AP Biology Unit 2 — Cell Organelles & Subcellular Components (Functions)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
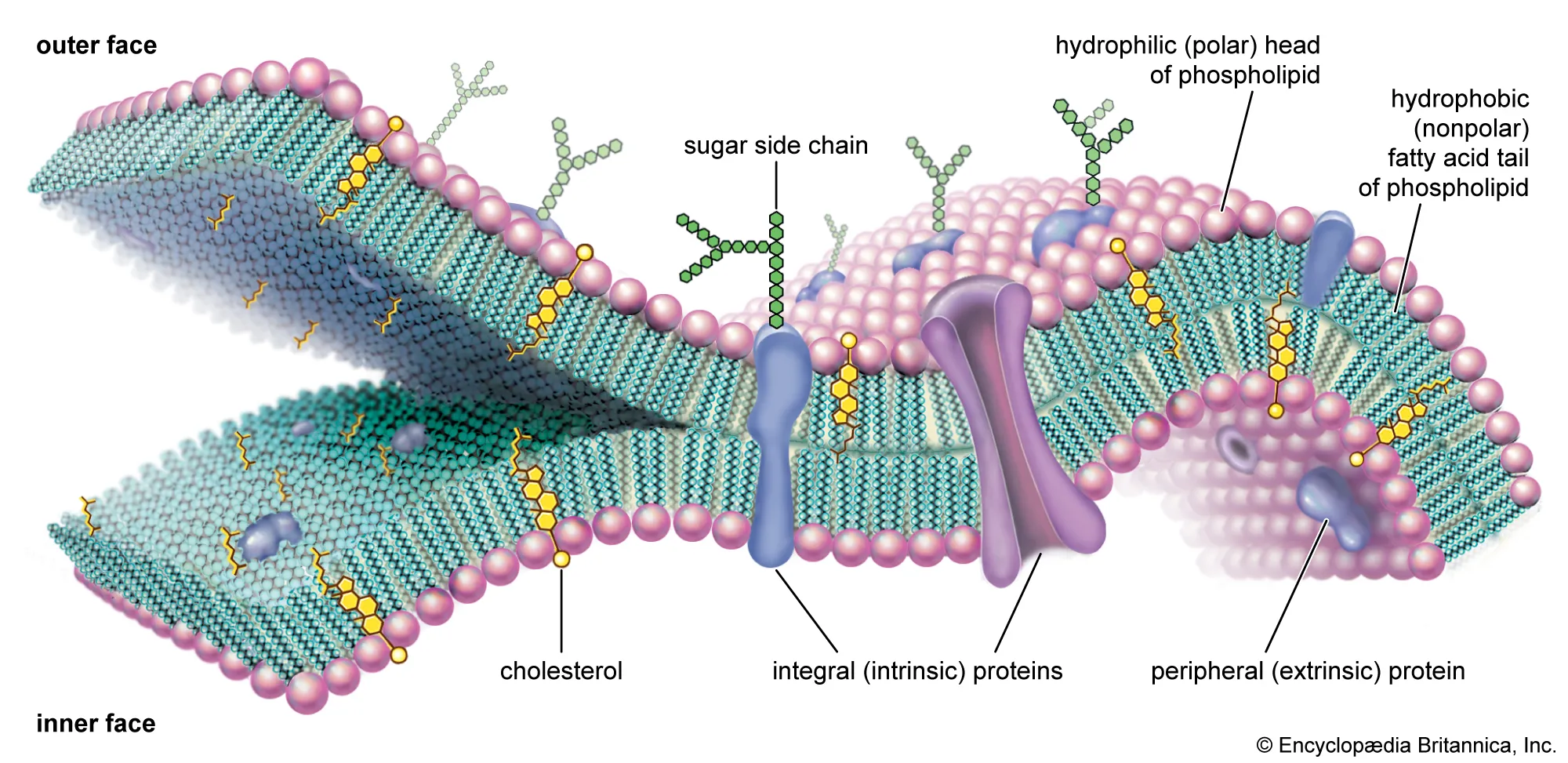
Plasma (Cell) Membrane
Phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins (fluid mosaic).
Selectively permeable: controls movement of ions, polar, and nonpolar molecules.
Functions in cell communication, recognition (glycoproteins), and maintaining homeostasis.
