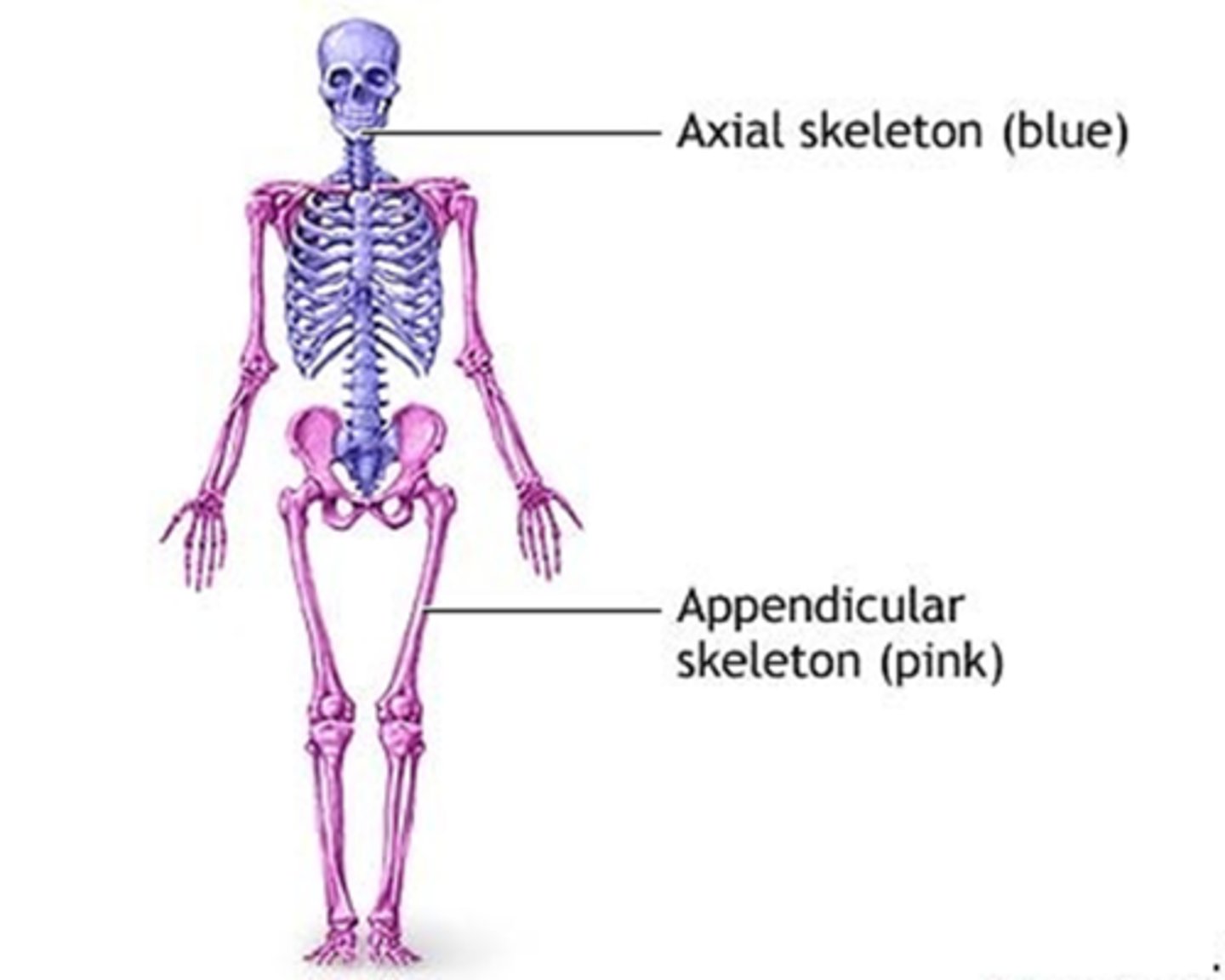
B) Head, neck, and trunk
What does the axial region of the body include?
