Forces TOPIC 4
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What do scalar quantities have and its examples ?
Magnitude ( a size or value)only and no direction
EXAMPLES:
SPEED ( e.g 50 km/h )
DISTANCE (e.g 10m)
TIME (e.g 5vsecknds)
MASS (e.g 70kg)
TEMPERATURE (e.g 20degrees)
ENERGY (e.g 100J)
What do vector quantities have?
Magnitude and direction
Examples:
Velocity (e.g m/s North)
Displacement (e.g 5m East) → the distance in a specific direction → state magnitude & direction
Force (e.g 10N downwards)
Acceleration (e.g 2m/s2 upwards)
Momentum(e.g 100kg or m/s to the right )
What’s the key difference between both ?
Speed is a scalar → tells us how fast something is moving
Velocity is a vector → tells us how fast something is & in which direction
What is displacement?
Is the Distance in a specific direction
- Has both magnitude(how far,big,size) and direction
How can a vector quantity be shown?
On an arrow.
The length of the arrow represents the magnitude.
The direction of the arrow represents the direction.
What is a force?
A push or a pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object.
When 2 objects react
Force is a vector quantity.
Measured in Newtons (N)
What is a contact force?
A force in that acts between two objects that are physically touching.
Examples of contact forces:
Friction force
Tension force
Air Resistance force
Normal Contact force
Friction
Two objects sliding past each other experience friction forces.
acts in opposite direction to the movement
Can cause objects to slow down or stop
Also produces heat → e.g rubbing hands together
E.g. a box sliding down a slope.
Car tyres and roads helps car grip and stop
What is Tension force ?
The pulling force that’s transmitted through an object when’s its being stretched by forces acting from opposite ends.
For example ;
in tug of war, there’s the force of tension pulling on the soldier.
What is Air resistance force?
type of frictional force that acts against the motion of an object moving the air
Increases with :
speed of object
Surface area of object
Shape → streamlines shapes reduces air resistance
For example :
a skydiver falling through the air.
Normal contact force
An object on a surface experiences normal contact force.
It’s the force when 2 objects are in direct contact
the object is exerting a downward force on the table and at the same time the table exerts an upward force on the lamp. e.g. a book on a table.
What is a non-contact force?
A force that act between two objects that are not physically touching each other.
Examples:
Magnetic force
Electrostatic force
Gravitational force
Magnetic force
A force experience by any magnetic material in a magnetic field.
KP:
Attractive → Opposite magnetic poles (N-S OR S-N)
repulsive →Like magnetic poles (N-N or S-S)
Strength of forces increases as objects get closer to the magnet
Electrostatic force
The force between two charged objects in an electric field.
KP:
Opposite charges attract (+ and -)
Like charges repel (- and -) or (+ and +)
Force acts at a distance through and electric field
The closer the charges , stronger the electrostatic force
Examples :
Gravitational force
A force of attraction between all objects
Kpoints:
Pulls objects towards each other
Earths gravitational field pulls an object towards its centre → this is what gives object weight
All objects with mass experience gravitational attraction →only noticeable when at least one object has a large pass (eg planet )
Example
. the gravitational force attracts the International Space Station to the Earth and the Earth to the International Space Station.→ objects fall to ground cos of earths gravity pulls the, down
What is mass ?
The measure of the amount of substance (or material ) in an object
What does the mass of an object tell us?
How much matter is in the object
Measured in kg
Mass is a scalar quantity
The mass of an object does not depend on where the object is- mass remains the same in all locations.
What is weight?
The force acting on an object due to gravity.
Measured in Newtons
Weight does depend on where it is as gravity isn’t the same everywhere.
What is gravitational field strength?
A measure of the force of gravity in a particular direction.
The gravitational field strength on Earth is 9.8 N/kg.
Weight formula
Weight= mass x gravitational field strength
N kg N/kg
What is the weight of an object directly proportional to?
The mass of the object
What can be used to measure weight?
A calibrated spring-balance- aka a newton metre.
