AP Bio Unit 5 HEREDITY
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
(sister) chromatid
Copies of a duplicated chromosome; when two sister chromatids are joined together it makes up one chromosome
Centromere
Attachment point of two sister chromatids
Interphase
Period of cell cycle when the cell is not physically dividing; consists of following stages:
G1= growth
S= replicates DNA
G2= continued growth; cell prepares for division
G0= cell is at rest (not preparing for division)
Growth factors
Proteins released by certain cells that stimulate other cells to divide; example platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
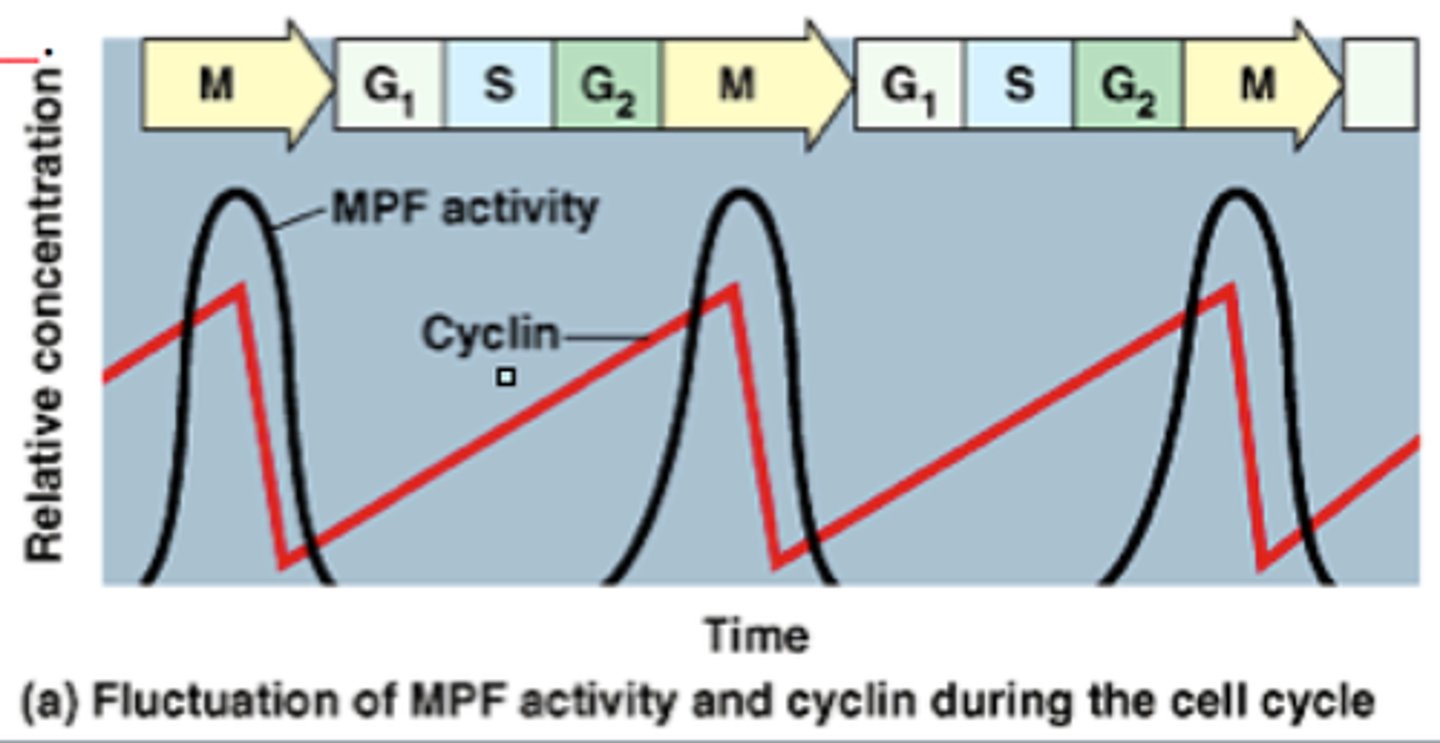
Cyclin
Family of proteins that control the progression of cells through the cell cycle by binding to and activating cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk)

Cyclin graph
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