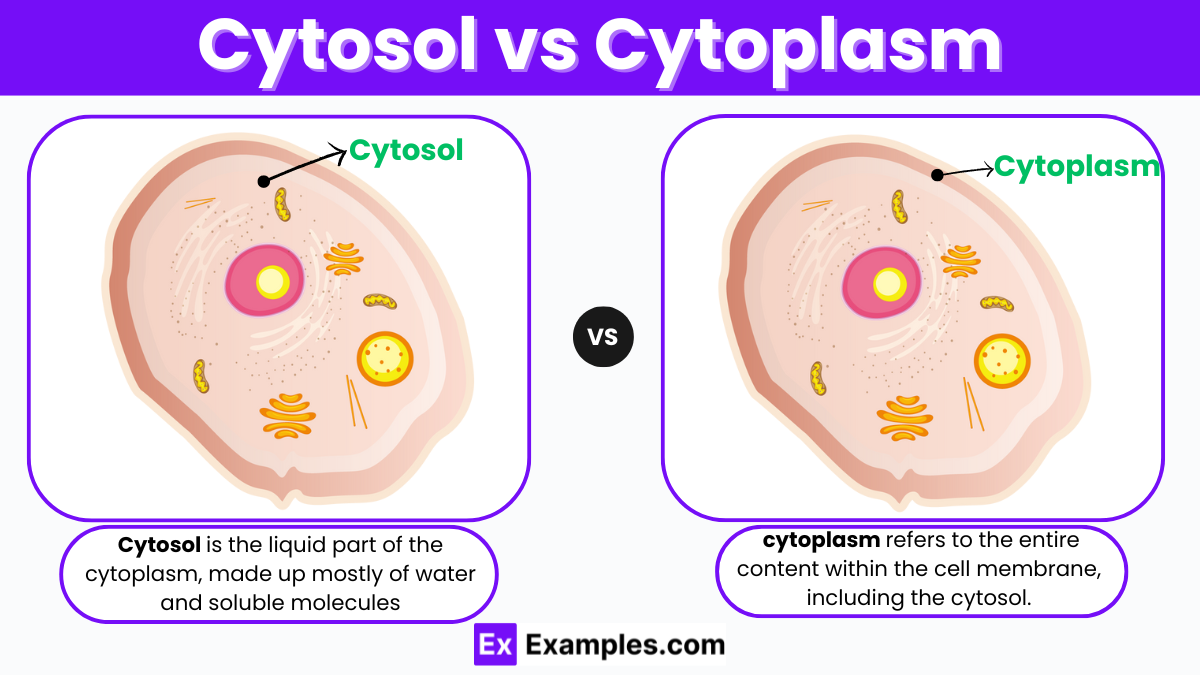
Cytosol
Aqueous interior of the cell (mostly water).
Site of many metabolic reactions (e.g., glycolysis).
Contains enzymes, metabolites, and cytoskeleton components.
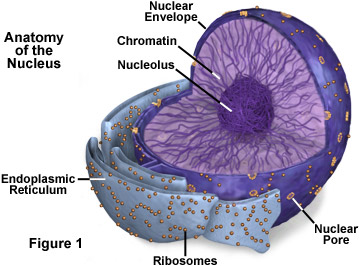
Nucleus
Stores genetic information (DNA).
Controls gene expression and cell activities.
Surrounded by a double membrane (nuclear envelope).
Nuclear Envelope
Contains nuclear pores that regulate RNA and protein transport.
Nucleolus
Synthesizes rRNA and assembles ribosomal subunits.
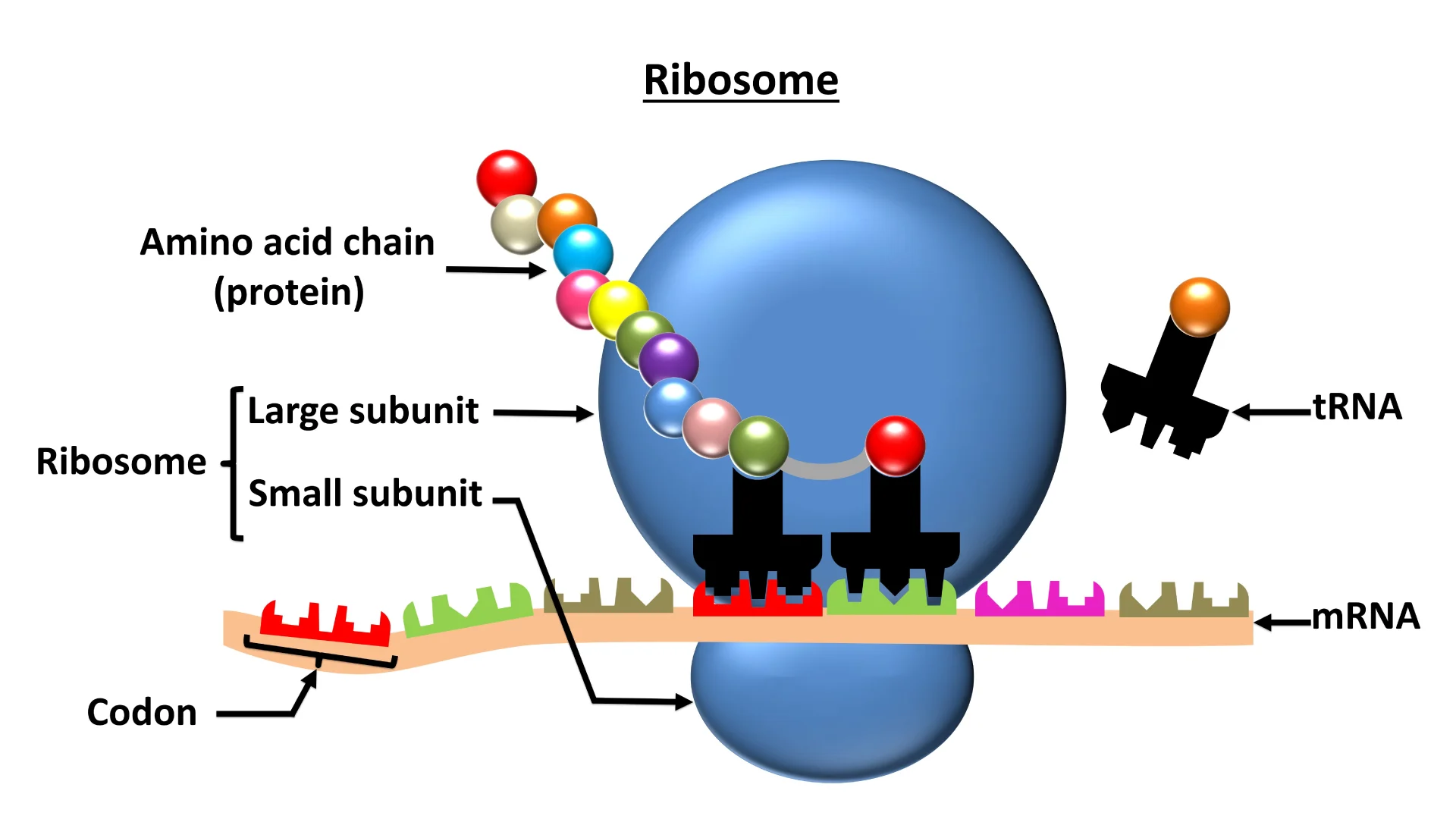
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis (translation).
Free ribosomes: synthesize cytosolic proteins.
