6.1 Intro to Urinary System
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What is the Purpose of the Urinary System? (4)
removal of wastes
pH regulation
electrolyte balancing
fluid balance
Of the main purposes, which is the most important on a short-term level?
fluid balance
Of all of our systemic circulation that the aorta is pushing to the rest of the body —> what fraction of it goes to the kidneys?
¼
___% of the blood sent to the kidney gets returned (veins → vena cava)
95%
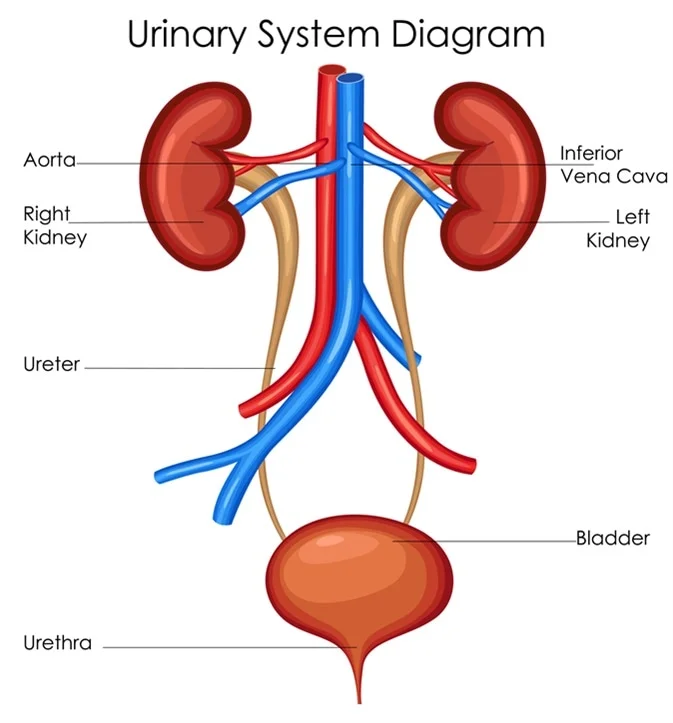
The overall structure of the Urinary System includes: (8)
renal artery, renal vein, kidneys, ureters, internal sphincter, external sphincter, bladder, urethra
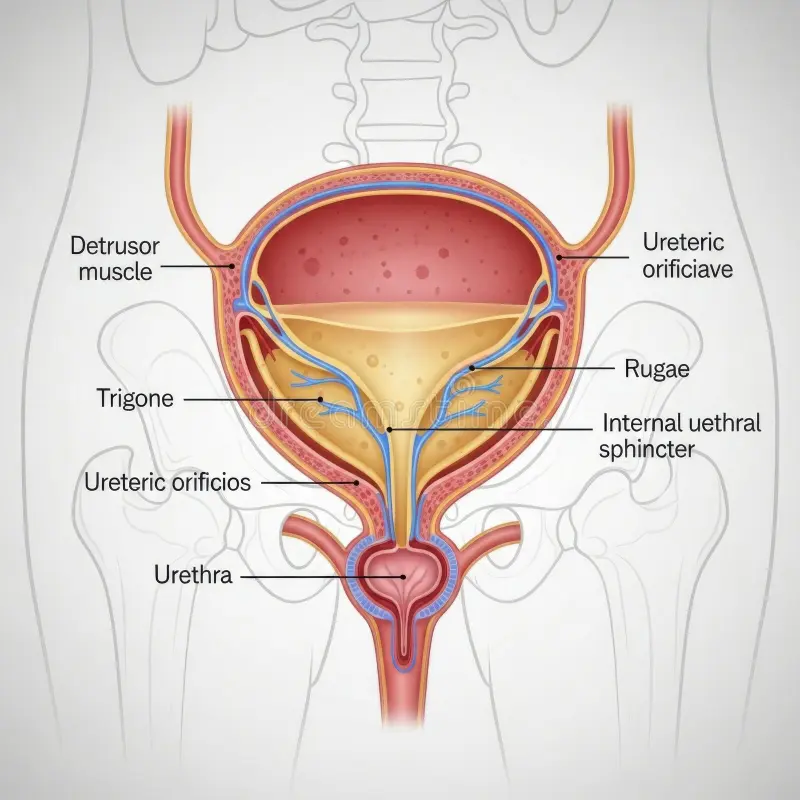
What does the bladder have embedded onto it’s wall?
stretch sensors
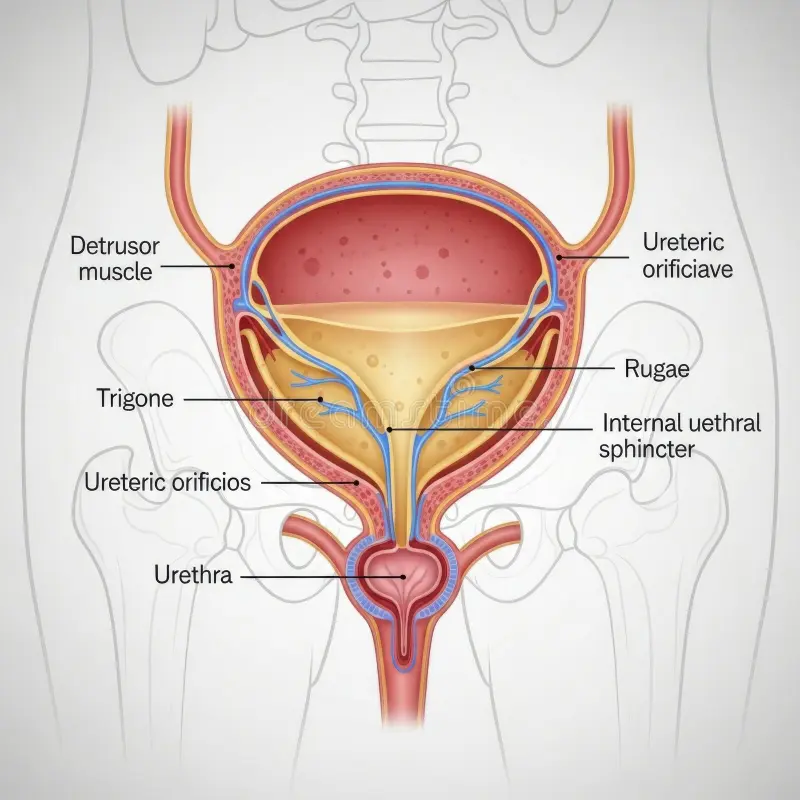
The bladder communicates with the outside world via _____.
urethra
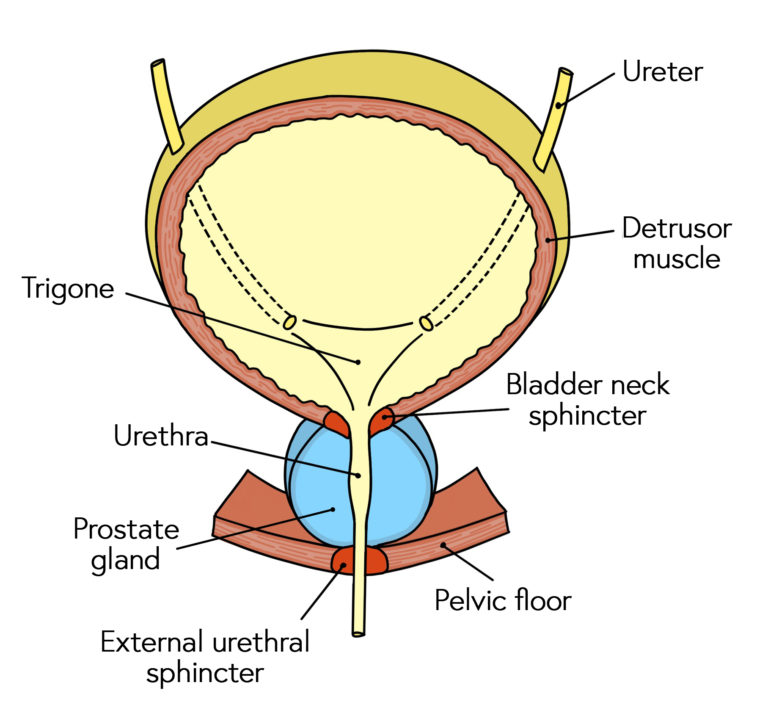
The internal sphincter is made of _____ muscle and is typically ______ _____.
smooth muscle; pinched shut
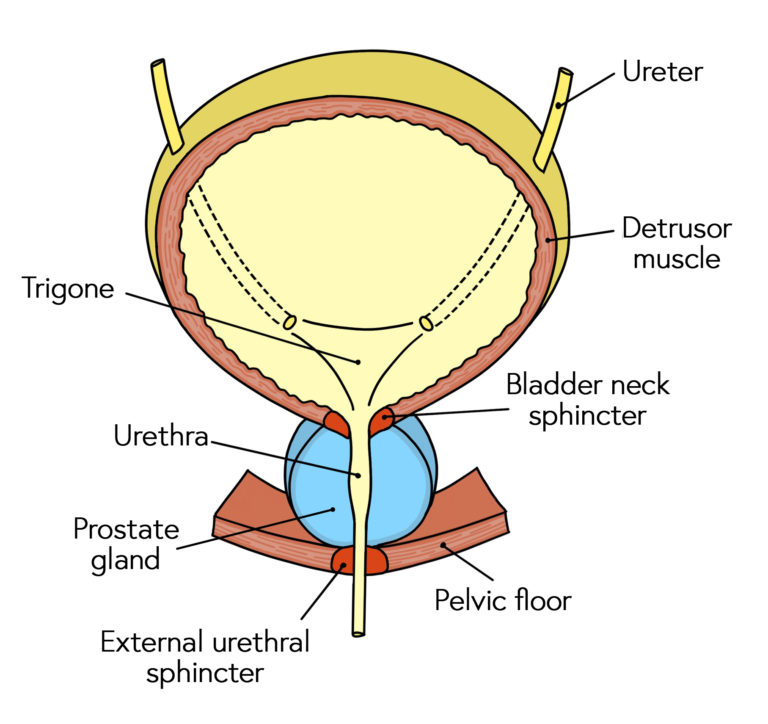
The external sphincter is made of ______ muscle and is ________ controlled.