Cancer
When cells begin dividing at an uncontrolled rate and become invasive
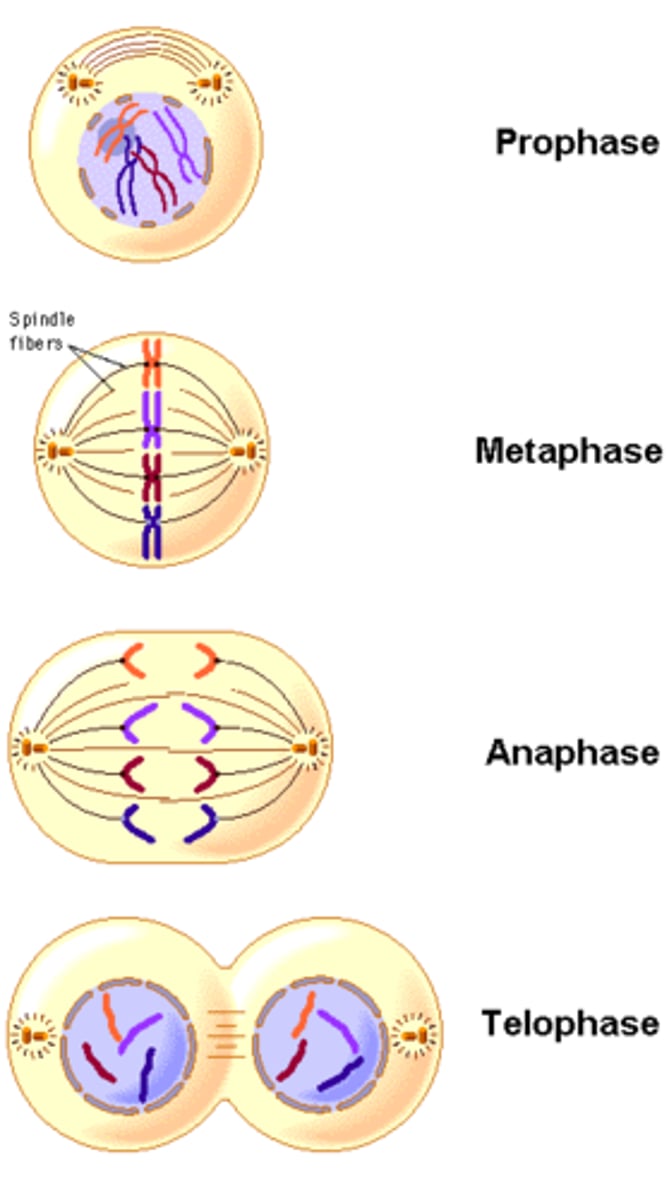
Mitosis
Division of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells
Consists of 4 stages- prophase, metaphase, anaphase, & telophase
Results in two genetically identical cells
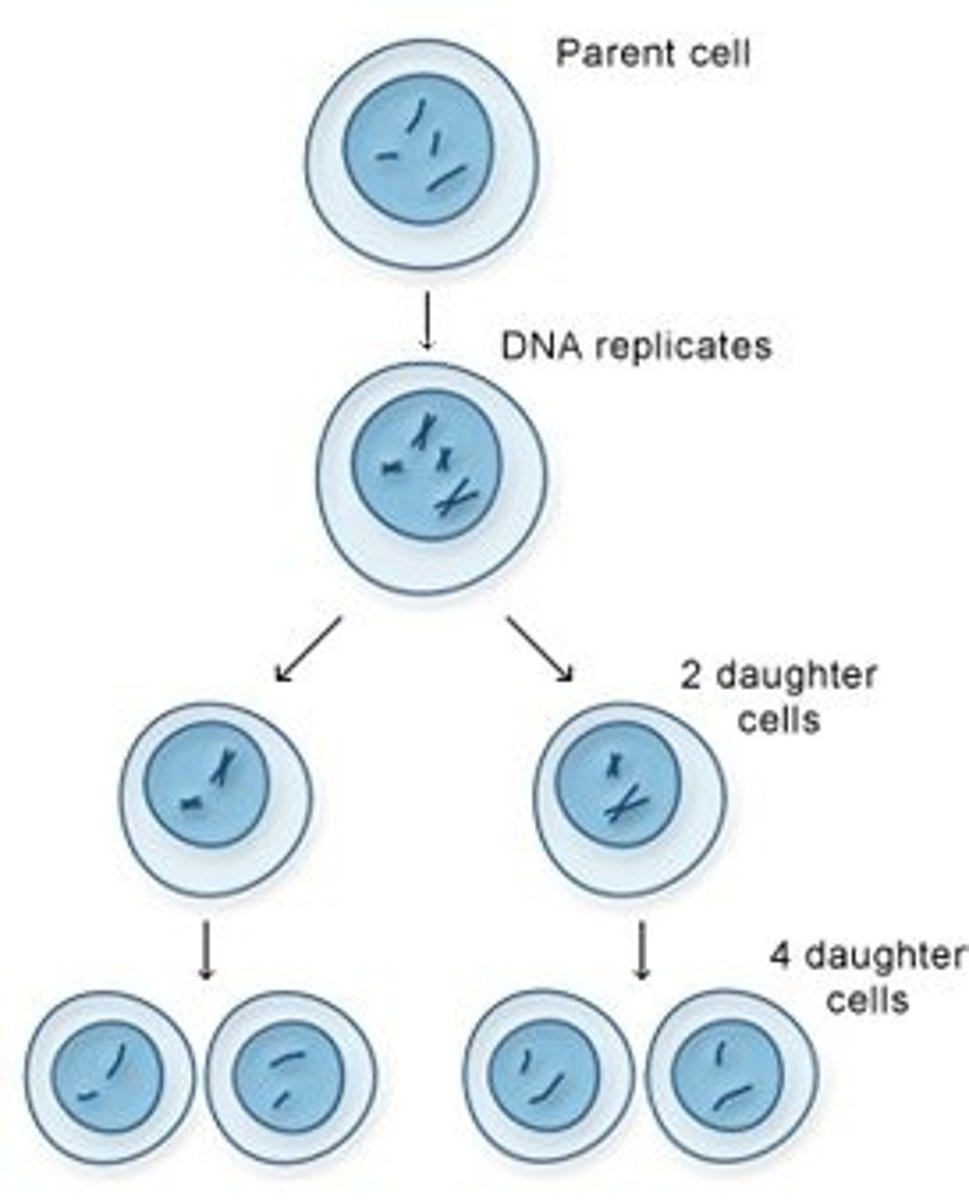
Meiosis
Cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that forms gametes
Consists of two rounds of cell division but only one round of DNA replication
Results in four cells with haploid chromosome number
Mitosis diagram
Meiosis diagram
Homologous chromosomes
Paired chromosomes; the same size, shape, and carry genes for the same traits
Diploid
Complete set of paired chromosomes
# found in somatic (body) cells
2n
Haploid
Set of unpaired chromosomes
# found in reproductive cells
1n
Autosomes
All other chromosomes except sex chromosomes
Sex chromosomes
Determines gender
