Science chapter 1.1-5
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is the contribution of Watson and Crick to our information of genetics?
They discovered DNA’s double helix structure, explaining DNA replication.
What is the contribution of Rosalind and Franklin to our knowledge of genetics?
They revealed the DNA’s shape, helping to prove the double helix structure.
What is the function of DNA?
DNA stores information for growth, development, and reproduction.
What are the 4 nitrogen bases in DNA?
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
How many chromosomes found in a adult skin cell and a baby liver cell?
46
How many chromosomes found in a sperm cell?
23
What is meant by complementary base pairing?
When nitrogen bases pair up with each other in DNA. AT+CG
Explain how DNA controls the production of proteins
DNA codes mRNA, which ribosomes read to link amino acids.
what is mRNA?
It is a copy of a gene from DNA
What is a chromosome?
DNA structure that carries genes, controlling traits and cell function.
What is a Homologous?
A name given to chromosomes that are of the same pair.
What is a sperm?
Sex cell/gamete produced by the male parent.
What is a Gamete?
A sex cell, carries genetic information from parent to the offspring.
What is a Karyotype?
Diagram displaying the complete set of chromosomes set out in pairs in order of size.
What is an Ovum?
A sex cell/gamete produced by the female parent.
What is a Genome?
Genetic information contained in an organism’s cell.
What is DNA?
A chemical which makes up chromosomes.
Explain Cancer:
A group of diseases characterized by uncontrolled mitosis.
What is a gene?
A unit of genetic information codded in DNA as part of a chromosome.
Define Diploid:
Cells with a full set of chromosomes- 2 copies of each from both parents.
What is Mitosis?
Cell division producing two identical daughter cells from one.
Define Haploid:
Cells with half the usual chromosomes- one copy of each. (found in sperm and egg)
How many cells are produced in Mitosis?
2
How many cells are produced in Meiosis?
4
Does Mitosis produce Haploid or Diploid cells?
Diploid
Does Meiosis produce Haploid or Diploid cells?
Haploid
What are the number of divisions for Mitosis?
1
What are the number of divisions for Meiosis?
2
What is the purpose of Mitosis?
Growth and repair
What is the purpose of Meiosis?
reproduction.
What is A?
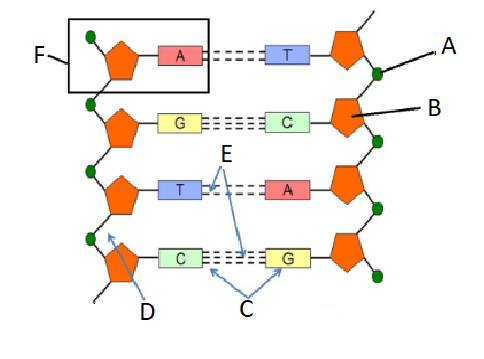
Phosphate
What is B?

Sugar
What is C?

Nitrogen Bases
What is D?

Sugar and phosphate backbone
What is E?

Hydrogen Bonds
What is F?

nucleotide
What is A?
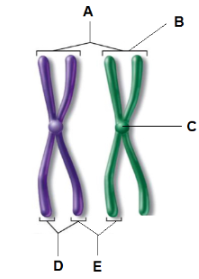
Homologous chromosomes
What is B?

Bivalent chromosome
What is C?

centromere
What is D?

Sister chromatids
What is E?

Non-sister chromatids
What phase is this?
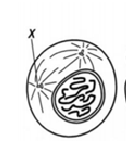
Prophase - Chromosomes start to condense. Nucleus disintegrates.
What phase is this?
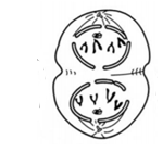
Telophase - Nucleus reforming. Cytokinesis begins
What phase is this?
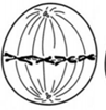
Metaphase - Chromosomes line up on equator
What phase is this?
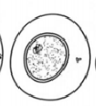
Interphase - Cell growth and normal functions. DNA replicates
What phase is this?
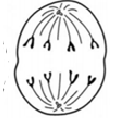
Anaphase - Chromatids pulled to opposite poles
Which one is interphase?
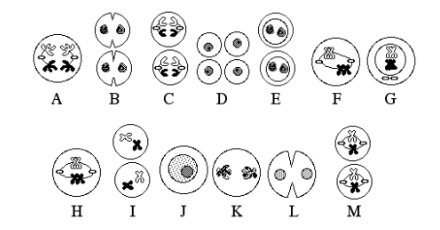
J
Which one is prophase 1?
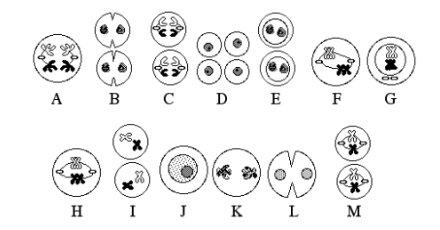
G
Which one is Metaphase 1?

F and H
Which one is Anaphase 1?

A
Which one is Telophase 1?

K and L
Which one is Prophase 2?

E and I
Which one is Metaphase 2?

M
Which one is Anaphase 2?

C
Which one is Telophase 2?

B and D
What is the difference between Mitosis and Meiosis?
Mitosis does not cross over, and Meiosis crosses over.