Introduction to the Brain and Brainstem in BIOL 214
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
What is gray matter primarily composed of?
Neurosomas, dendrites, and synapses.
What color is gray matter and why?
Dull color due to little myelin.
Where is gray matter found in the brain?
Forms the surface layer (cortex) over the cerebrum and cerebellum, and forms nuclei deep within the brain.
What is white matter composed of?
Bundles of axons.
What gives white matter its pearly white color?
Myelin around nerve fibers.
Where is white matter located in relation to gray matter?
Lies deep to cortical gray matter.
What are the four internal chambers within the brain called?
Ventricles.
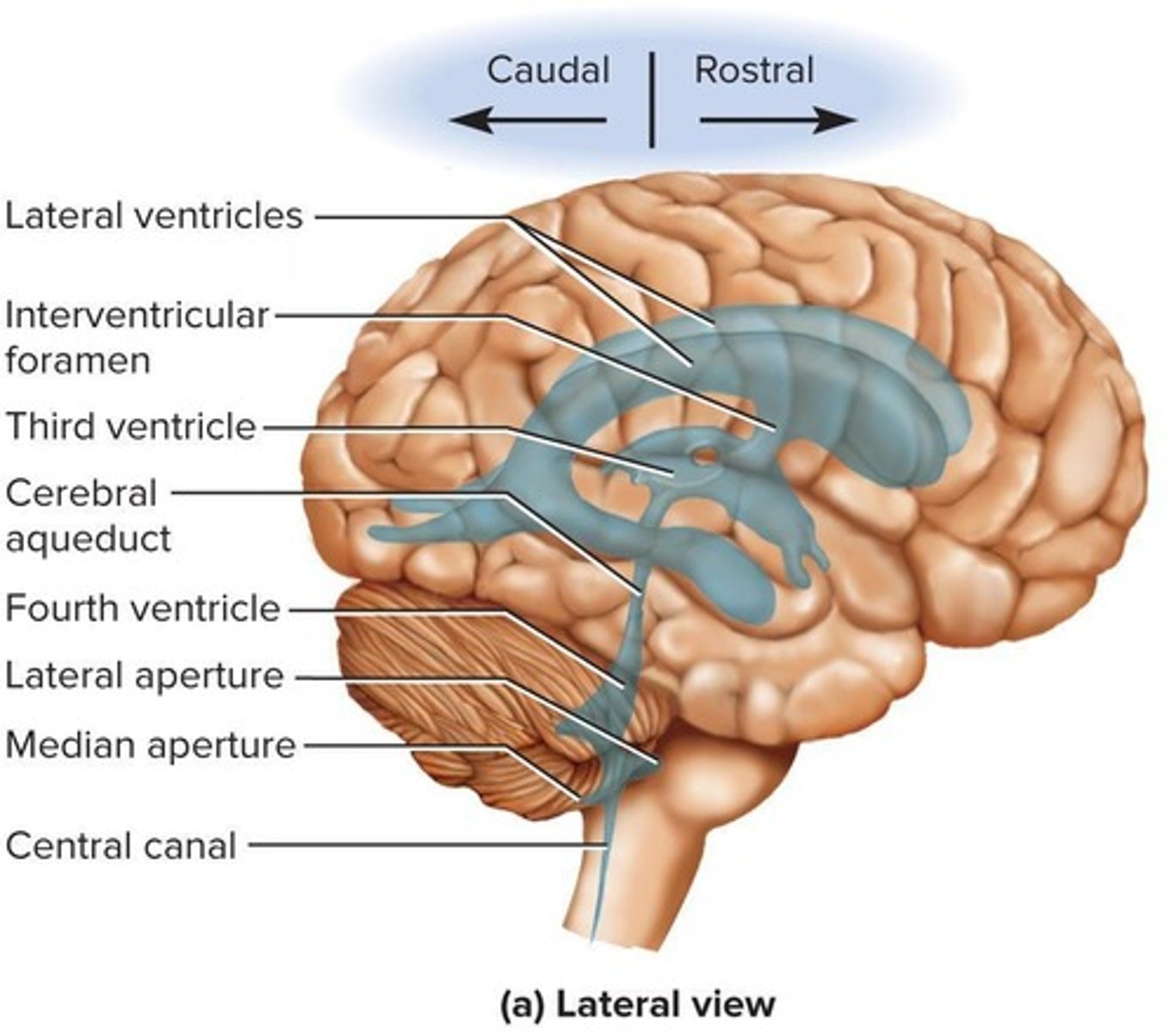
What connects the two lateral ventricles to the third ventricle?
Interventricular foramen.
What is the function of the cerebral aqueduct?
Connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle.
Where is the fourth ventricle located?
Between the pons and cerebellum.
What is the choroid plexus?
A spongy mass of blood capillaries on the floor of each ventricle.
What type of cells line the ventricles and cover the choroid plexus?
Ependymal cells.
What is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
A clear, colorless liquid that fills the ventricles and canals of the CNS.