skeletal; voluntarily
What are the 4 functions of the Urinary System (not the purpose):
filtration, reabsorption, secretion, excretion
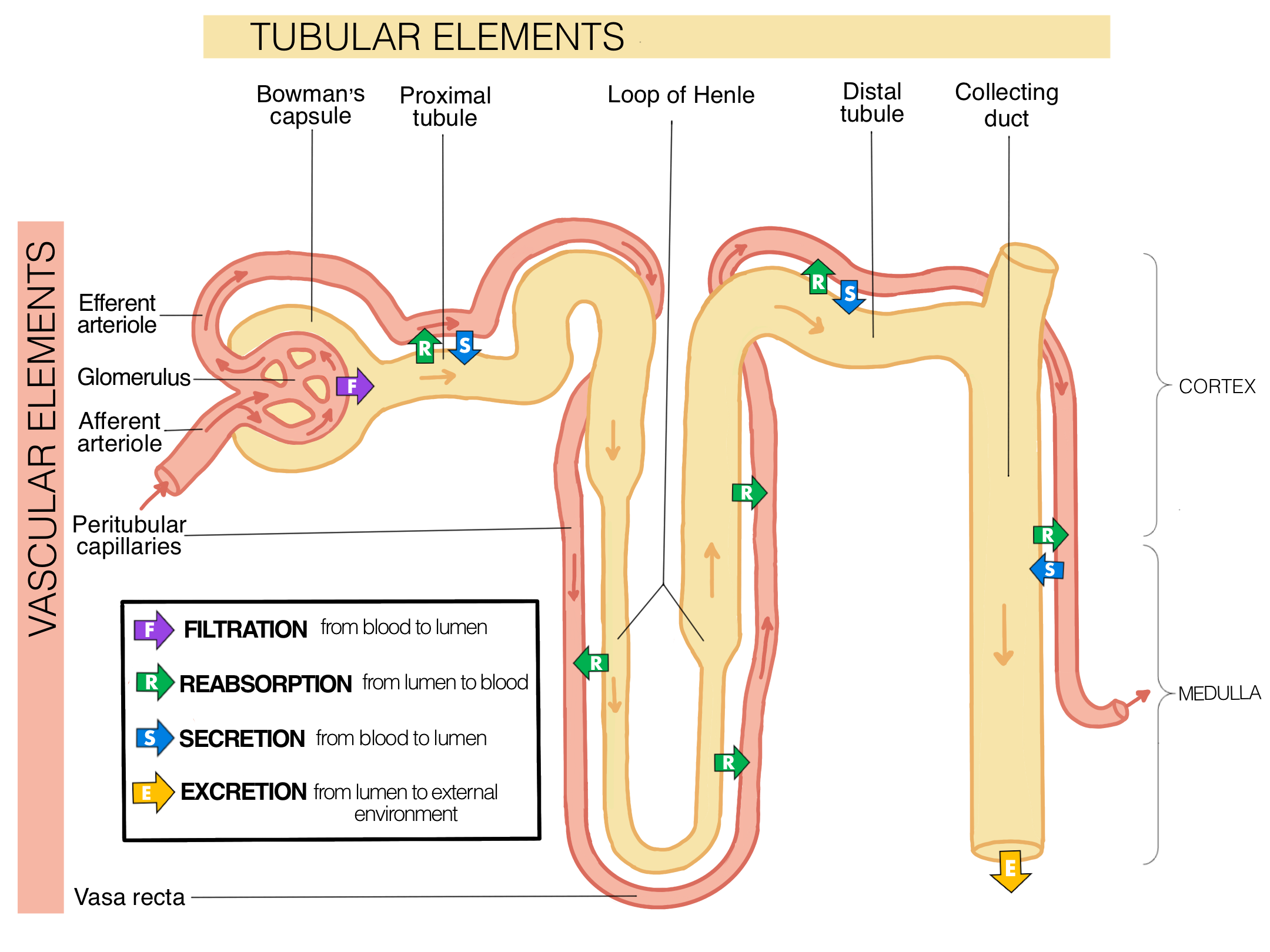
Filtration of Urinary System describes the…
non-selective movement of solutes and water from blood to (urinary) tubule
How many L of filtrate is produced per day?
180 L (per day)
The “non-selective” filtration just means anything small enough to pass filter like —> (3)
water, ions, small organics
What are 2 things you wouldn’t see in filtrate?
cells or proteins (most)
Reabsorption involes the …
selective movement from urinary tubule to blood
What’s ALWAYS 100% reabsorbed in the body from the filtrate?
glucose
Describe Secretion:
selective movement from blood to urinary tubule
What are some things that get excreted during secretion? (3)
penicillin/antibiotics, K+, drugs

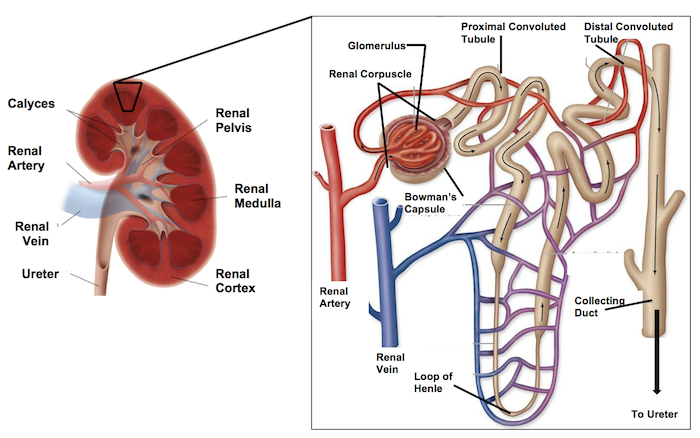
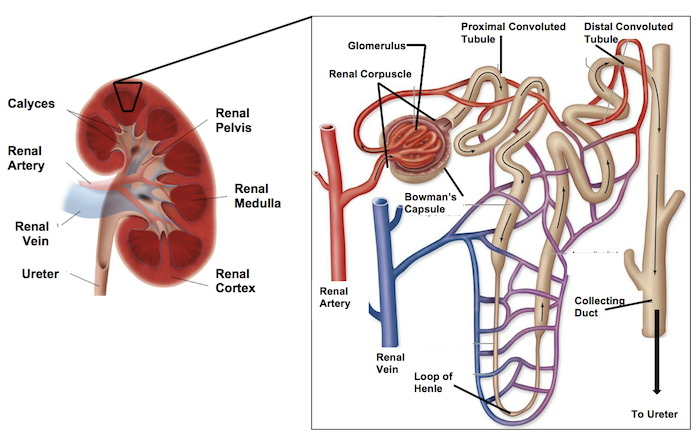
The anatomy of a kidney has a renal artery and renal vein feeding into it, the renal arteries turn into _____ _______.
afferent arterioles
The renal vein is used during the _____ portion of the urinary system.
reabsorption
The outer layer of the kidney is the ____ and the inner layer is called the _____.
cortex; medulla
The afferent arterioles lead to a group of tubes that make up the _____.
nephron
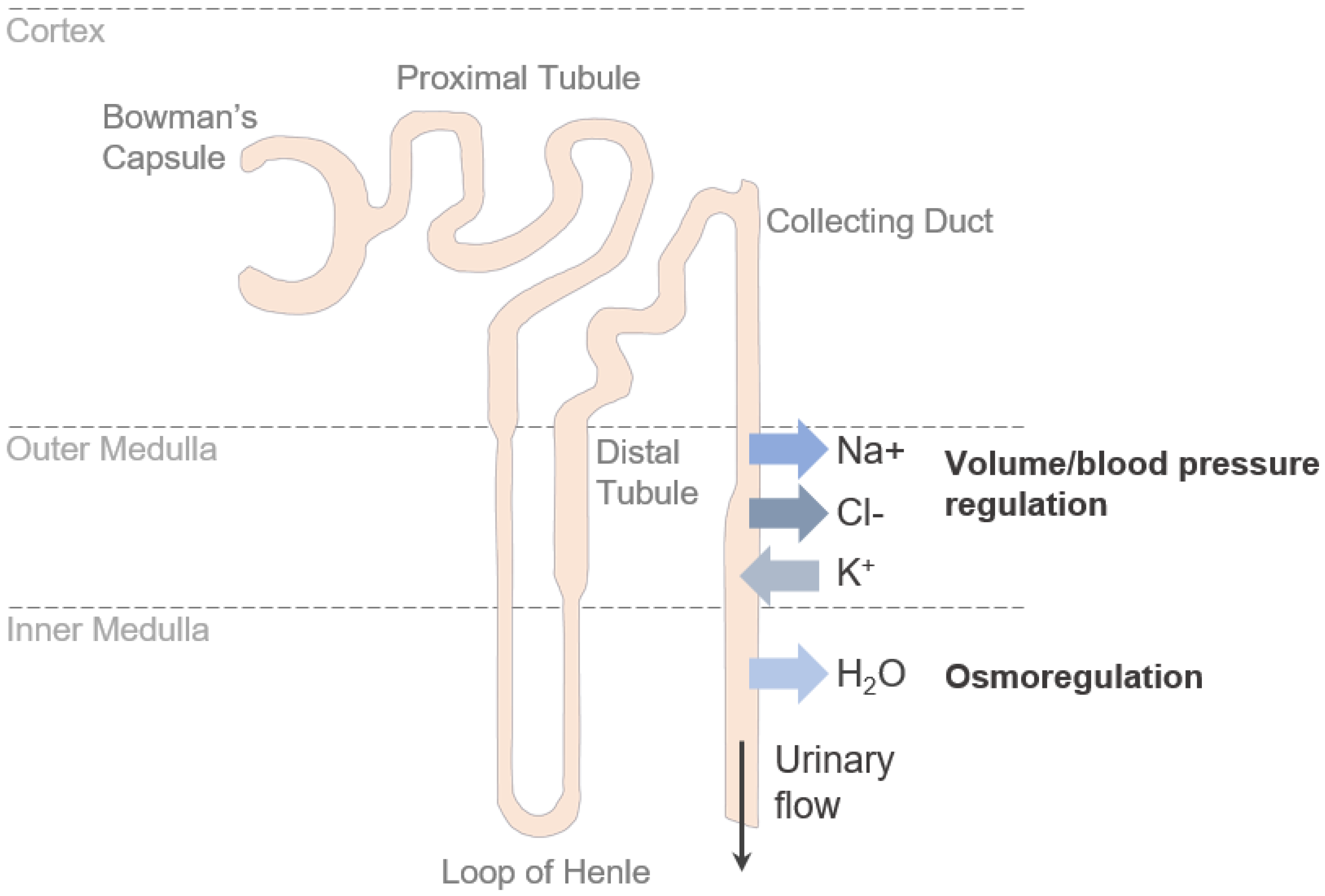
In the nephron, things will get reabsorbed or excreted —> If things get secreted/excreted, where do they go into (to get rid of)?
