1st Chem finals units 1-3
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Qualitative
Description/ story’s
Quantitative
Numbers / data
Leading zeros (sig fig rule)
No significant
Ex: 0.0025 —> 2 sf
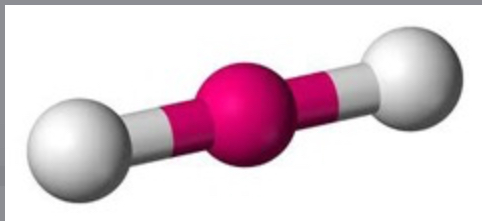
Linear
2 bonding sites, 0 lone pairs, nonpolar, 2d
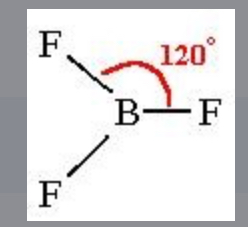
Trigonal planar
3, boding sites, 0 lone pairs, non polar, 2D
Tetrahedral
4 bonding sites, lone pairs, nonpolar, 3D
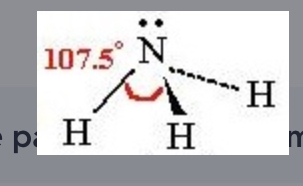
Trigonal pyramidal
3 bonding sites, 1 lone pairs, polar, 3D, asymetrical
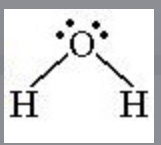
Bent
2 bonding sites, 2 lone pairs, polar 3D
Symmetrical
They cancel each other, nonpolar
Asymmetrical
They compound each other, polar
Intermolecular attraction
Strength of attractive force that holds it particles together
gas< liquid< crystalline solid
INTRAmolecular attractions
Found within te molecule (covalent, ionic,) stronger
Intermolecular attractions (IMA’s)
Attractive forces between separate molecules
holds the molecules close to other molecules, (weaker)
Substances with …… IMA’s will be gases at room temp
Weak
Substances with…..Ima will be liquid at room temp
Middle
Substances with … IMA’s will be solids at room temp
Strong
Dipole- Dipole attractions
Polar, no H-F, H-O, or H-N
Hydrogen bonding
H is boned to either N,O or F, polar, strongest
Dispersion forces (London dispersion forces)
Only Nonpolar molecules and unbounded atoms, temporary dipoles, weakest
The strength of dispersion forces depend on ……
The # of electrons: more electrons = stronger dispersion forces
the number of atoms in a molecule
Network covalent
very hard, very high melting points, most are nonconductors
Diamon and graphite (both carbon), silicon & silicon dioxide, any combinations of C, SI, W, B
Metallic
When a metal sits by its self
More electrons = …. Boiling point
Higher
Weak IMA’s means evaporation happens…..
Quickly, higher vapor pressure
Strong IMA’s means evaporation happens…..
Slowly, lower vapor pressure
Vapor pressure
A measure of pressure exerted by vapor on liquid below
Larger surface area = …. Evap
Faster
Increase in temp= …. Evaporation
Quicker
The longer the length of a molecule chain leads to …..interactions and a …..boiling point
Stronger interactions and a higher boiling point
Ionic bond
Metal and nonmetal
Substance melts about 100º C, dissolves in water, and conducts in water, its a …… type of solid
Ionic
substance melts about 100ºC, and conducts as a solid, its a ..... type of solid
Metalllic
substance melts in building water, does not conduct when dissolved in water and is soft, its a ...... type of solid
Covalent
substance melts above 100º C, does not dissolve, does not conduct, and is hard, its a ....... Type of solid
Network covalent
The..., the T value = the... the intermolecular force (IMA)
Smaller… stronger
The.....the bond the ...... the bond length
the more the bonds the shorter the bond length is
Atoms are more stable when they are …..
