NRES 251 Exam 3
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What percentage of Earth's water is freshwater?
About 2.5%, with less than 1% accessible to humans.
What are major threats facing oceans today?
Overharvesting, sea level rise, CO2 induced acidification, coastal eutrophication
Define groundwater.
Location in the soil profile where 100% of the pore space is filled with water.
What is the state of glaciers globally?
Rapid melting due to climate change, contributing to sea level rise.
How does temperature affect vapor content in the air?
Warmer air holds more water vapor, increasing evaporation.
What causes condensation in clouds?
Lower pressure from higher altitude causes lower temperature, resulting in the cooling of air and formation of water droplets.
Name and define three types of fog.
Advective: Warm air over cool surface. Radiative: Ground cooling overnight. Evaporation: Cold air over warm water.
What is a contrail?
Ice crystals formed from airplane exhaust at high altitudes.
What are the components of net precipitation?
Precipitation - Evaporation - Interception - Runoff.
What factors affect infiltration?
Slope, land use, vegetation, soil structure, o.m. content, precipitation intensity
Why are we concerned with increased surface runoff?
It increases flooding, erosion, and reduces groundwater recharge, water quality concerns.
Define evaporation and transpiration.
Evaporation: Water turning from liquid to vapor. Transpiration: Water released from plants.
What is evapotranspiration (ET)?
Combined water loss from evaporation and transpiration.
What is PET?
Potential ET assuming unlimited water supply.

What is ETo?
Reference ET based on a standard crop (like grass).
What is actual ET?
Real ET based on soil moisture and conditions.
How does ET change seasonally?
Higher in warmer seasons; PET often exceeds precipitation in summer.
Strengths of empirical ET methods?
Easy and quick to calculate.
Weaknesses of direct ET measurements?
Expensive and complex, but very accurate.
What happens during El Niño in the Midwest US?
Warmer, wetter winters.
What about La Niña?
Cooler, drier winters.
What drives El Niño/La Niña patterns?
Pacific Ocean sea surface temperatures due to cool water upwelling.
How does land use alter the hydrologic cycle?
Deforestation reduces transpiration, urbanization removes pervious surfaces, reduced water table due to groundwater usage.
Name undeniable impacts of climate change.
CO2 traps heat in atmosphere, greenhouse gas concentrations going up, atmosphere has warmed, warmer air holds more moisture
Name one likely impact of climate change.
More intense storms or shifting precipitation.
What is a watershed?
Land area where all water drains to a common point.
Can watershed size change?
Yes, it can range from small to massive.
Can any aquatic system have a watershed?
Yes!
What is lag time?
Time required to achieve peak discharge.
What is peak discharge?
Max discharge achieved after a precip event.
What is base flow?
Normal streamflow from groundwater.
How is stream discharge measured?
Streamflow = velocity × cross-sectional area.
What is the 10% rule for streamflow?
No subsection q can be greater than 10% of total Q
Where should discharge be measured?
Wadeable streams → 6/10 depth
Non-wadeable → avg between 2/10 and 8/10
Look where thalweg is in the middle
How does velocity vary in stream depth?
Fastest in the center near the surface, slowest near banks/bottom.
What are recurrence intervals based on?
1/recurrence interval x 100
What’s the probability of various storm events?
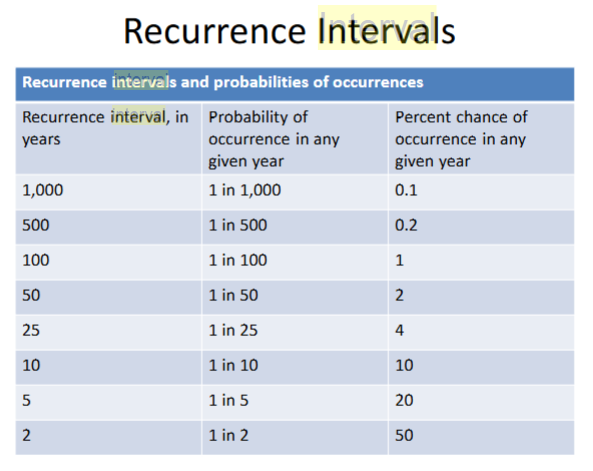
Can multiple big events happen in one year?
Yes.
Do recurrence intervals predict the future perfectly?
No, they are estimates.
What connects groundwater and surface water?
Groundwater feeds surface water (base flow), and vice versa.
Name two runoff mechanisms.
Hortonian: Rainfall exceeds infiltration.
Saturation Excess: Soil is already full.
What formula is used to calculate peak runoff?
Rational Runoff Method: Q = CiA.

How does urban land use affect streams?
intense peak discharges, high erosion, destabilized stream banks, stream straightens itself.
What hydrograph components are affected by urbanization?
Increases peak flow, shortens lag time, reduces base flow.
How does stream ordering work?
Two 1st-order streams form a 2nd order, and so on.
What is stream sinuosity?
Degree of meander in a single thread stream.

How do streams change from headwaters to large rivers?
Increase in width, depth, floodplain size, and sediment transport.
What law regulates US water quality?
Safe Drinking Water Act.
What agency regulates drinking water in the US?
EPA.
What is an MCL?
Maximum Contaminant Level allowed in drinking water.
Major water contaminants
Heavy metals, inorganic/prganic compounds, radionuclides, microbes
Main stages of surface water treatment
Flocculants → Sedimentation → Sand filtration → Additives
Main stages of wastewater treatment?
Gravity/screens → settling → aeration tubs to decomp and remove BOD → anerobic/aerobic cells remove phosphorus and nitrates → gravity to remove microorgs → UV disinfect
How does irrigation impact groundwater?
Can lower water tables and cause salt buildup.
Two types of cooling systems in power plants?
Once-through: Cheaper, more water loss, thermopollution, organisms caught in uptake.
Recirculating: Expensive, uses less water, no thermopollution.