A) Arms and legs
B) Head, neck, and trunk
C) Hands and feet
D) Shoulders and hips
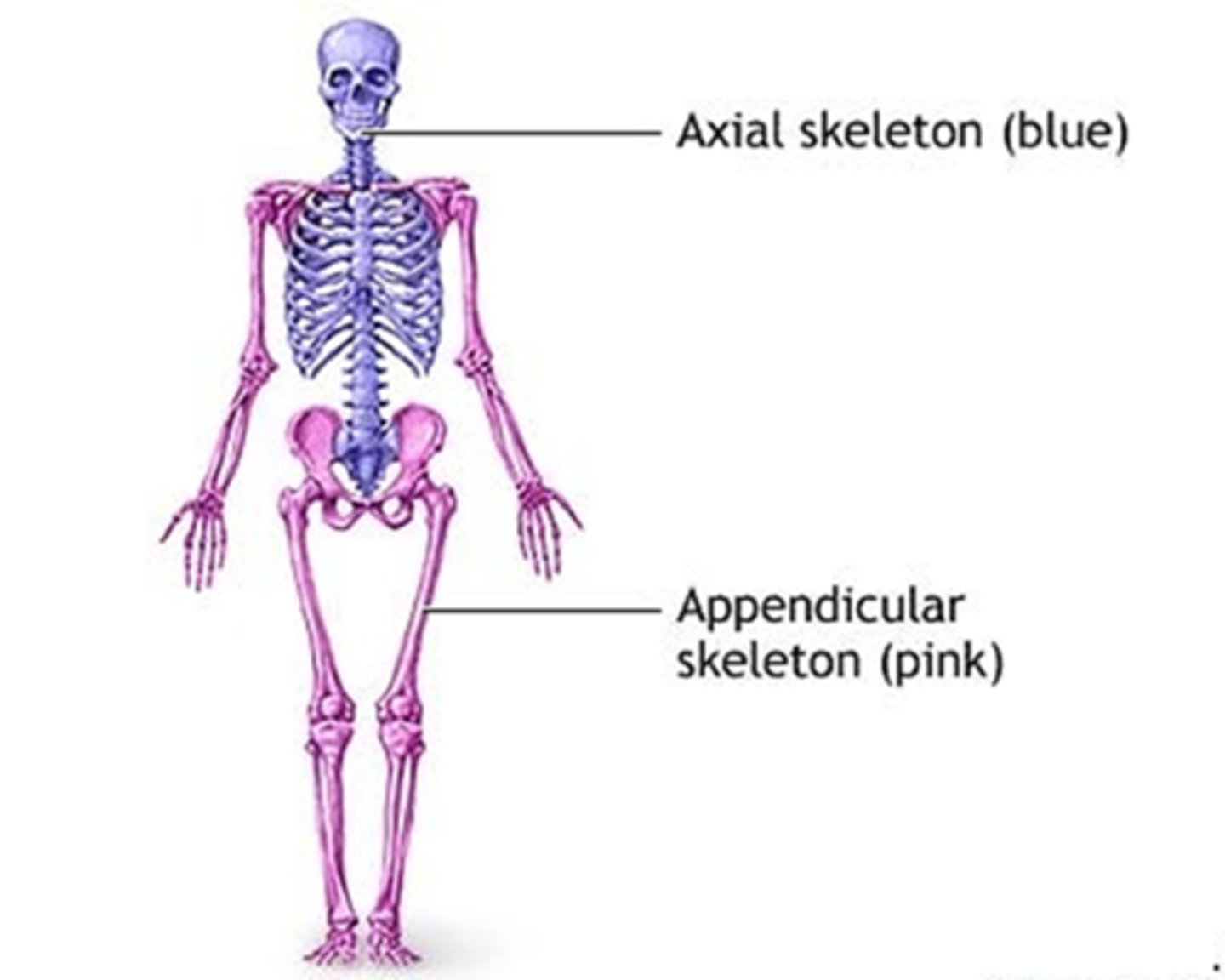
B) Appendicular region
Which region of the body includes the appendages (upper and lower limbs)?
A) Axial region
B) Appendicular region
C) Cranial region
D) Thoracic region
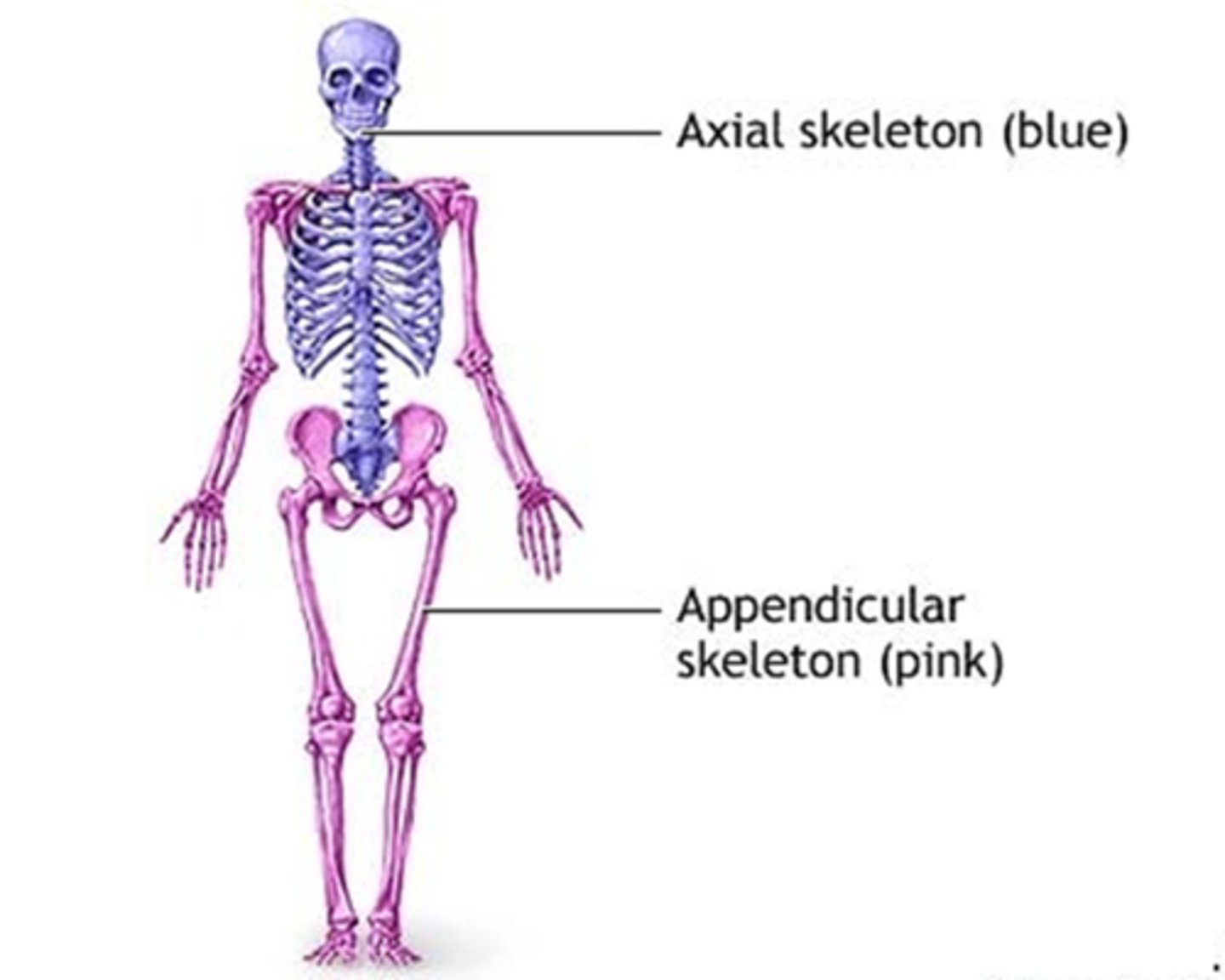
C) Upper and lower limbs
The appendicular region includes which of the following?