Bonded
Types of bonds are … (4)
Ionic bonds (+ and - ions), Covalent bonds (sharing), Nonpolar covalent bonds, Polar covalent bonds
Electronegativity is the ability of…
An atom to attract electrons in a bond
En (electro negativity) increase from
L→R, and Top to bottom
An En difference of .7 or greater (bond)
Ionic bonds
An En difference of 0 (bond)
Nonpolar covalent
An En difference between 0 and 1.7 (bond)
Polar covalent bonds
Ionic bonding in metals
Like to lose electrons, low ionization energy, produce positive ions
Ionization energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom
Exceptions to the octet rule
Hydrogen [H], Helium [He], lithium [Li]: 2 valence e
Beryllium [Be]: stable with 4 ve
Boron [B]: stable with 6 ve
Covalent bonding
When 2 nonmetals bond they must share electrons
Polar covalent bonds
Electrons are shared unequally between atoms
huge En difference
Partial charge
0<En<1.7
Nonpolar covalent bonds
Electrons are shared equally
no charge
En= 0
Oxoacids
They hydrogen is attached to an oxygen which is attached to the central acid (non metals
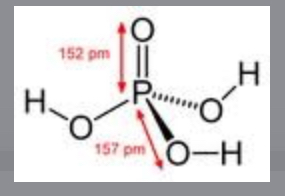
Bond strength (least to greatest)
Single bond < double bond< triple bond
Valence shell electron Pair repulsion theory (Vsepr)
You can predict the shape of a molecule depending on repulsion of electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom
electrons repel each other
Steric groups are…
Single bond, triple bonds double bond, lone electron pairs
Which would repel other bonds more within a molecule, Why
lone electron pairs (lone pair): it’d closer to the central atoms nucleus so it has greater repulsion
Diatomic molecules (7)
Br, I, N, CL, H, O, F
Intermolecular molecular bonds
Dispersion, Dipole-Dipole, hydrogen bonding
INTRAmolecular bonds
Ions (+,-), metallic(+), network covalent
Element
substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by a chemical change
Compounds
Formed of 2 or more element chemically bonded
cannot separate by physical means
Mixtures
A physical combination of 2 or more substances
Alloys
Homogeneous mixture of metals
Steel, brass, bronze, Nichrome, solder
Chemistry
Study of matter and how it changes
Zeros in between (sig fig rule)
Are significant
Ex: 1.0025 —> 5 sf
Trailing Zeros (sig fig rule)
Significant if there’s decimals
Ex: 100–> 1 sf or 1.00 —> 3 sf
Rounding sig fig.
Round 19,876 to 3 sf
1.99×10^4
Rounding sig fig.
Round 19876 to 2 sf
2.0×10^4
Multiplication/division (sig figs)
Same # sig figs as lowest #
Ex: 9.325 × 1.2 =11.19 = 11
rounds to 2 sig figs
Addition / subtraction
Same # decimal places smallest decimal place
12.15+ 1.1+3.125 =16.375 = 16.4
rounds to 1 decimal place
Rounding on a calculator (sig figs)
Only round at the end or when hanging operation types
Ex: addition/ subtraction —> multiplying/dividing
Scientific Notation rule
Express # between 1 and 10
Ex: 1230 = 1.2×10³ Or 0.024 = 2.4×10^-2
positive exponents = big numbers
Negative exponents = small numbers
Physical change
Different physical form but sill same substance
phase changes, bending, tearing, dissolving sugar in water
Chemical change
You get something new
burning, color change, cooking, rusting baking, rotting
Density, Mass, Volume equations
D=m/v, M= DxV, V=M/D
Percent Error Equation
(Experimental - theoretical)/ theoretical x100
experiment = data from lab
Theoretical = correct/ accepted value
Heterogeneous
Visible appearance
M&M cookies, salad, pizza
Homogeneous
Uniform appearance
air, sea water, kool Aid
Protons
Mass: 1 amu
Charge: +1
Location: Nucleus
Role: identity of the atom
Neutrons
Mass: 1 amu
Charge:0
Location: Nucleus
Role: “glue” inside nucleus
Electrons
Mass: 0.005 amu
Charge: -1
Location:outside nucleus
Role: responsible for charge
Atomic Number
The number of protons in the nucleus
Mass Number
The sum of protons + neutrons
Neutral atoms
Contain equal # of protons and electrons
Isotope
Same element different numbers of neutrons
Ions
Atoms which have unequal numbers of protons and electrons
Anion
Gain electrons = negative
Cation
Loses electron = positive
Avg atomic mass equation
(Exact mass x decimal abundance) + (m x a) ….
Avg weighted cost equation
(#/ total of all combined items) (Avg. cost) +….
Orbitals
As energy level increase, the number of different shapes and types of spaces increase (the spaces are orbitals)
each orbital holds only 1 pair of electrons
S sub shell
2 electrons , 1 orbital
P sub shell
6 electrons, 3 orbitals
D sub shell
10 electrons, 5 orbitals
F sub shell
14 electrons, 7 orbitals
Aufbau Principle
Electrons always fill low energy level to high
1s,2s,2p,3s,3p,4s,3d,4p….
Hunds rule
The lowest energy config. Fro an atom is the one having the max # of unpaired electrons
Smallest to largest of : energy level, atom, sublevel, and orbital
Smallest —————> largest
Orbital → sublevel →energy level → atom
Pauli Exclusion principle
Each orbital can hold a max of 2 electrons as long as they have opposite “spin”

Paramagnetic
Atoms have unpaired electrons affected by a magnet
the more electrons = the more it is affected by a magnet
Diamagnetic
Have only paired electrons, not affected by magnets
Short hand configurations / orbital configurations
[Nobel gas], rest of subshell config
![<p>[Nobel gas], rest of subshell config </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/39f63e22-9219-44c5-a7cb-2034eb2eb9f2.jpg)