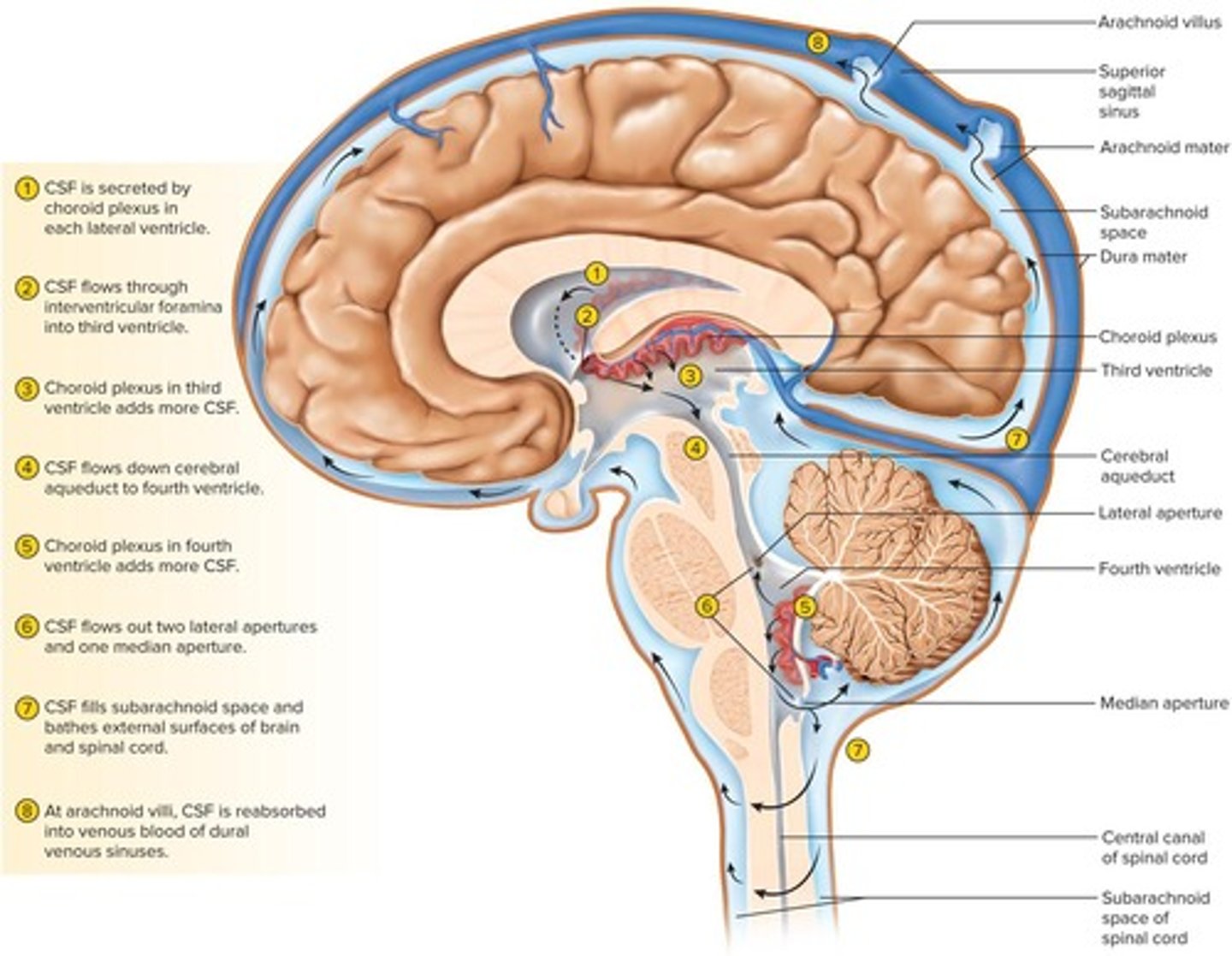
How much cerebrospinal fluid does the brain produce daily?
500 mL/day.
What is the normal volume of cerebrospinal fluid present at one time?
100 to 160 mL.
What is one function of cerebrospinal fluid?
Buoyancy, allowing the brain to attain considerable size without being impaired by its own weight.
How does cerebrospinal fluid protect the brain?
It protects the brain from striking the cranium when the head is jolted.
What happens to neural function after a 10-second interruption of blood flow?
Loss of consciousness may occur.
What can happen after 4 minutes without blood flow to the brain?
Irreversible brain damage.
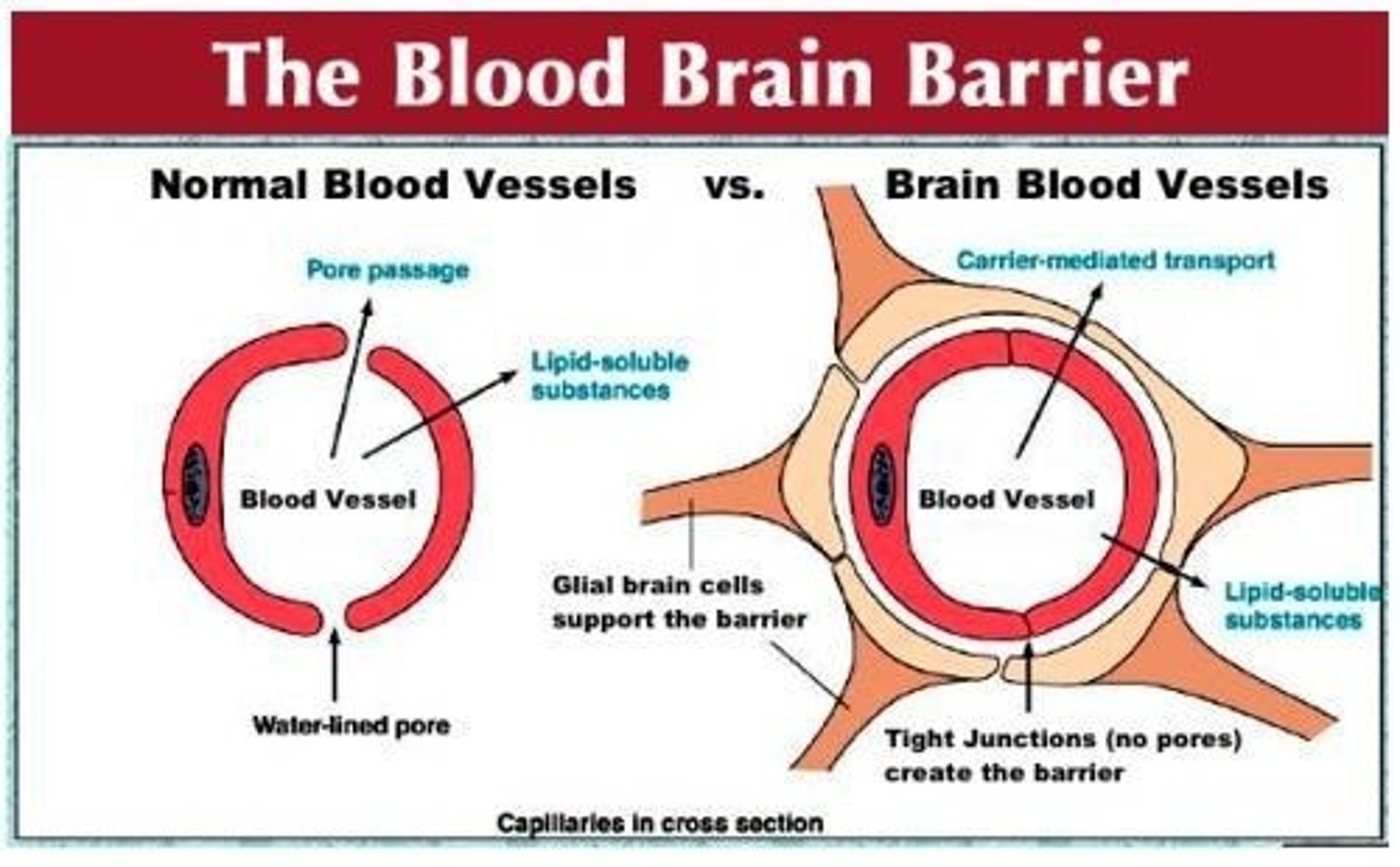
What is the blood-brain barrier?
A system that regulates what substances can get from the bloodstream into the tissue fluid of the brain.
Why is a constant supply of blood critical for neurons?
Neurons have a high demand for ATP, oxygen, and glucose.
What can harmful agents in the blood potentially affect?
They can affect the brain tissue.
What are the two points of entry that must be guarded against pathogens in the brain?