collecting duct
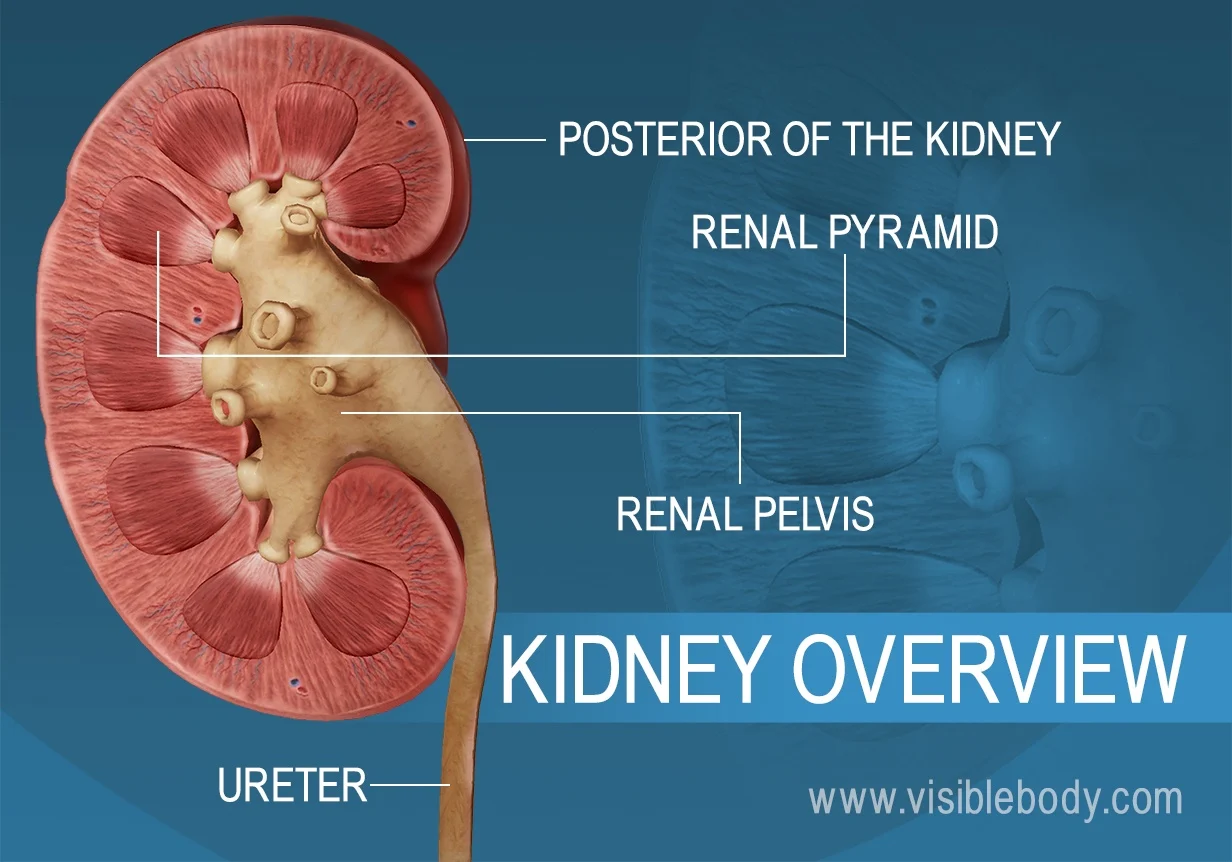
The collecting duct brings ___ to the ____ _____.
fluids; renal pelvis
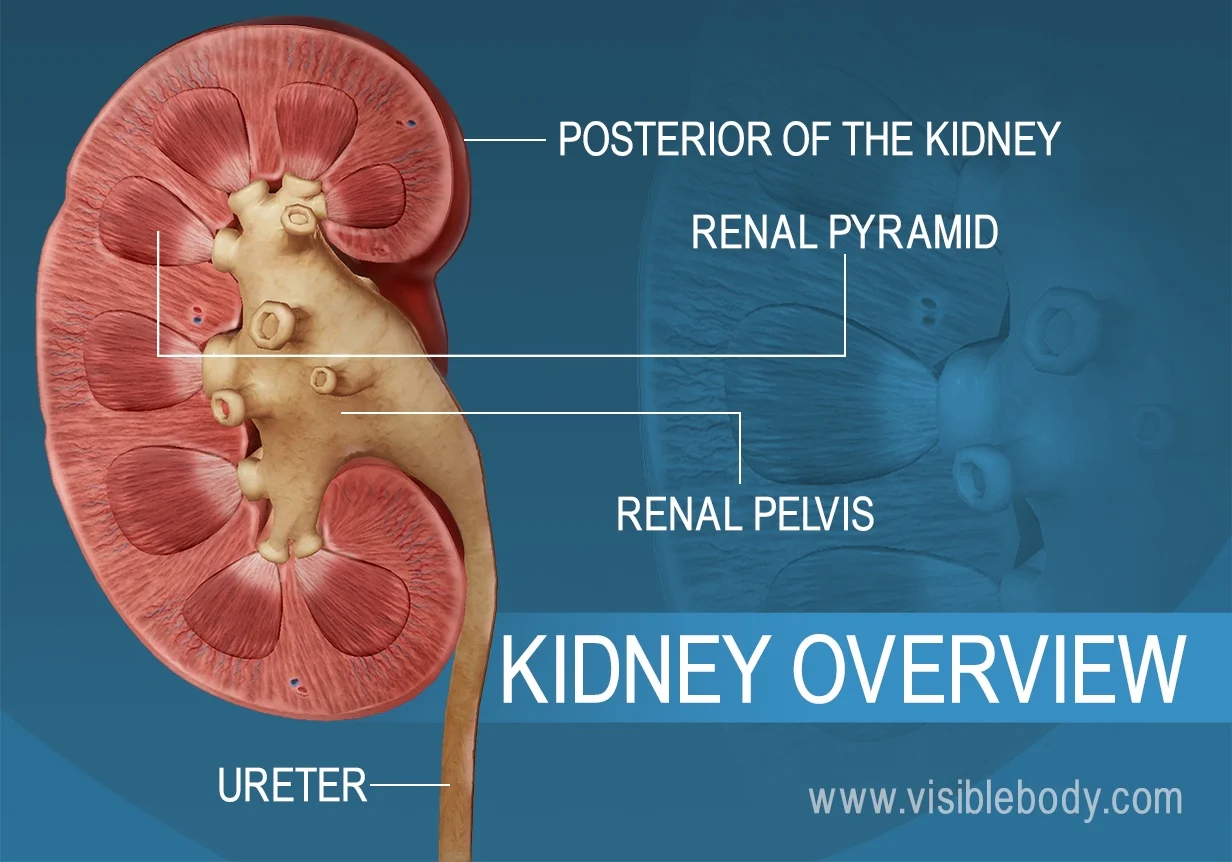
The renal pelvis feeds into the _____.
ureter
So the renal artery is bringing ______ blood, and the renal vein brings back ____ blood.
unfiltered; filtered
How many nephrons is there in a single kidney?