A) Head and neck
B) Thoracic and abdominal areas
C) Upper and lower limbs
D) Spine and pelvis
B) Transverse, Sagittal, and Coronal
What are the three primary planes of section used to divide the body or a body part?
A) Axial, Radial, and Horizontal
B) Transverse, Sagittal, and Coronal
C) Dorsal, Ventral, and Lateral
D) Proximal, Distal, and Medial
C) Sagittal plane
Which anatomical plane divides the body into right and left sections, including two variations?
A) Coronal plane
B) Transverse plane
C) Sagittal plane
D) Frontal plane
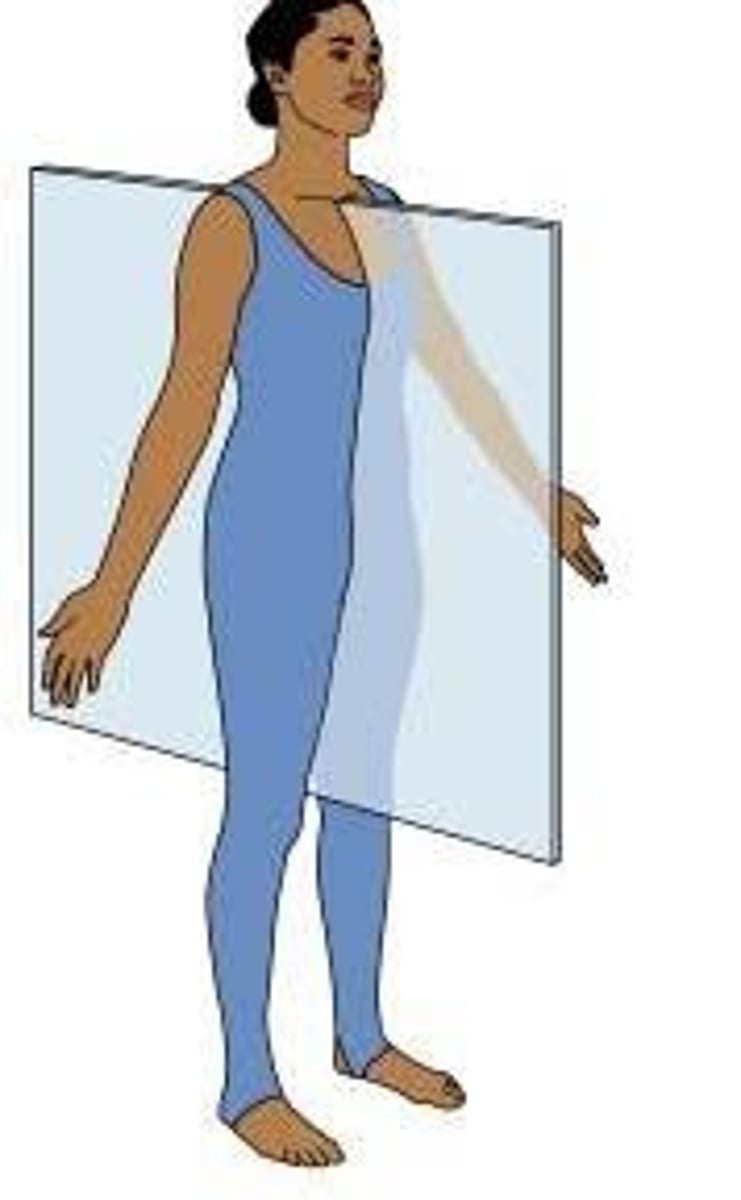
B) Midsagittal and Parasagittal
The sagittal plane divides the body into right and left sections. What are the two variations of the sagittal plane?