Blood capillaries throughout the brain tissue and capillaries of the choroid plexus.
What is the function of the blood-brain barrier?
It protects blood capillaries throughout brain tissue.
What forms the blood-brain barrier?
Tight junctions between endothelial cells that form the capillary walls.
How do astrocytes contribute to the blood-brain barrier?
Astrocytes reach out and contact capillaries with their perivascular feet.
What must substances do to leave the blood and enter the brain tissue?
They must pass through tight junctions and not through the cells between them.
What types of substances can endothelial cells exclude from passing to brain tissue?
Harmful substances.
What is the blood-CSF barrier and where is it located?
It protects the brain at the choroid plexus and forms tight junctions between ependymal cells.
Why are tight junctions absent from ependymal cells elsewhere?
To allow exchange between brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
What is the permeability of the brain barrier system to water, glucose, and lipid-soluble substances?
Highly permeable.
What are some examples of lipid-soluble substances that can pass through the brain barrier system?
Oxygen, carbon dioxide, alcohol, caffeine, nicotine, and anesthetics.
How permeable is the brain barrier system to sodium, potassium, chloride, and waste products?
Slightly permeable.
What can damage the brain barrier system and allow pathogens to enter?
Trauma and inflammation.
What are circumventricular organs (CVOs)?
Places in the third and fourth ventricles where the barrier is absent, allowing blood direct access to the brain.
What is one function of circumventricular organs (CVOs)?
They enable the brain to monitor and respond to fluctuations in blood glucose, pH, osmolarity, and other variables.
What risk do circumventricular organs (CVOs) pose?
They afford a route for invasion by pathogens such as the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Where does the medulla oblongata begin?
At the foramen magnum of the skull.
How long is the medulla oblongata?
About 3 cm rostrally.
What is the reticular formation?
A loose web of gray matter that runs vertically through all levels of the brainstem.
What does the reticular formation occupy space between?
White fiber tracts and brainstem nuclei.
How many small neural networks does the reticular formation connect?
More than 100 small neural networks without distinct boundaries.
What is the role of the reticular formation in somatic motor control?
It adjusts muscle tension to maintain tone, balance, and posture, especially during body movements.
How does the reticular formation contribute to balance?
It relays signals from the eyes and ears to the cerebellum and integrates visual, auditory, balance, and motion stimuli into motor coordination.
What are gaze centers in the reticular formation responsible for?
They allow the eyes to track and fixate on objects.
What are central pattern generators in the reticular formation?
Neural pools that produce rhythmic signals to the muscles of breathing and swallowing.
What cardiovascular functions does the reticular formation control?
It houses the cardiac and vasomotor centers of the medulla oblongata.
How does the reticular formation modulate pain signals?
Some pain signals ascend through the reticular formation, while descending analgesic pathways begin there and block transmission of pain signals in the spinal cord.
What role does the reticular formation play in consciousness and sleep?
It is central to consciousness, alertness, and sleep; injury here can result in irreversible coma.
What is habituation in the context of the reticular formation?
The reticular activating system modulates activity in the cerebral cortex to ignore repetitive, inconsequential stimuli.
What is the cerebellum's significance in the brain?
It is the largest part of the hindbrain and second largest part of the brain overall, containing more than half of all brain neurons.
What are the main structural components of the cerebellum?
It consists of right and left cerebellar hemispheres connected by the vermis, with a superficial cortex of gray matter and branching white matter (arbor vitae).
What are some functions of the cerebellum beyond motor coordination?
It is involved in sensory processing, linguistic tasks, emotional control, and other nonmotor functions like judging pitch and recognizing objects.
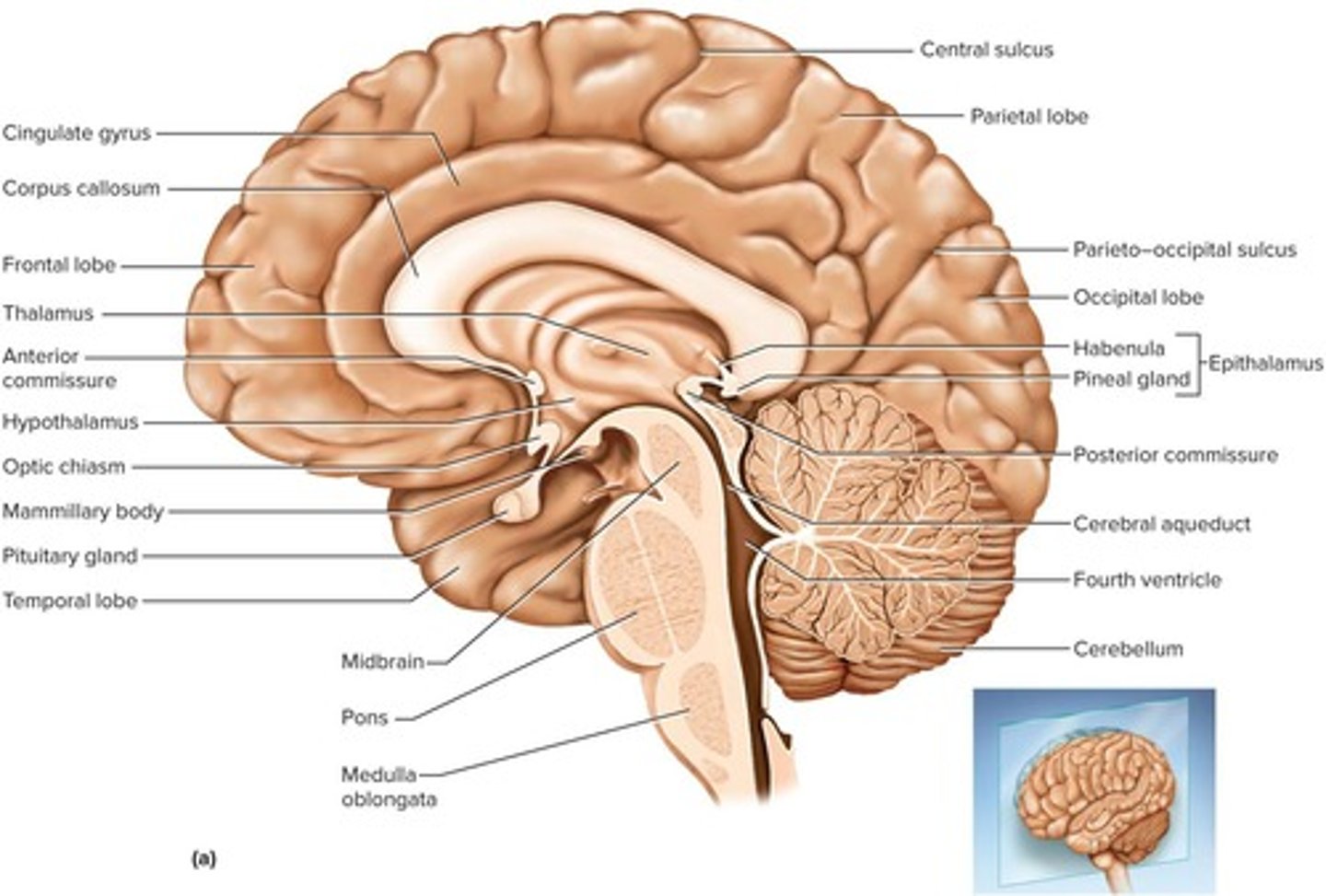
What are the two main parts of the forebrain?
