Intro, JIA, RA
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Rheumatology
A branch of internal medicine devoted to managing/diagnosing disorders with inflammation of the joints, muscles, tendons, and internal organs
Warmth, swelling, systemic symptoms, lab abnormalities, erythema, prolonged stiffness
Inflammatory Rheumatologic clues
Mechanical pain, improves with rest, stiffness, absence of systemic signs
Non-Inflammatory Rheumatologic clues
Mono, Oligo (2-4), Poly (4+), symmetric, asymmetric, distal, proximal
Patterns of Rheumatologic joint pain
fever, rash, nodules, neuropathy, ocular inflammation
Extra-articular manifestations of rheumatic diseases
CBC (WBC, Hgb, platelets), BMP (creat), Hep panel, ESR/CRP, HLA-B27 (AS, PSA), RF (RA, Sjogren’s SLE, sarcoidosis), CCP (RA), ANA (Lupus, MCTD, Sjogren’s, Scleroderma, Dermatomyositis), Uric Acid (gout)
General lab workup for rheumatic diseases (after OLDCARTs, family hx, PE, etc)
Xrays, U/S, MRI, CT
General imaging workup for rheumatic diseases (after OLDCARTs, family hx, PE, etc)
gout, pseudogout, inflammatory, infections (DO NOT PASS THROUGH CELLULITIS OR PSORIASIS)
An arthrocentesis with cell count and crystals can be use to diagnose…
Sjogren’s (lip), dermatomyositis (muscle)
A biopsy can be helpful in diagnosing…
Sjogren’s, Dermatomyositis
An EMG can be helpful in diagnosing…
Lupus, psoriasis, vasculitis, dermatomyositis
A dermatology consult can be helpful in diagnosing…
lube, shock absorption, nutrient distribution, joint health
What is the purpose of Synovial Fluid?

T cells (release cytokines), Dendritic cells (APCs)
What are the immune response initiators
Macrophages (release TNF-alpha, Il-1), Mast cells (release histamine), PNMs
What are the Inflammatory mediators?
Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (proliferate abnormally and produce cartilage/bone degrading enzymes), Osteoclast (activity is increased in inflammatory arthritis)
What are the Tissue Destruction contributors?
Cytokines
Small proteins released by cells that act as signaling molecules, regulate immune responses, inflammation, and hematopoiesis.
Antigen
Substances (proteins, polysacchs, lipids, nucleic acids, etc) deemed foreign or dangerous by the immune system that trigger an immune response
Antibody (Immunoglobulin)
Proteins produced by plasma B cells in response to a specific antigen that work to neutralize or target it for destruction (ADCC)
TNF-alpha, IL-1, IL-6, IL-17 (early and chronic), Granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF - stimulates immune cells)
Pro-inflammatory Cytokines
IL-10, Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta - regulates immune responses and promotes repair)
Anti-inflammatory Cytokines
Juvenile Idiopathic arthritis (JIA)
The most common type of chronic (6+ weeks), inflammatory arthritis in kids and teens (prior to 16 y/o) that is idiopathic in nature and more common in females.
Genetic predisposition or environmental triggers lead to the autoimmune destruction cartilage, increased synovial fluid, and thickening of the synovium (TNF-alpha, IL-1, IL-6)
Patho for JIA
Joint pain, stiffness, swollen/warm joints, fatigue, eye symptoms, rash, loss of appetite, high fever
General symptoms of JIA - depends on the subtype
Uveitis (can become chronic and lead to blindness), macrophage-activation syndrome (MAS), contractures, joint destruction and deformities, limb length discrepancy, growth retardation (early epiphyseal closure), Pericarditis, pleuritis
Complications of general JIA
Uveitis (get a slit lamp exam at diagnosis)
One of the most serious complications (20%) of JIA that involves the ciliary body and iris
young at diagnosis, ANA+, shorter disease duration in oligoJIA and RF neg polyJIA
Risk factors for Uveitis in JIA
Macrophage Activation syndrome
A potentially life threatening complication of JIA (mostly systemic) that is treated with high dose steroids, IL-1 blockade (anakinra), and a calcineurin inhibitor (cyclosporin, tacrolimus)
Fever with confirmed/suspected systemic JIA with a serum ferritin level above 684 ng/ml PLUS 2 of these (platelets less than 181, AST above 48, Triglycerides above 156, fibrinogen under 360)
