233 Unit 1 Ch 4 - Cell membrane, tonicity, membrane transport
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
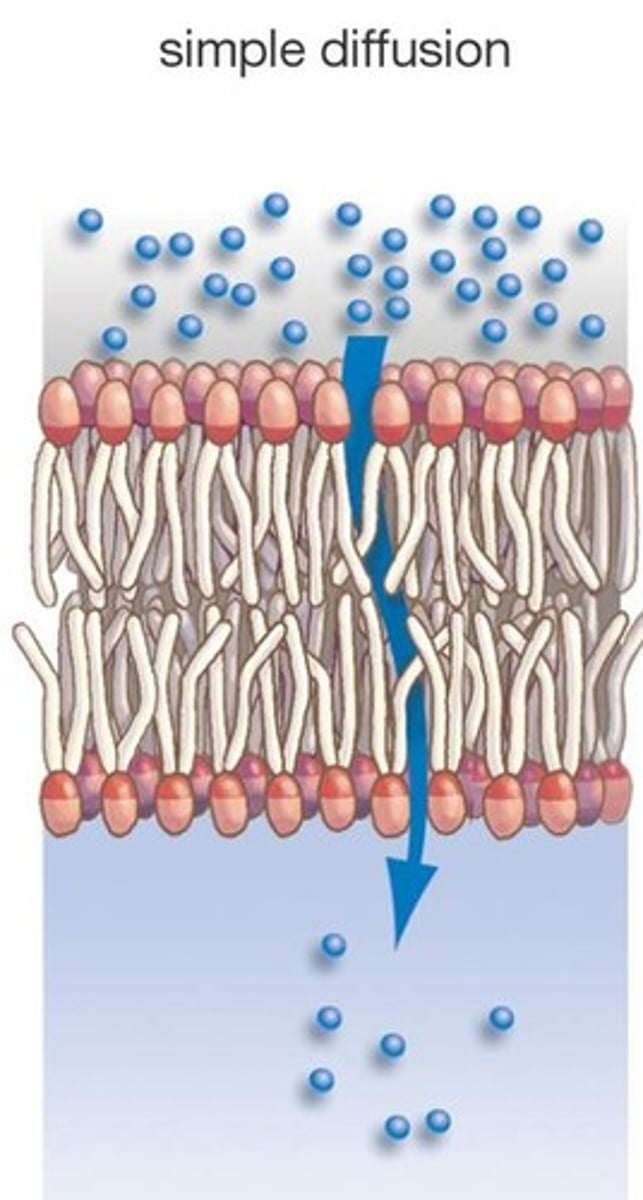
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
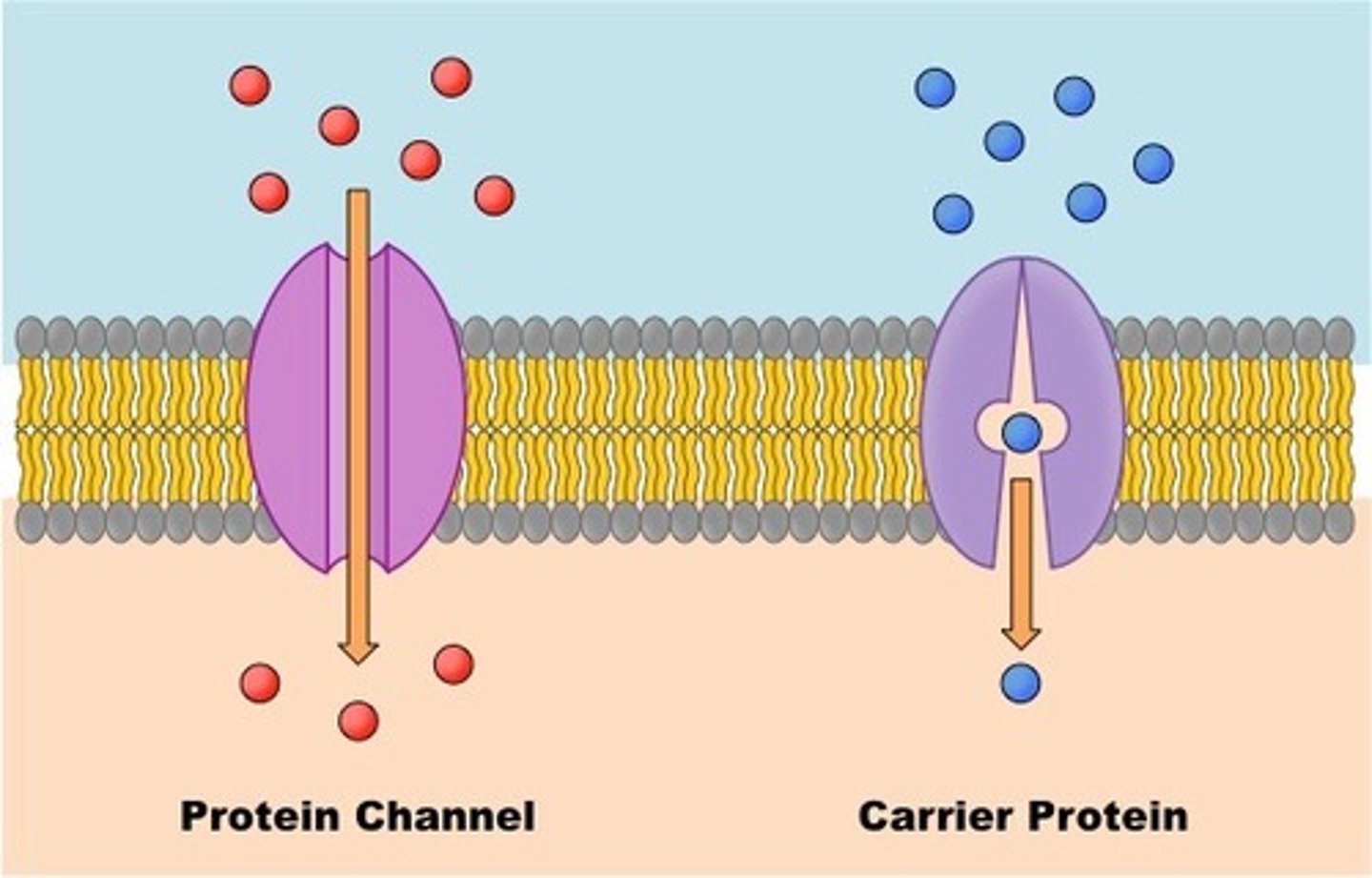
facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels moving DOWN their concentration gradient (from high to low concentration) --PASSIVE (no energy needed)
Osmosis
movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from area of its own HIGH to LOW concentration
