Data representation
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
what is data representation
method of encoding information in a format the computer can process
what are the basic building block in computers
binary number system with 1s and 0s
what is another name for binary number system
base 2
what is the representation of switches
on and off positions of 1s and 0s
what are logic gates in computers used for
to store and process data efficiently in computers
what is the other name for denary
base 10
what is the other name for hexadecimal
base 16
numbers in binary
0, 1
numbers in denary
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
what are the numbers in hexadecimal
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F
convert 00110011 to denary
51
convert 01111111 to denary
127
convert 56 into binary
00111000
convert 10011001 into hexadecimal
99
convert 10110011 into hexadecimal
B3
convert F2 into denary
242
convert 6F into binary
01101111
why do computer scientists find hexadecimal ore convenient to use than binary
one hex digit represents four binary digits
what is 1101 0010 1010 1111
D2AF
what are four uses of hexadecimal
error codes, MAC address, IP address, HTML
what do error codes refer to
memory location of the error
who needs to know how to interpret error codes
the programmer
What is a MAC address
a number that uniquely identifies a device on a network
what is a MAC address made up of
48 bits shows as 6 groups of two hexadecimal digits
what do the two halves of a MAC address represent
first half is manufacturer’s identity number and second half is serial number of the device
difference between IPv4 and IPv6
IPv4 is 32-bit in denary or hexadecimal, IPv6 is 128-bit in hexadecimal
what is HTML used for
writing and developing web pages
how are colours represented in HTML
six hexadecimal digits preceded by # symbol
how many possible colours can be represented in HTML
over 16 million
write the format of MAC addresses
NN-NN-NN DD-DD-DD
which IP address uses colon
IPv6
benefits of HTML
takes less space, easier to read, 1 HTML digit is 4 binary digits
format of IPv6
broken down into 16-bit chunks with a colon separator
add 0101 and 1110
00010011
What is a logical binary shift?
It is moving a binary number to the left or right.
what does a shift left in binary mean
equivalent to multiplying the binary number by 2
what does a shift right in binary mean
equivalent to dividing the binary number by 2
What happens to empty positions in a binary number during a logical shift?
They are replaced with a zero.
shift 01110000 five places to the left
00000000
What is two’s complement used for in binary numbers?
It is used to represent negative integers.
How is the left-most bit interpreted in two’s complement
1 indicates negative, 0 indicates positive
range of numbers in two’s complement
−128 to +127
10000000 to 01111111
00110011 in two’s complement
51
11001111 in two’s complement
-49
what does ASCII stand for
American Standard Code for Information Interchange
when was ASCII set up
1963
How many bits are in the standard ASCII code character set?
7 bits
range of standard ASCII in denary and hexadecimal
0 to 127 in denary
00 to 7F in hexadecimal
how many control codes in ASCII
32
what is the range of the ASCII control codes in denary and hexadecimal
0 to 31 in denary
00 to 19 in hexadecimal
what are the limitations of logical binary shifts
limit to the number of shifts before all zeros in an 8-bit register
what is the main disadvantage of ASCII
does not represent non-western languages
what coding system developed ASCII limitations
unicode
how many characters can Unicode support compared to ASCII
several thousands over 128 characters
How many bytes per character does Unicode use compared to ASCII?
Unicode is four per character
ASCII is 1 per character
When was the Unicode consortium set up
1991
Unicode’s five goals
covering all languages, uniform encoding, more efficient, unambiguous encoding, reserve part of code
What are sound waves
Sound waves are vibrations in the air
how are sound waves interpreted by the human ear?
ear senses these vibrations in ear drum
Why do sound waves need to be sampled to be stored in a computer?
sound waves are analogue and computers cannot work with analogue data
What is sampling in the context of sound waves?
measuring the amplitude of the sound wave at regular time intervals
What tool is used to convert analogue sound waves to digital?
analogue to digital converter (ADC)
What is sampling resolution (bit depth)
number of bits used to represent each sampled amplitude value
How is sampling rate measured
measured in hertz (Hz)
what does the measurement of sampling rate signify
number of sound samples taken per second.
What happens when you use a higher sampling rate or larger resolution in sound sampling?
increases file size and produces more faithful representation
what are the benefits of large sample rate
better quality, less distortion, larger dynamic range
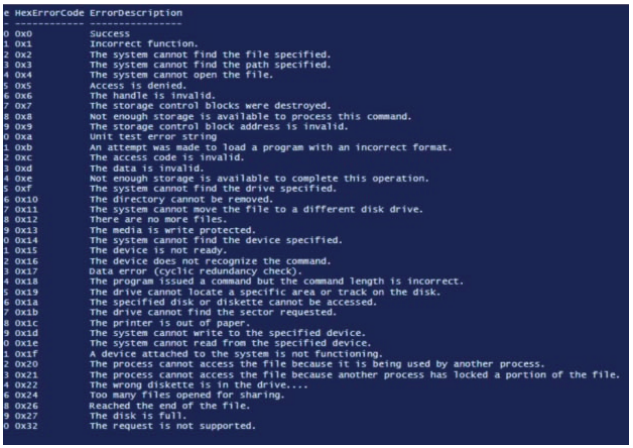
what does this represent
error codes
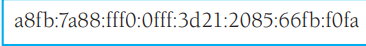
what does this represent
IPv6