Male= XY
Female= XX
Gamete
Reproductive cell
Contains haploid # of chromosomes
Generated during meiosis
Somatic cell
Body cell
Contains diploid # of chromosomes
Generated during mitosis
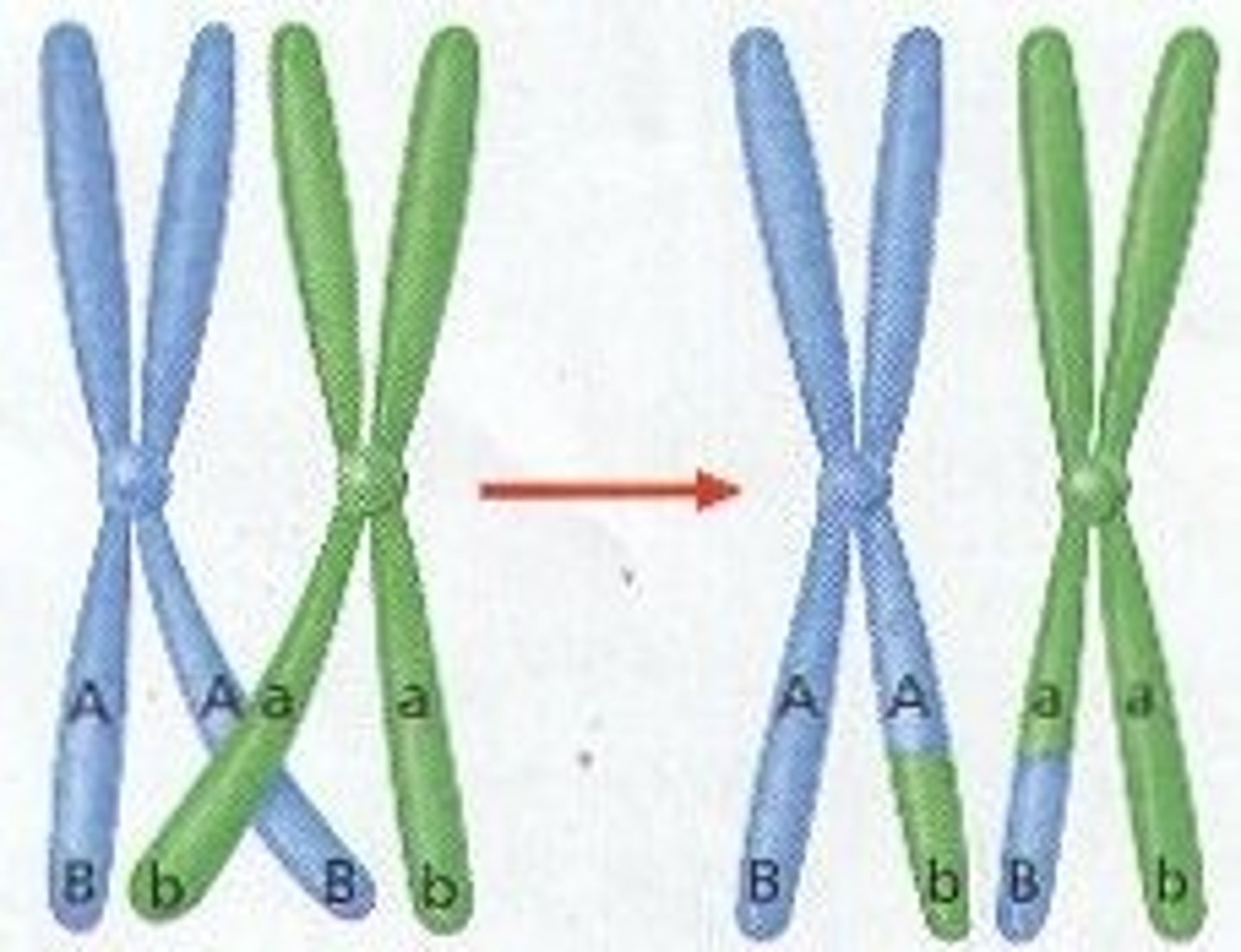
Crossing over
Exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes
Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
Genes are carried from parents to their offspring on chromosomes
Zygote
Diploid cell produced by the union of haploid gametes (egg and sperm) during fertilization
True-breeding
Organisms that produce offspring of the same variety over many generations of self-pollination; homozygous
P generation
True-breeding (homozygous) parent individuals from which F1 hybrid offspring are derived; "p" stands for parental
F1 generation
Hybrid (heterozygous) offspring arising from a parental (P generation) cross
F2 generation
Offspring of a hybrid cross resulting in a 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive phenotypes