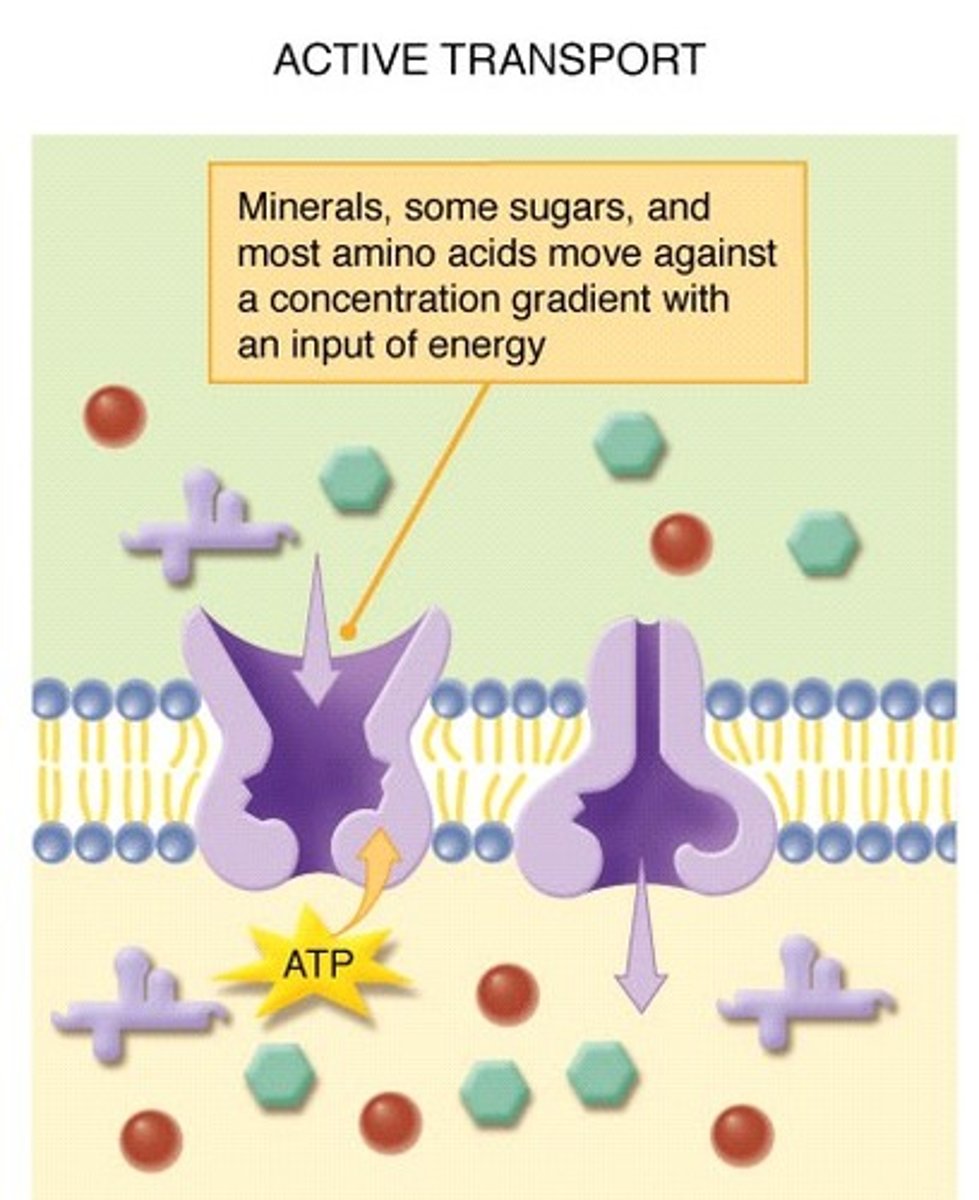
active transport
the movement of materials through a cell membrane using energy (ATP)
Endocytosis
ACTIVE TRANSPORT - process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
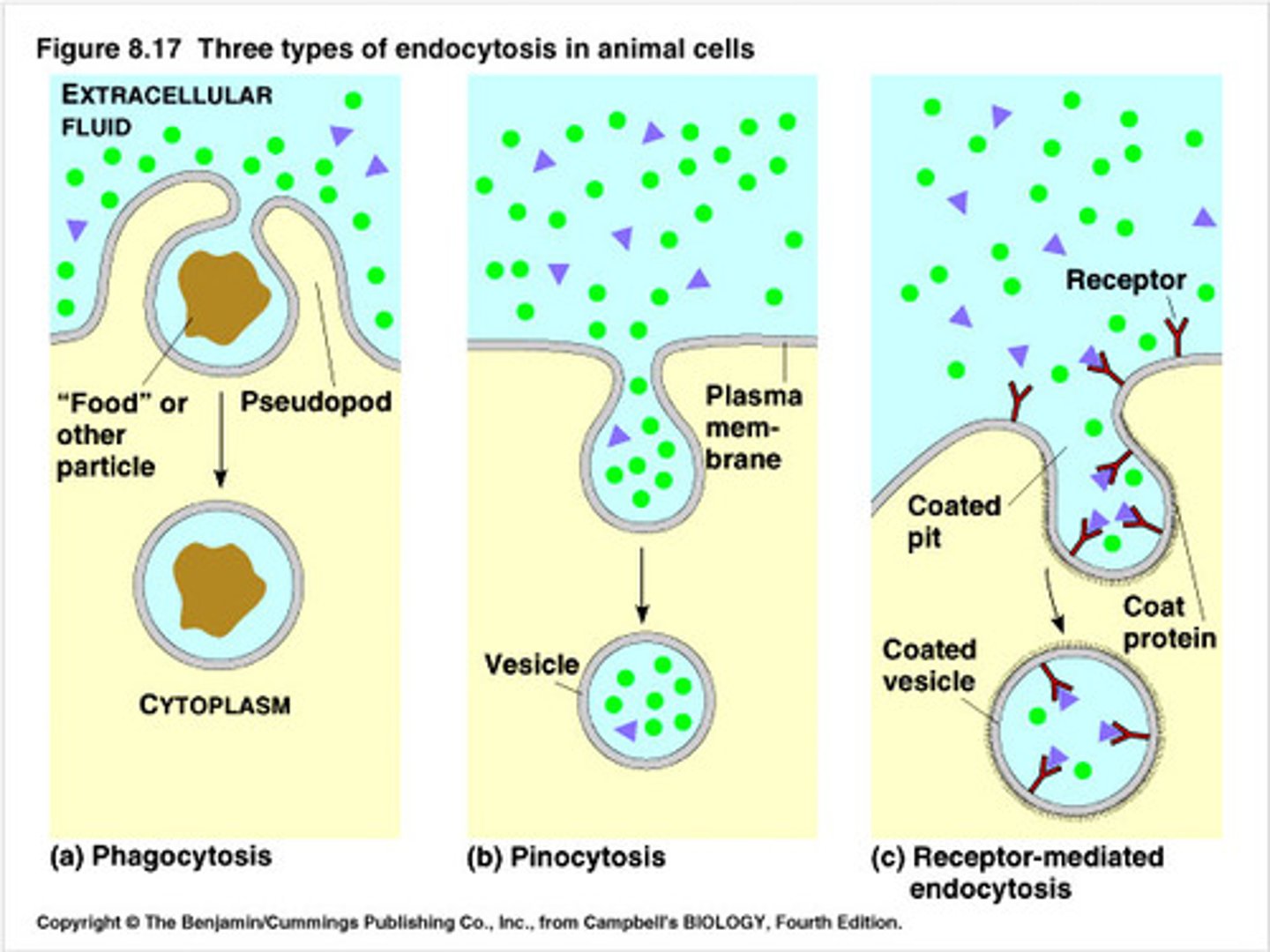
Phagocytosis
ACTIVE TRANSPORT - process in which extensions of cytoplasm surround and engulf large particles and take them into the cell
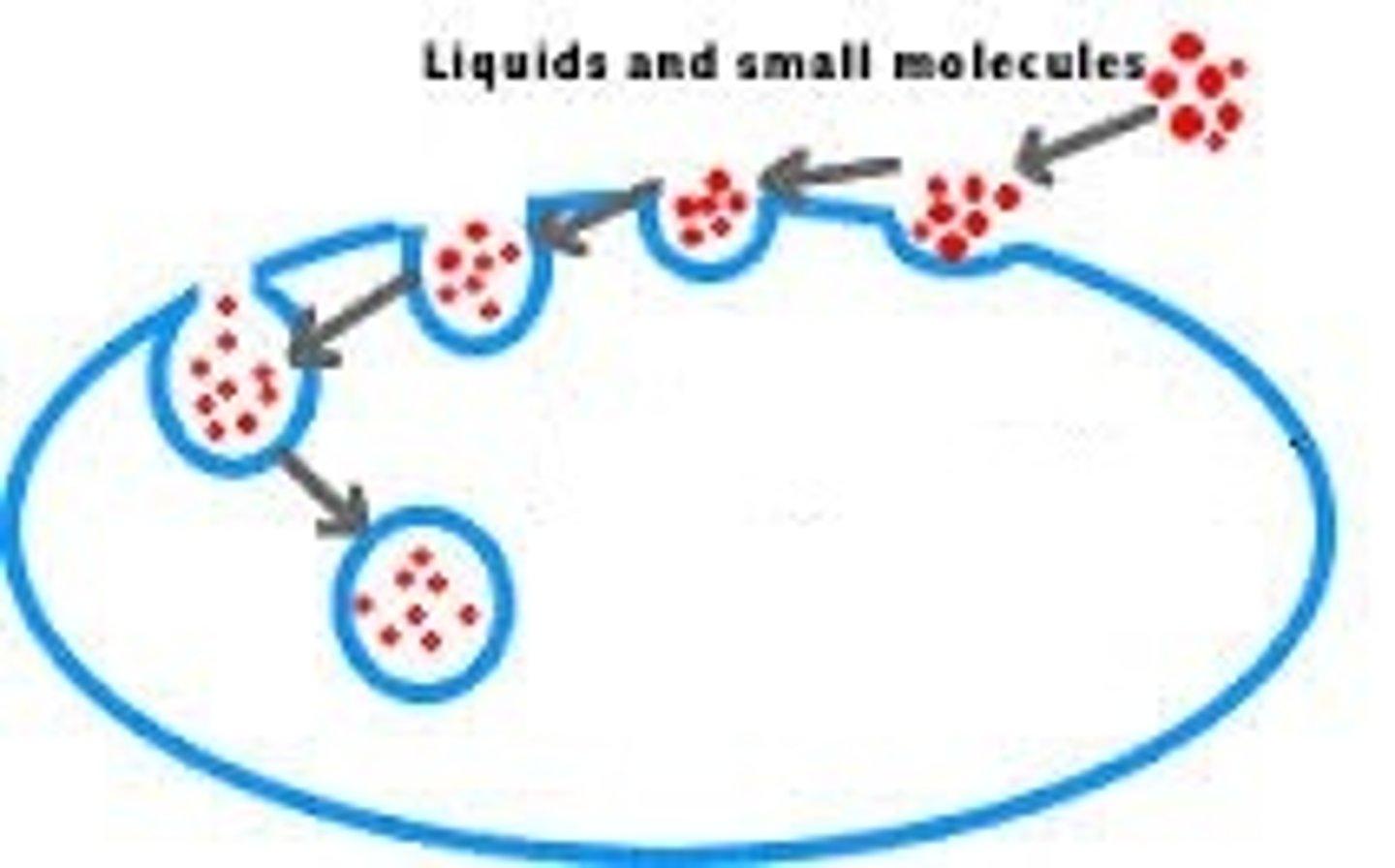
Pinocytosis
ACTIVE TRANSPORT - A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes.