The diencephalon and the telencephalon.
What are the three parts of the diencephalon?
Thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus.
What is the primary function of the thalamus?
It acts as an information relay station and is the 'gateway to the cerebral cortex' for nearly all input to the cerebrum.
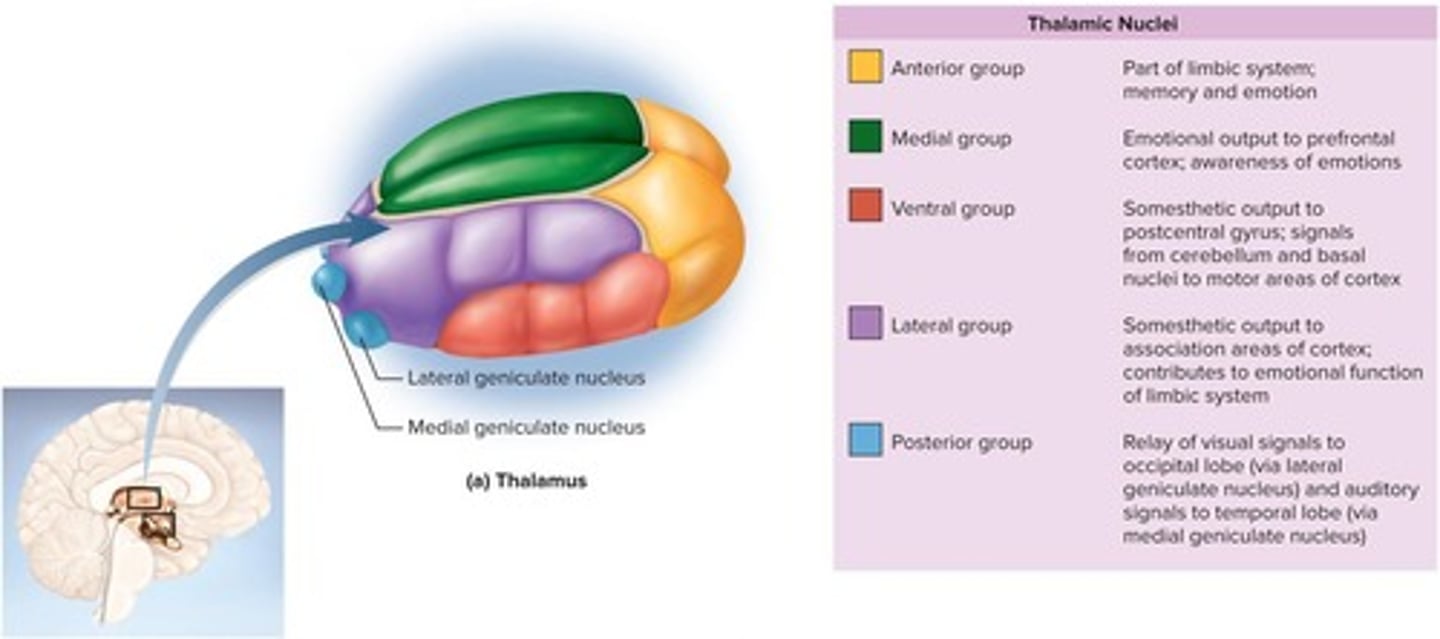
How does the thalamus play a role in motor control?
It relays signals from the cerebellum to the cerebrum and provides feedback loops between the cerebral cortex and the basal nuclei.
What is the function of the hypothalamus in the brain?
It is a major control center for the autonomic nervous system and endocrine system, playing a key role in homeostatic regulation.
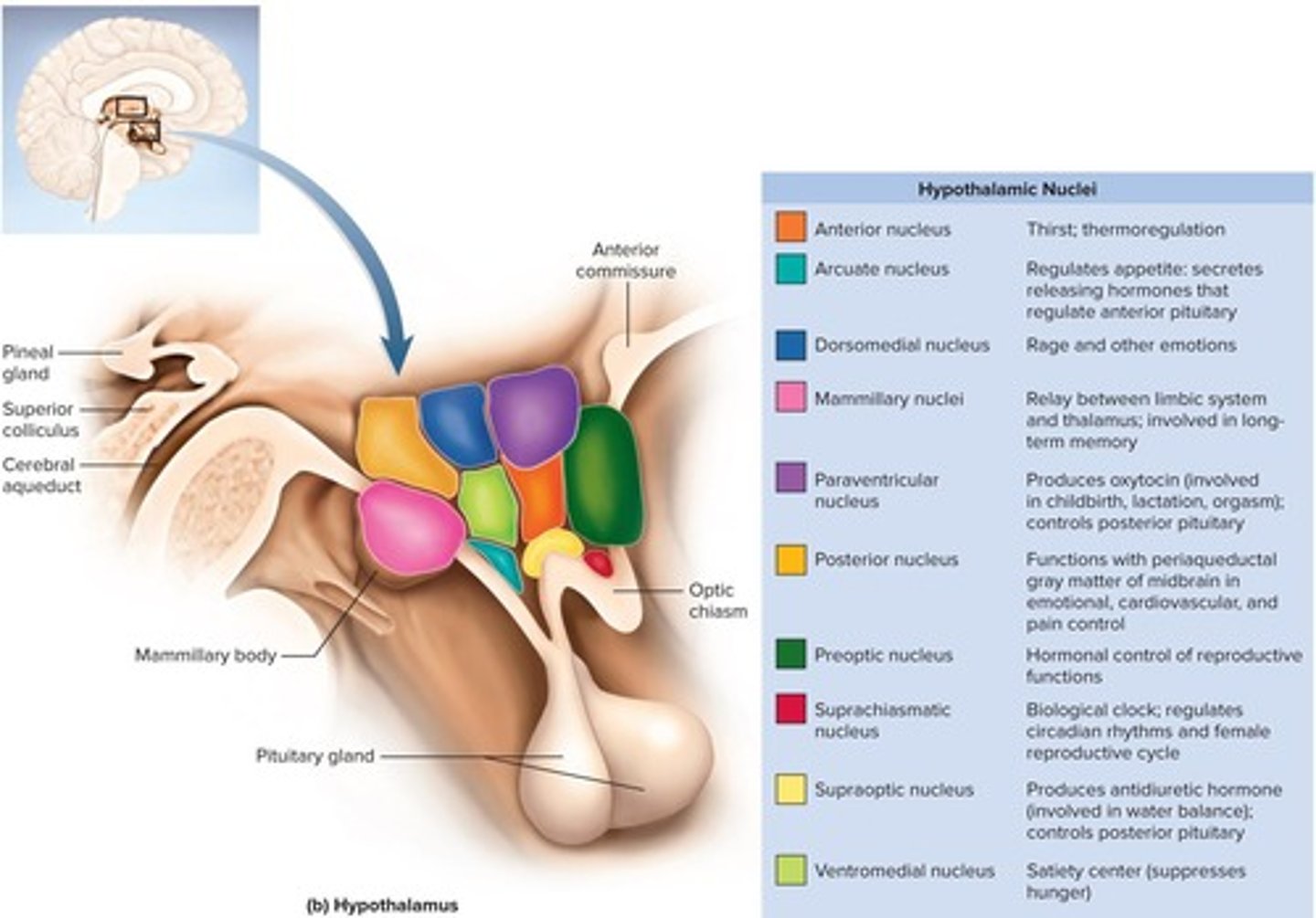
What are some functions of the hypothalamic nuclei?