Where is the weight of an object (force due to gravity) considered to act?
At a single point.
This is referred to as the centre of mass.
What is a resultant force?
A single force that has the same effect as all the original forces that act in a straight line.
How is resultant force found?
by adding or subtracting all the forces acting in the same direction or opposite directions
If forces balanced → resultant force = 0
If resultant force not 0 the object will:
accelerate,decelerate,change direction or change shape
EXAMPLE
2 ppl push a box
one person pushes right with 10N
One person pushes left with 6N
Then resultant force = 10N-6N - 4N to the right
Draw free body diagram to show the forces acting on an object
Lift = Force of the same magnitude as the weight but acting in the opposite direction
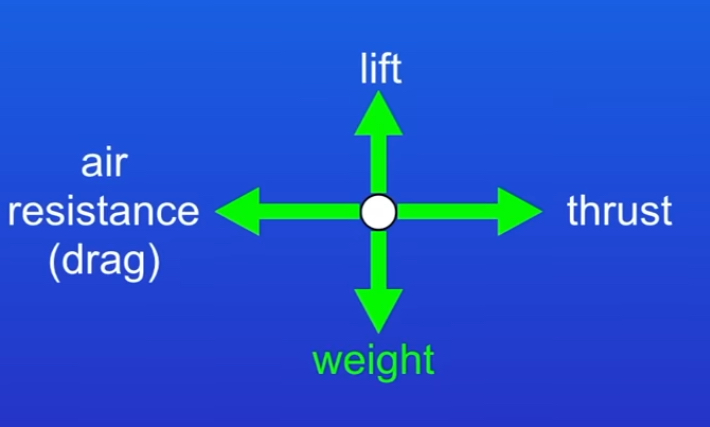
What is thrust in airplanes?
Forward force provided by engine
What is a single force and what can it be resolved into?
Sing force → one force that can replace multiple forces acting on an object and still have the same overall effect
EXAMPLE ;
Two components acting at right angles to each other. The two component forces together have the same effect as the single force.
How to use a vector diagram to calculate the resultant of 2 forces acting at an angle
Start by making a scale drawing showing the forces involved
Using ruler and protracter and choose a scale → draw the first force as an arrow in its correct direction
Draw second force :’tip to tail’
From arrowhead of first force→draw second force at the correct angle
Use correct scale & direction
Draw the resultant:
draw straight line from the start of the first force to the tip of second force
This is resultant force
Measure the length of this line with a ruler & convert it back into a force using the scale
draw as right angles triangle
Use Pythagoras theorem for exact result
what is Resolving forces
Resolving force = breaking a single force into 2 components (forces) that act at right angles to each other , usually horizontal and vertical
Used to :
simplify problems involving angled forces (e.g sled up a hill)
Analyse motion in horizontal & vertical directions separately
Using resolving factors →using vector diagrams to resolve single forces into 2 forces
EXAMPLE; a 10 N force acting at 30 degrees above the horizontal
1) draw the force:
use a scale (e.g 1cm = 2N)
Draw the 10N force at the correct angle (30 degreees above horizontal)
2)create a right angled triangle :
from tail off the force arrow→ draw a horizontal line
From tip of false Arrow→ draw vertical line straight down to meet horizontal completing the triangle
3) measure the sides or use trigonometry
Measure:
Use ruler to measure lengths of horizontal and vertical sides
Convert back using your scale→e.g 5cm =10 N , so 2.5cm= 5N etc)
Trigonometry:
Horizontal force= Fcos(angle)
Vertical force=Fsin(angle)
Answer:
8.66N horizontal
5N vertical
What is work done?
The energy transferred by a force when it moves an object through a distance.
The distance must be in the line of action of the force.
Work done formula
Work Done (J) = Force (N) x Distance (m)
W=Fs
Scientists also use the unit newton-metre
1 newton-metre = 1 joule
What happens to elastic materials when the forces acting on them are removed?
They always return to their original length.
What is elastic deformation?