what does this represent
HTML
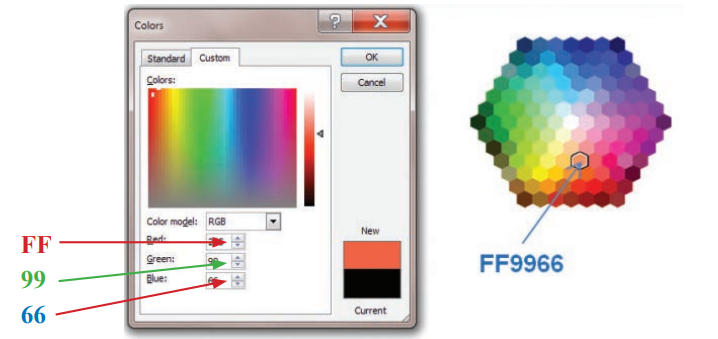
what does this represent
HTML hex colour code
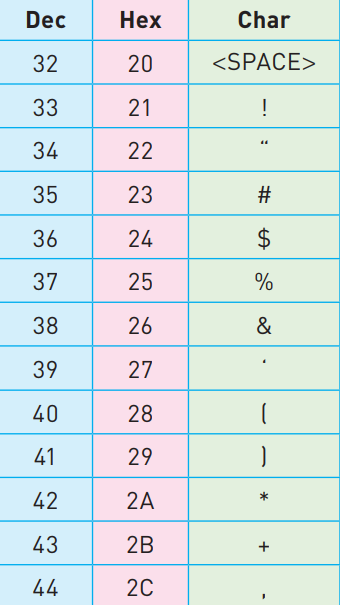
what does this represent
ACSII code
what is this
sound wave

what do these represent
different pixel shapes

what does this represent
different image resolution

which image has the highest resolution
image a
what do we call an image with a low resolution
pixilated
What is the sampling resolution of CD’s
16-bit
what is the sample rate of CD’s
44.1 kHz
How many samples per second does a CD take
44,100 every second
What is a bitmap image composed of?
pixels arranged in a two-dimensional matrix
How is each pixel in a bitmap image represented?
Pixels represented as a binary number.
How many bits per pixel are required for a black and white image?
1 bit per pixel.
How many colours can be represented with 2 bits per pixel?
Four colours
how are the four colours represented in 2 bits per pixel
00, 01, 10, 11
How many colours can be represented with 3 bits per pixel?
Eight colours
how are eight colours represented with 3 bit pixels
000, 001, 010, 011, 100, 101, 110, 111
What is colour depth
number of bits used to represent each colour in a pixel
How many colours can an 8-bit colour depth represent?
256 or 2^8
How many colours can a 24-bit colour depth represent
Over 16 million
What is image resolution?
number of pixels that make up an image.
How does increasing the colour depth affect file size?
increases colour depth, increases file size
What is the main drawback of using high-resolution images?
increase file size
How does the resolution of an image affect storage and transfer?
takes up more space on storage and longer to transmit
What happens to image quality when resolution is reduced?
loss of quality slowly becomes noticeable
What is the basic unit of all computing memory storage terms?
a bit
what does a bit consist of
either 1 or 0
What does the term "byte" refer to?
The smallest unit of memory in a computer
how much is a byte
8 bits
What is a 4-bit number called
a nibble