motion velocity
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Reference point
Place or object used for comparison to determine if an object is in motion.
Formula for distance traveled per unit time
formula for average:
s=d/t
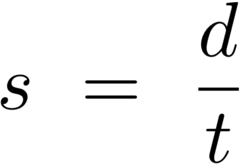
constant speed
Speed that does not change
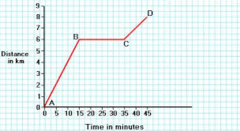
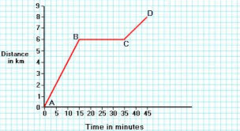
Position-time graph or distance-time graph
Graph with distance on the vertical axis and time on the horizontal axis that displays motion of an object over time.
m/s
SI units of speed
m/s^2 or m/s/s
SI units of acceleration
Instantaneous Speed
a moving object's speed at any instant or given moment of time; A speedometer in a car measures this

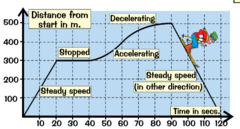
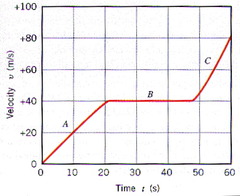
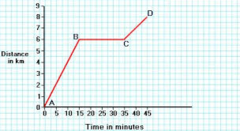
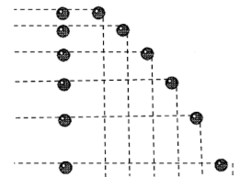
B-C
Which segment shows a car not moving?
A-B
Which segment shows a car moving at a faster speed?
C-D
Which segment shows a car moving at a slower speed?
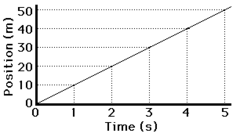
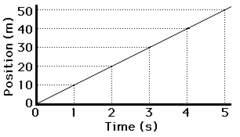
10 m/s
What is the average speed of this Position-Time graph in m/s?
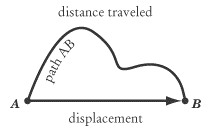
displacement
the distance and direction of an object's change in position. Ex: 20 m East
They are added when in the same direction, and subtracted when in the opposite direction.
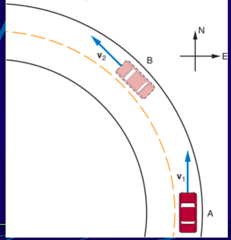
velocity
the speed of an object along with the direction of its motion, ie. 20 m/s West.
True
True or False:
Velocity can change, even if speed stays the same.
momentum
the product of an object's mass and velocity. It is represented by the letter "P," in the equation: P = mv, and its SI unit is kg/m/s. Its direction is always the same as the velocity of the object. For a car at 30 m/s: 45,000 kg/m/s
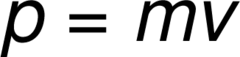
acceleration
the rate of change of velocity which includes the speed and direction of the object so includes a change in either speed or direction or both. Its SI unit is m/s/s
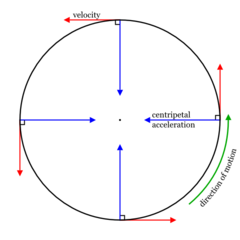
centripetal acceleration
acceleration toward the center of a curved or circular path such as Earth's orbit of the Sun.
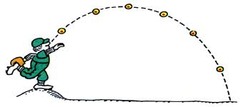
projectile motion
the curved motion of an object that has been projected (thrown, shot, kicked,...) giving the object a horizontal velocity which remains constant. But gravity causes the object to accelerate downward. The horizontal and vertical components are independent of each other and cause the object to have a curved path.
c. same
If 2 identical balls are held at the top of a building and one is dropped while the other is thrown at the same time, which one will hit the ground first?
a. the dropped one
b. the thrown or projected one
c. same
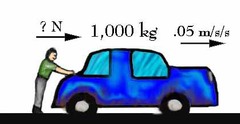
force
a push or pull upon an object
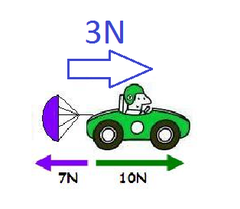
balanced force
when forces on an object are of equal magnitude and in opposite directions; no acceleration

unbalanced force
when forces on an object do not cancel out; causes acceleration

net force
the sum of all the forces acting on an object
friction
a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact

inertia
the tendency of an object to resist a change in motion unless an outside force ac

weight
the measure of the force of gravity on an object

gravitational force
the attractive force existing between any two objects that have mass; depends on the objects' respectif masses and the distance between them
terminal velocity
the constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity.The maximum velocity a falling object can achieve

Mass
The amount of matter in an object

Newton
A unit of measure that equals the force required to accelerate one kilogram of mass at 1 meter per second
Momentum
The product of an object's mass and velocity
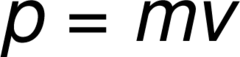
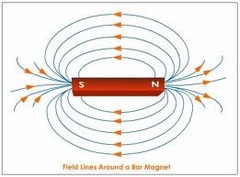
field
region of space that has a physical quantity (such as a force) at every point.
Newton's 1st Law of Motion
scientific law of inertia: an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity and an object at rest will remain at rest unless an unbalanced force acts on it

Newton's 2nd Law of Motion
scientific law that can be expressed in the formula: F = ma (the more force, the more acceleration) or when written a = F/m (an object's acceleration is in the same direction as the net force on the object and is equal to the net force exerted on it divided by its mass.)

Newton's 3rd Law of Motion
Scientific law which states that when one object exerts a force on a 2nd object, the 2nd object also exerts a force on the 1st that is equal in strength and opposite in direction.

air resistance
a friction-like force that opposes the motion of objects that move through the air. It acts in the direction opposite to the motion of an objecct moving through the air

centripetal force
a force exerted toward the center of a curved path
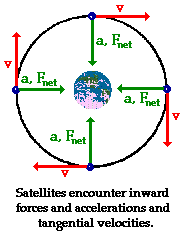
free fall
the motion of a body when gravity is the only force (no air resistance) acting on it such as when a satellite or our moon is orbiting Earth

law of conservation of momentum
scientific law which states that if no external forces (such as friction) act on a group of colliding objects (like billiar balls), their total momentum does not change during the collision