They are involved in hormone secretion, autonomic effects, and regulating body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure.
What is the infundibulum in relation to the hypothalamus?
It is the stalk that attaches the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus.
What is the significance of mammillary bodies in the hypothalamus?
They contain nuclei that relay signals from the limbic system to the thalamus.
What is the role of the reticular formation in sleep?
It plays a central role in regulating consciousness and alertness.
What happens if the reticular formation is injured?
Injury can result in irreversible coma.
How does the reticular formation help with habituation?
It modulates activity in the cerebral cortex to ignore repetitive, inconsequential stimuli.
What is the relationship between the cerebellum and hyperactivity in children?
Many hyperactive children have been found to have smaller cerebellums.
What are the main functions of the hypothalamus?
Thermoregulation, food and water intake, sleep and circadian rhythms, memory, emotional behavior, and sexual response.
How does the hypothalamus regulate body temperature?
Through a hypothalamic thermostat that monitors body temperature.
What role does the hypothalamus play in hunger and satiety?
It regulates hunger and satiety and responds to hormones influencing hunger, energy expenditure, and long-term control of body mass.
What does the thirst center in the hypothalamus monitor?
It monitors the osmolarity of blood and can stimulate the production of antidiuretic hormone.
What is the function of the suprachiasmatic nucleus?
It regulates sleep and circadian rhythms.
Which nuclei in the hypothalamus receive signals from the hippocampus?
The mammillary nuclei.
What emotional behaviors does the hypothalamus influence?
Anger, aggression, fear, pleasure, contentment, and sexual drive.
What is the epithalamus composed of?
The pineal gland and habenula, which relays signals from the limbic system to the midbrain.
What is the largest part of the human brain?
The cerebrum.
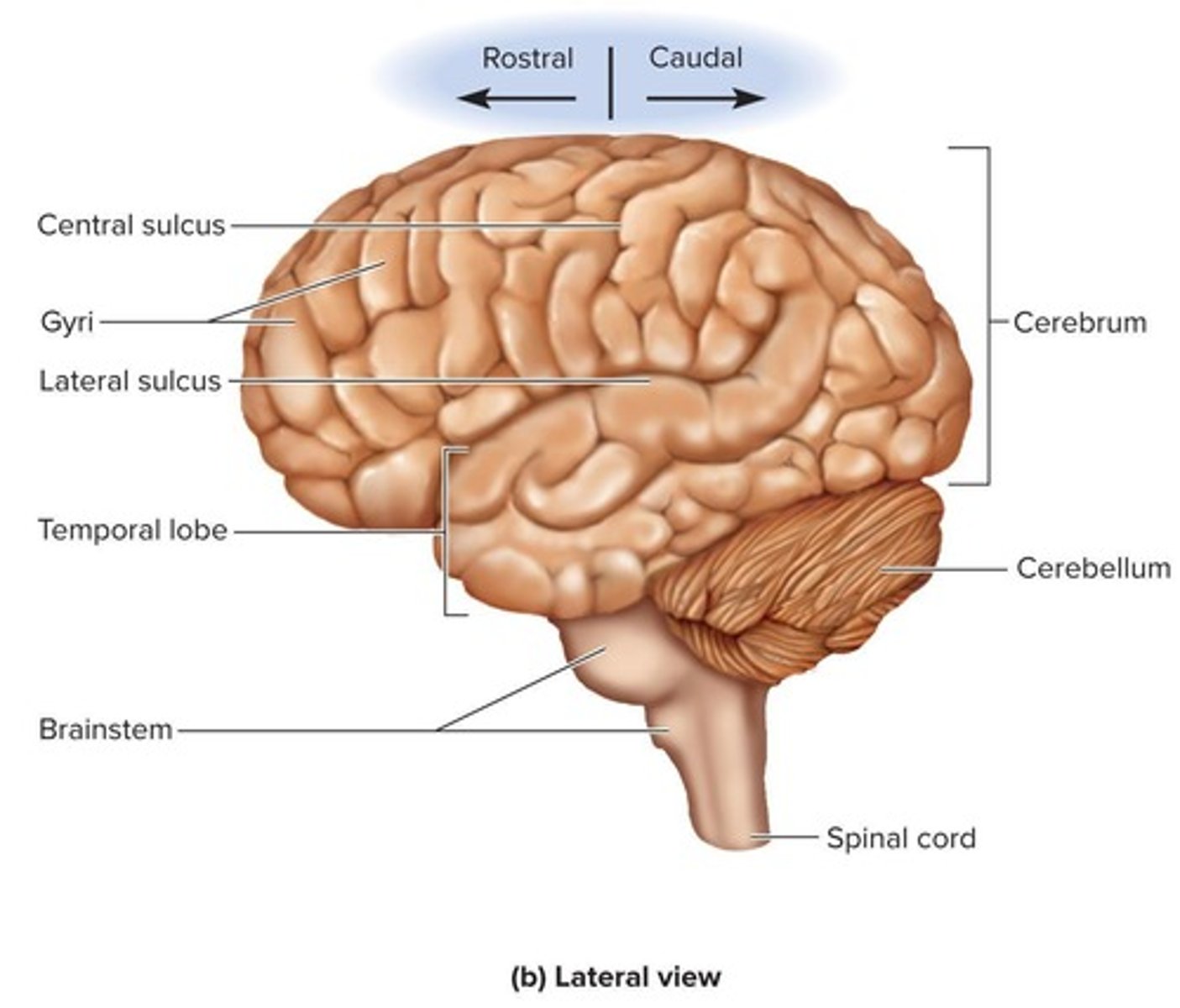
What are the two cerebral hemispheres connected by?