1 million
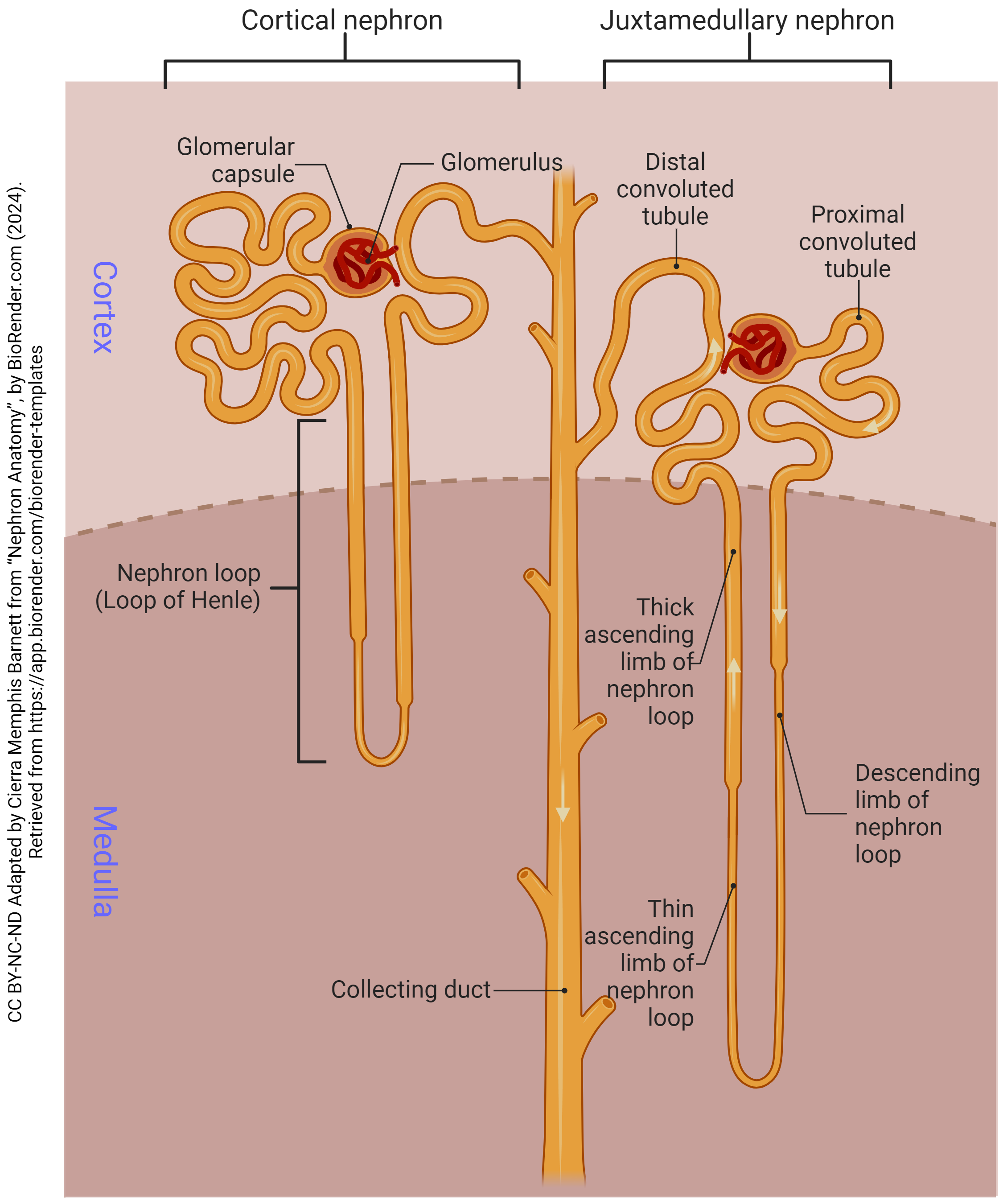
What are the 2 different types of nephrons? (names only)
corticol nephron, juxtamedullary nephron
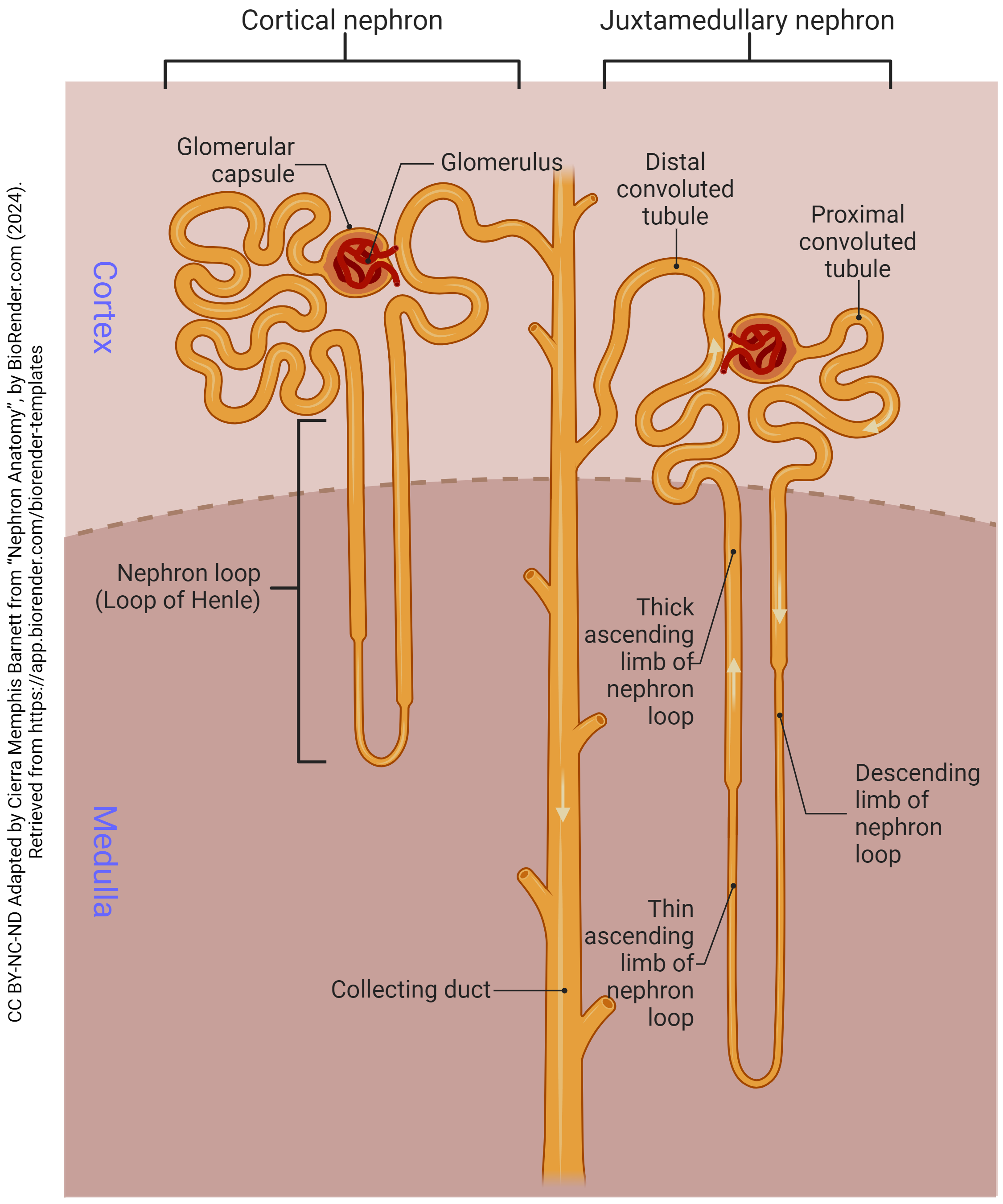
The cortical nephron stays within the _____. Makes up __% of the nephrons.
cortex; 80%
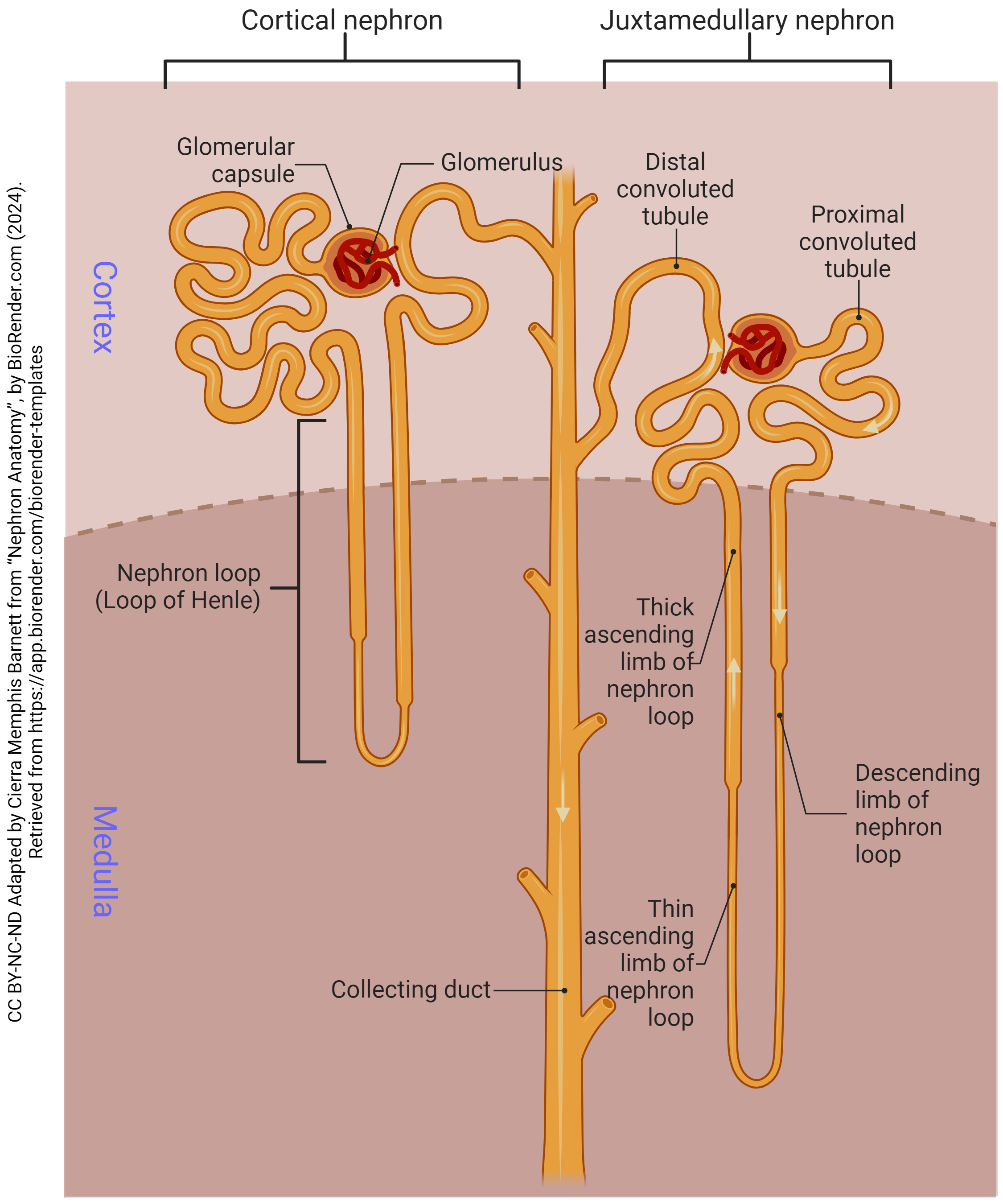
The juxtamedullary nephrons go ____; makes up ___% of the nephrons.