A) Horizontal and Vertical
B) Midsagittal and Parasagittal
C) Superior and Inferior
D) Anterior and Posterior
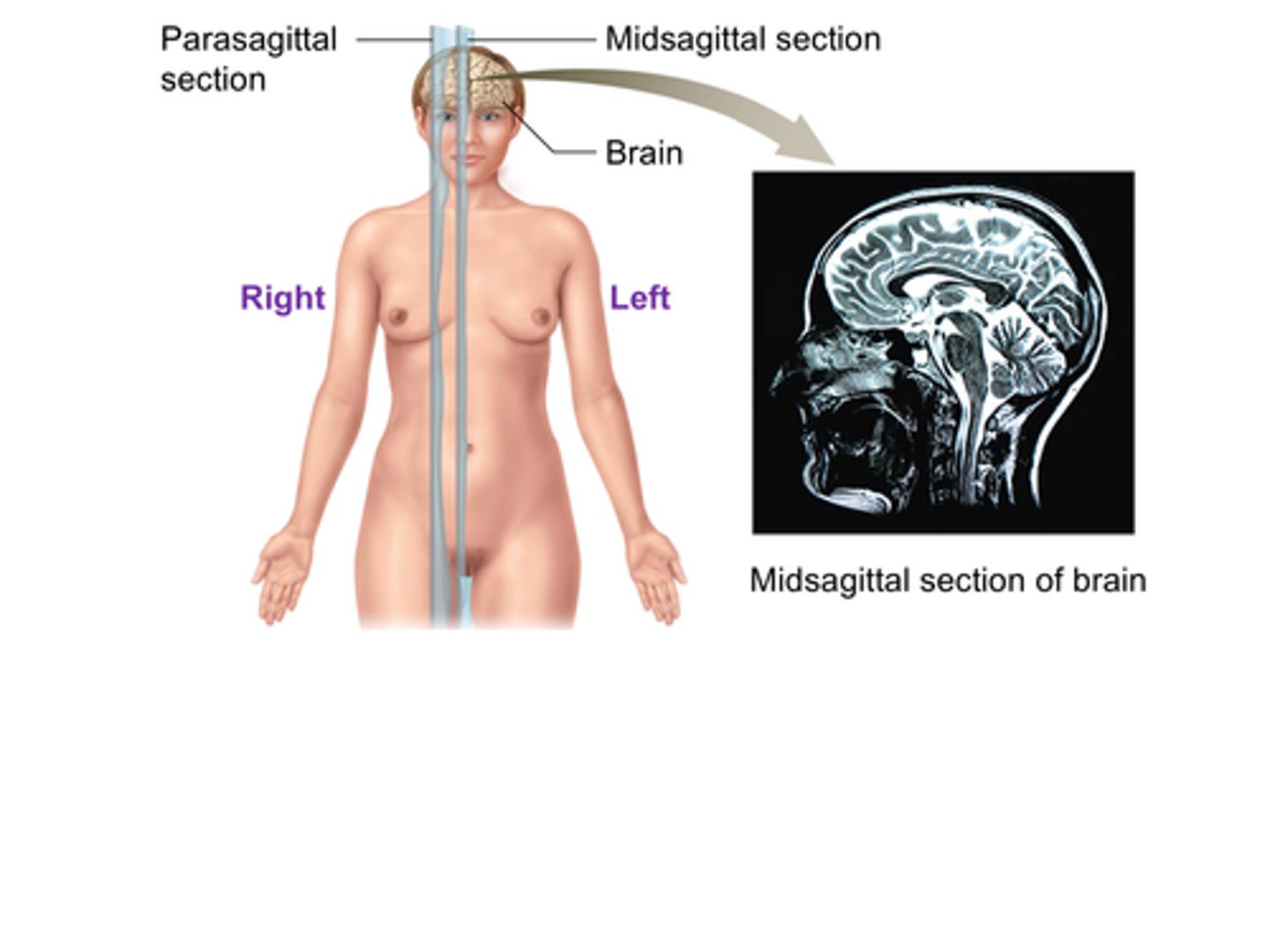
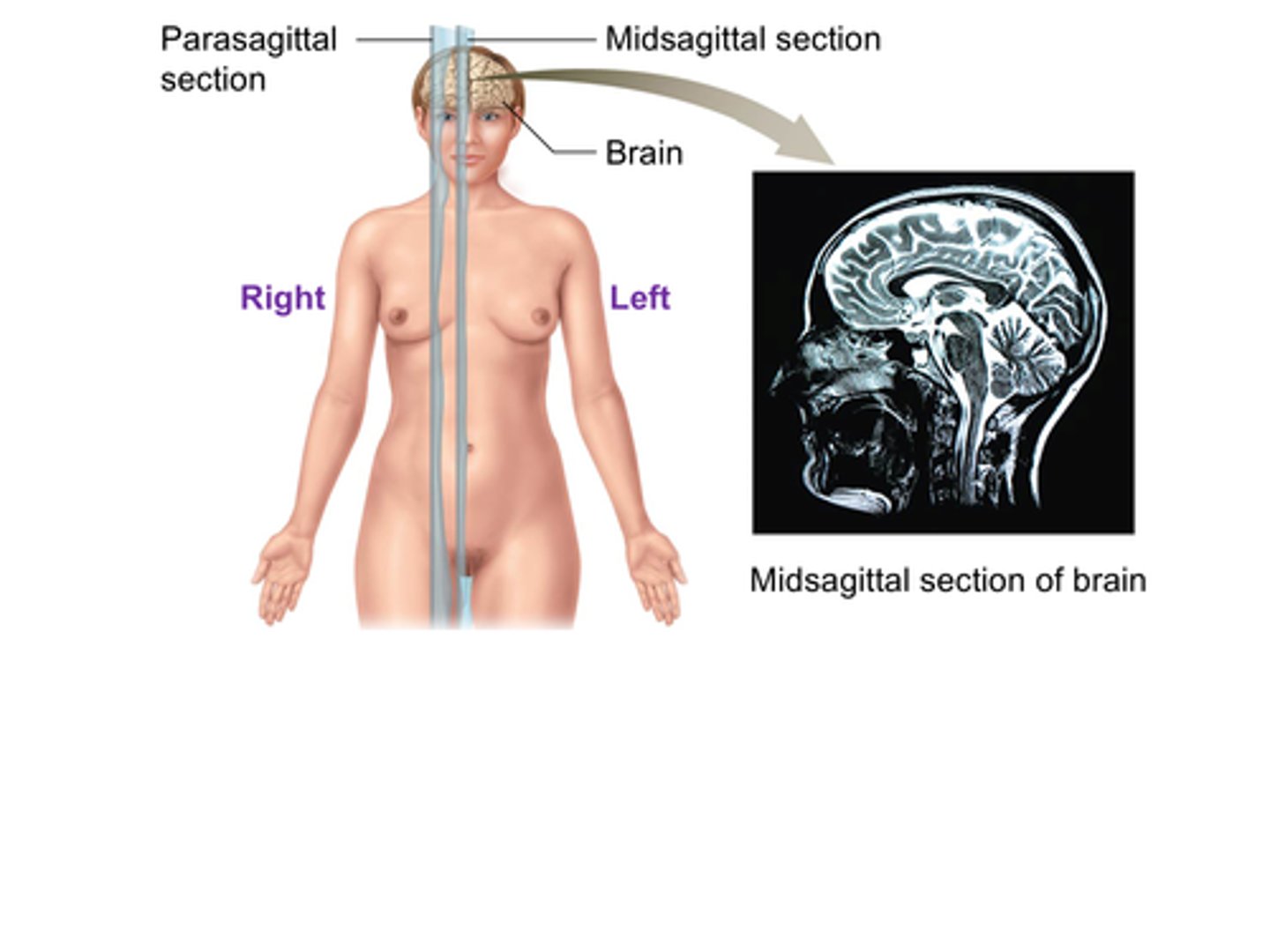