When a material returns to it’s original length or shape after the forces that were
What needs to be done in order to change an object’s length or shape? (stationary objects only)
More than one force needs to be applied.
If only one force is applied to a stationary object, then the forces are no longer balanced.
Therefore, the object would simply move rather than changing length or shape.
What happens to inelastic materials when the forces acting on it are removed?
They do not return to their original length or shape.
What’s inelastic deformation?
When a material doesn’t return to it’s original length or shape after the forces that were acting on it are removed.
Formula for force needed to stretch an elastic object.
Force= spring constant x extension
N
What is being used to stretch or compress an elastic object?
Force
Because elastic potential energy is stored in the object, the work done= the elastic potential energy.
This is only true if the object is not inelastically deformed.
How to investigate the relationship between force and extension for a spring?
RP6
Get a clamp stand, two bosses and two clamps
Then place a heavy weight on the clamp stand to stop it falling over.
Next attach a metre ruler and a spring to the clamps.
Make sure the top of the spring is at 0 point on the ruler
It’s crucial that the metre ruler is vertical otherwise the reading will be inaccurate.
The bottom of the spring has a wooden splint attached as a pointer and this must be horizontal or the readings will be inaccurate.
Now read the position of the pointer on the metre ruler-this is the y stretched length of the spring. (Length with no force attached)
Next hang a 1 N weight on the spring and read the new position of the pointer on the metre ruler.
Continue adding 1 N weights to the spring and reading the position of the pointer.
Then calculated the extension produced by each weight by taking away the stretched length from the original unstretched length
Then plot the extension against the weight.
If asked the work out the the weight of a mystery object, measure the extension of the spring when the object is hanging from it and find the extension on the graph and use it to determine the weight.
What is the relationship between weight and extension?
Linear
If it goes through origin then it’s directly proportional.
What would be the result of the same experiment with a rubber band?
Non-linear relationship between force and extension
How do we know the spring is elastic?
Because when the weight is removed the extension returns to 0.
What happens to the spring of too much force is added to it?
It becomes inelastically deformed meaning that when the forces are removed the spring would still show an extension
This makes the graph non-linear as the limit of proportionality has been exceeded.
How can the spring constant be determined from the graph?
Use the linear part of the graph to get your force and extension values.
Then use formula F=ke and rearrange to k=F/e to calculate constant.
This value will be the same throughout as long the limit of proportionality hasn’t been exceeded
What is distance ?
how far an object has travelled
Scalar → magnitude (size) only
The total path taken → no direction
Can’t be negative
E,g→ you walk 10m around a circle
What is displacement?
how far and in what direction from the starting point
Vector → has magnitude & direction
The shortest straight-line from start to end with direction
Can be negative (e.g 5m west )
E,g→ displacement is 0m if you return to the starting point Vector
What is speed ?
rate at which an object moves → tells you how much distance is covered per unit of time
Kp:
scalar quantity→ magnitude only ,no direction
Measured in metres per second (m/s)
Can vary→depends on changes of how fast an object is going
Formula for speed
Speed (m/s) = distance (m)/ time (s)
v=s/t
Speed tells us the rate at which a distance is travelled per second.
Normal walking speed
1.5 m/s
Running speed
3 m/s
Cycling speed
6 m/s
Car on main road speed
13 m/s
Fast train in UK speed
50 m/s
Cruising aeroplane speed
250 m/s
Speed of sound in air
330 m/s
This can vary e.g. sound travels faster on warmer days than colder ones.
What is velocity?
Speed in a given direction.
Vector quantity.