Bound ribosomes (on RER): synthesize proteins for secretion, membranes, or lysosomes.
No, mRNA and tRNA don't come from ribosomes; rather, they are essential partners that work with ribosomes during protein synthesis (translation). Ribosomes, made of rRNA and proteins, provide the factory where mRNA (the blueprint) is read and tRNA (the delivery trucks) bring the specific amino acids needed to build a protein chain
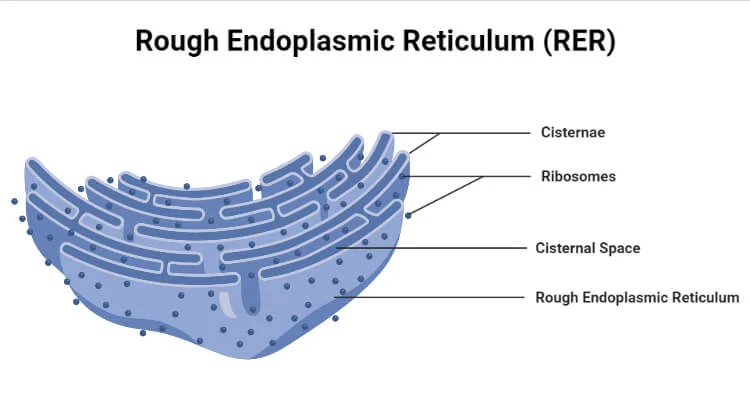
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
Studded with ribosomes.
Synthesizes, folds, and modifies proteins (e.g., adding initial carbohydrates).
Transports proteins to the Golgi apparatus.
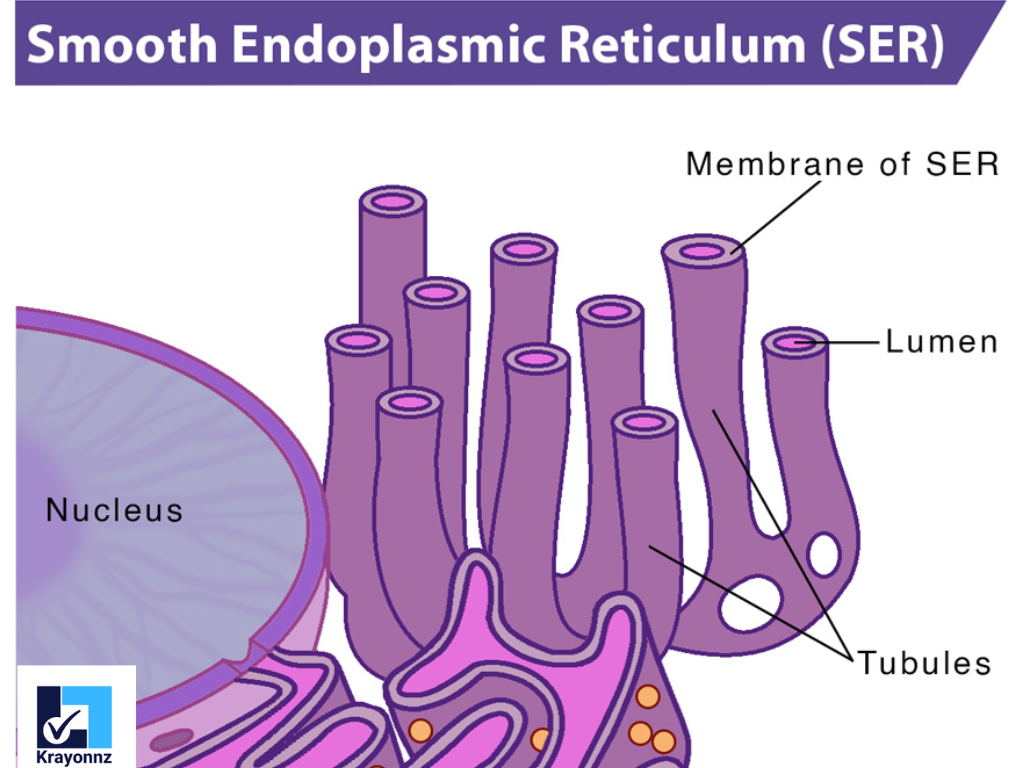
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
Lacks ribosomes.