Hybrid
Heterozygous
Allele
Different versions of a gene
Ex: A or a
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an individual
Phenotype
Physical traits
Heterozygous
Having different alleles for a gene
Ex: Aa
Homozygous
Having identical alleles for a gene
Ex: AA or aa
Law of Segregation
Two alleles for a trait separate (segregate) during gamete formation and end up in different gametes
Law of Independent Assortment
Each pair of alleles segregates independently of each other pair of alleles during gamete formation
Traits are independent and require own Punnett square
Testcross
Crossing an organism with recessive individual
Monohybrid cross
A cross between two organisms that are heterozygous resulting in 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive phenotypes
Dihybrid cross
A cross between two organisms that are heterozygous for TWO traits resulting in a 9:3:3:1 ratio
Polygenic
Traits that involve multiple genes
Ex: eye, skin, and hair color
Multiple allele traits
Traits that have more than two alleles contributing to phenotype
Ex: blood type
Sex-linked traits
A gene located on either sex chromosome
Most sex-linked genes are on the X chromosome
Wild-type
Phenotype that most commonly observed in natural populations
Recombinants
Offspring with non-parental phenotypes (new combinations of traits) due to crossing over between linked genes
Recombination frequency
Divide total number of recombinants (non-parental phenotypes) by the total number of offspring
Linked genes
Genes located close enough together on a chromosome that they tend to be inherited together
Linkage map
A genetic map of a chromosome based on recombination frequencies
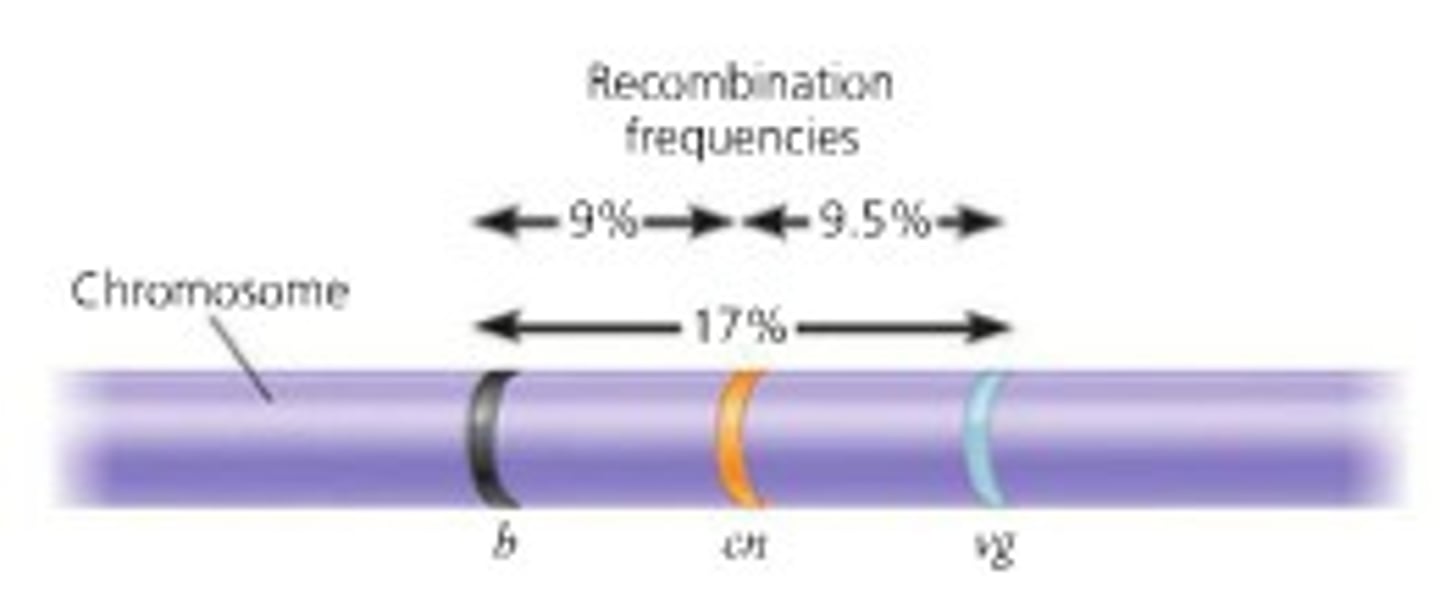
Map units
Distances between genes; one map unit represents a 1% recombination frequency