Lecture 8 Weathering and Erosion
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Weathering
Disintegration of rock at or near the earths surface
Mass wasting
Transfer of material downslope in response to gravity
Erosion
Transport of material by mobile agents
Wind, water, ice

Exfoliation
Concentric or spherical shells of decayed rock are successively separated from a block of rock
Horizontal fracturing due to release of pressure
Commonly results in the formation of a rounded boulder of decomposition
Factors that impact mechanical weathering
Temperature
Frost heaving
Frost wedging
Water action
Frost heaving
Ice forming beneath the surface of soil during freezing conditions in the atmosphere
Frost wedging

Water action
Causes pot holes
Hydrolysis
occurs especially with granite, causes rock to whiten (erodes slowly), and creates clay.
Oxidation
occurs especially with rock containing iron nitrate, creates rusty red rock, and erodes and forms soil.
Hydration
a physio-chemical process in rocks containing salt minerals.
Chemical weathering
The alteration of the internal structure of minerals by chemical reactions
Carbonate dissolution
Ground water forms with carbon dioxide to form a slightly acidic solution

Lichens
make your skin irritated and itch
Grow on rocks and produce weak acids that chemically weather rocks
Erosion by water
The process by which water, ice, wind, or gravity moves fragments of rock and soil
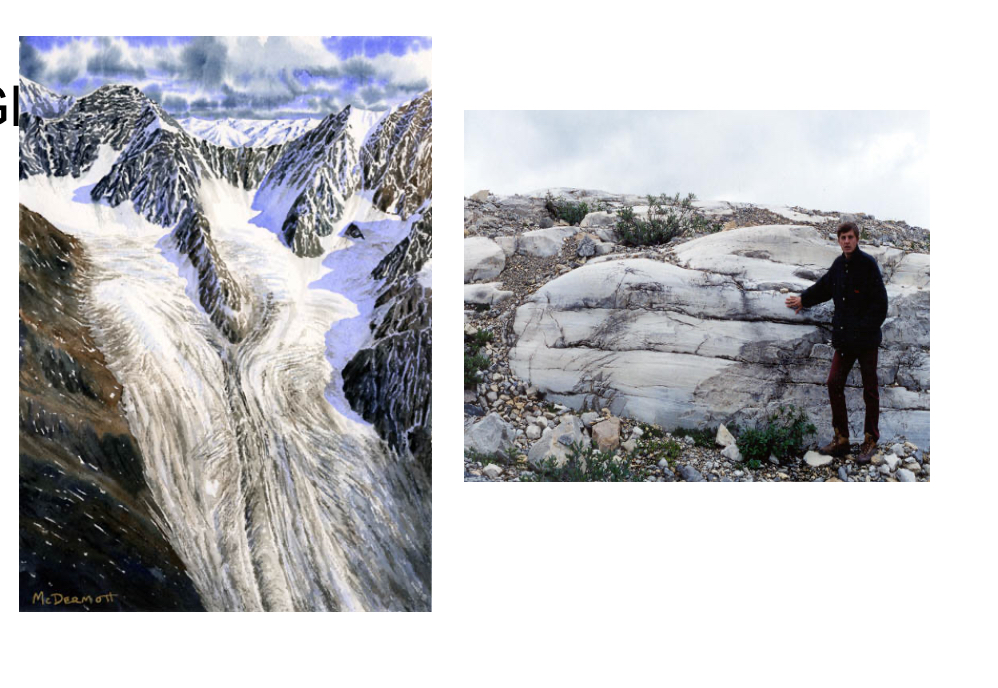
Erosion by ice glaciers

