Practice Exam 3 Genchem 2
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Determine the molar solubility of Lead(II) Fluoride given that Ksp = 4E-8
A. 2.89E-9
B. 7.24E-6
C. 4.39E-4
D. 2.15E-3
D
Select the Scenarios that are spontaneous
1.a cube of ice melts at room temp
2.a ball rolls up a hill
3.iron rust at room temperature
4.water freezes at room temperature
5.scattered cards reassemble into a stack
A. i, ii, iii, iv, v
B. i, iii
C. iv, i
D. i, ii, iv
B
3. If there are initially 0.0834 moles of HBr in a flask and a student titrates the acid with 0.0834 moles of KOH, what point is the titration in and what will determine the pH?
A. The titration is at before equivalence, the concentration of acid will determine pH
B. The titration is at half equivalence, the conjugate base will determine pH
C. The titration is a equivalence, water autoionization will determine the pH
D. The titration has passed the equivalence point, excess titrant will determine pH
C
Select the correct statement(s) concerning buffer systems:
I. The best buffer results when the concentrations of [HA] = ½ [A-]
II. Buffer systems do not apply to strong acids or bases
III. The approximation method is always applicable to buffer systems
IV. Adding a common ion to a weak acid equilibrium will shift the equilibrium to the left
A. I, II, IV
B. II, III, IV
C. II, IV
D. All of the above
B
Which of the following show the correct Ksp expression for Mercury(I) bromide?
A. Ksp = [Hg22+ ] [Br-]^2
B. Ksp = [Hg22+ ]^2[Br-]^2
C. Ksp = [Hg22+ ][Br-]^2/ [Hg2Br2]
D. Ksp = [Hg22+ ]^2[Br-]^2/ [Hg2Br2]
A
6. What is the pH of a solution containing 0.015 M KCN and 0.040 M of HCN? pKa of HCN = 9.31.
A. 8.88
B. 9.47
C. 8.66
D. 9.74
A
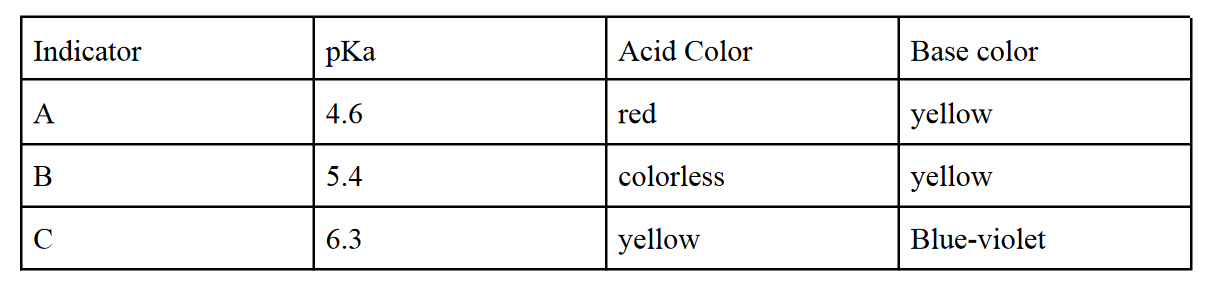
7. Which of the following indicators will be best for a titration with an equivalence point at pH = 6.0?
A
B
C
D:None of the above
B
8. Consider a titration of 15 mL of 0.25 M of HI with 25 mL of 0.15 M KOH. What is the pH?
A. 4.0
B. 6.6
C. 7.00
D. 1.17
C
Identify the base and its conjugate acid from the reaction below:
HNO3 (aq) + LiOH (l) ⇋ H2O (aq) + NO3-(aq)
A. HNO3 / NO3-
B. LiOH/HNO3
C. LiOH/H2O
D. H2O/H3O+
C
If 0.033 L of 0.100 M nitrous acid is titrated with 0.100 M KOH, determine the pH of the titration if 40 mL of titrant is added to the flask. Ka of nitrous acid = 4.5 x 10-7
A. 7.01
B. 12.5
C. 7.07
D. 11.98
D
11. Rank the following compounds by increasing molar solubility.
i. CaCO3 Ksp = 5.4 x 10-8
ii. PbCl2 Ksp = 3.4 x 10-5
iii. Ba3(PO4)2 Ksp = 7.2 x 10-9
iv. CuCO3 Ksp = 6.7 x 10-15
A. i, ii, iii, iv
B. iv, i, iii, ii
C. ii, iii, iv, i
D. iii, ii, iv, ii
B
13. Consider the titration of 0.5 L of 0.25 M HCl by 0.12 L of 0.15 M KOH and answer the
following questions:
a. Identify the titrant
b. What is the initial pH before the titration?
c. At what point is the titration at? Circle ONE of the following
Initial
Before equivalence
Half equivalence
Equivalence
After equivalence
a.0.15 M KOH
b.pH = 0.602
c.Before equivalence
15. Write the Ksp expression for barium perchlorate
Ksp = [Ba2+][ClO4-]^2
Which of these salts will form an acidic solution upon dissolving in water?
