AP BIO Chapter 15/16 (Clades and Phylogenetic Trees)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
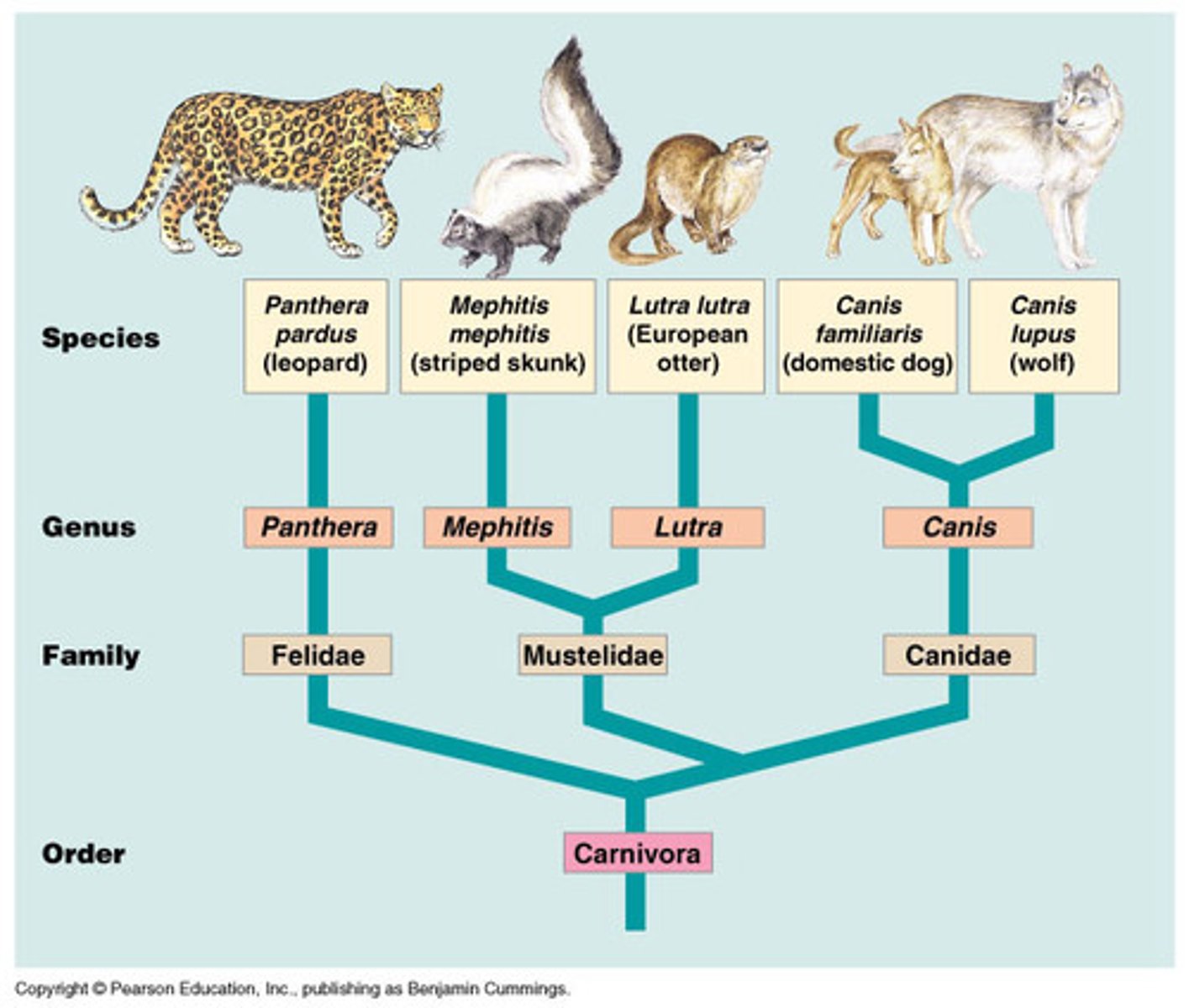
Phylogenetic Tree
Diagram reconstruction of the evolutionary history of relationships between organisms
Root
The common ancestor of all the organisms on a phylogenetic tree
Node
When a lineage on a phylogenetic tree splits into two
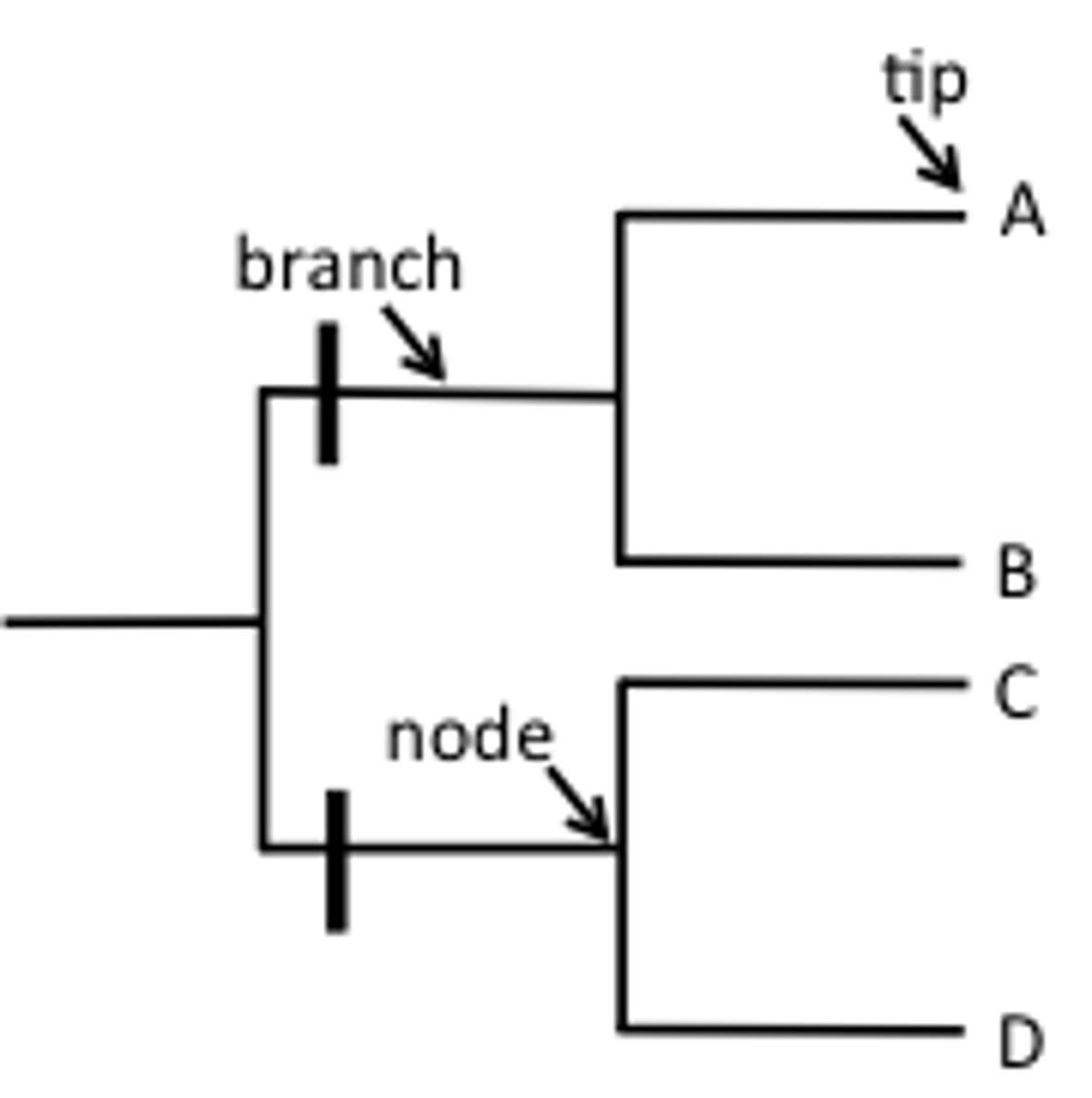