deeper (in the medulla); 20%
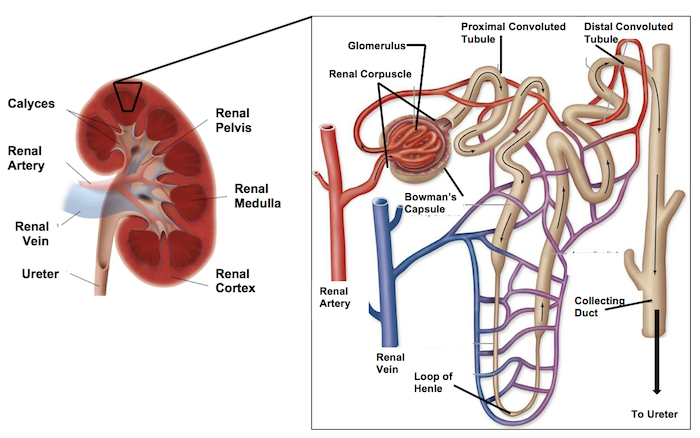
The flow of the Nephron:
Afferent arterioles bring the blood to the _____ _____.
glomerulus
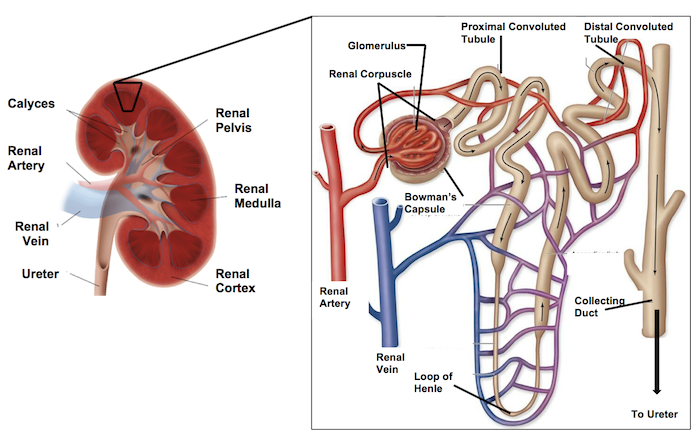
The glomerulus is surrounded by this capsule called?
bowman’s capsule
The glomerulus leads/connects to the ____ convulated tubule. (where the filtrate immediately goes)
proximal
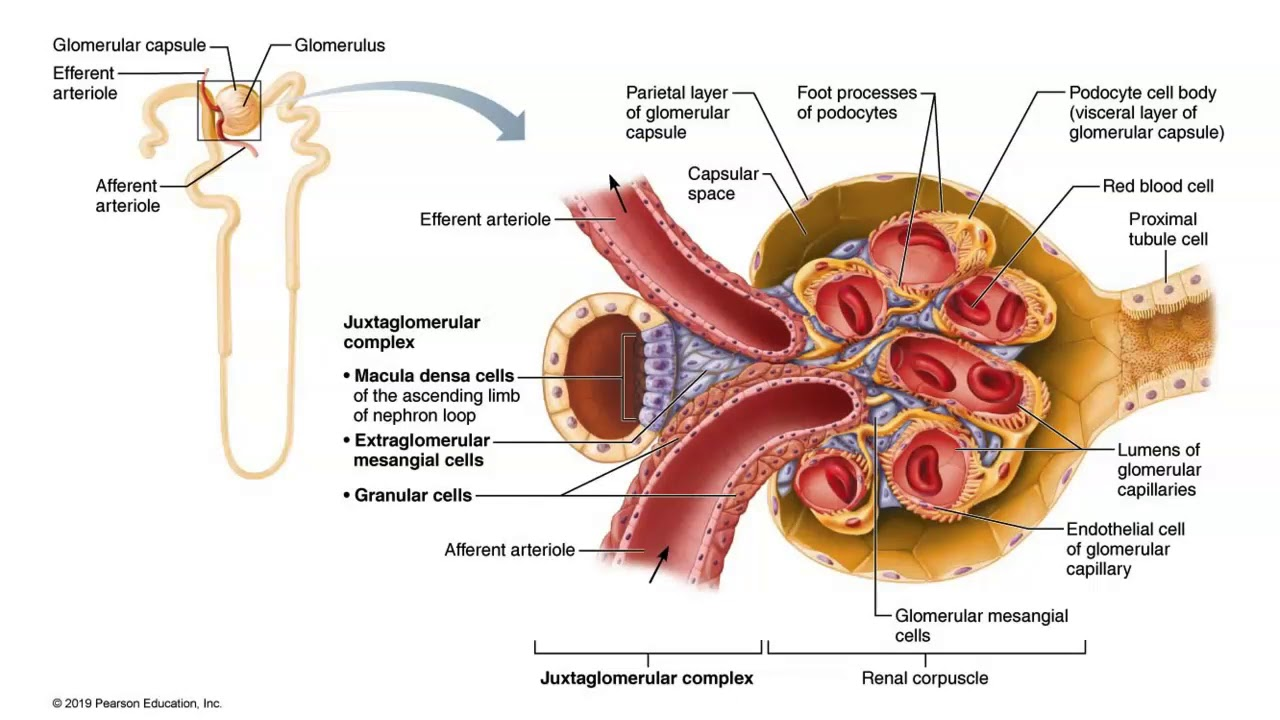
There are also _____ cells located on the afferent arterioles.
glomular
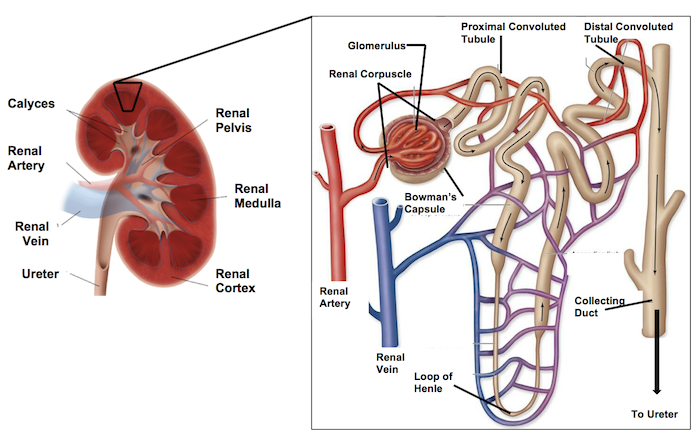
The flow of the Nephron:
Coming OUT of the glomerulus/bowman’s capsule is the _____ _____.
efferent arteriole
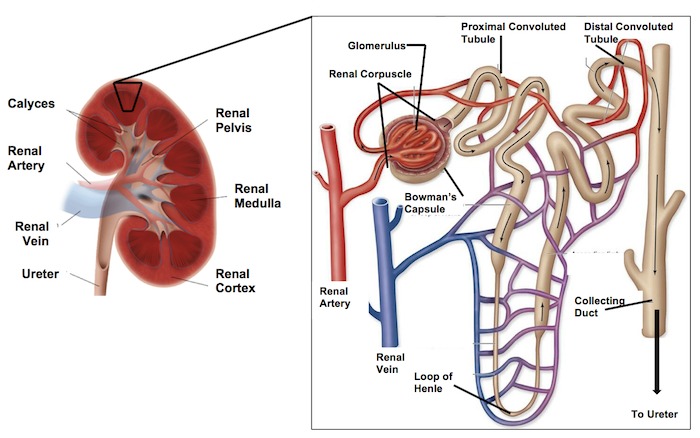
The flow of the Nephron:
The efferent arteriole branches into the _____ _______ which intertwine with the urinary tubule.
peritubular capillaries
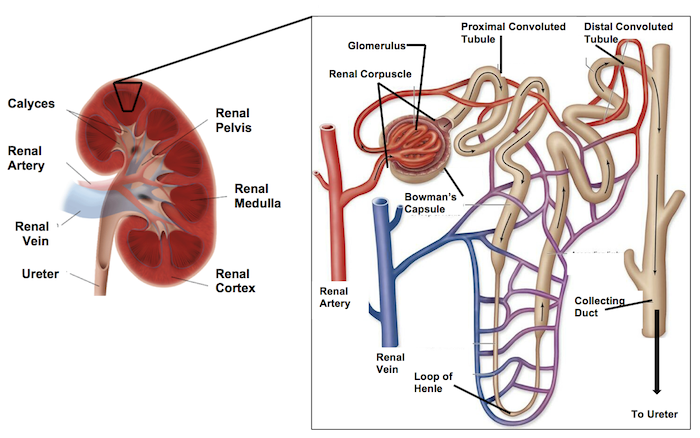
Then the initial renal tubule is called the ______ ______ ______, which brings filtrate in a downwards direction.
proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
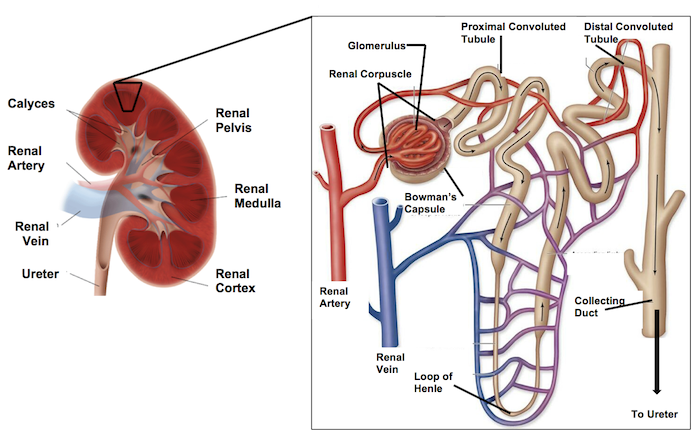
Then the PCT leads to the ___ __ _____.