The corpus callosum, a white fibrous tract.
What are gyri and sulci?
Gyri are ridges and sulci are grooves that increase the surface area of the cortex for more information-processing capability.
How many lobes does each hemisphere of the cerebrum have?
Five lobes.
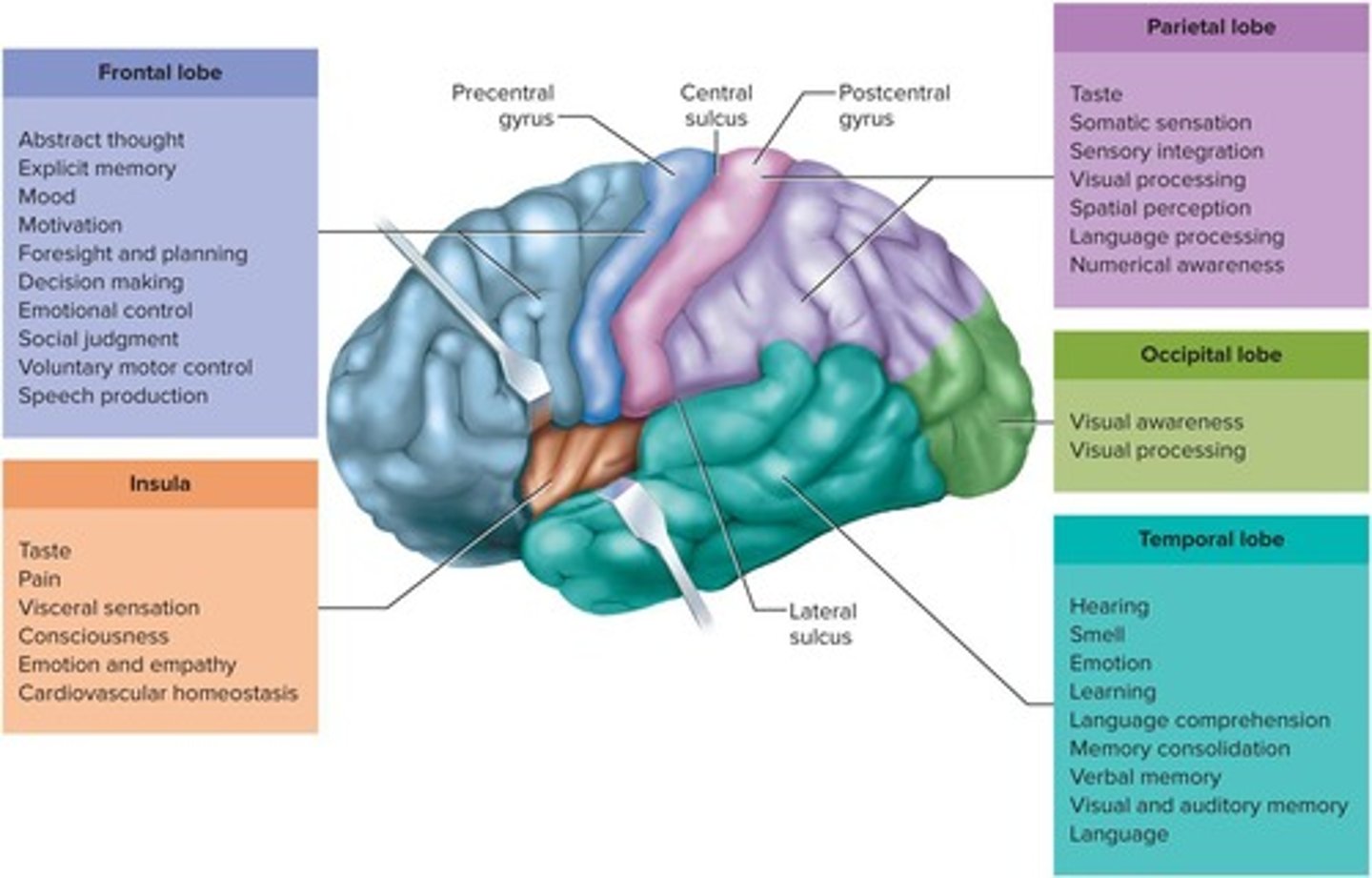
What is the primary composition of the cerebrum's volume?
White matter, which consists of glia and myelinated nerve fibers.
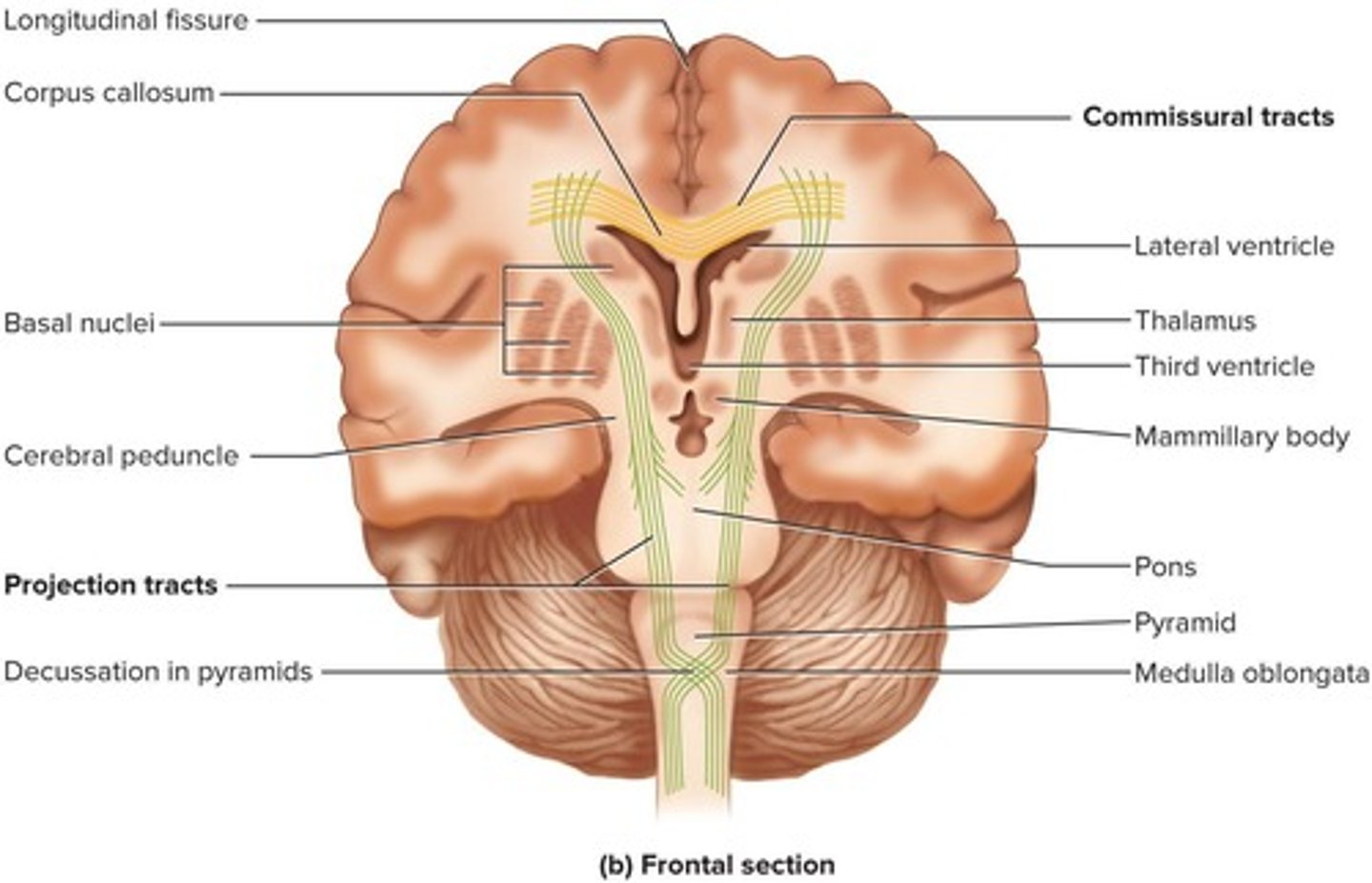
What are tracts in the central nervous system?