Taxon
A group of species that we designate with a name
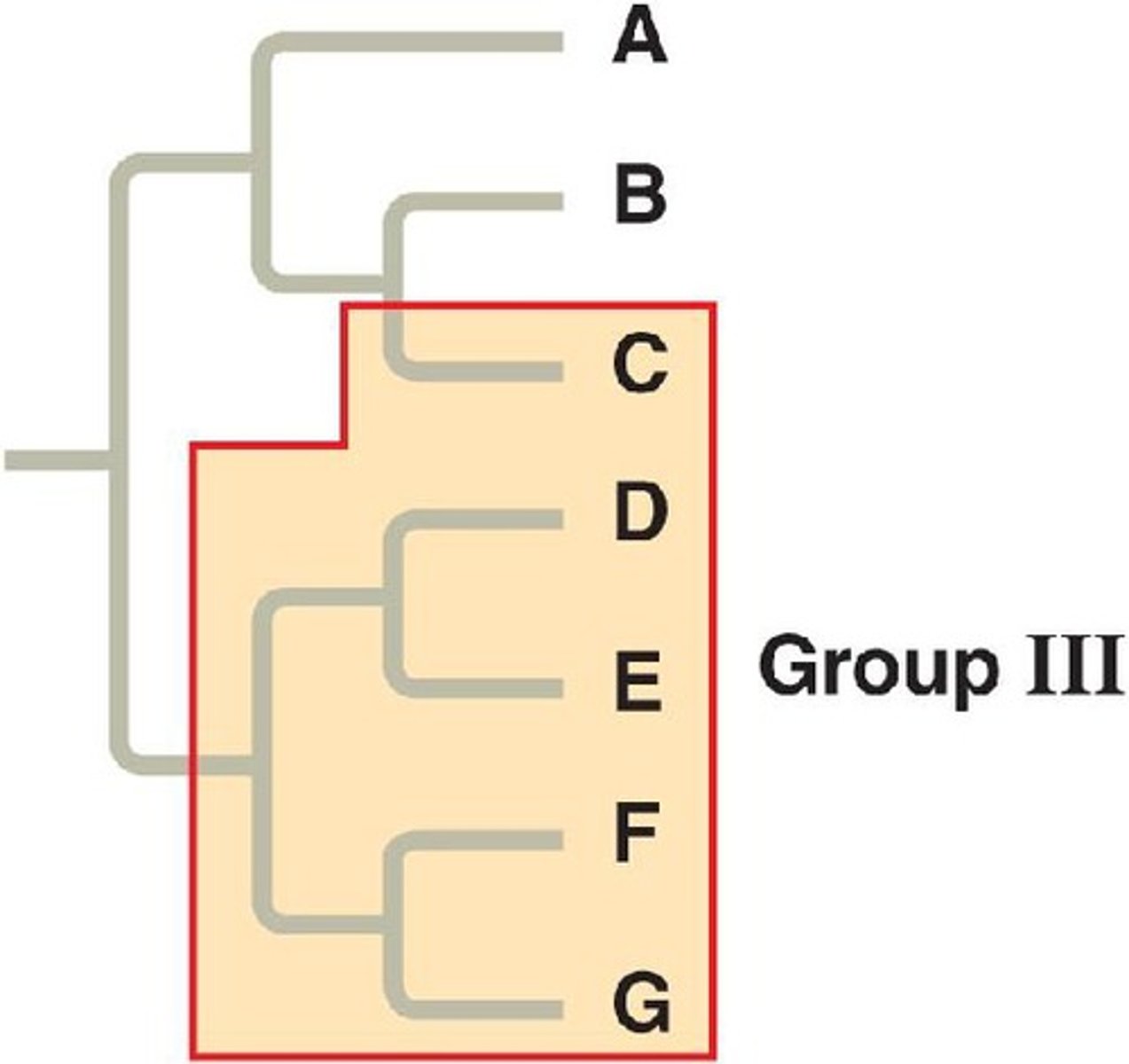
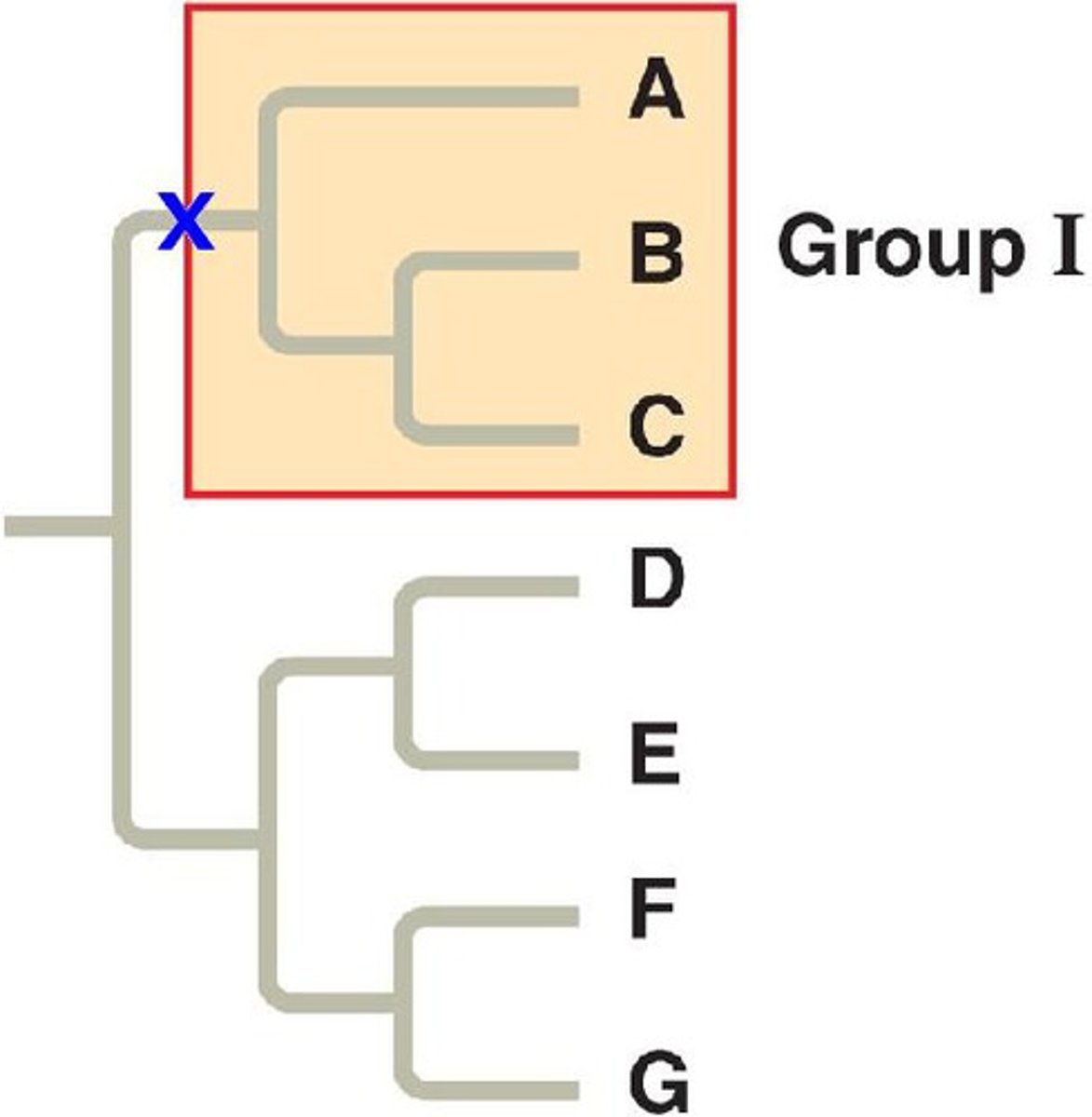
Clade
A taxon that includes the evolutionary descendants of a given ancestor
Systematics
the study of biodiversity
Cladogram
a diagram that does not show common ancestors/evolutionary relationships, instead showing when a given species branched off
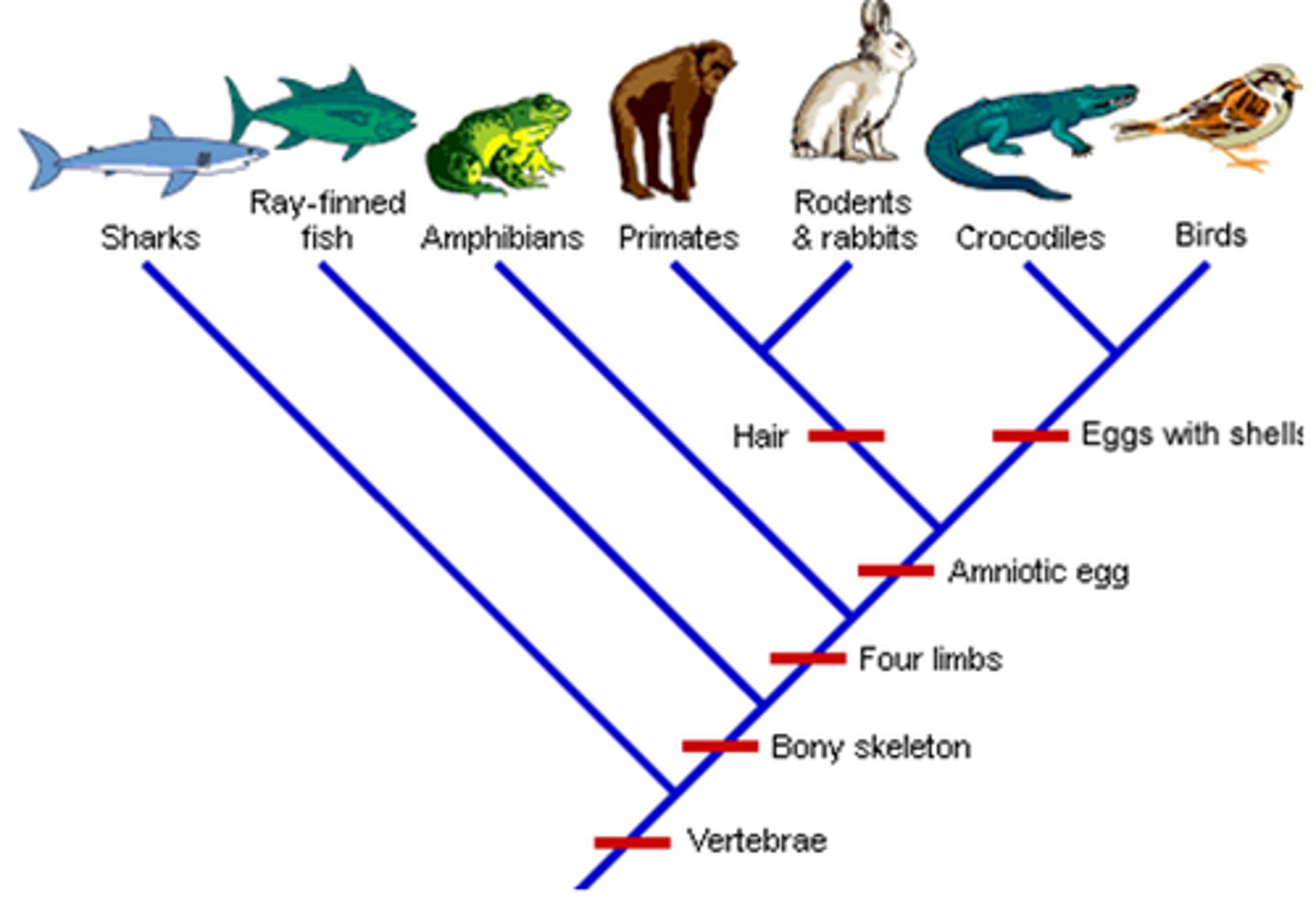
Homologous traits
a feature shared by multiple species, that IS inherited from a common ancestor (one bone, two bone, many bone)
Convergent Evolution
a feature shared by multiple species by that developed INDEPENDENTLY (ie: bird wings and bat wings). Analogous
Mutations
Any change in nucleotide sequences, occur randomly and is the cause of natural selection/evolution
Migration
Movement of individuals between populations, the cause of gene flow
Population Bottleneck
An environmental event results in the survival of only a few individuals
Homoplasies
Similar structures in organisms to have a shared way of life (analogous).
Parsimony Principle
the preferred explanation of observed data is the simplest explanation (the one that requires fewest homoplasies)
Nomenclature
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Binomial Nomenclature: genus and species name (ie: homo sapiens)
Adaptation
A trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce more efficiently.
Sexual selection (non-random mating)
When individuals of one sex prefer certain traits of the opposite sex more than others (preferential)
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
Equilibrium; allele frequencies do not change across generations.