Macrophage Activation syndrome diagnostic criteria
joint space narrowing and erosions → lower limb discrepancies, contractures, limited ROM, bony deformities
Chronic joint inflammation (like in polyarticular arthritis) can lead to
Pannus
An unusual, additional layer of tissue that forms in the joints, leading to discomfort, inflammation, and harm to bones, cartilage, and surrounding tissues
Oligoarthritis, Polyarthritis (RF+ and neg), Systemic JIA, Psoriatic, Enthesis-related, Undifferentiated
Types of JIA
Oligoarthritis (2-4 joints)
The most common form of JIA (30-80%) that tends to affect the females 1-3 y/o
Asymmetrically affects large joints (knees, elbows, wrist, ankles), ANA+ (but don’t rely on this), Risk of Asymmetric uveitis
Tell me about oligoarthritis JIA
Polyarthritis JIA
Another form of JIA (20% of cases) that affects 5+ joints (large and small) during the 1st 6 months of disease and involves a more widespread autoimmune response
Associated weight loss, fatigue, and low grade fever; Can be RF + or neg
Tell me about Polyarthritis JIA
Peaks at 1-3 y/o and later in adolescence, Female dominant, symmetrical, larger joints including cervical spine and TMJ, ANA+
Tell me about RF neg (seronegative) Polyarthritis JIA
Onsets during early adolescence, female dominant, Symmetric and erosive, Large and small joints, Rheumatoid nodules over elbows and achilles
Tell me about RF+ (seropositive) Polyarthritis JIA
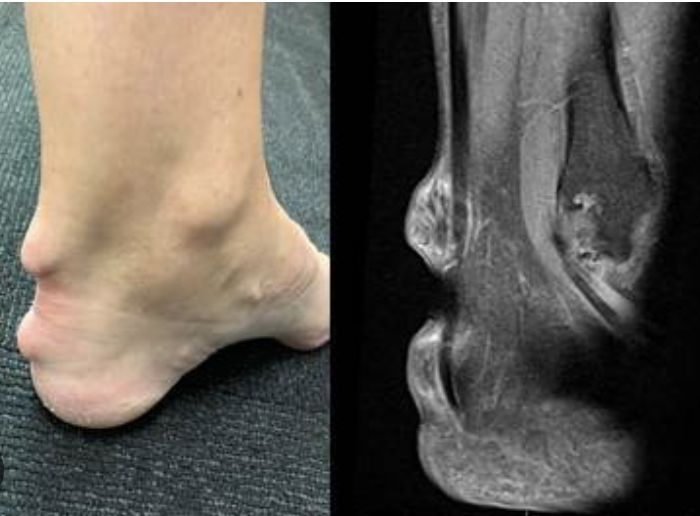
Systemic JIA
JIA characterized by inflammation in the joints, skin, and internal organs that affects with equal sex distribution and a peak onset of 2 y/o
Pain in 1+ joints with a intermittent fever of a least 2 weeks in duration PLUS one of these (transient, non-fixed erythematous rash, generalized lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, or serositis)
Diagnostic criteria for Systemic JIA
RF neg, Elevated ESR/CRP, Elevated Ferritin, anemia, leukocytosis, thrombocytosis
What do the labs look like for Systemic JIA
Psoriatic JIA
A subtype of JIA that involves both arthritis and psoriasis caused by genetic factors and immune dysregulation (T cells) that peaks during preschool years (mostly females) OR middle-late childhood
Arthritis and Psoriasis OR arthritis plus 2 of these (dactylitis, nail pitting, onycholysis, or psoriasis in a 1st degree relative), chronic uveitis
Psoriatic JIA Diagnostic Criteria
ANA +, elevated ESR/CRP
What do the labs look like for Psoriatic JIA
Enthesis-Related JIA
What subtype of JIA is strongly associated with HLA-B27 characterized by inflammation at tendon and ligament attachment sites - more common in older males and teens
Arthritis AND enthesitis (pain where the tendon/ligament attaches); OR either one + 2 of theses (SI joint tenderness or inflammation on imaging, Positive HLA-B27, hx of anterior uveitis, 1st degree relative with HLA-B27 associated disease, Onset of arthritis in a male over 6 y/o)
Enthesis-Related JIA Diagnostic criteria
Asymmetric peripheral arthritis, anterior uveitis, IBD, hip involvement is a red flag
Manifestations of Enthesis-Related JIA
undifferentiated
The catch all category for JIA - like if they meet for 2 subtypes or none of them
X-ray (joint space narrowing in RF+ late in disease, erosive changes), U/S (synovial hypertrophy, early bone erosions), MRI (monitor progression in TMJ, SI, cervical)
Imaging work up for JIA (general)
Synovial biopsy (infiltration of Bs and Ts - definitive), Slit lamp (screen for anterior uveitis q3 months in high risk, q 1yr everybody else)
Other testing for JIA (general)
NSAIDs (Naproxen, ibuprofen, maloxicam, celecoxib)
1st line therapy for JIA (no longer a monotherapy longer than 1-2 months)
DMARDs (methotrexate (most common), leflunomide, Sulfasalazine in ERA), Biologic DMARD if no response to 3 months methotrexate (polyJIA that’s moderate/severe)
Second line therapy for JIA
Severe systemic involvement (severe serositis in Still’s), bridge DMARDs, acute anterior uveitis
When do you use short-course systemic glucocorticoids in JIA treatment?