Functions:
Lipid and steroid synthesis
Phospholipid production
Detoxification of drugs and poisons
Calcium ion storage (important in muscle cells)
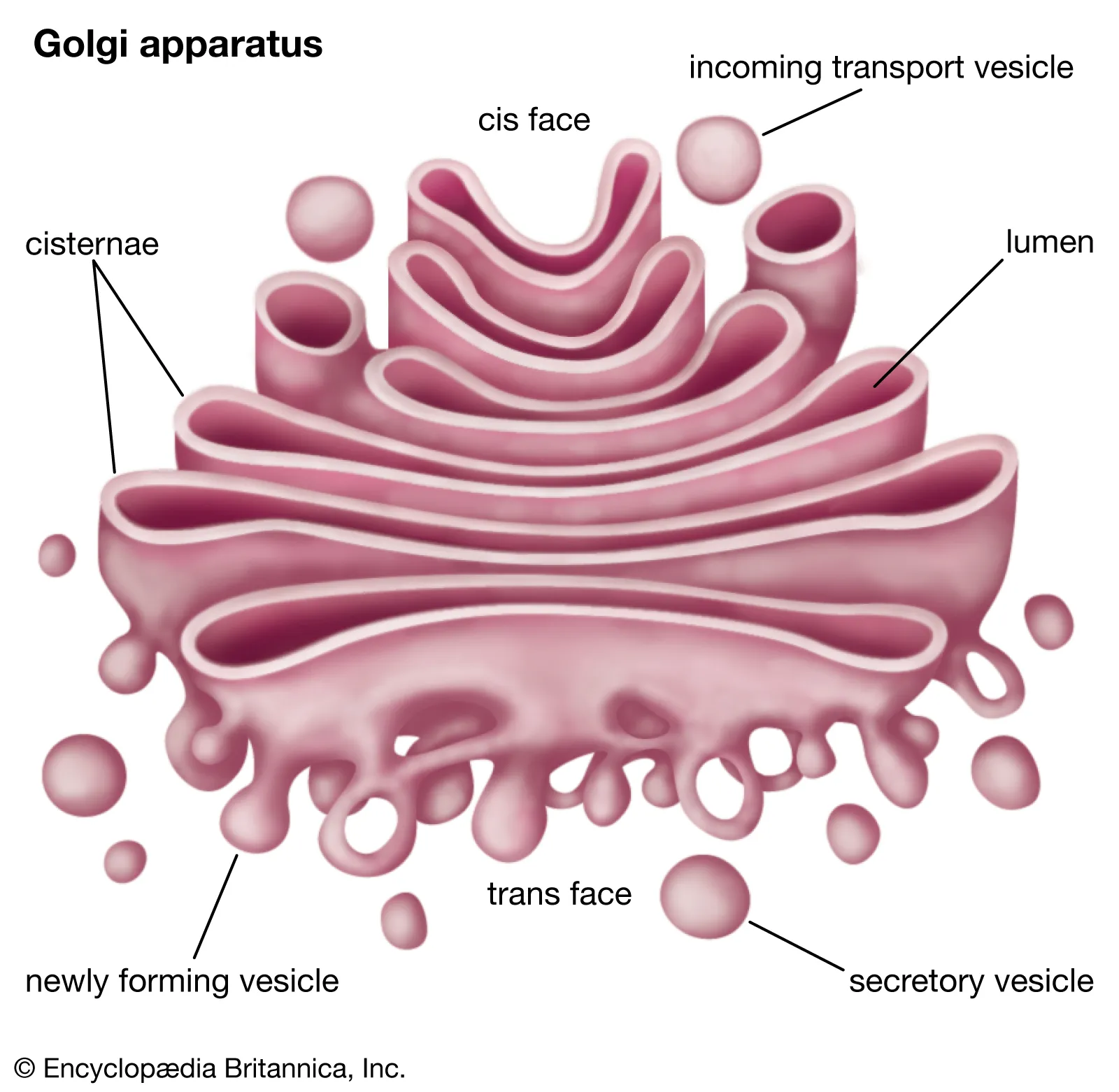
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids.