Taxonomy
The scientific study of how living things are classified
Stabilizing selection
Natural selection that favors intermediate variants by acting against extreme phenotypes
Directional Selection
Natural selection that favors traits in one direction different from the mean
Disruptive selection
Natural selection that favors traits in either direction from the mean (small beak or large beak, not middle)
Muller's ratchet
Asexually reproducing species can accumulate deleterious mutations (ones that increase the likelihood of a certain disease)
Phylogeny
Evolutionary history of a species
Monophyletic
A clade, containing an ancestor and all of their descendants.
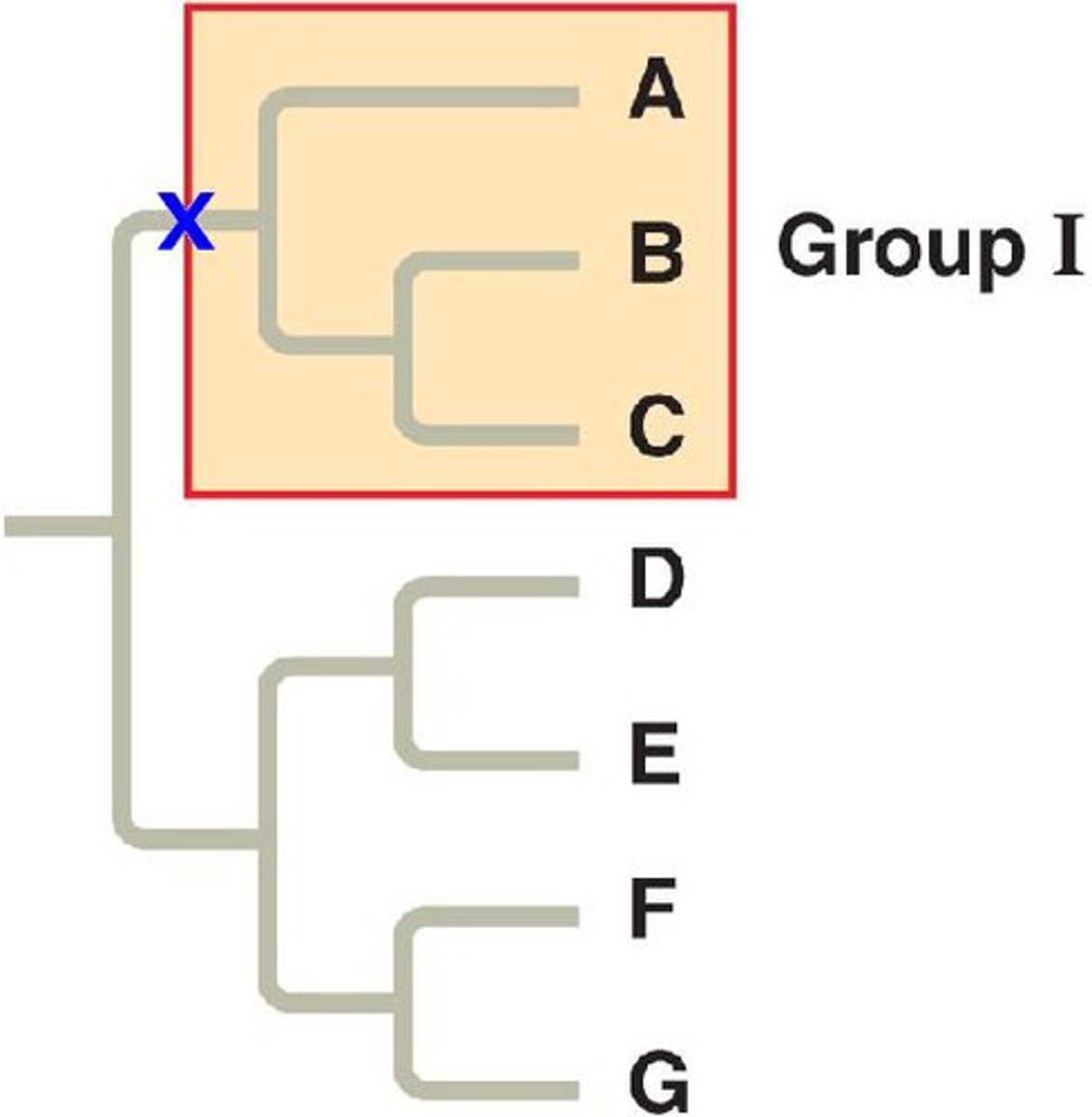
Paraphyletic
A group that does not include all of the decendants of the common ancestor
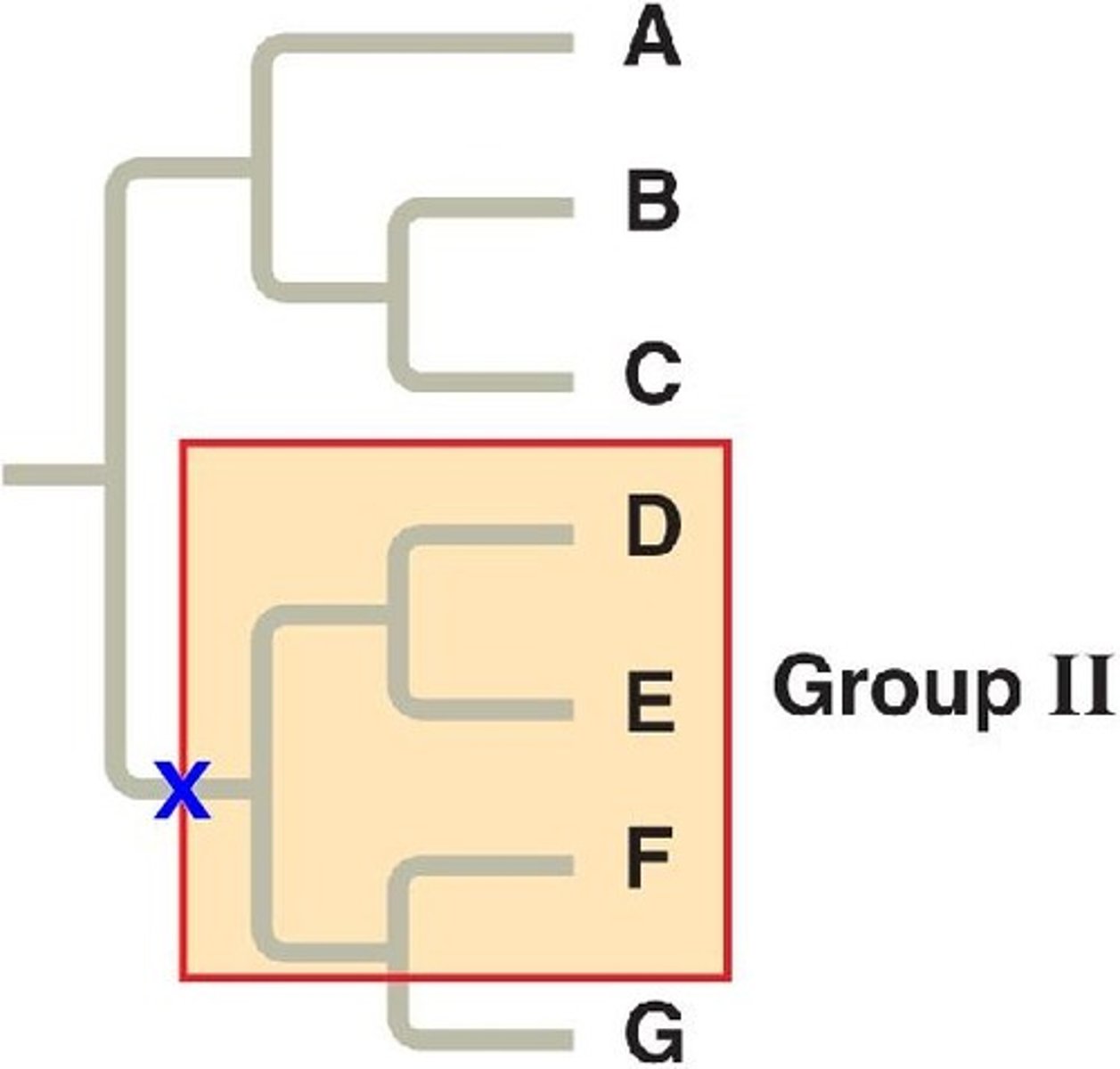
Polyphyletic
A group that does not include the common ancestor of the entire group