Bundles of nerve fibers.
What are the three types of tracts in the cerebral white matter?
Projection tracts, commissural tracts, and association tracts.
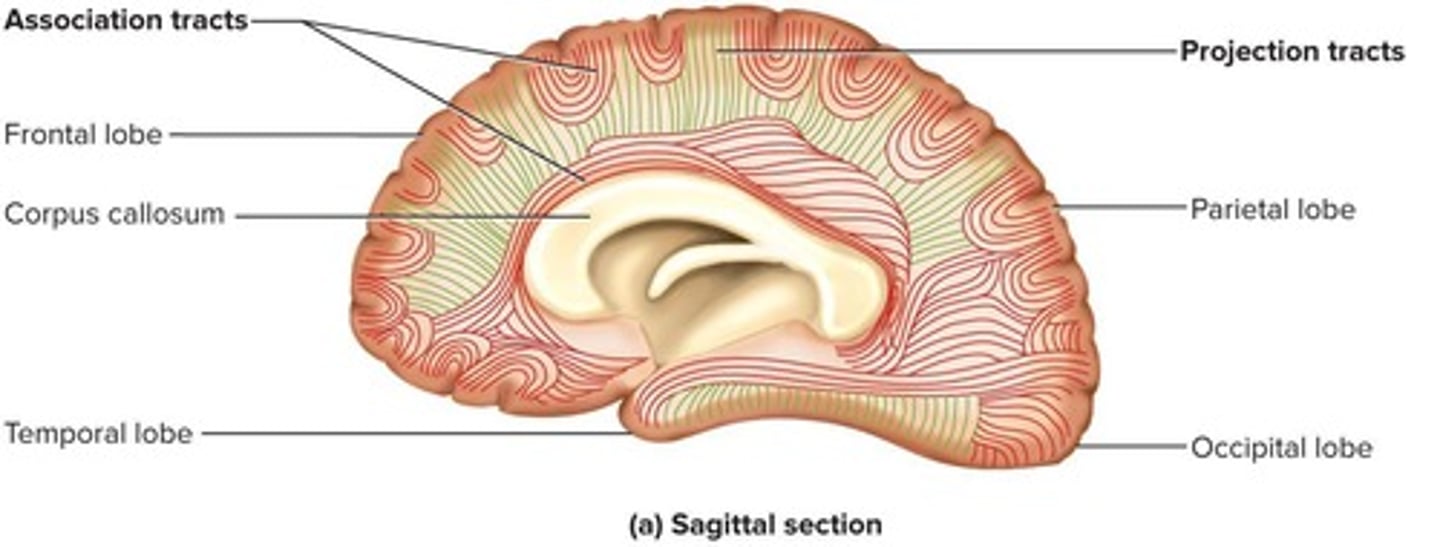
What do projection tracts do?
They extend vertically between higher and lower brain centers and spinal cord.
What is the function of association tracts?
They connect different regions within the same cerebral hemisphere.
What do commissural tracts allow?
Communication between the two sides of the cerebrum.
What is the largest commissural tract?
The corpus callosum.
Where is cerebral gray matter found?
In the cerebral cortex, limbic system, and basal nuclei.
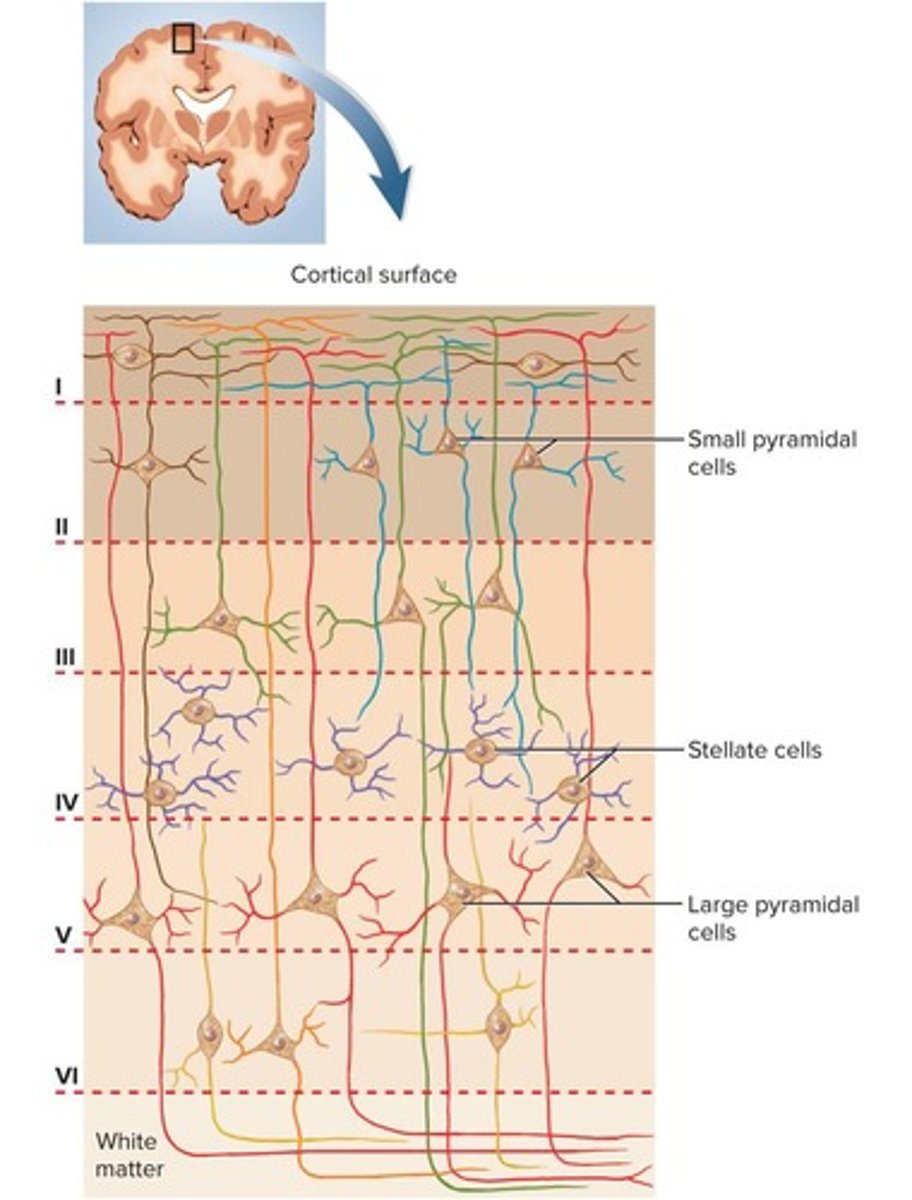
What percentage of brain mass does the cerebral cortex constitute?