I. CaCl2
II. AlCl3
III. NH4Cl
IV. LiCl
A. I only
B. II only
C. III only
D. I and II only
E. II and III only
E
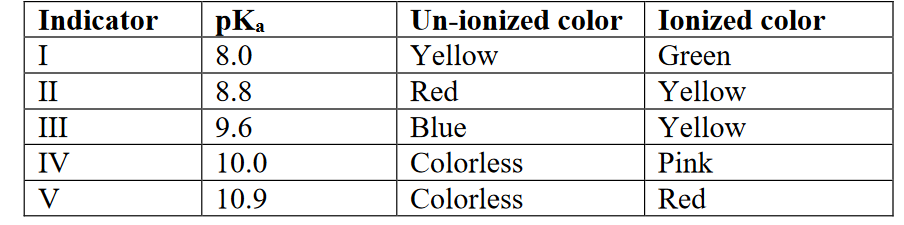
A colorless acid is titrated by a colorless titrant. The equivalence point for this titration is at pH 9.4. Given the indicators below, which of the following statements is necessarily true?
A. Indicators I and II will all work for this titration because they may change color before the
equivalence point.
B. Indicators III, IV, and V will all work for this titration because they may change color
slightly passed the equivalence point.
C. Indicators II, III, and IV will work for this titration but IV is the best to use.
D. Indicators IV and V will all work for this titration because they both change from colorless
to color.
E. Indicators II, III, and IV will work for this titration but III is the best to use
C
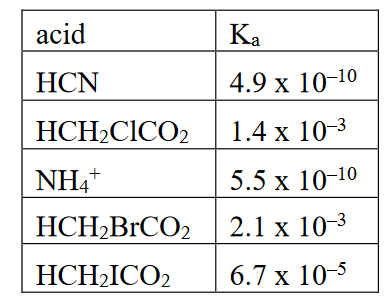
Using the information in the table below, which of the answer choices is the strongest base?
A. CN–
B. CH2ClCO2–
C. NH3
D. CH2BrCO2–
E. CH2ICO2–
A
4. A 20-mL volume of 0.40 M methylamine (Kb = 4.4×10–4) is titrated by a 0.40 M HI solution.
Determine the pH at the equivalence point.
A. 2.03
B. 5.52
C. 1.92
D. 5.67
E. 1.88
D
If you start with 50.0 mL of a solution that contains 0.50 M in HOCl and 0.79 M in NaOCl, what is the pH after 10.0 mL of 1.0 M NaOH has been added (Ka for HOCl = 3.5 × 10–8)?
A. 7.75
B. 6.94
C. 6.00
D. 7.66
E. 7.98
E
The pH of a 0.03 M solution of formic acid (HCHO2) is 2.1. What is its Ka value?
A. 1.8 x 10–5
B. 7.9 x 10–3
C. 6.3 x 10–5
D. 2.9 x 10–3
E. 2.1 x 10–3
D
You begin with 2.4 L of water at 25 °C and generate a saturated solution of SrCO3. Determine the molar solubility of SrCO3 [molar mass of SrCO3 = 147.63 g mol–1; Ksp of SrCO3 at 25 °C =
5.60 x 10–10].
A. 1.86 x 10–10 M
B. 1.19 x 10–5M
C. 2.37 x 10–5 M
D. 9.88 x 10–6 M
E. 5.60 x 10–10 M
C
A diprotic acid, glycine, has a Ka1 = 4.5 x 10–4 and a Ka2 = 1.7 x 10–10. What is the pH of a 0.25 M solution of this acid?
A. 0.602
B. 3.35
C. 9.78
D. 12.03
E. 1.97
E
A solution is made by combining 15 mL of a 0.75 M HBrO solution and 15 mL of a 0.41 M NaBrO
solution. What is the pH of the final solution? [Ka for HBrO = 2.0 × 10–9]
A. 10.26
B. 8.44
C. 5.55
D. 7.14
E. 8.96
B
Which of the following compounds is least soluble in water at the same temperature?
A. PbBr2 Kc = 6.6 ´ 10–6
B. Li2CO3 Kc = 8.2 ´ 10–4
C. CaF2 Kc = 3.5 ´ 10–11
D. Ag2SO3 Kc = 1.5 ´ 10–14
E. Mg(OH)2 Kc = 5.6 ´ 10–12
D
In the reaction below, which reactant is the Lewis acid?
Cr3+ + 6 CN– → Cr(CN)63–
A. Cr3+
B. CN–
C. Cr(CN)63–
D. None of these are Lewis acids
A
Iodoacetic acid (HCH2ICO2) has a Ka value of 6.7 x 10–5 at 25 °C. What is the Kb for its conjugate
base, the iodoacetate ion at the same temperature?