Velocity is calculated with the speed formula, you just add direction
Why is velocity a vector quantity?
it has both : magnitude & direction
Velocity of an object moving at a constant speed in a circle.
although speed is constant
Velocity is still changing because the direction of motion is constantly changing
How to construct a distance-Time graph
Label your axes:
x-axis = time(S)
Y-axis= distance(M)
Plot the data points from the table/information given
Join the point with a smooth line or straight segments:
A straight diagonal line = constant speed
Horizontal line= stationary
Curved line(steepening)= accelerating
Curved line(flattening)= decelerating stuff
Check your scales or even inconsistent
How to determine an object speed from a Distance-Time graph
Formula:
Speed = change in distance/change in time
Steps:
Pick two points on the straight part of the graph
Read their distance(y-axis) and time(x-axis) values
Use formula to calculate speed
Using a tangent to determine the speed of an accelerating object
Pick a point on the curve
Draw a tangent line → using a ruler →line that just touches the care at the point → it should follow the curves slope at that moment
Find two points on the tangent→ pick too easy to read points on the tangent line, not the cave
Use speed formula:
Speed = change in distance/change in time
What does an upwards sloping curve on a distance-time graph represent?
Acceleration as the object’s speed is constantly.
To calculate speed at any point use gradient.
What does a downward sloping curve represent on a distance-time graph?
Deceleration as the speed in constantly decreasing.
To calculate speed at any point use gradient.
What does acceleration tell us?
The change in an object’s velocity over a given time.
Formula for velocity
v=d/t
What does a horizontal line on a velocity-time graph tell us?
The object is travelling at a constant velocity.
What does a straight line show on a distance-time graph?
Object is moving at a constant speed.
What does an upward sloping line show on a velocity time graph?
Constant acceleration
What does a downward sloping line show on a velocity-time graph?
Constant deceleration
What does the total area under a velocity-time graph tell us?
The distance/displacement travelled
When we see constant acceleration or deceleration, we simply divide the graph into shapes and calculate their total areas.
When the acceleration and deceleration are not constant, we count the squares and then estimate the total of the parts of squares.
Or you could split each row and calculate area or triangle or trapezium and add up total area.
Formula for constant acceleration
v² - u²= 2as
final velocity² - initial velocity (m
When any object falls towards the surface of the Earth, what does it initially accelerate by?
9.8 m/s²
Describe skydiver who just jumped out of an aeroplane.
He initially accelerates due to the force of gravity acting on the object.
As the skydiver falls, he experiences an upward force of friction with the air particles- air resistance.
After some time the force of air resistance balances the force of gravity.
At this point the object stops accelerating and moves at a constant velocity.
This is called the terminal velocity.
This applies to any object falling through a fluid in this case the air.
What does the terminal velocity an object reaches depend on?
The object, some objects experience a greater force of friction due to their shape so they will have a lower terminal velocity.
What’s Newton’s first law of motion?
If the resultant force acting on a stationary object is 0, then the object will remain stationary.
If the resultant force acting on a moving object is 0, the the object will continue moving with the the same speed in the same direction (with the same) velocity.
Velocity will only change (object will accelerate) if there’s a resultant force acting on an object.
What force opposes and balances the driving force of a vehicle travelling at a constant velocity.
Resistive forces
The resistive forces include friction with the air and friction with the road.
What is Newton’s second law of motion?
The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.
This can be used to calculate the force needed to accelerate an object.
What is the formula for the force needed to accelerate an object?
Force (N) = Mass (kg) x Acceleration (m/s²)
Cars main road speed (UK)
13 m/s
Cars motorway speed (UK)
30 m/s
Acceleration from main road to motorway
2 m/s²
For a typical family car that would require a force of 2000 N.
Inertia
An object will stay stationary, or continue moving at the same speed and direction (with the same velocity) unless a resultant force is applied.
This property of objects is called inertia.
What’s inertial mass?
A measure of how difficult it is to change the velocity of an object.
The inertial mass is defined as the ratio of the force needed to accelerate an object/ acceleration produced.
An object with a large inertial mass will require a larger force to produce a given acceleration than an object with a smaller inertial mass.
What’s Newton’s third law of motion?
Whenever two objects interact, the forces they exert on each other are opposite and equal.
Investigate how varying the force affects the acceleration of an object of constant mass.
Get a toy car and attach it to a piece of string.
The string should be looped around a pulley and the other end of the string should be attached to a 100g mass.