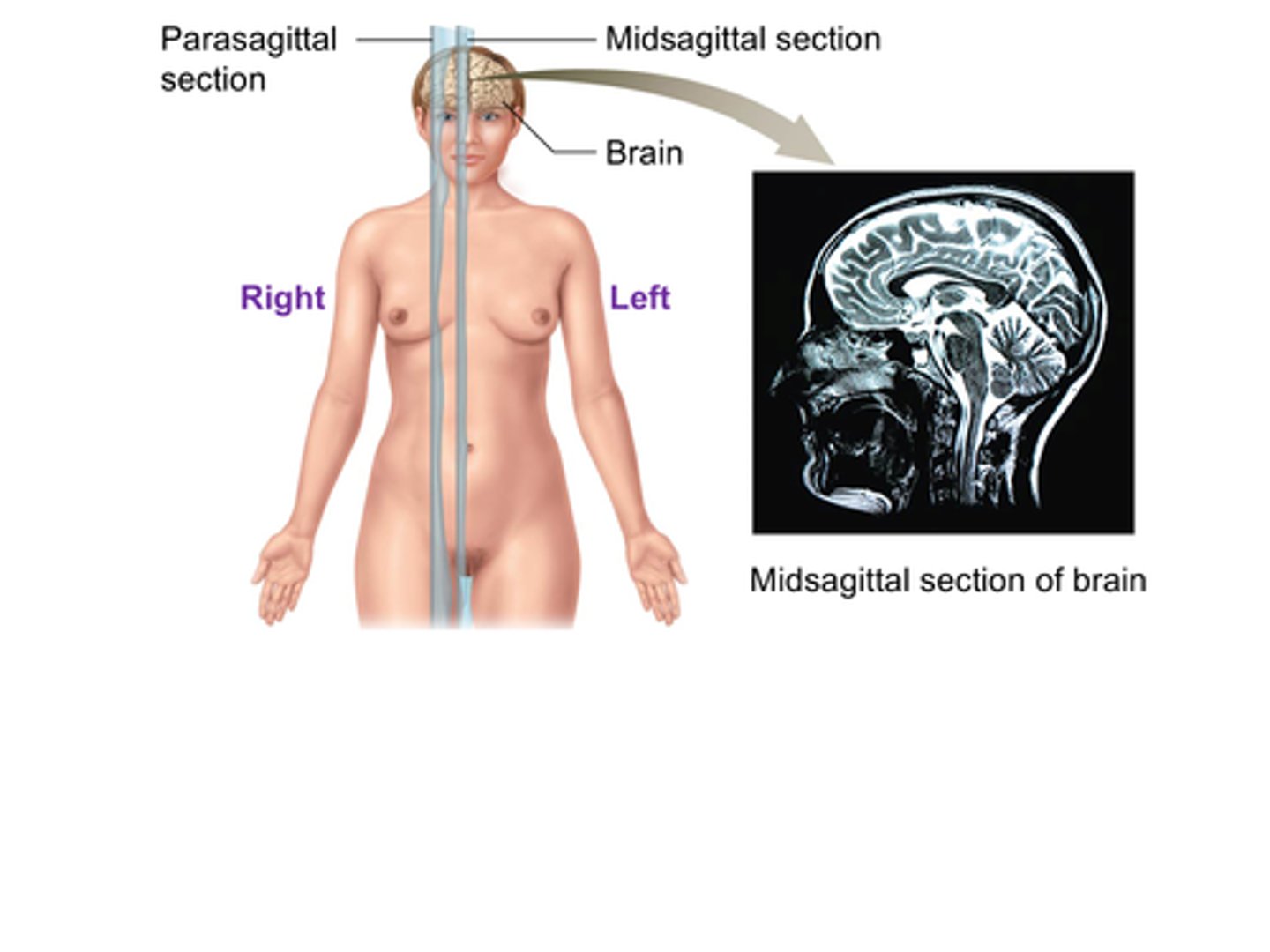
C) Midsagittal
The ______________________ plane (also called the median plane) divides the body into equal left and right sections.