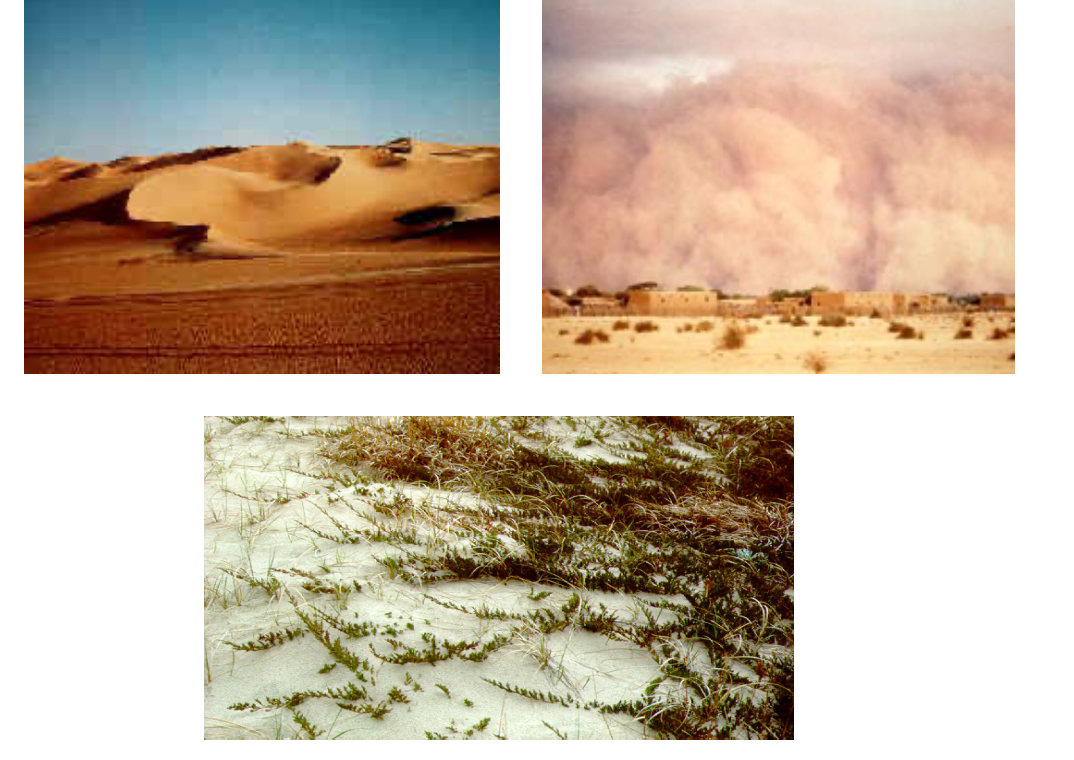
Wind erosion

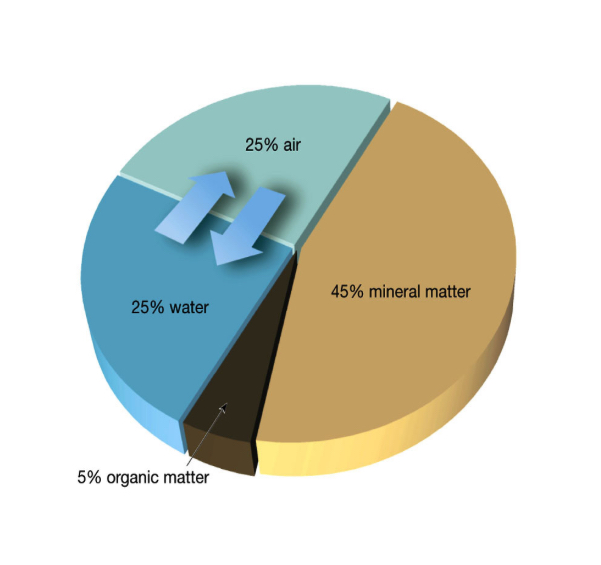
What is soil
The layer of rock and mineral fragments along with organic matter, water and air supports the growth of plants
Thin layer of material covering the earth ‘s surface and formed from weathering of rocks
Talik
Layer of year round unfrozen ground that lies in permafrost areas
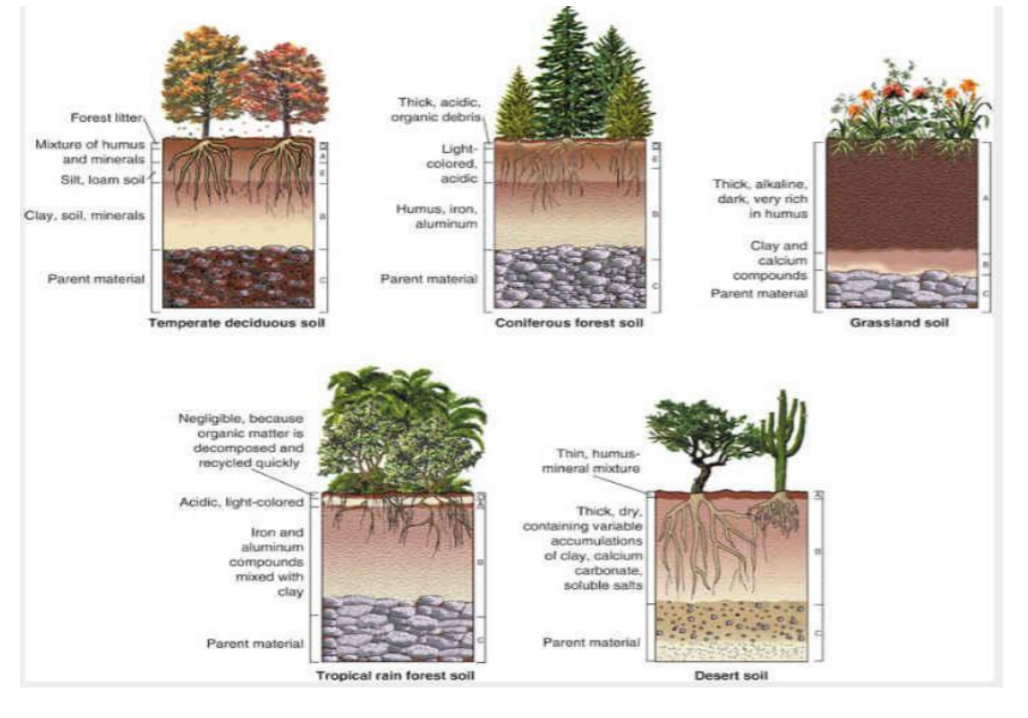
Soil profiles by biome