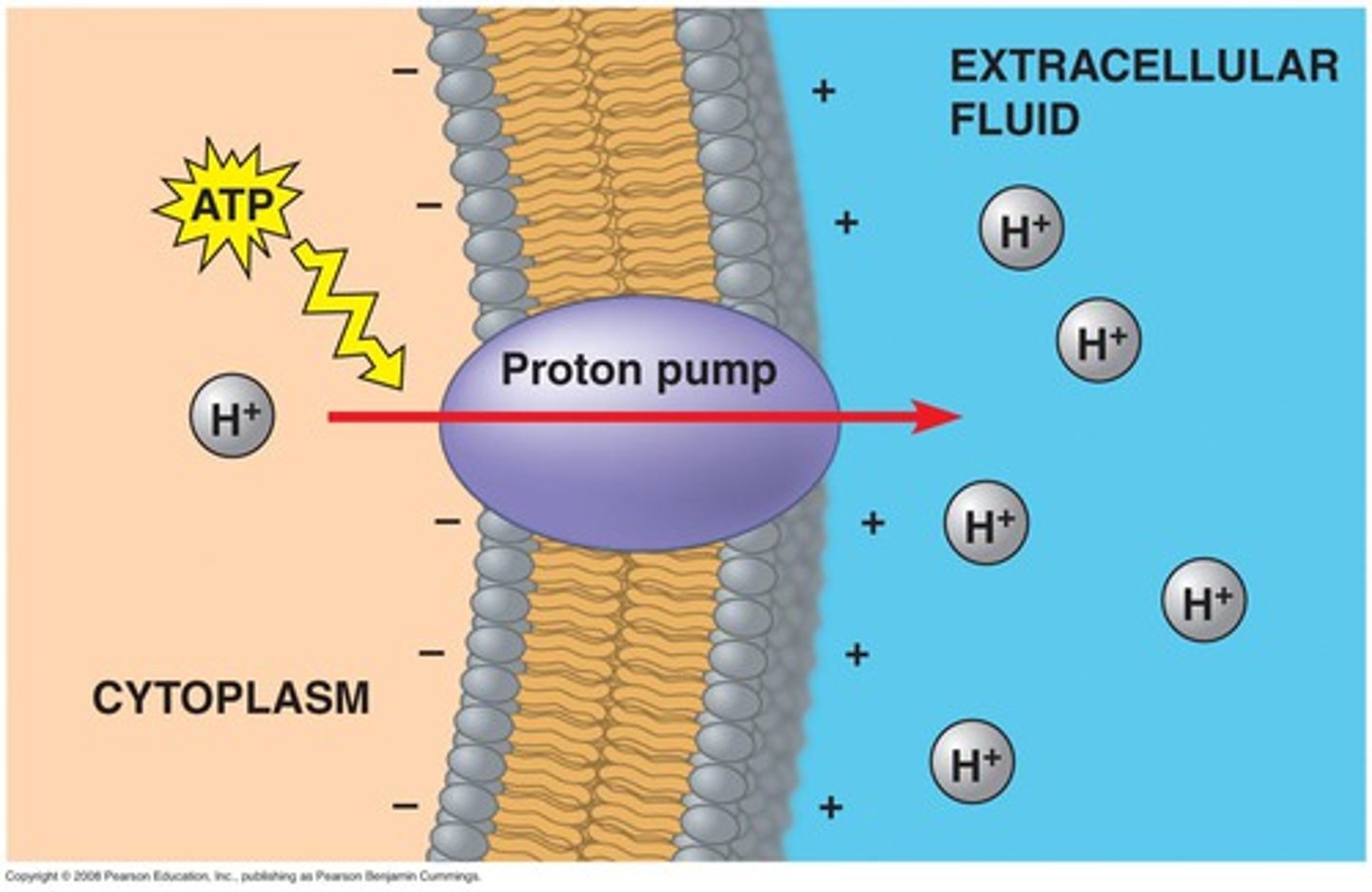
pump
active transport mechanism that works against electrochemical gradients (from area of LOW to HIGH concentration)
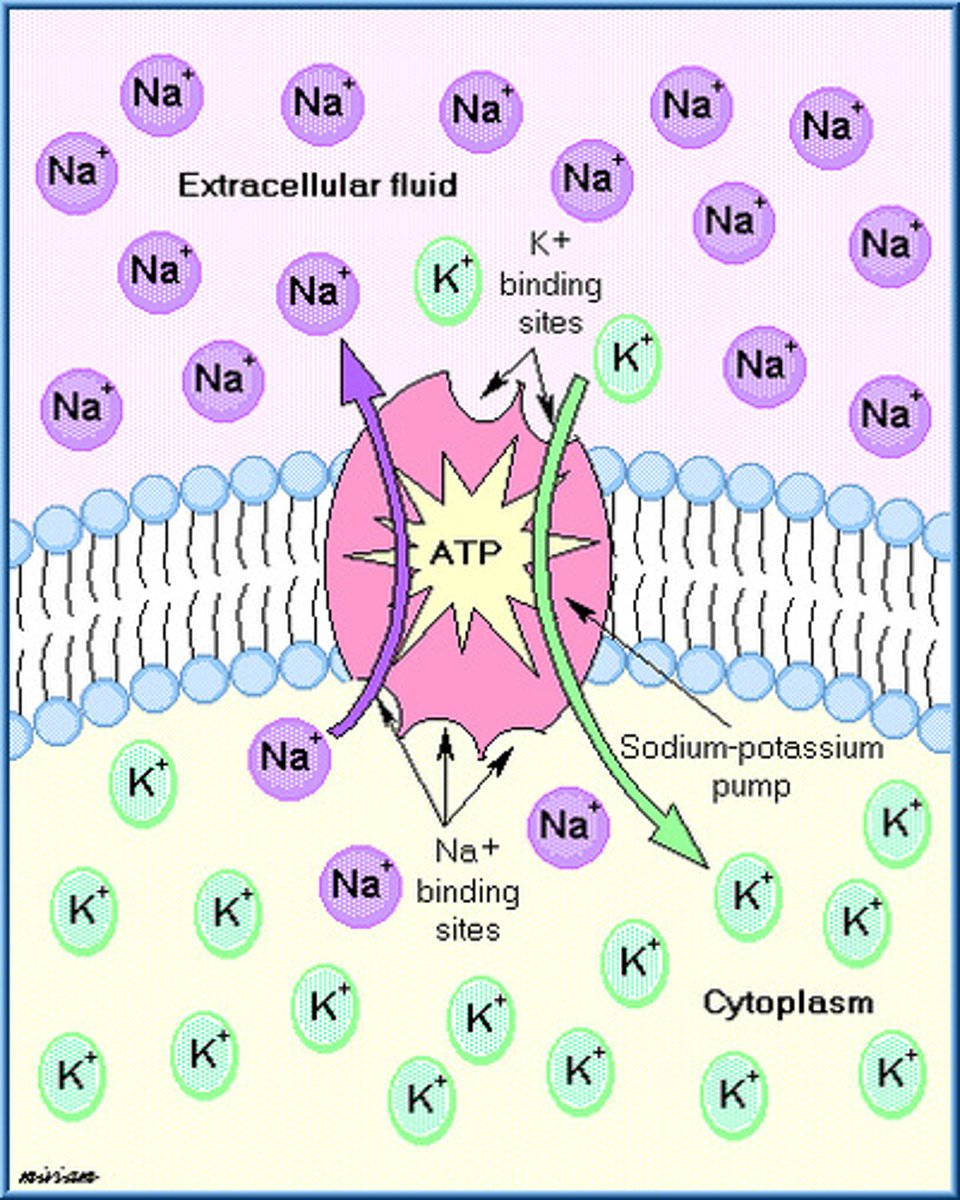
sodium-potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell AGAINST their concentration gradient
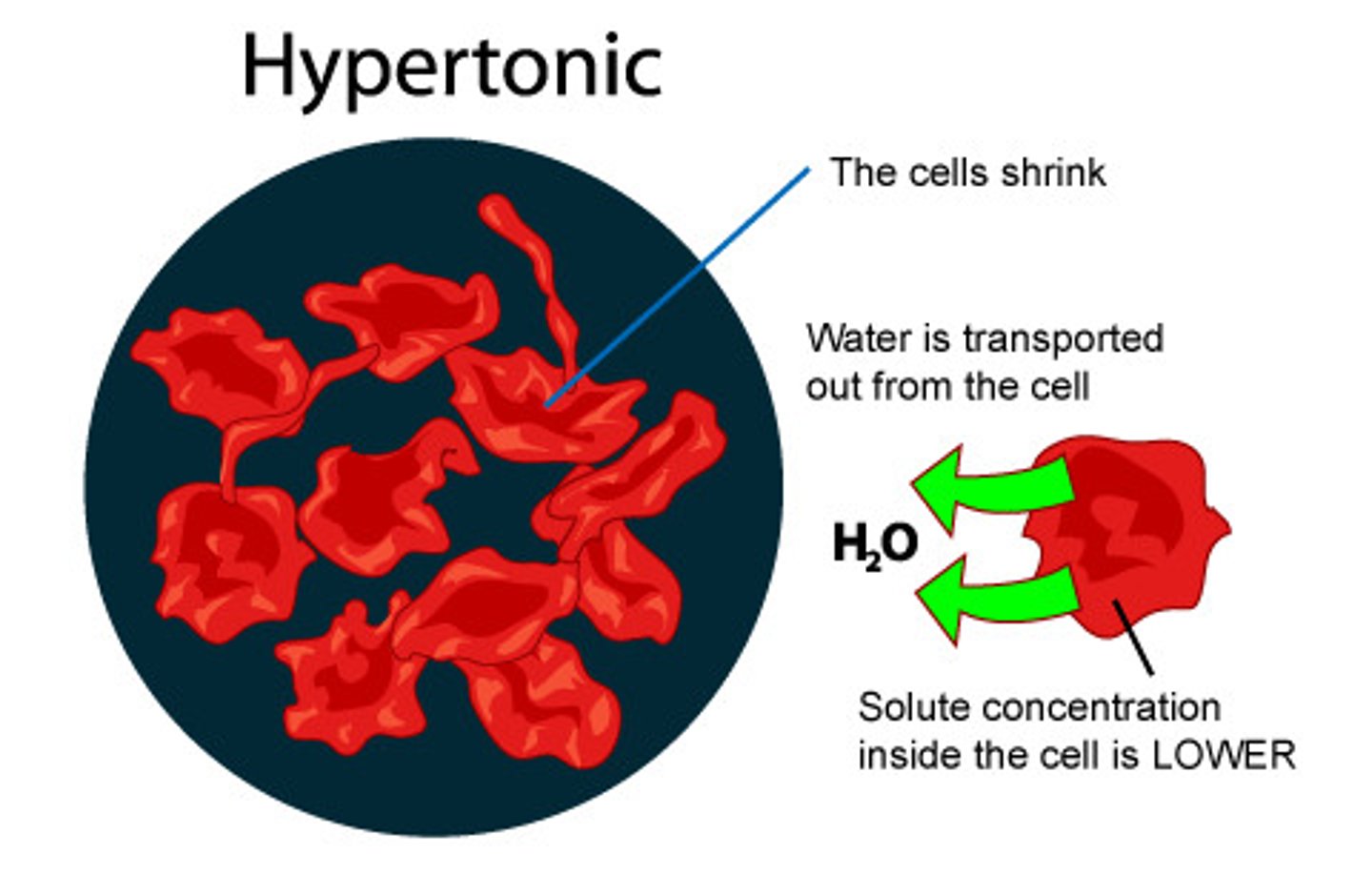
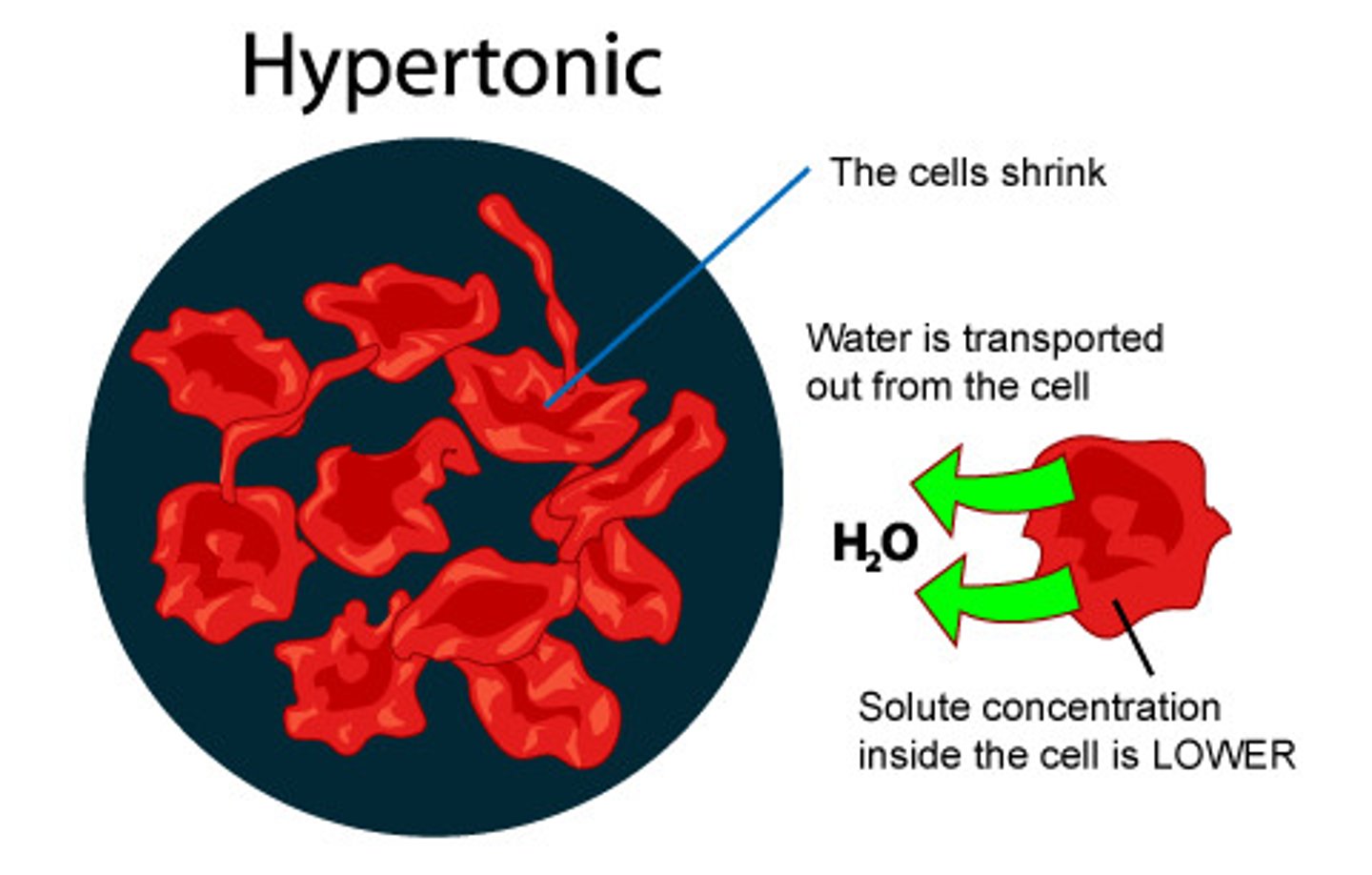
Hypertonic