Loop of henle
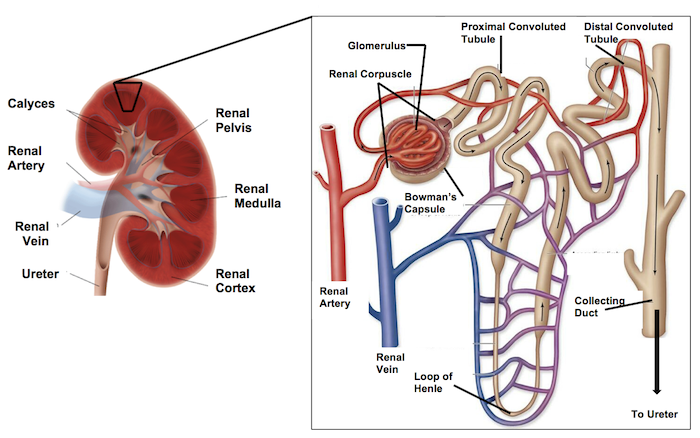
Then the loop of henle comes upwards leading to the ___ _____ _____. (filtrate is flowing in an upward motion)
distal convoluted tubule (DCT)

At the highest portion of the DCT, there is the ____ ____. (type of cell)
macula densa
From the DCT it leads into the _____ ____.
collecting duct
The collecting duct and DCT have filtrate flowing in _____ directions.
opposite
Once the afferent arteriole brings blood into the glomerulus, that’s where filtration occurs, therefore the fluid from that is now called ____.
filtrate
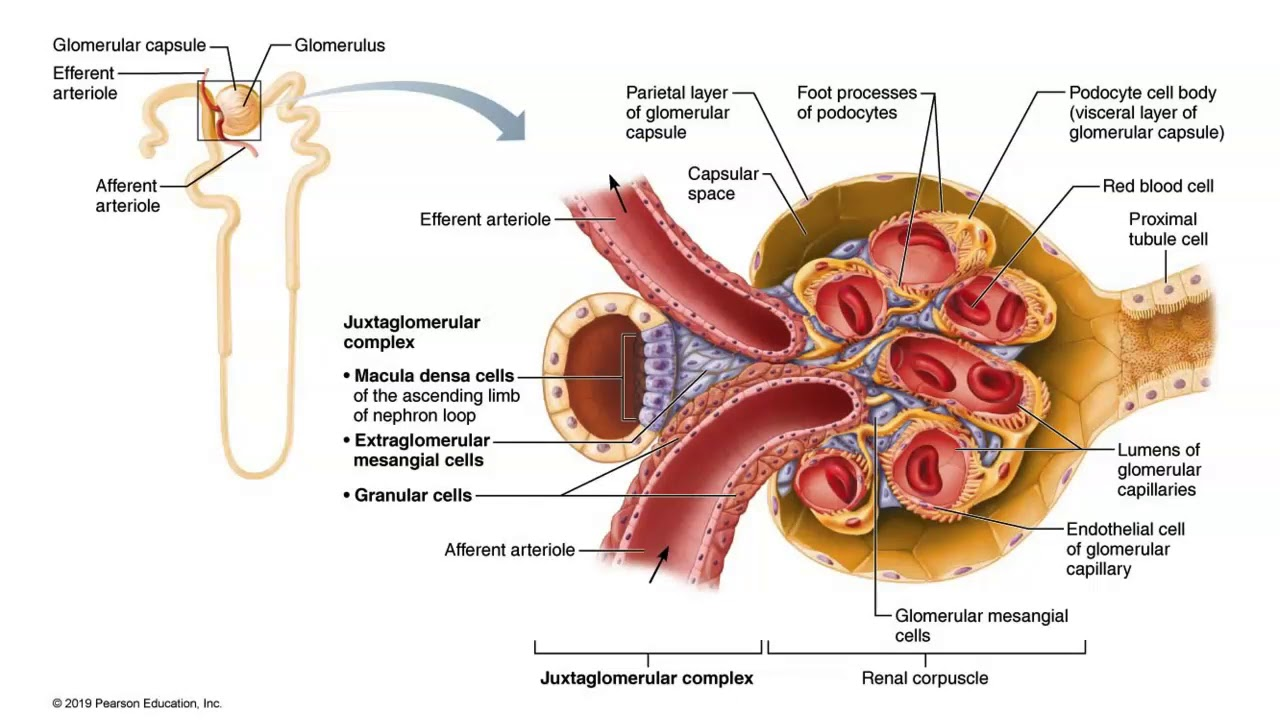
The macula densa is a special set of cells that act as a ____ _____.
flow detector
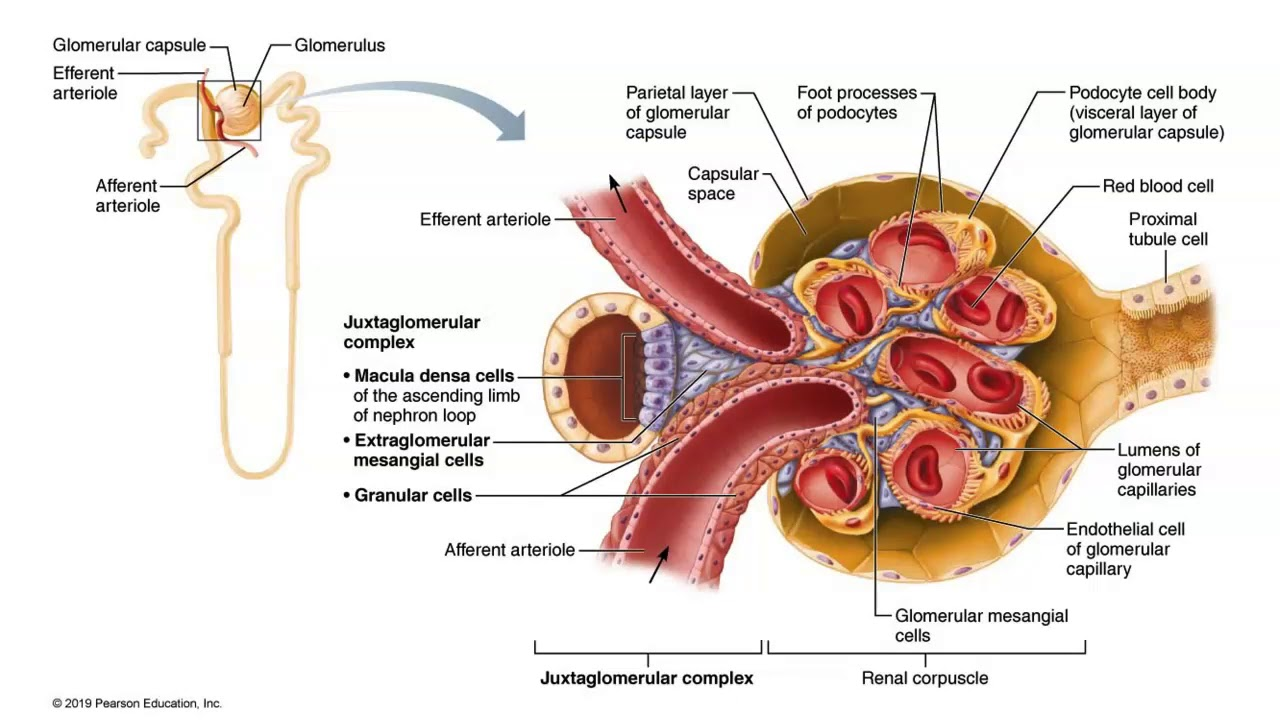
The granular cells are modified ___ ____ cells.