Sickle cell, infection, malignancy, trauma, other autoimunes
DDX for JIA
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
A chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease that tends to erode the small joints symmetrically that can lead to deformity and loss of physical function - early treatment and diagnosis is the standard
Females (3x), Onset tends to be 30-40s (female), 50s (male)
Epi Stats for RA
Age, sex, smoking, hx of live births, early life exposures (infectious, viral, etc), obesity, genetics, breastfeeding decrease risks
Risk factors of RA
Synovium becomes thickened with a pannus (erodes cartilage and bone) as well infiltrated by immune cells that release TNF-alpha, IL-1/6/17, or MMPs (matrix metalloproteinases)
Patho for RA
Initiation (unknown trigger), Propagation (cycle of immune activation and inflammation), Chronic inflammation (leads to joint damage, pain, and loss of function)
Stages of RA disease progression
morning stiffness for 2 hours, low-grade fever, weight loss, fatigue, myalgias, depression, decreased energy, symmetric polyarthritis joint swelling (most common), subcutaneous nodules, difficulty with ADLS
Clinical features of RA (usually an insidious onset)
PIP, MCP, wrist, MTPs
Most common joints affected by RA
Boutonniere (Pip flexed, DIP hyperextended), Swan Neck (MCP flexed, pip extended, DIP flexed)
Late stages joint changes in RA
C1-C2 (subluxation and instability - may compress central spinal cord)
Spinal involvement of RA
Nodules in the heart can lead to BBB, AV blocks, pericarditis, pericardial effusions
Cardiac involvement of RA
Pleural effusions, pleurisy, interstitial lung disease, pulmonary fibrosis (restrictive, honeycomb pattern), pulmonary infiltrates, rheumatic lung nodules
Pulmonary involvement of RA
Normocytic normochromic anemia, thrombocytosis, thrombocytopenia, Felty’s (splenomegaly with neutropenia), nonspecific transaminitis, peripheral nerve entrapment, cervical myelopathy, muscle atrophy, low grade membranous glomerular nephropathy, vasculitis