A solution that has a higher solute concentration (such as .25% NaCl solution compared to 0.01% NaCl solution)
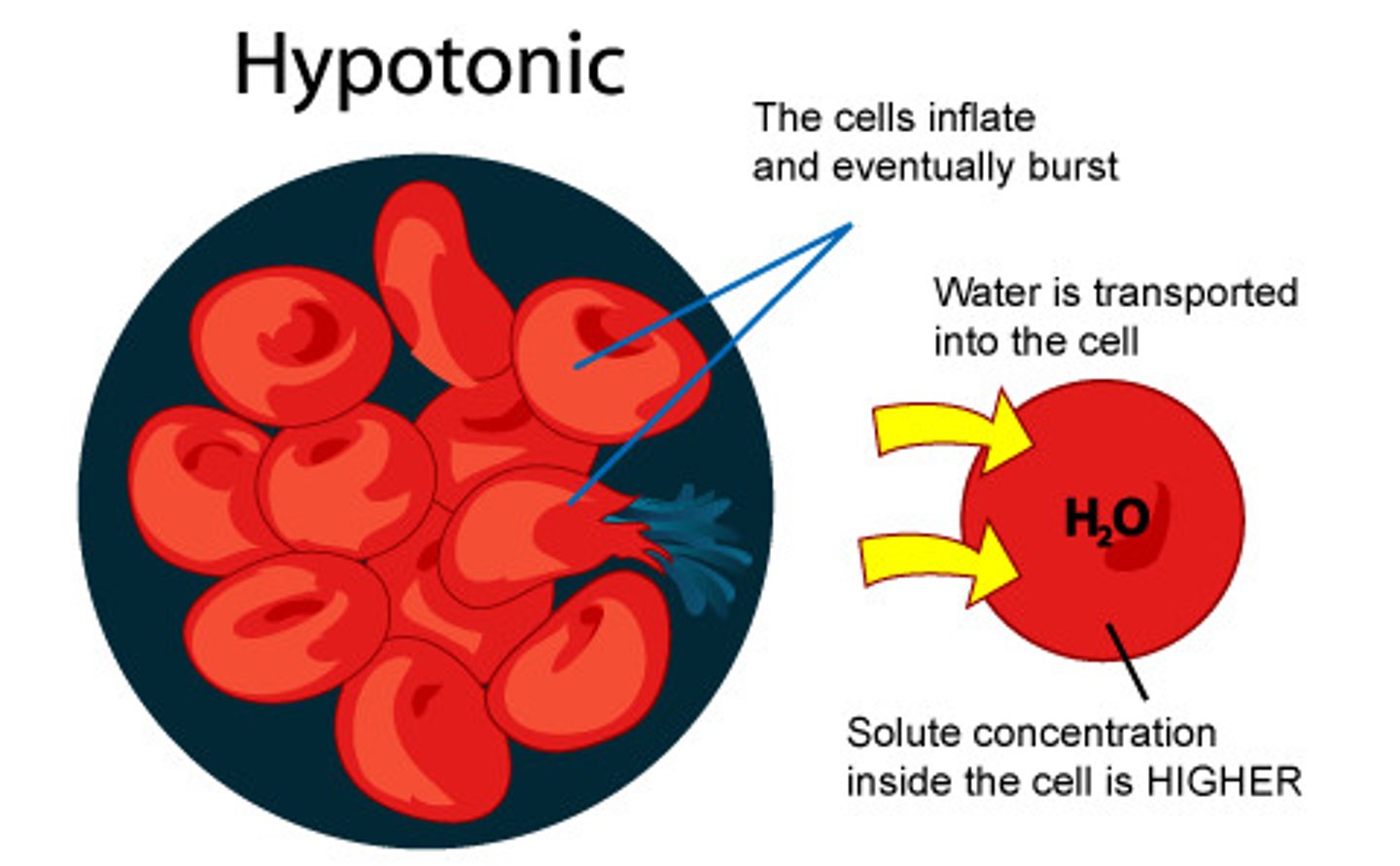
Hypotonic
A solution that has a lower concentration (such as .25% NaCl solution compared with a .90% NaCl solution)
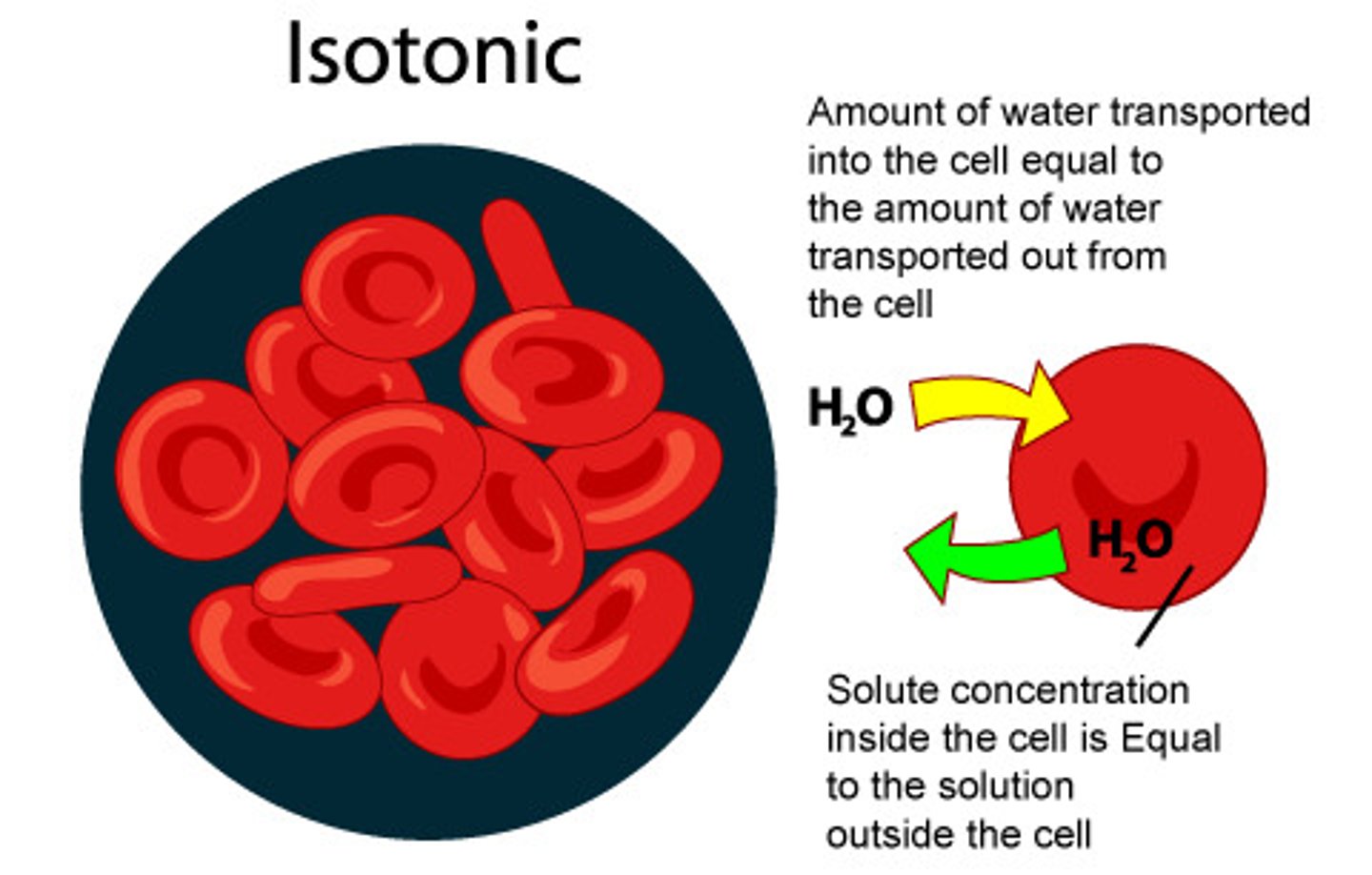
Isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same (water will move in