smooth muscle
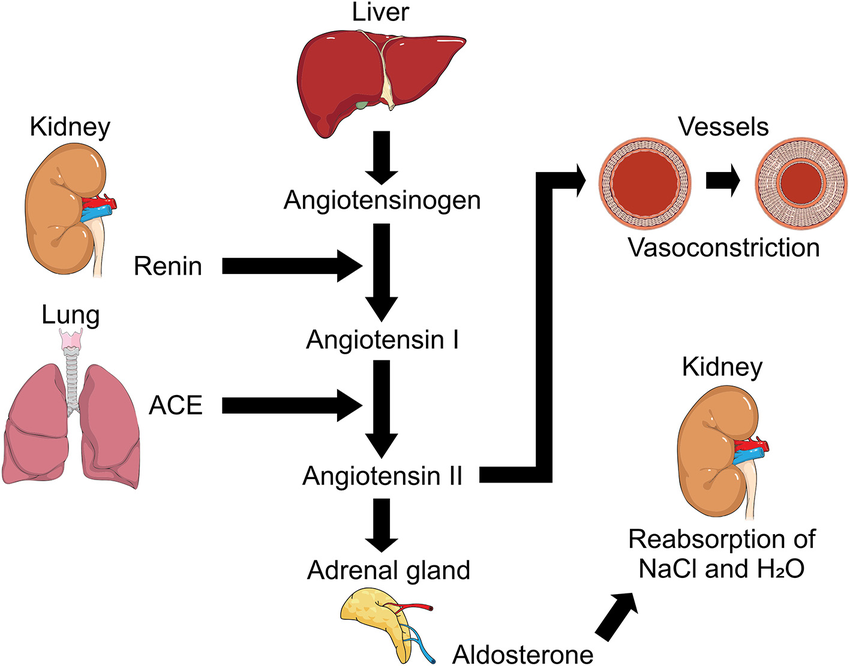
Granular cells secrete a chemical called ____.
renin
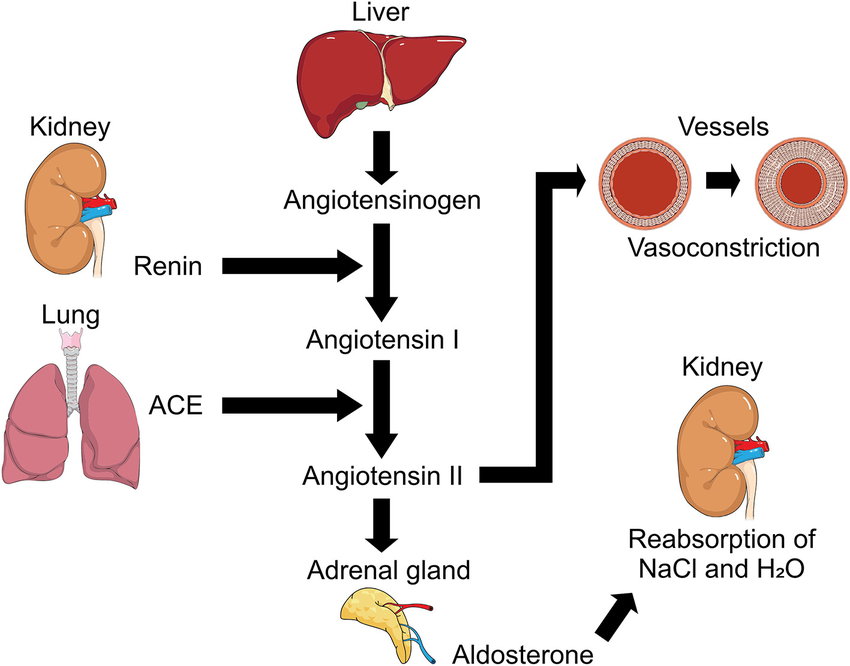
When granular cells dilate, they will secrete ____ renin.
more
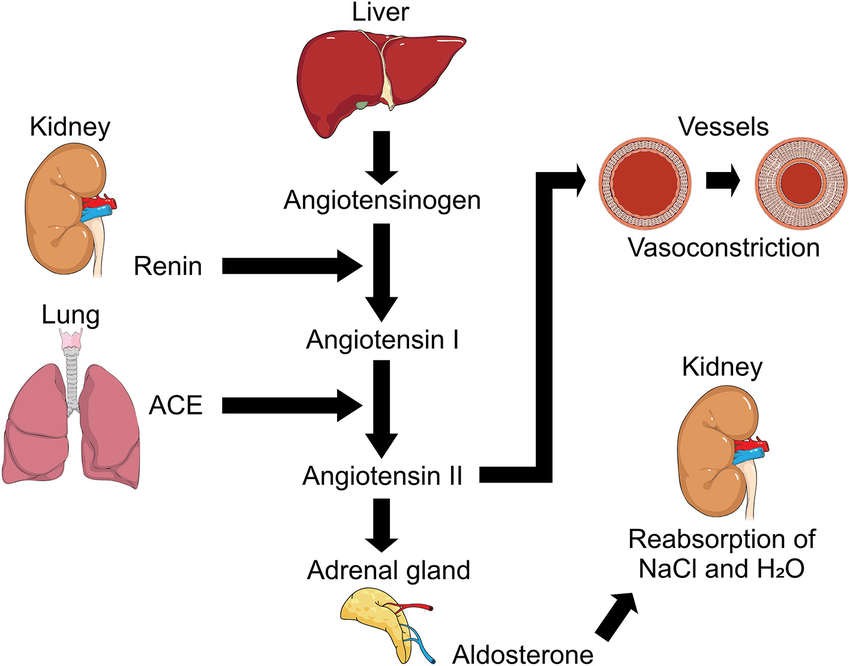
When granular cells constrict they will secrete ____ renin.
less
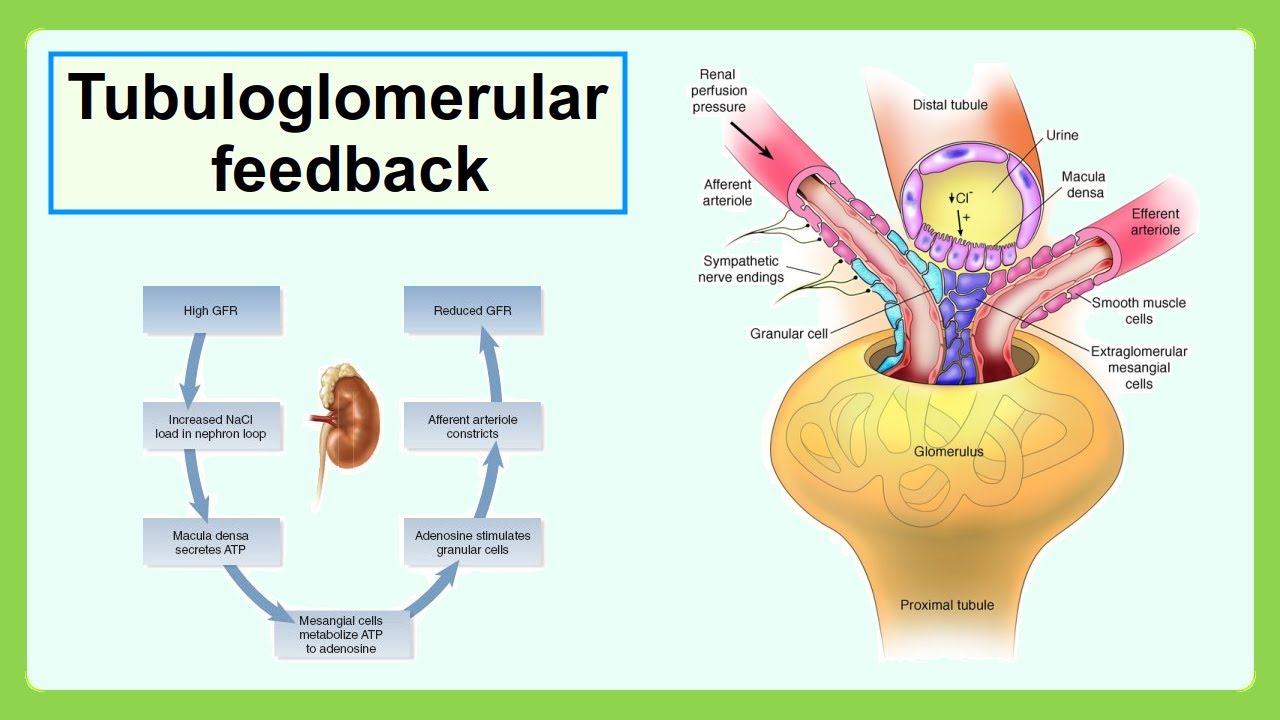
If the macula densa detects increased flow, it will signal the granular cells to _____.
constrict (secrete less renin)
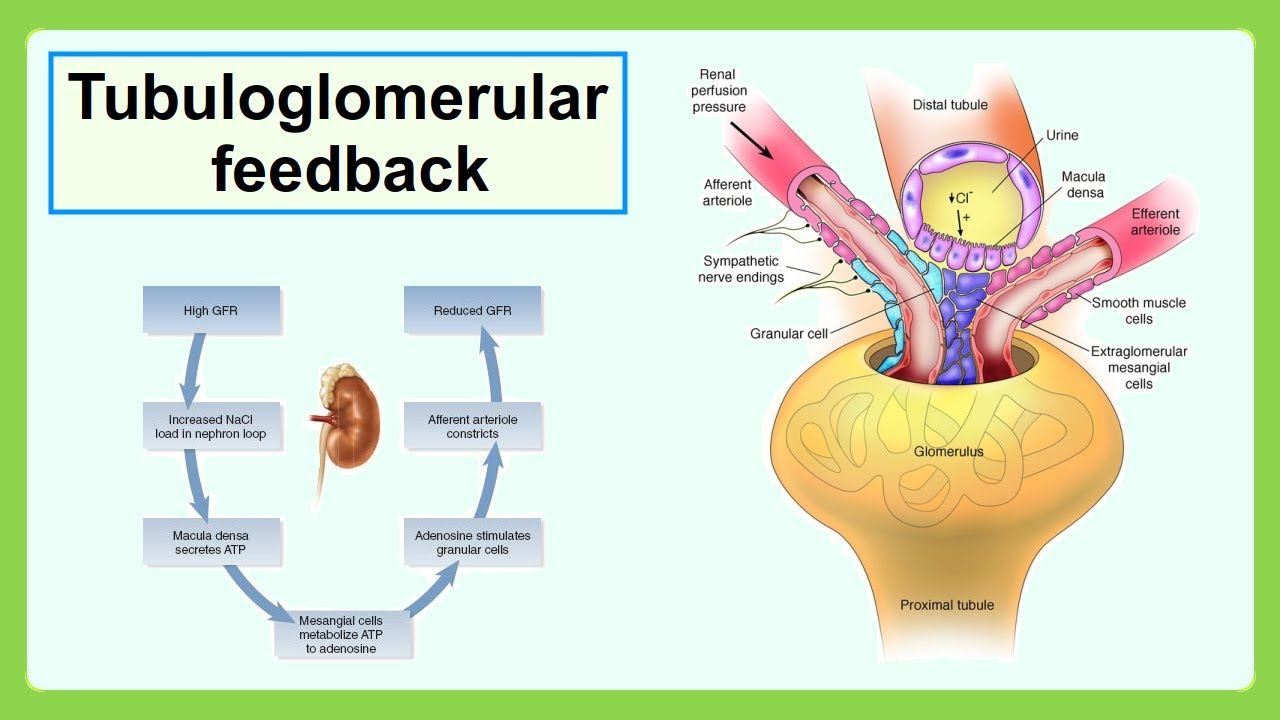
If macula densa detects decreased flow, it will signal granular cells to ____.