A. 6.7 x 10–5
B. 9.8
C. 1.0 x 10–14
D. 1.5 x 10–10
E. 4.2
D
Which of the following acids is best to use to prepare a buffer with a pH of 5.70?
A. HC5H5O5CO2, Ka = 3.98 × 10–6
B. HC8H5O2, Ka = 2.88 × 10–4
C. HBrO, Ka = 2.29 × 10–9
D. HC7H5O4, Ka = 1.00 × 10–3
E. HC2H3O2, Ka = 1.81 × 10–5
A
What is the pH of a 0.25 M solution of HCN (Ka = 4.9 x 10–10)?
A. 0.602
B. 2.65
C. 4.96
D. 11.35
E. 9.04
C
A 35.0-mL volume of a 0.34 M HC6H5CO2 solution is titrated by a 0.43 M CsOH solution. If a total of 21.2 mL of the CsOH solution is added to the HC6H5CO2 solution, determine the pH value of the mixed solution. [Ka for HC6H5CO2 is 6.5×10–5]
A. 4.70
B. 3.67
C. 4.29
D. 4.09
E. 4.19
A
Which of the following substances has the largest value for its standard entropy?
A. HNO3(l)
B. PCl5(g)
C. PbCl2(s)
D. CO(g)
E. Mg(s)
B
What is the pH of a 0.887 M KClO2 solution at 25 °C (Ka for HClO2 = 1.1 × 10–2)?
A. 7.95
B. 7.00
C. 6.05
D. 12.99
E. 1.01
A
When HCN is titrated by KOH, which of the following species are present in the net ionic
equation?
I. H+
II. H2O
III. K+
IV. CN─
V. HCN
A. II and V only
B. II, IV, and V only
C. I, II, and V only
D. I, III, and IV only
E. I and IV only
B
A 1.0 M solution of a diprotic acid, H2A comes to equilibrium. The concentration of [A2–] is found to be 4.3 x 10–12 M. The Ka1 = 5.7 x 10–5. What is Ka2 for this acid?
A. 5.7 x 10–5
B. 5.7 x 10–8
C. 4.3 x 10–12
D. 1.3 x 10–7
E. 7.5 x 10–8
C
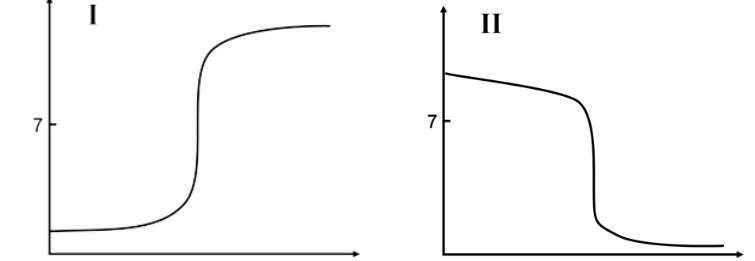
Determine the type of titration for the given titration curves.
A. Graph I is a strong base titrated by a strong acid and graph II is a weak base titrated by a
strong acid.
B. Graph I is a strong acid titrated by a strong base and graph II is a weak base titrated
by a strong acid.
C. Graph I is a strong acid titrated by a strong base and graph II is a strong base titrated by a
strong acid.
D. Graph I is a weak acid titrated by a strong base and graph II is a strong base titrated by a
strong acid.
E. Graph I is a weak acid titrated by a strong base and graph II is a weak base titrated by a
strong acid.
B
Which statement about buffers is necessarily true?
A. A buffer is an aqueous solution composed of two weak acids.
B. A buffer can absorb an unlimited amount of acid or base.
C. The pH of a buffer will change drastically when it is diluted with water.
D. The function of a buffer is to maintain a neutral pH.
E. A buffer's pH will change when strong acid or base is added
E
At a specific temperature, 1.10 x 10–10 mol of Fe(OH)3 (molar mass = 106.87 g mol–1) will dissolve in water to form 1.0 L of a saturated solution. What is the Ksp for Fe(OH)3?
A. 3.95 x 10–39
B. 4.04 x 10–10
C. 3.06 x 10–20
D. 1.12 x 10–37
E. 1.18 x 10–8
A
Which of the following could be added to a solution of hypochlorous acid to produce a buffer?
I. sodium hypochlorite
II. sodium hydroxide
III. hydrochloric acid
IV. sodium chloride
A. IV only
B. IV and III only
C. I only
D. I and II only
E. III only
D
56-mL volume of a 0.23 M KOH solution is mixed with 38 mL of a 0.41 M HClO4 solution.
Determine the pH of the mixed solution.