both directions across membrane at same rate--dynamic equilibrium).
What would happen to a red blood cell if it were placed in a hypertonic solution?
crenation (water would leave the cell and it would shrivel)
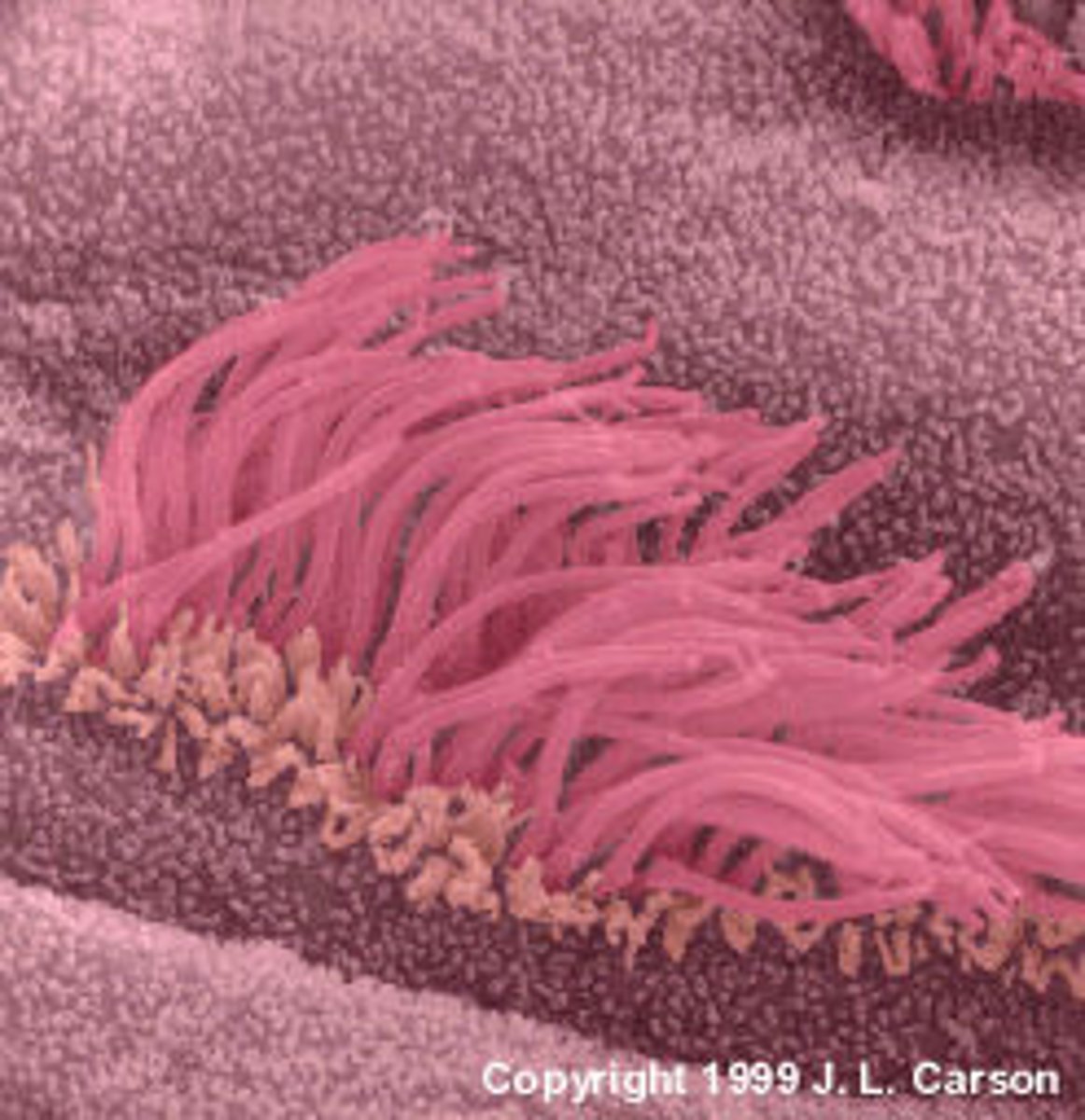
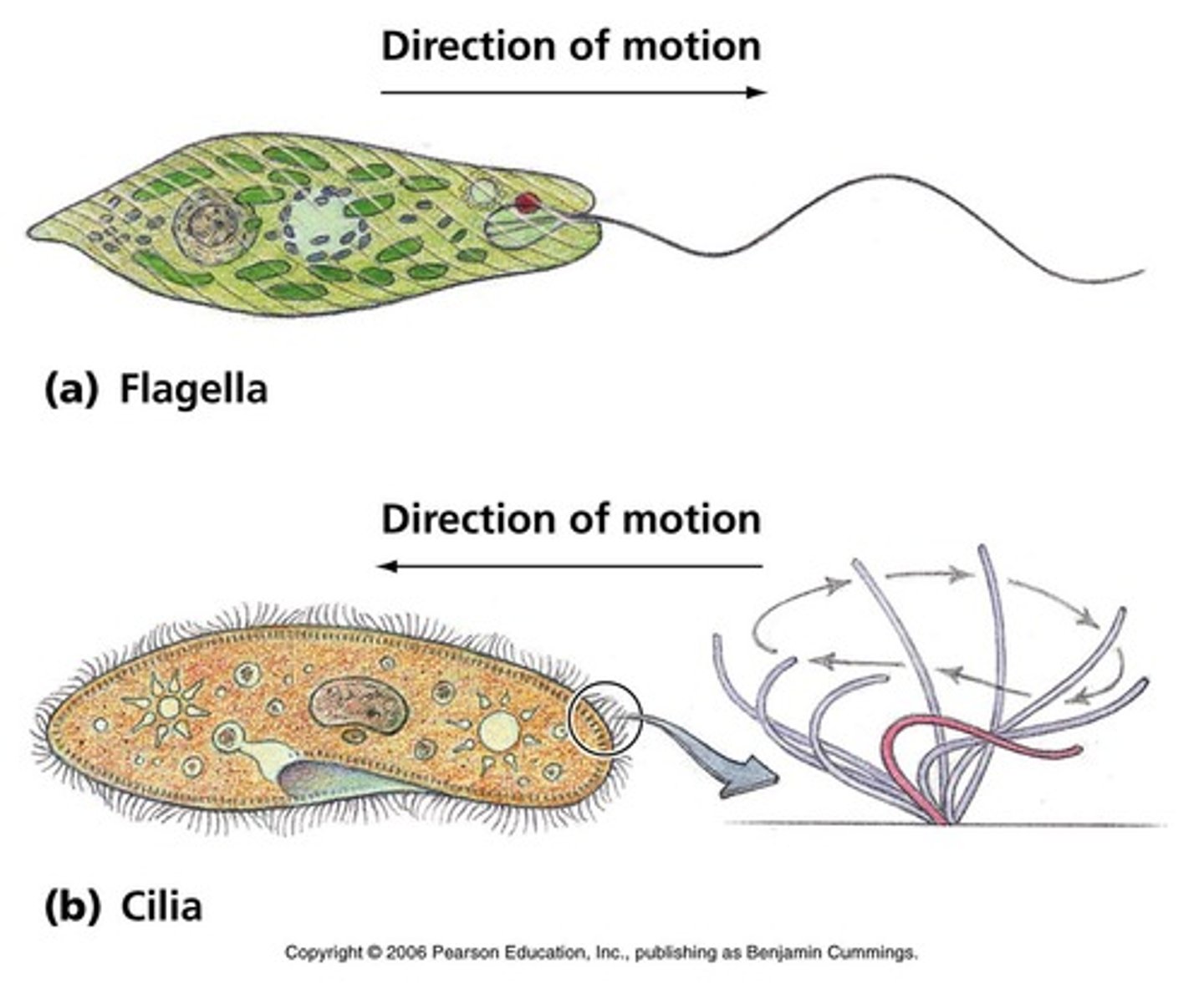
cilia
HAIR-like extensions of the cell membrane that are present on some cells, such as in the trachea.