About 40%.
What types of neurons are found in the cerebral cortex?
Stellate cells and pyramidal cells.
What is the function of stellate cells?
They receive sensory input and process information on a local level.
What characterizes pyramidal cells?
They are tall and conical with a thick dendrite and include the output neurons of the cerebrum.
What is the limbic system responsible for?
It is an important center of emotion and learning.
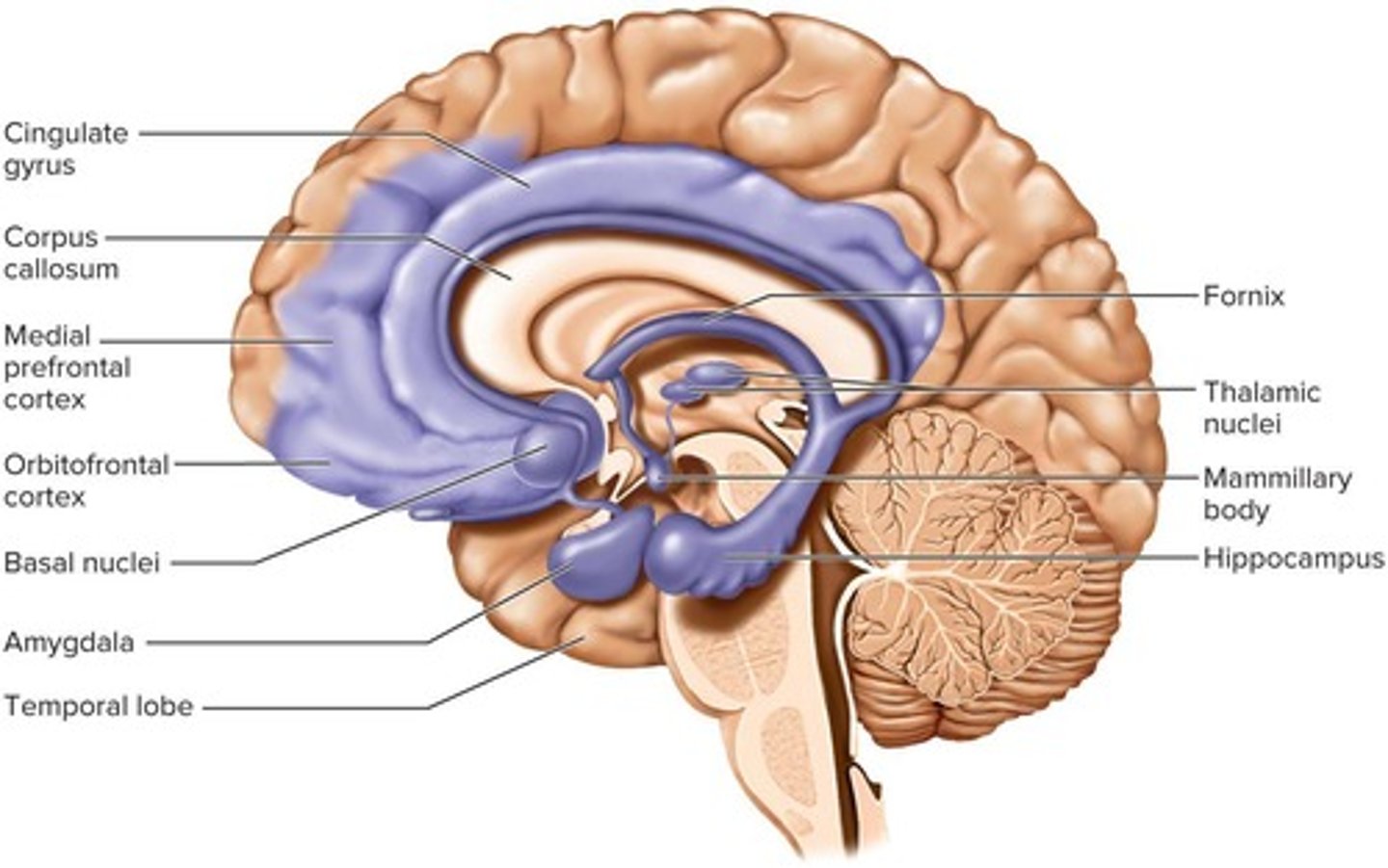
What are the prominent components of the limbic system?
Cingulate gyrus, hippocampus, and amygdala.
Where is the cingulate gyrus located?
It arches over the corpus callosum in the frontal and parietal lobes.
What is the function of the hippocampus?
It is involved in memory functions.
What role does the amygdala play in the limbic system?
It is involved in emotion functions.
How many limbic systems are present in the brain?
There is a limbic system in each cerebral hemisphere.
What type of feedback pattern do limbic system components allow for?
They allow for somewhat circular patterns of feedback.
What sensations are associated with the limbic system?
Gratification (pleasure or reward) and aversion (fear or sorrow).
What are the basal nuclei?
Masses of cerebral gray matter buried deep in the white matter, lateral to the thalamus.
What inputs do the basal nuclei receive?
They receive input from the substantia nigra of the midbrain and the motor areas of the cortex.
What is the role of the basal nuclei in motor control?
They send signals back to the substantia nigra and motor areas of the cortex.