A. 1.32
B. 1.15
C. 1.54
D. 12.9
E. 12.5
C
In a particularly exciting gen chem lab, you mix 75.0 mL of a 5.50 x 10–5 M (NH4)2CO3 solution with 45.0 mL of a 1.50 x 10–6 M CdCl2 solution. Select the answer that correctly predicts whether a precipitate (ppt) forms, why or why not, and if so, what the precipitate is [Ksp of CdCO3 = 1.05 x 10–12].
Will a ppt form? Why or why not? What is the ppt?
A. yes Qsp > Ksp NH4Cl
B. no Qsp > Ksp none
C. yes Qsp < Ksp CdCO3
D. no Qsp < Ksp none
E. yes Qsp > Ksp CdCO
E
What molar ratio of NaF to HF should be used (HF, Ka = 7.1 x 10–4) to prepare a buffer solution
with a pH of 4.00?
A. 7.08
B. 1.24
C. 3.45
D. 2.43
E. 0.41
A
Chloroacetic acid (HCH2ClCO2) has a Ka value of 1.4 x 10–3 at 25 °C. When the temperature rises, the Ka value changes. When this acid is 32% ionized at a temperature of 95 °C, what is the pH of a 0.2 M solution of this acid?
A. 0.5
B. 1.8
C. 2.9
D. 1.2
E. 3.3
D
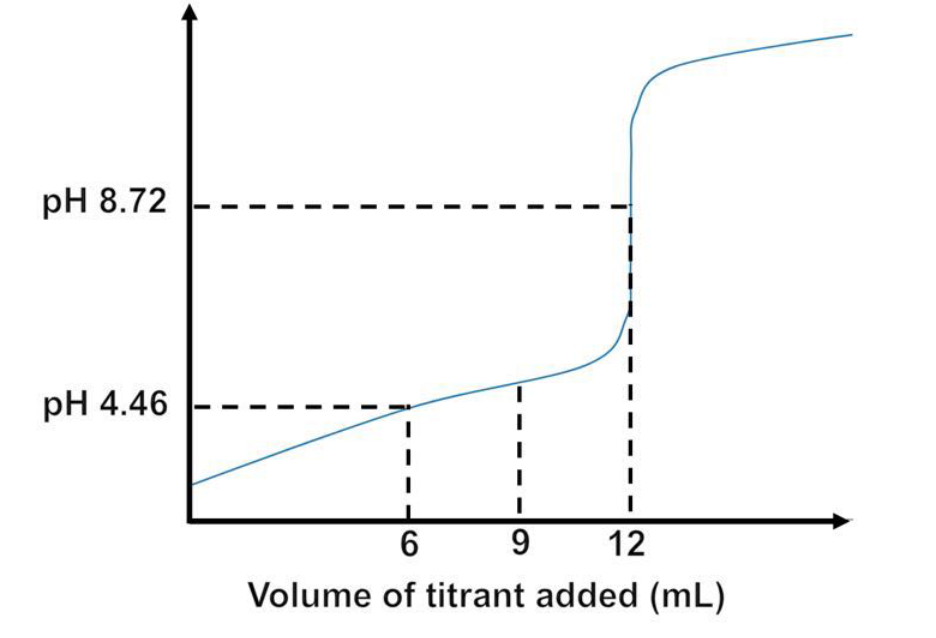
A volume of 6-mL of 0.20 M monoprotic acid HA is titrated by a 0.10 M monobasic B solution. The titration curve is shown below.
A) is HA a strong or weak acid
b)If HA is a strong acid, then determine the Kb for B; if HA is a weak acid, then determine the Ka for HA. Show all work to receive full credit
c)Using the Ka or Kb calculated from part II, determine the pH when 9 mL of B is added to HA. Show all work to receive full credits.
a) weak acid
b) 3.46E-5
c) 4.94
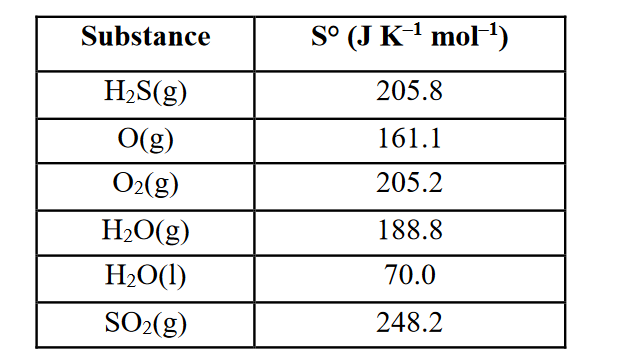
Use the data in the table provided to calculate DS° (J mol–1 K–1) for the following reaction (show ALL work to get full credit):
2 H2S(g) + 3 O2(g) → 2 H2O(l) + 2 SO2(g)
delta S° = 2(70.0) + 2(248.2) – 2(205.8) – 3(205.2) =
–390.8 J mol–1 K–1