The weight of the mass will provide the force acting on the toy car.
We also need a timer.
On the desk/surface draw chalk lines at equal intervals such as every 20 cm.
Now hold the toy car at the starting point and when ready let go of the car.
Because there’s a resultant force acting through the string, the car will accelerate along the bench.
Record the time the car passes through each distance marker and to do this accurately take a video of the experiment so you can replay for accurate results.
Repeat the experiment but decrease the mass on the end of the string to explore the impact of decreased weight.
But make sure that the mass you remove is added back to the toy car to maintain constant mass of the object as the object is the toy car, the string as well as the mass on the end of the string/ because they’re all attached to each other.
Your results should show that the acceleration of the toy car is directly proportional to the mass of the other end of the string which Newton’s second law states.
Investigate how varying the mass of the object affects the acceleration produced.
Get a toy car and attach it to a piece of string.
The string should be looped around a pulley and the other end of the string should be attached to a 100g mass.
The weight of the mass will provide the force acting on the toy car.
We also need a timer.
On the desk/surface draw chalk lines at equal intervals such as every 20 cm.
Now hold the toy car at the starting point and when ready let go of the car.
Because there’s a resultant force acting through the string, the car will accelerate along the bench.
Record the time the car passes through each distance marker and to do this accurately take a video of the experiment so you can replay for accurate results.
Repeat the experiment but decrease the mass attached to the toy car.
You should find that as the mass of the toy car increases, the acceleration decreases which Newton’s second law states.
What is the stopping distance?
The total distance travelled from when the driver first spots the obstruction to when the car stops.
The stopping distance can be divided into two parts:
Thinking distance
Braking distance
What is the thinking distance?
The distance travelled by the car during the drivers reaction time.
The reaction time is the time taken for the driver to spot the obstruction, make a decision and then move their foot to the brake.
What is the braking distance?
The distance the car travels from when the driver applies the brakes to when the car stops.
What is the relationship between the speed of the vehicle and the stopping distance?
The greater the speed of the vehicle, the greater the stopping distance (assuming that the same braking force is applied)
What is a typical range of reactions times?
0.2-0.9 seconds
What affects reaction time, therefore affecting thinking distance?
Tiredness
Alcohol and certain drugs.
Distractions such as phone.
What affects braking distance?
Wet or icy conditions reduce the friction between the tyres and the road, increasing the braking distance.
Work tyres reduces the friction between the tyres and the road, increasing the braking distance.
Worn brakes also increase the braking distance
Describe the energy changes taking place when a vehicle brakes.
During braking, the brake pressed against the wheel.
The force of friction now acts between the brake and the wheel.
The kinetic energy of the car is now converted to thermal energy in the brakes.
This causes the temperature of the brakes to increase.
At the same time, the car slows down as it loses kinetic energy.
The greater the speed, the greater the braking force needed to stop the car in a certain distance.
A large braking force will require a vehicle to decelerate rapidly and a large amount of kinetic energy is transferred to thermal energy in the brakes.
This can cause the brakes to overheat.
This could also cause the driver to lose control of the vehicle
What is the formula for the force involved in the acceleration of vehicles?
Combine F=ma with A=Change in velocity/time to get
F=m x change in velocity/time
What is momentum ?
A measure of how much motion and object has
Depends on both its mass and its velocity
Momentum - the movement ent of objects
1)moving objects have momentum :
faster & heavier object →more momentum it has
E.g truck moving at 10m/s has more momentum than a bicycle because it has more mass
2)change in momentum means change in movement :
if object slows down, speeds up, or changes in direction→ it’s momentum changes
3) momentum transfers in collision
went to objects collide→ momentum is transferred between them
If not external forces act→ total momentum stays the same(conservation of momentum)
Example :
Moving car hits a stationary trolley .the car slows down,and trolley starts moving →momentum is transferred from car to trolley
What is conservation of momentum?
In a close system(No external forces), The total momentum before and after a collision or explosion is the same