Adds carbohydrates → glycoproteins & glycolipids.
Ships products in vesicles to final destinations (secretion, membrane, lysosome).
Vesicles (little taxi of the cell)
Membrane-bound sacs for transport and storage.
Move materials between ER, Golgi, plasma membrane, and lysosomes.
Small sac fluid filled
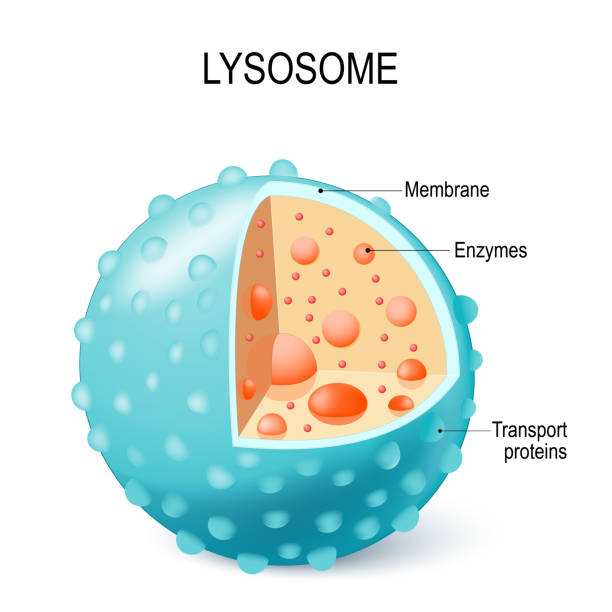
Lysosomes
(mostly animal cells)
Contain hydrolytic enzymes for intracellular digestion.
Functions:
Breakdown of macromolecules
Recycling of damaged organelles (autophagy)
Defense against pathogens
Programmed cell death or cellular suicide by apoptosis
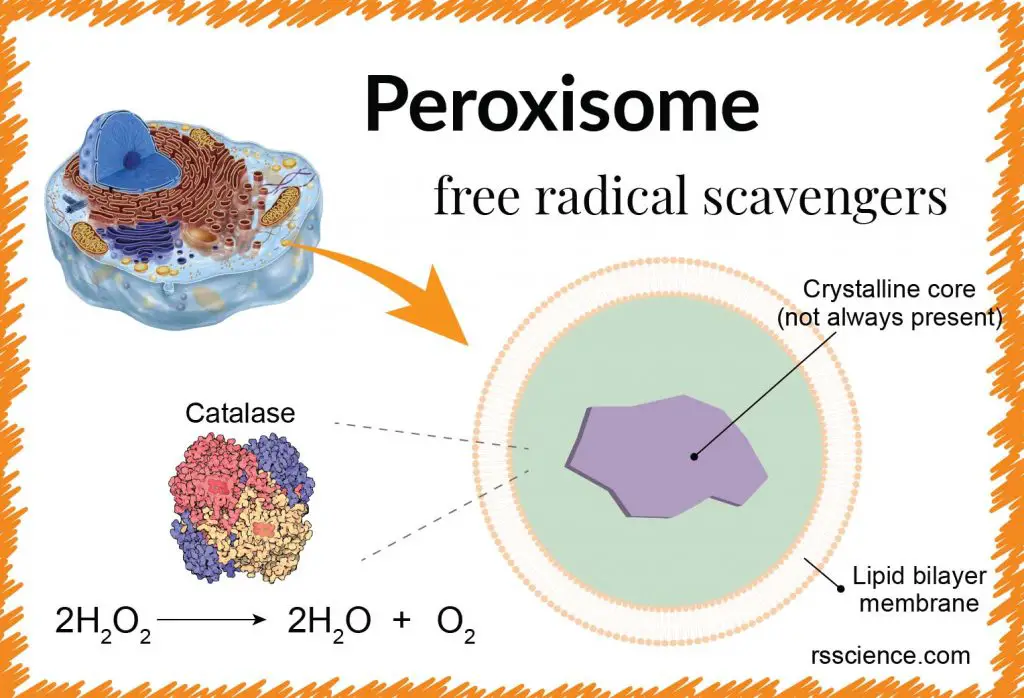
Peroxisomes
Break down fatty acids and toxins.
Contain enzymes that produce and degrade hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂).
Important for detoxification and metabolism.
