Operational Amplifiers
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:56 PM on 6/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
Amplifier
Devices used for signal processing
2
New cards
Amplifier
Performs AMPLIFICATION to increase the magnitude of voltage
3
New cards
Amplifier
Other functions include signal inversion, differentiation, integration, addition, subtraction, and comparison
4
New cards
Amplifier
Generally, we model an ___ as a two-port device, with an input and output voltage referenced to ground
5
New cards
Amplifier
defines the factor by which the voltage is changed
6
New cards
Input Impedance
Defined as the ratio of the input voltage and current
7
New cards
Operational Amplifiers
Also referred to as OP AMP
8
New cards
op amp
aka operational amplifiers
9
New cards
op amp
low-cost and versatile integrated circuit consisting of many internal transistors, resistors, and capacitors manufactured into a single chip of silicon
10
New cards
differential input
Ideal Op Amp has a ___, single output amplifier that is assumed to have infinite gain
11
New cards
inverting input, noninverting input
The two inputs are called the ___, labeled with a minus sign, and the ___, labeled with a plus sign.
12
New cards
minus, plus
The two inputs are called the inverting input, labeled with a ___ sign, and the noninverting input, labeled with a ___ sign.
13
New cards
feedback
Op amps usually includes a ___ from the output going to the inverting (closed loop configuration) input to stabilize the amplifier and control of gain
14
New cards
\- it has infinite impedance at both inputs
\- it has infinite gain
\- it has zero output impedance
\- it has infinite gain
\- it has zero output impedance
Golden rules on op amps
15
New cards
Inverting Amplifiers
Constructed by connecting two external resistors to an op amp
16
New cards
Inverting Amplifiers
Circuit inverts and amplifies the input voltage
17
New cards
Inverting Amplifiers
Feedback loop always goes from the output to the inverting input of the op amp, implying negative feedback.
18
New cards
Inverting Amplifiers
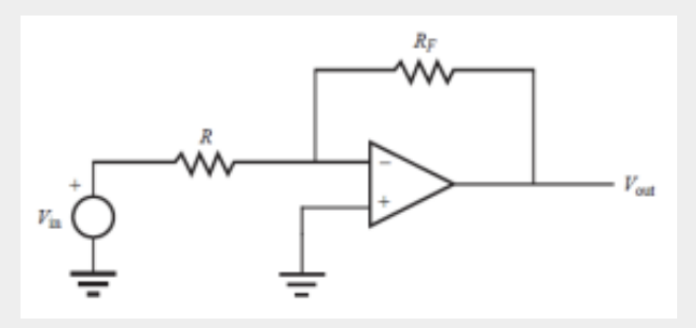
19
New cards
Inverting Amplifiers
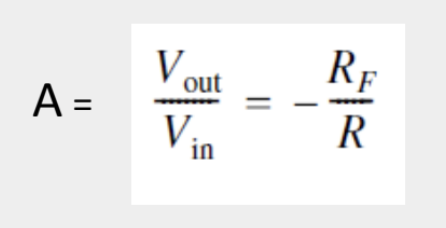
20
New cards
Inverting Amplifiers
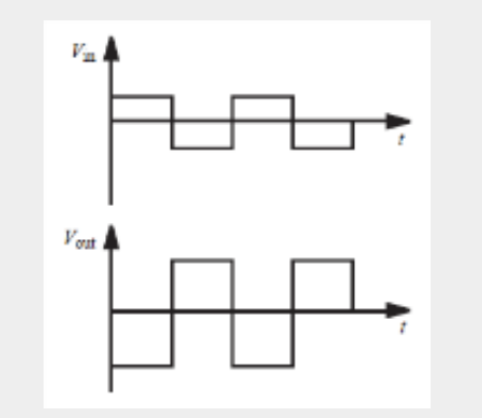
21
New cards
Non-inverting Amplifiers
Circuit amplifies the input voltage without inverting the signal