A) Frontal
B) Transverse
C) Midsagittal
D) Coronal
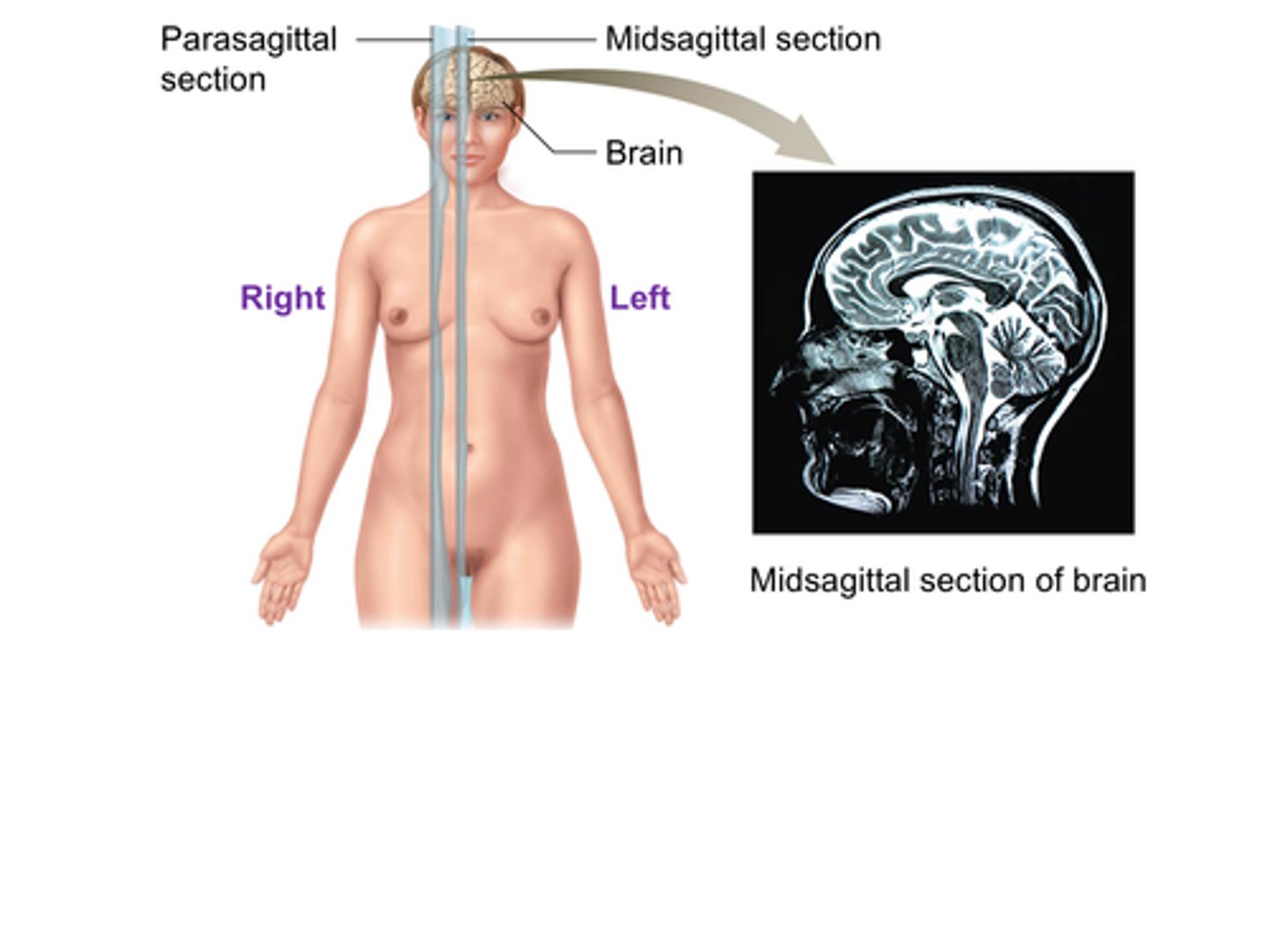
C) Midsagittal plane
Which anatomical plane divides the body into equal left and right sections?
A) Frontal plane
B) Transverse plane
C) Midsagittal plane
D) Oblique plane
B) Parasagittal
The ______________________ plane divides the body into unequal right and left sections.