Flagella
Long whip-like projections of the cell membrane that allow rapid movement of certain cells
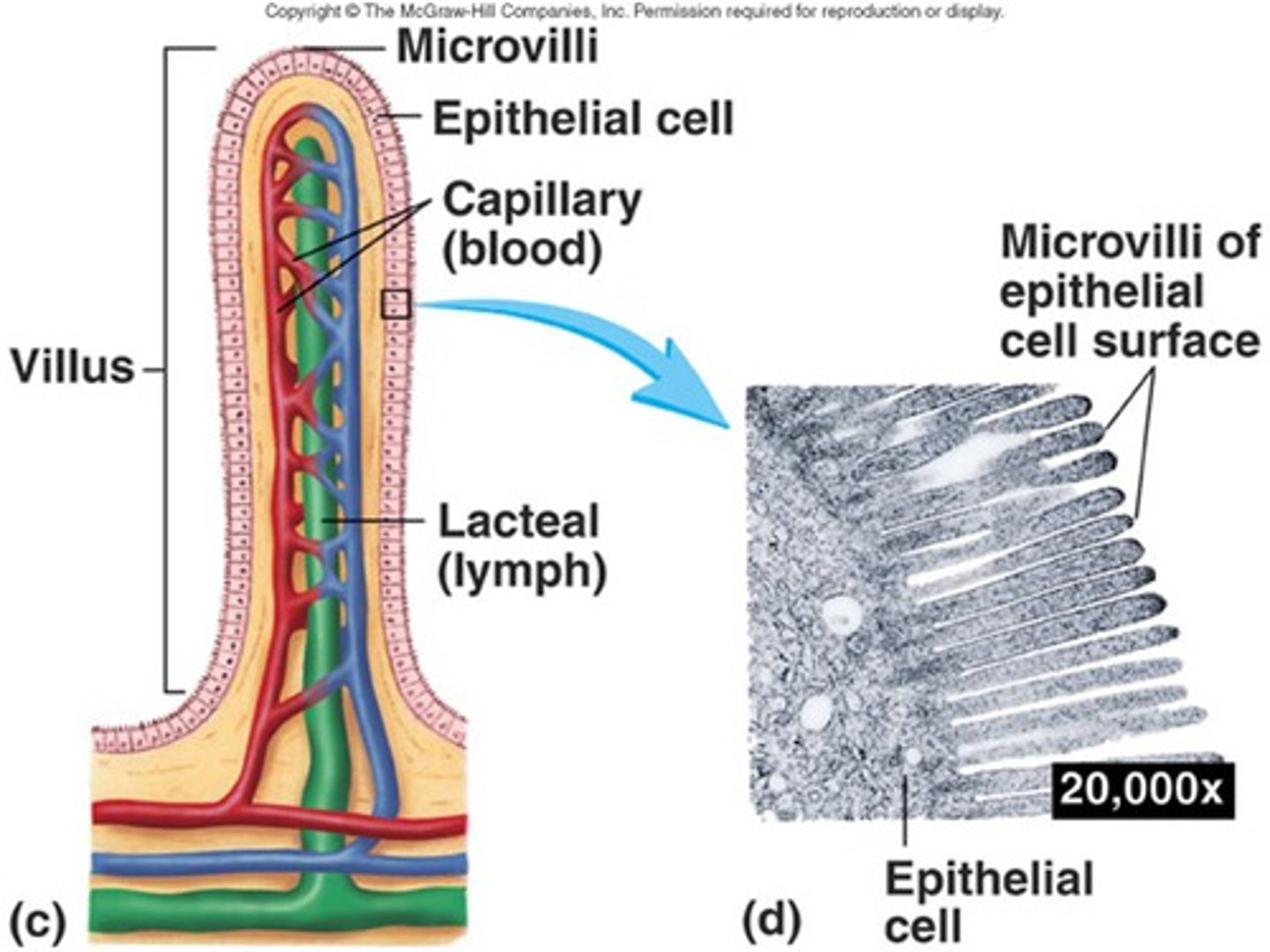
Microvilli
Tiny finger-like projections that aid in ABSORPTION of nutrients in the small intestine
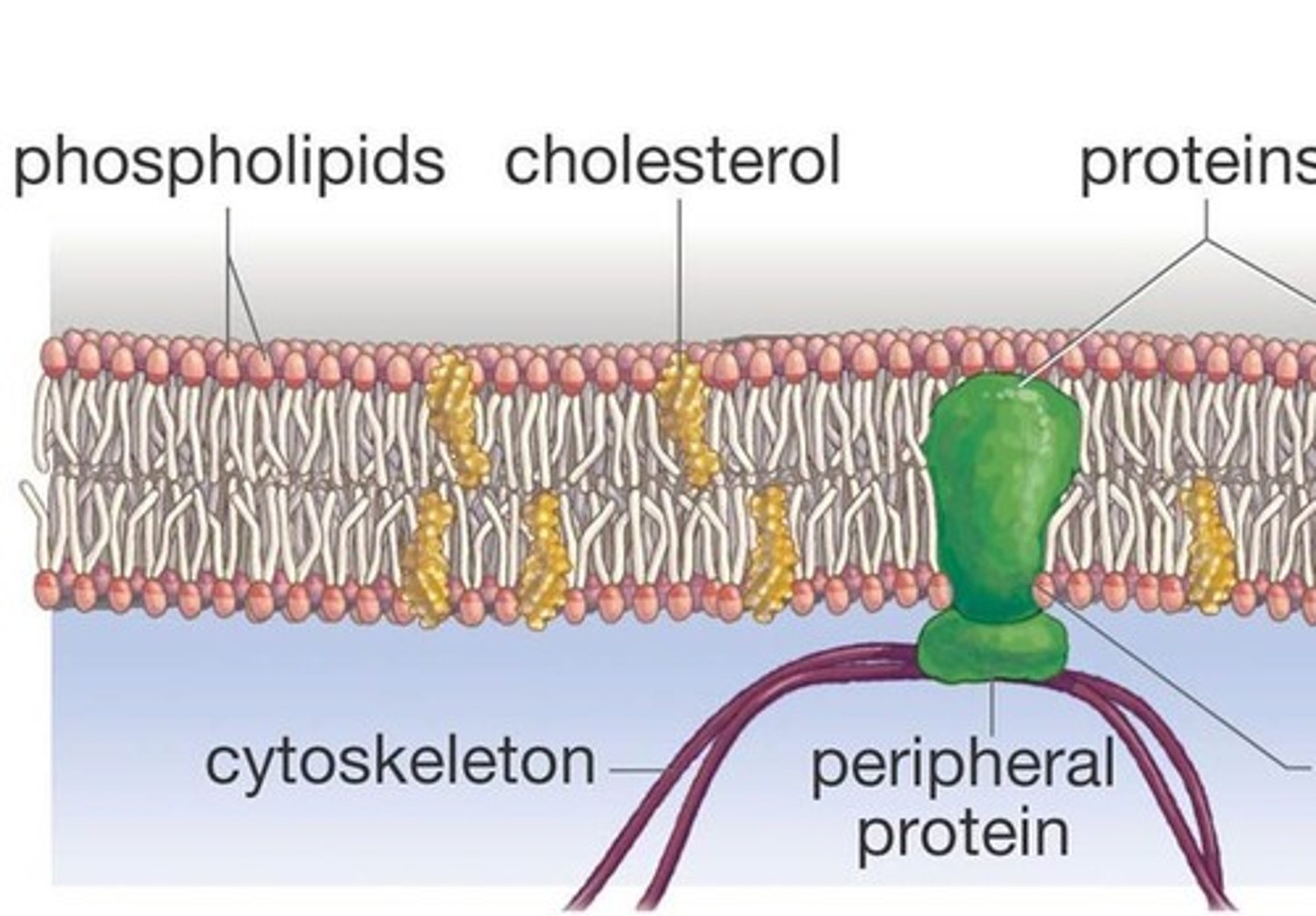
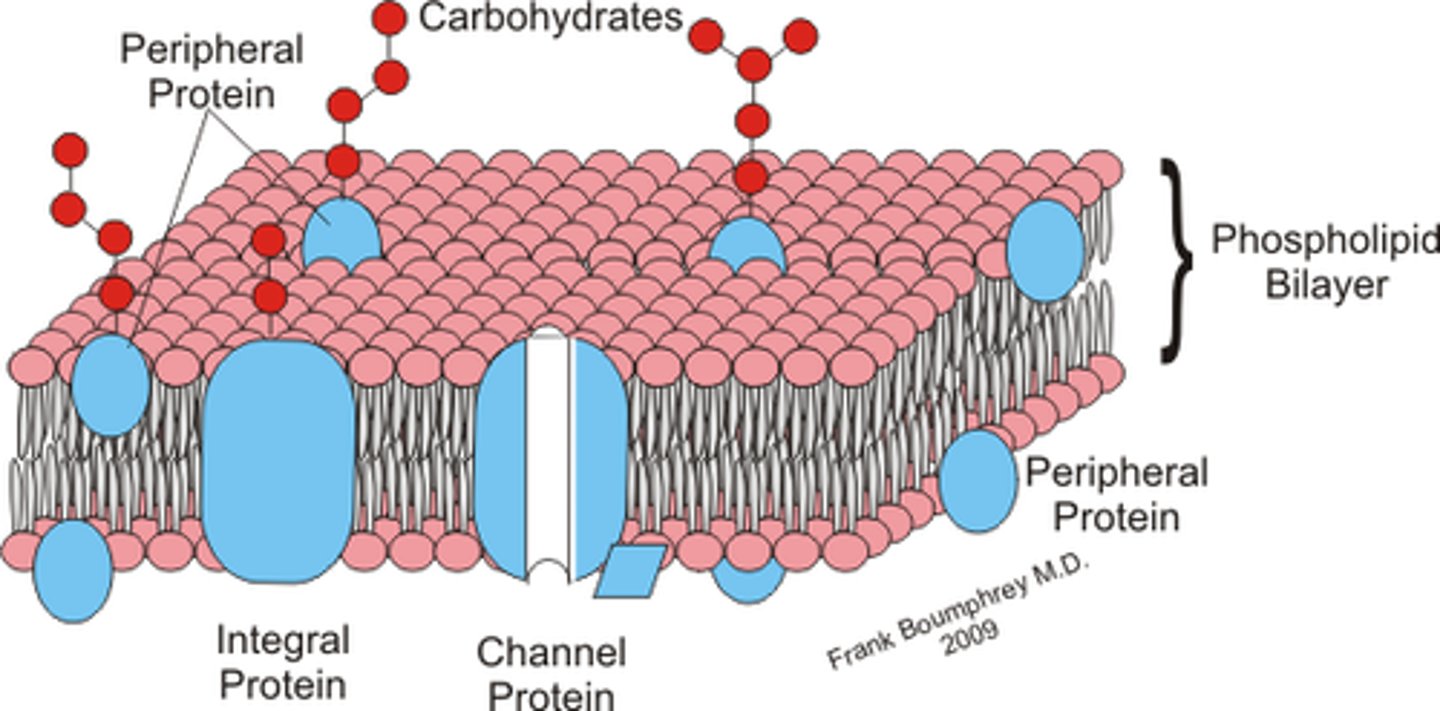
fluid mosaic model