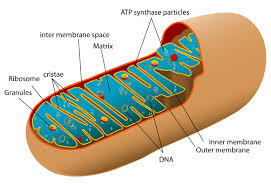
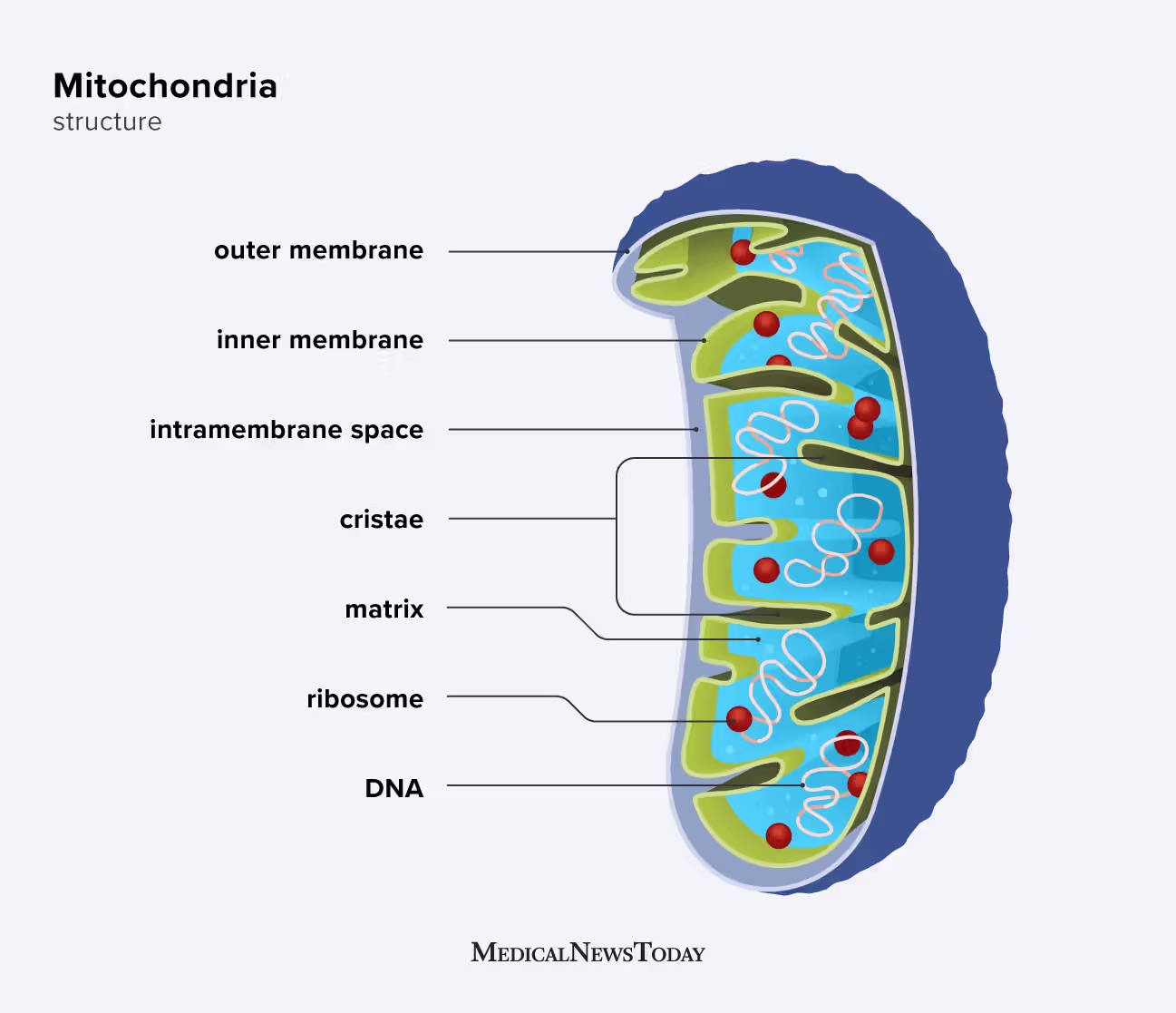
Mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration and ATP production.
Double membrane:
Inner membrane folds → cristae (increase surface area).
Contains its own DNA and ribosomes (supports endosymbiotic theory).
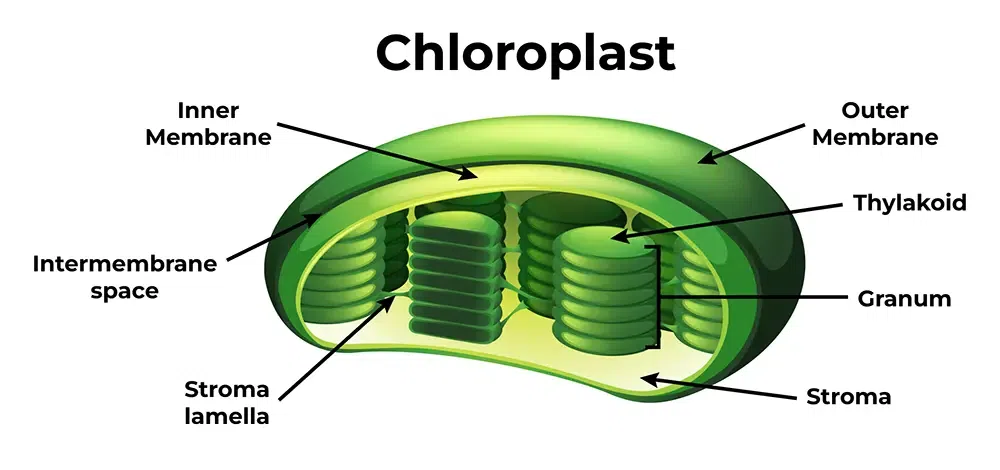
Chloroplasts
(plant cells)
Site of photosynthesis.
Thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll (light reactions).
Stroma contains enzymes for the Calvin cycle.
Double membrane + internal membrane system.
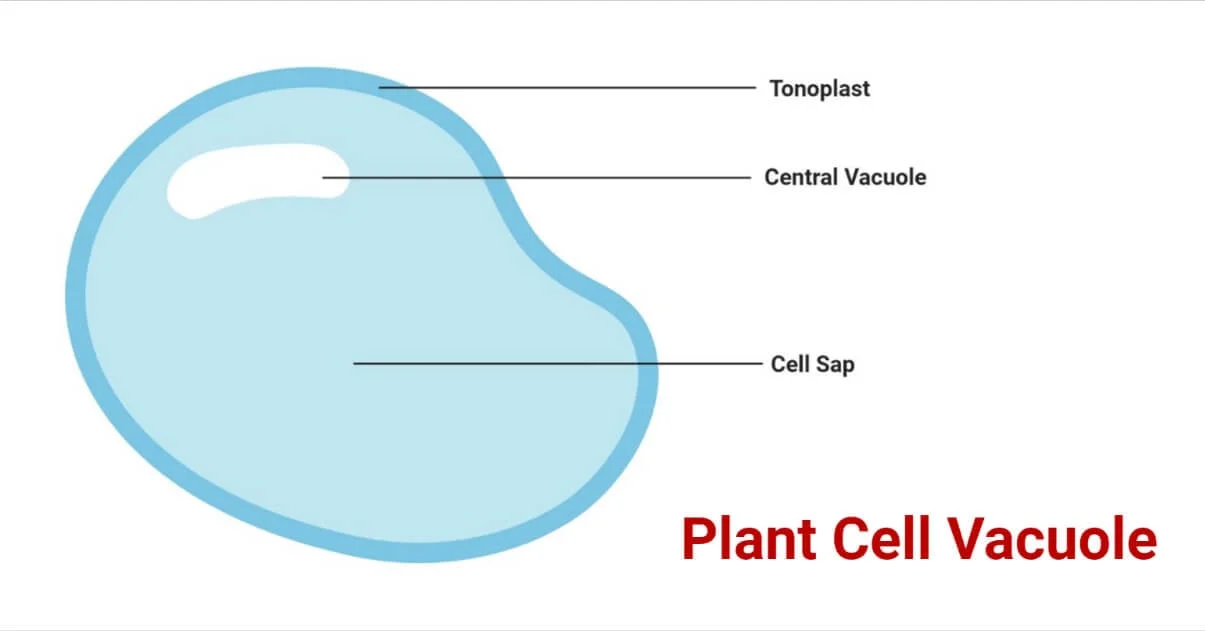
Central Vacuole
(plant cells)
Maintains turgor pressure (the water pressure acting upon the plasma membrane from inside the cell, usually caused by water) which provides structure, support, stability, strength, and rigidity to the plant
Stores water, ions, pigments, and wastes.
Helps regulate cell size and homeostasis.
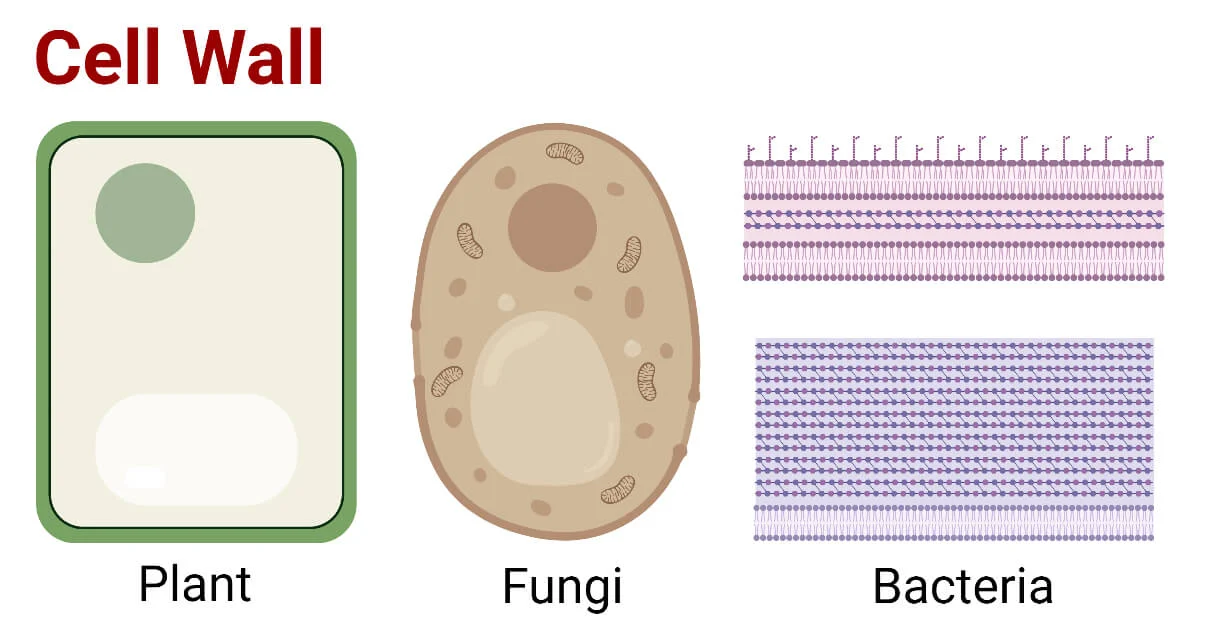
Cell Wall
(plants, fungi, prokaryotes)
Provides structural support and protection.