A) Midsagittal
B) Parasagittal
C) Coronal
D) Transverse
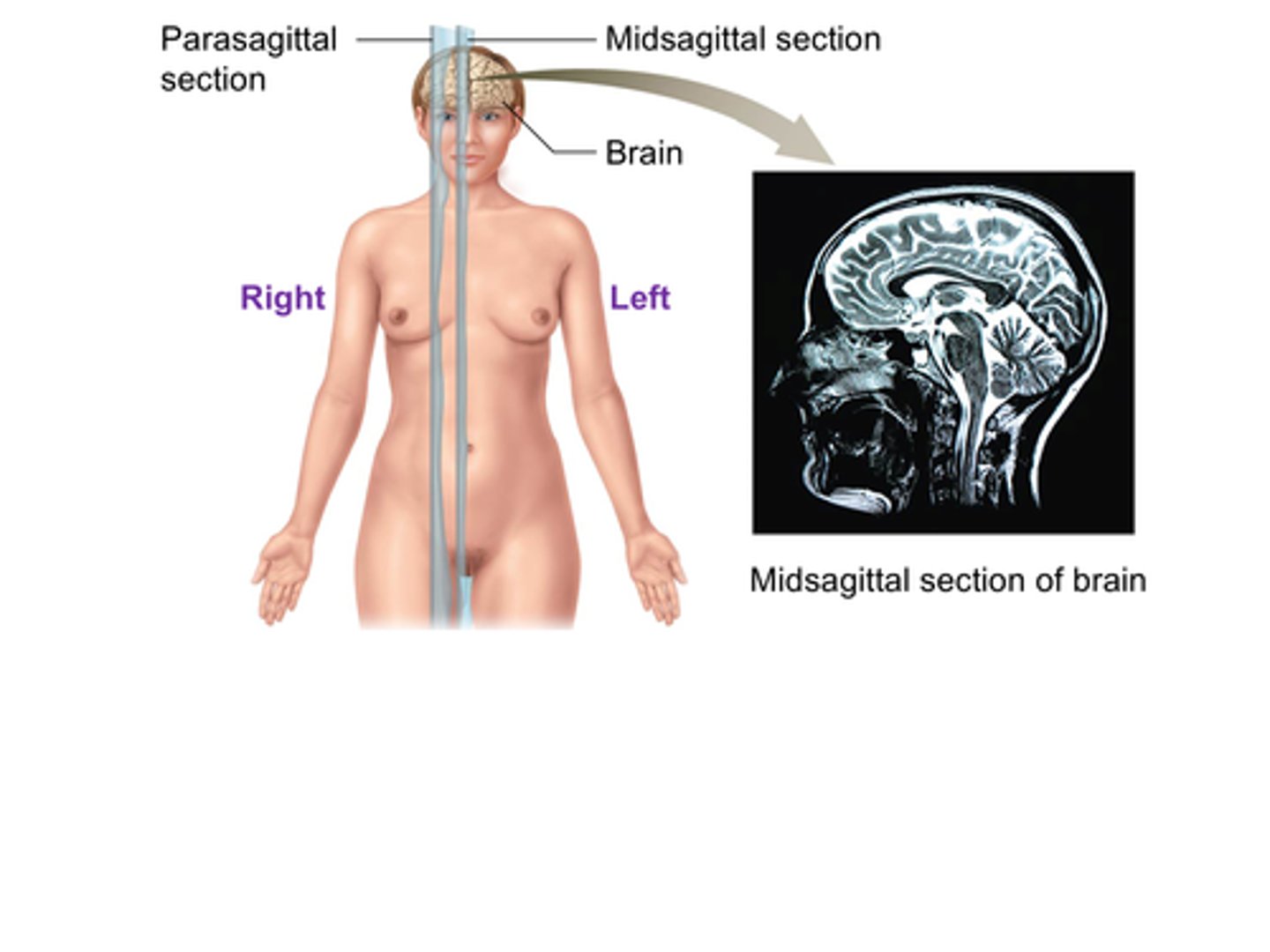
B) Parasagittal plane
Which plane divides the body into unequal right and left sections?
A) Midsagittal plane
B) Parasagittal plane
C) Coronal plane
D) Transverse plane
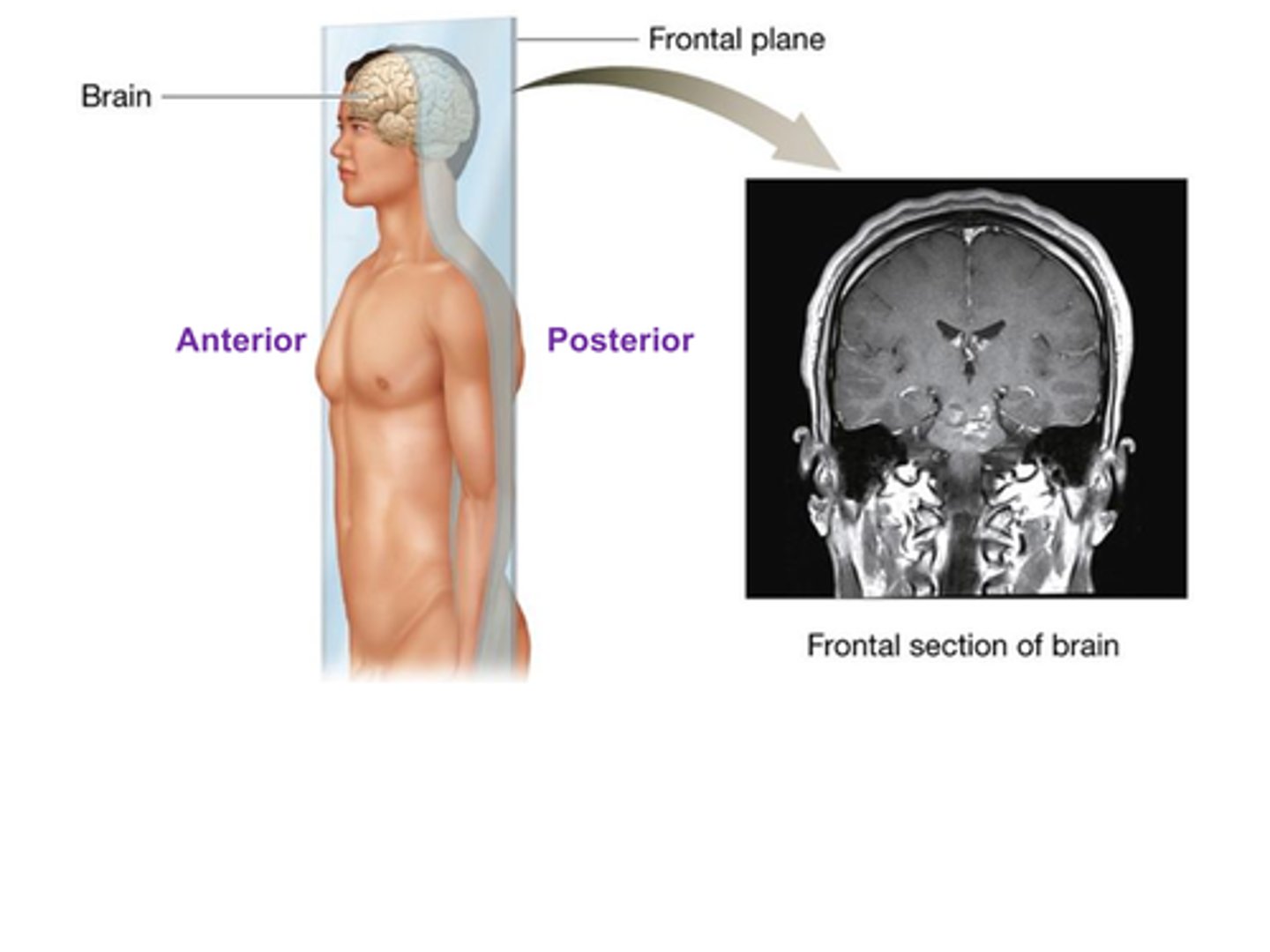
C) Frontal
The ________________ plane (also called the coronal plane) divides the body into anterior and posterior sections.