Structural model of the plasma membrane where molecules are free to move sideways within a lipid bilayer.
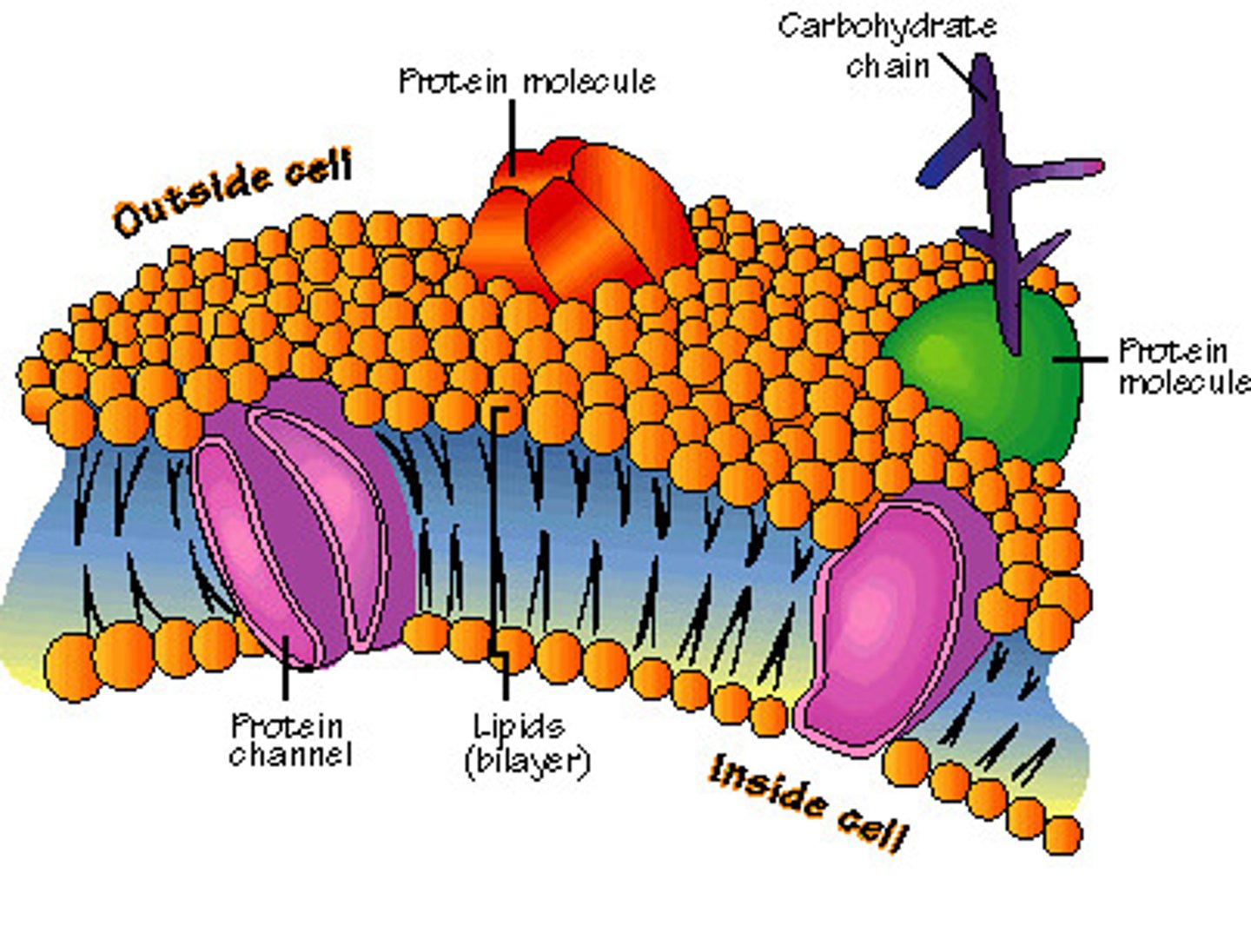
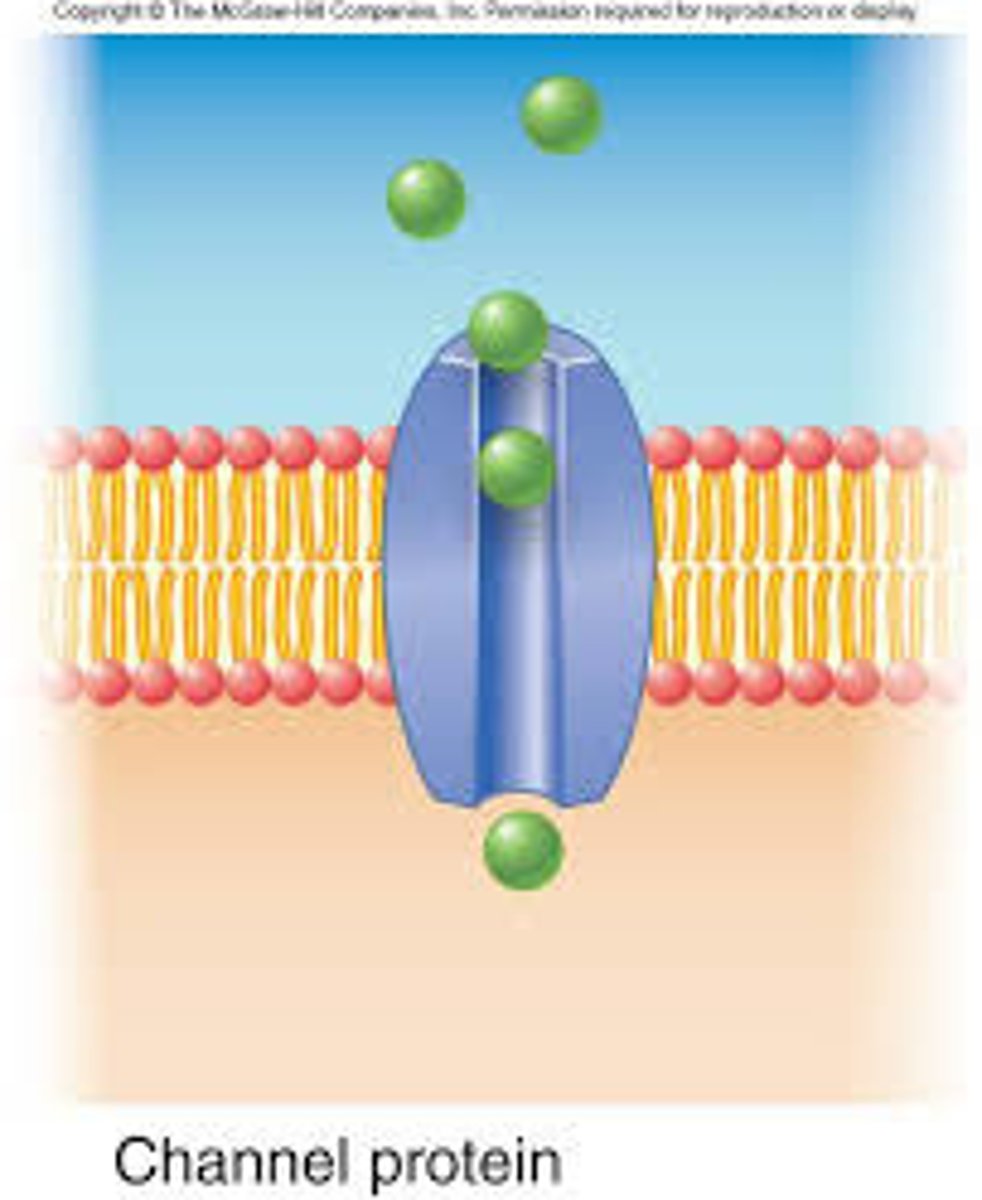
Protein channels (function)
Allow certain molecules to pass in/out of the cell
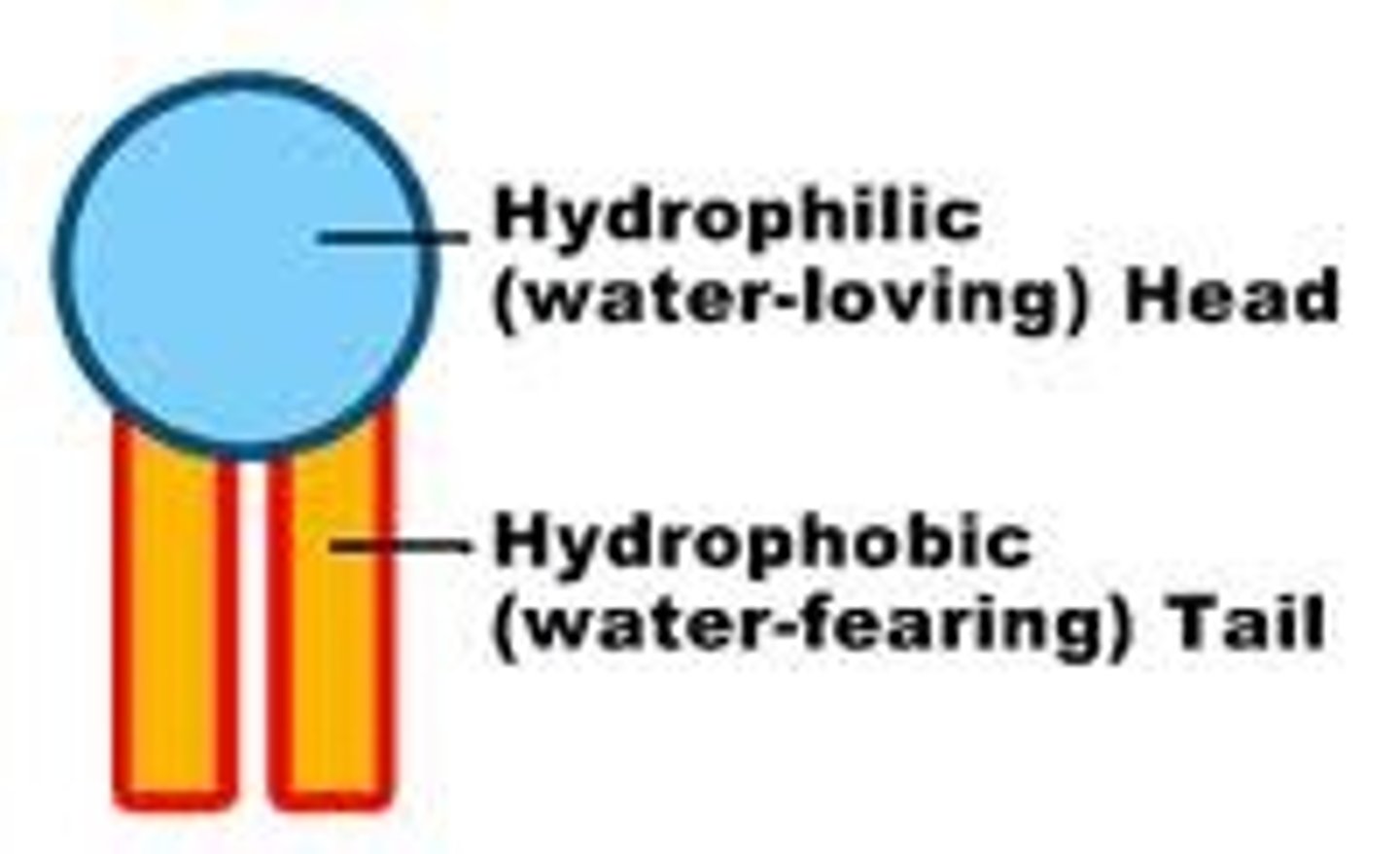
Phospholipid