22
New cards
Non-inverting Amplifiers
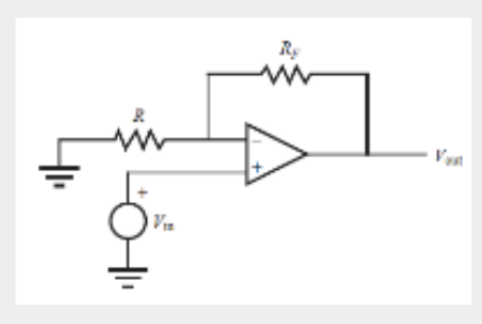
23
New cards
Non-inverting Amplifiers
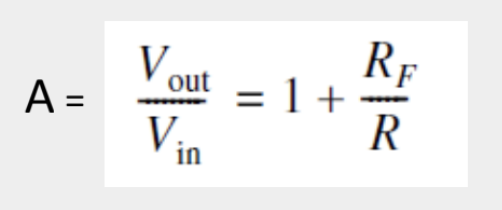
24
New cards
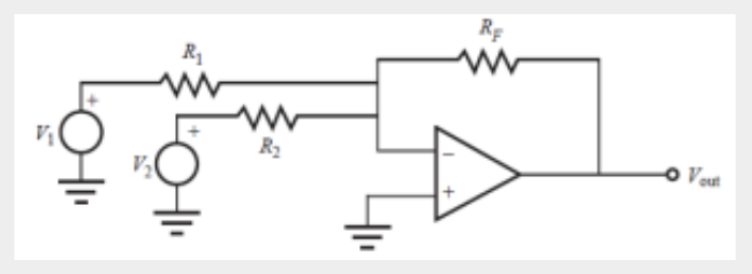
Summer Amplifiers
Circuit adds the input signals
25
New cards
Summer Amplifiers
Output is the negative sum of the inputs
26
New cards
Summer Amplifiers
27
New cards
Summer Amplifiers
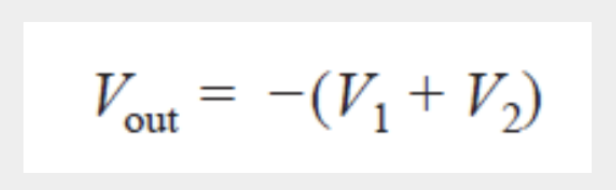
28
New cards
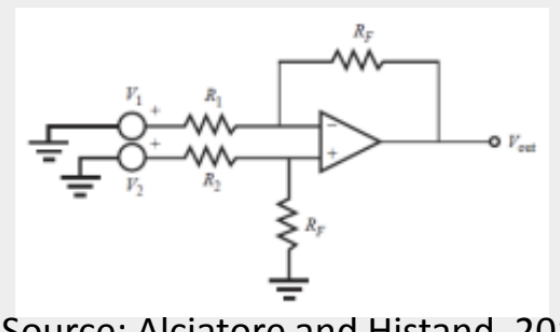
Difference Amplifier
29
New cards
Difference Amplifier
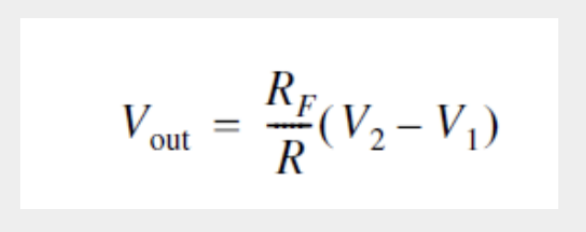
30
New cards
Instrumentation Amplifier
Has a very high input impedance
31
New cards
Instrumentation Amplifier
Capability to amplify low-level signals in a noisy environment, often a requirement in differential-output sensor signal-conditioning applications
32
New cards
Instrumentation Amplifier
Consistent bandwidth over a large range of gains
33
New cards
Instrumentation Amplifier
Has large common mode rejection ratio (CMRR). The CMRR is the ratio of the difference mode gain to the common mode gain.
34
New cards
common mode rejection ratio
aka CMRR
35
New cards
CMRR
the ratio of the difference mode gain to the common mode gain
36
New cards
Instrumentation Amplifier
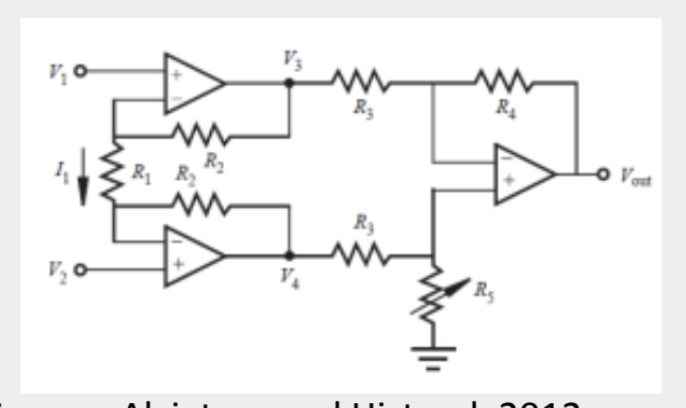
37
New cards
Instrumentation Amplifier
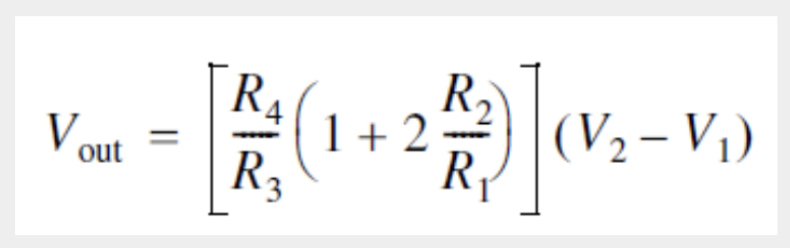
38
New cards
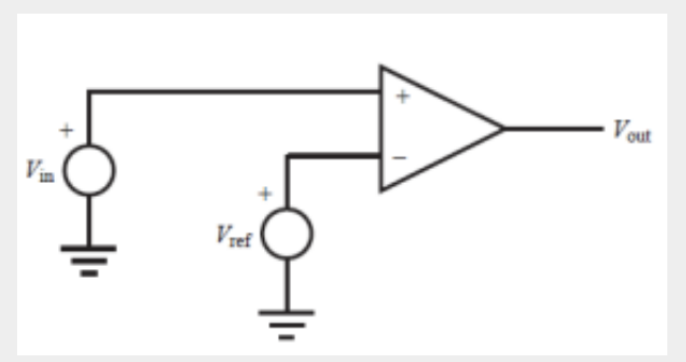
Comparator
Circuit is used to determine whether one signal is greater than another
39
New cards
Comparator
an example of an op amp circuit where there is no negative feedback and the circuit exhibits infinite gain
40
New cards
Comparator
Output is saturated, where it remains at its most positive or most negative value
41
New cards
Comparator
The positive saturation value is slightly less than the positive supply voltage, and the negative saturation value is slightly greater than the negative supply voltage.
42
New cards
Real Op Amps
aka Non-ideal amps
43
New cards
Real Op Amps
have a very high input impedance, so very little current is drawn at the inputs.
44
New cards
Real Op Amps
There is very little voltage difference between the input terminals.
45
New cards
not infinite, magnitude
However, input impedance of a real op amp is ___, and its ___ is an important terminal characteristic of the op amp.
46
New cards
gain bandwidth product
aka GBP