A) Sagittal
B) Transverse
C) Frontal
D) Oblique
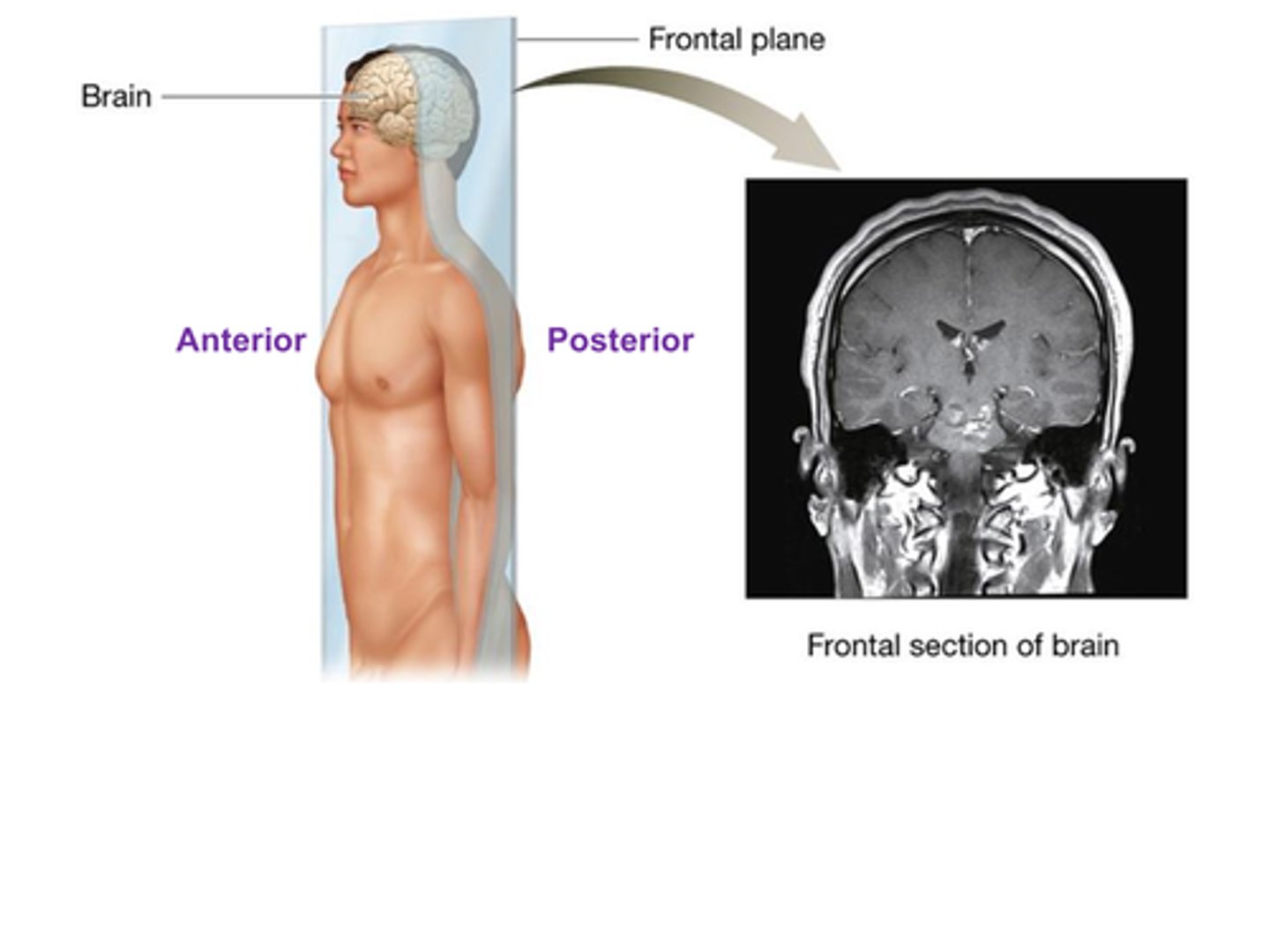
B) Frontal plane
Which plane divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections?
A) Sagittal plane
B) Frontal plane
C) Transverse plane
D) Midsagittal plane
C) Transverse plane
The ______________________ plane (also called the horizontal plane)
i. Divides the axial region into superior and inferior sections
ii. Divides the appendicular region into proximal and distal sections
A) Sagittal plane
B) Frontal plane
C) Transverse plane
D) Parasagittal plane