molecule that has a water loving (hydrophilic) head and 2 water "fearing" (hydrophobic) tails (be able to label)
integral proteins
proteins that form tunnels or channels across the entire cell membrane
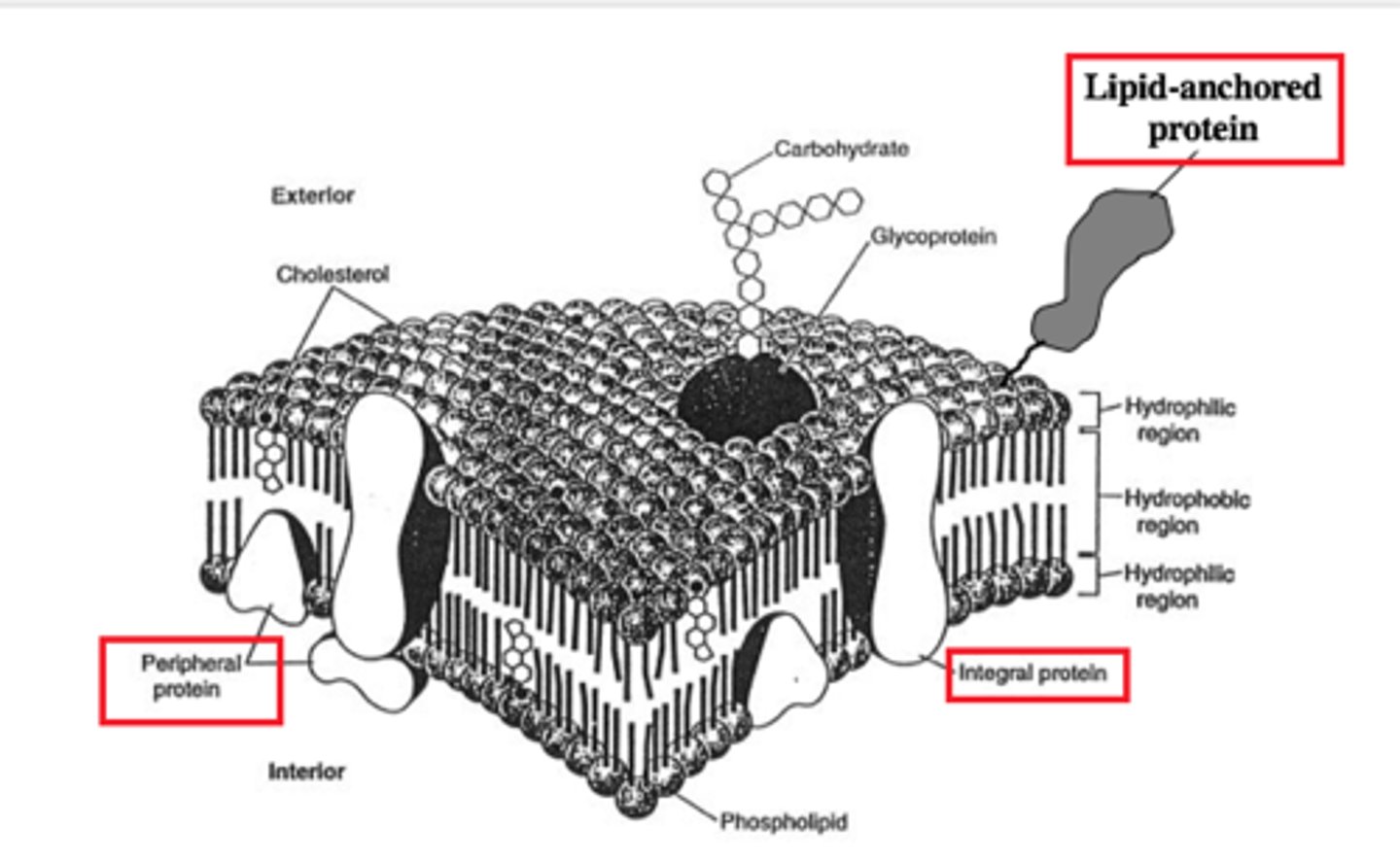
peripheral proteins
bound to only one surface of the cell membrane
cholesterol in membrane
a lipid embedded in the cell membrane that helps give the membrane structure