dilate

The whole macula densa signaling to granular cells is called ______ _______.
tubuloglomerular feedback

The glomerulus’ hydrostatic pressure is? (mmHg)
50 mmHg
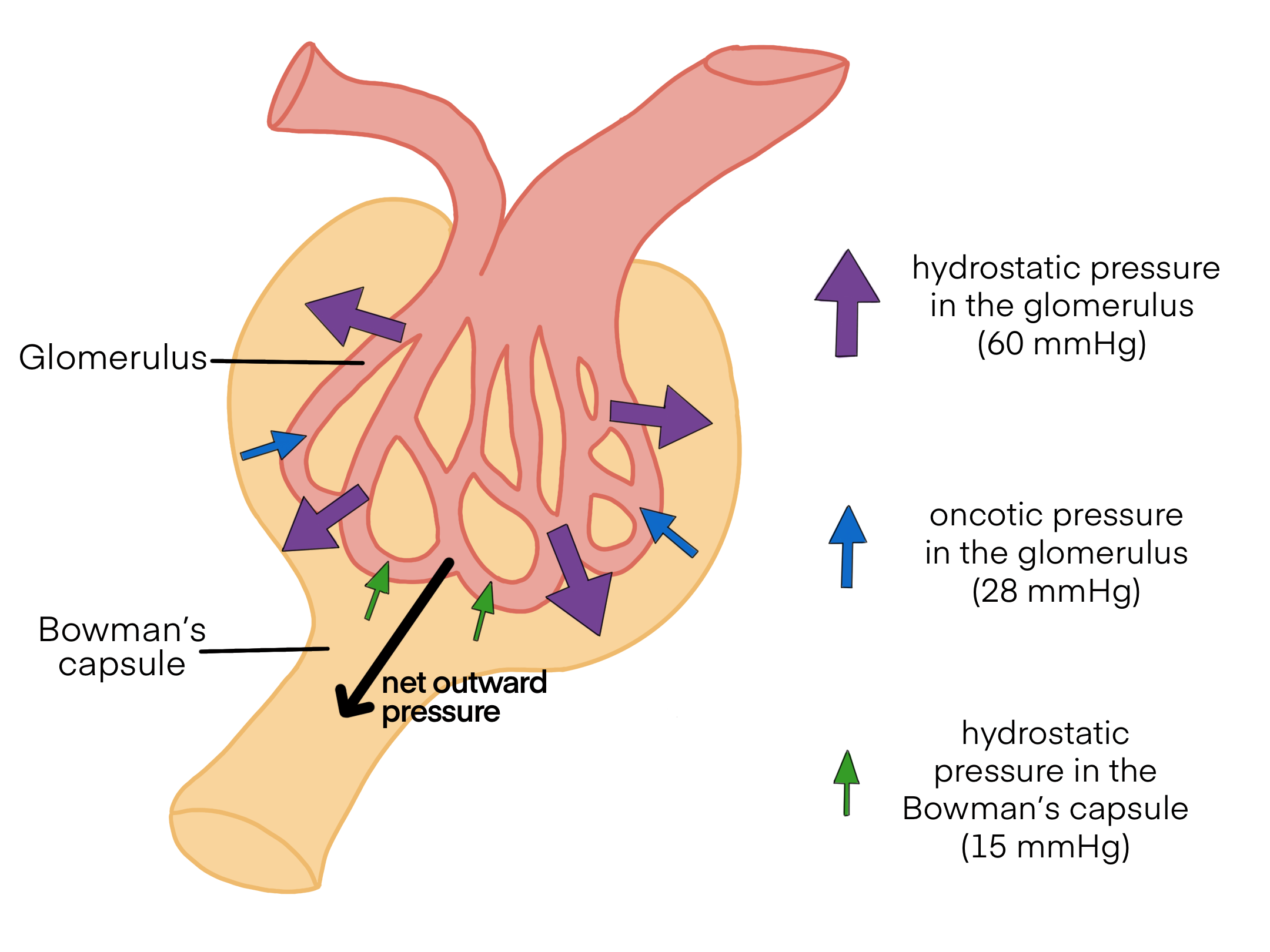
The osmotic pressure of the glomerulus is? (mmHg)
25 mmHg
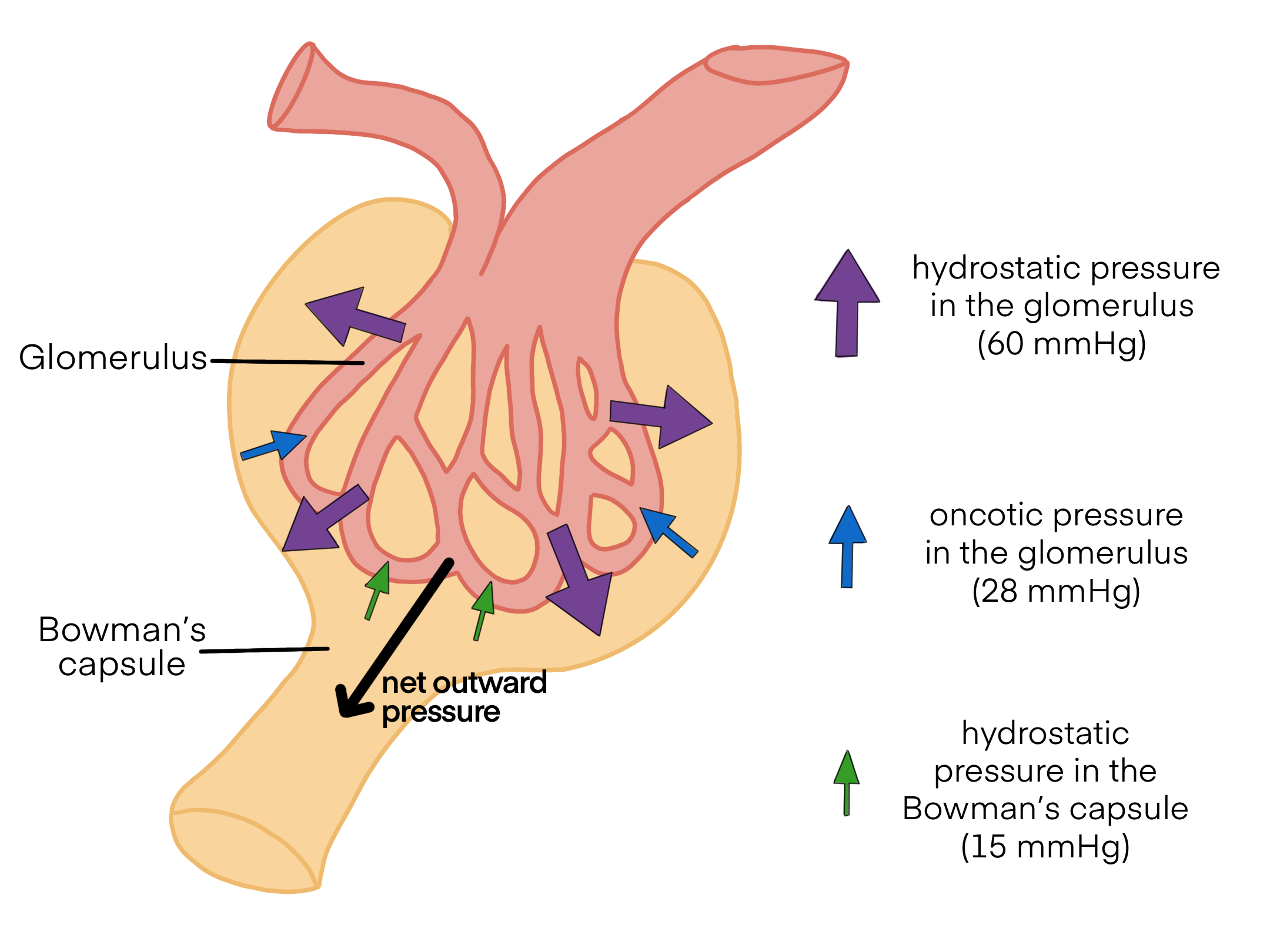
The fluid pressure of the Bowman’s capsule is? (mmHg)
15 mmHg
We use Tubuloglomerular feed back to ensure that if our bodies overall blood pressure increases, that the glomerular pressure stays ______.
constant
Higher pressure in the glomerulus =
more filtration
Lower pressure in glomerulus =
less filtration