Other extra-articular involvements of RA
Scleritis, uveitis, ulcerative keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis sicca
Ocular involvement of RA
Subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules (usually extensor surfaces or visceral)
What is pathognomonic for RA (usually RF+)
Persistent symmetric polyarthritis of hands and feet
Hallmark of RA
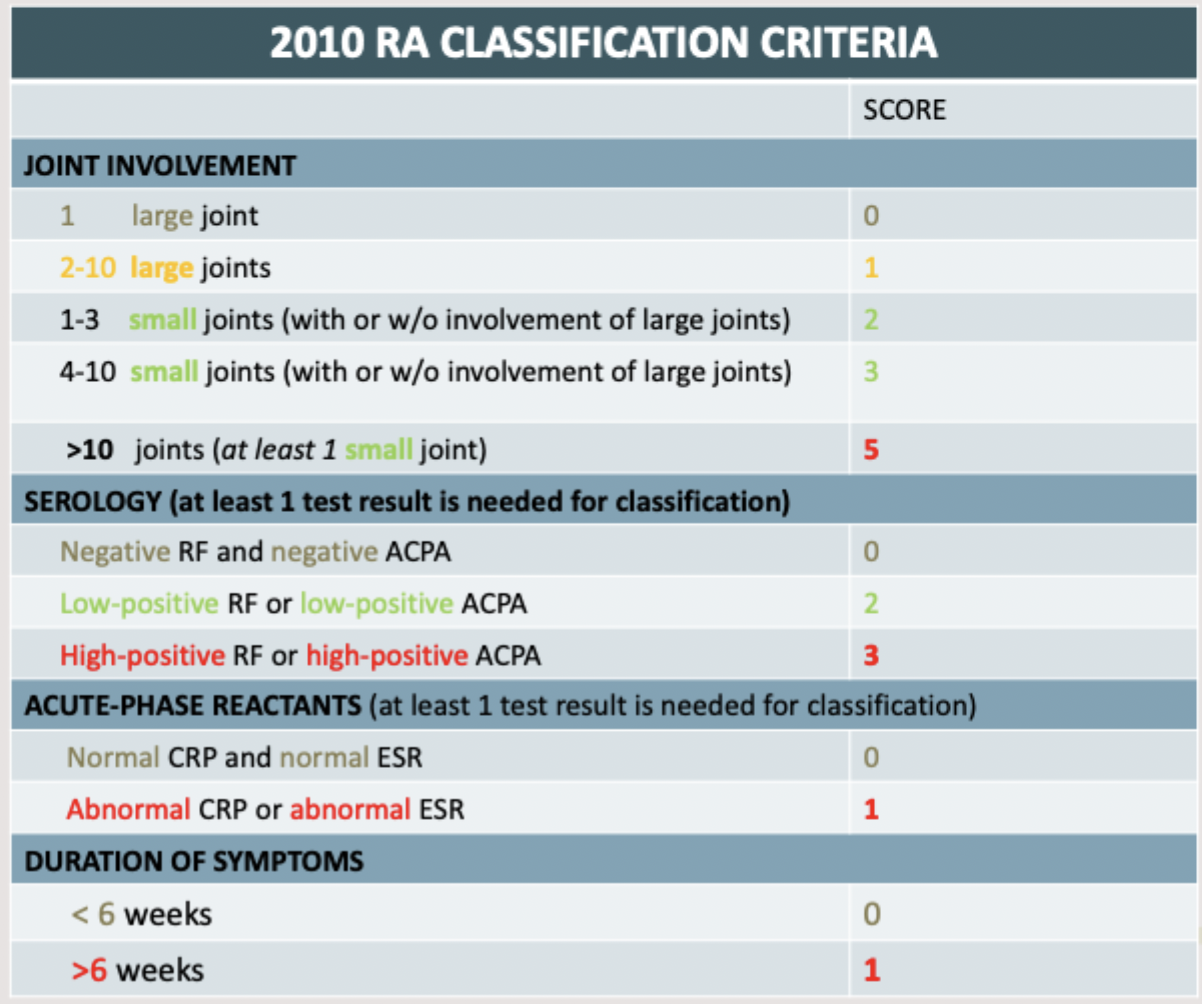
ACR criteria, PE, Hx, labs, imaging, and synovial fluid analysis
Diagnosis of RA is based on
CMP, CBC with Diff, ESR/CRP, RF (nonspecific), CCP (95% specific), Fluid analysis (non-specific)
Lab workup for RA
X-rays (erosions, joint space narrowing (get neck too), ulnar deviation), U/S (erosions, synovial hypertrophy, tenosynovitis)
Imaging workup for RA
Reduce pain/inflammation, prevent/halt joint destruction, preservation of function, prevention of deformity
primary objectives of treating RA
PT/OT, reconstructive surgery, NSAIDs (Naprosyn 500 mg, Celecoxib for GI concerns), Analgesics (Tylenol - watch LFTs), corticosteroids (short-dose prednisone), DMARDs
Treatment plan for RA
Use to bridge DMARDs, adjunct for active or flare ups, taper!!
Rules for steroids in RA
DOC w/ improvement in 4-6 weeks, weekly injections or pill, Watch kidneys and liver, take with folic acid, TERATOGENIC
Tell me about Methotrexate in RA
Alt to methotrexate, daily, watch the liver, TERATOGENIC
Tell me about Leflunomide in RA
Get an eye exam (retinopathy), okay for pregs, based on weight 200-400 mg/day
Tell me about Hydroxychloroquine in RA
Check G6PD, NOT FOR LUPUS, SULFA OR ASA allergy
Tell me about Sulfasalazine in RA
Screen for TB (quantiferon gold), CXR, hep panel, NO live vaccines
Before starting biologics, what do we need to do?
TNF-inhibitor, T-cell inhibitors, IL-6 inhibitors, IL-1 inhibitors, JAK inhibitors
Examples of biologic classes