Plant cell walls made of cellulose.
Bacteria cell walls made of peptidoglycan (carbohydrates/polysaccharide)
Archaea cell walls made of psuedomurein
Fungi cell walls is made of chitin
Prevents excessive water uptake.
Most cell walls are made up of polysaccharides or carbohydrates
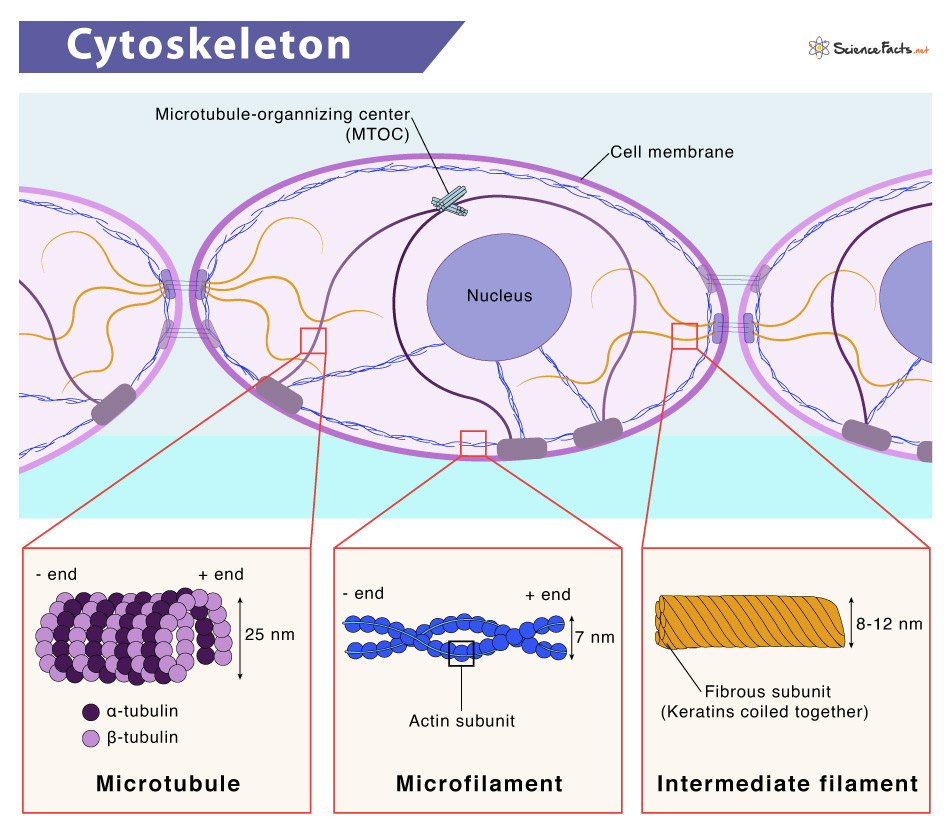
Cytoskeleton
Provides structural support and enables movement.
Microfilaments (Actin)
Maintain cell shape.
Muscle contraction and cell motility.
Intermediate Filaments
Provide tensile strength.
Stabilize cell structure.
Microtubules
Made of tubulin.
Form mitotic spindle, cilia, and flagella.
Serve as tracks for vesicle transport.
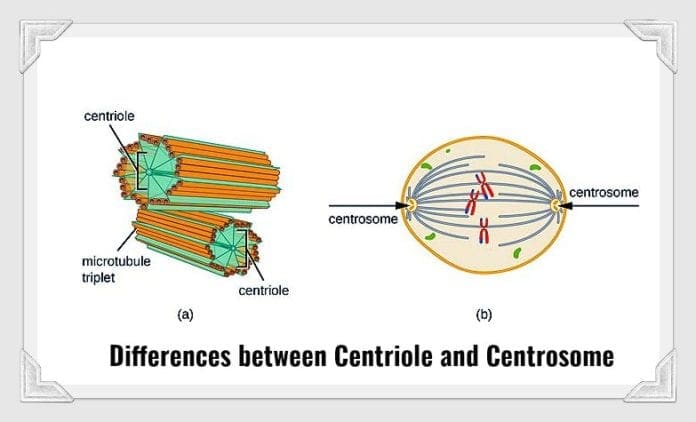
Centrosome & Centrioles
(animal cells)
Microtubule-organizing center.
Important for spindle formation during cell division.
Organized in a 9+0 arrangements
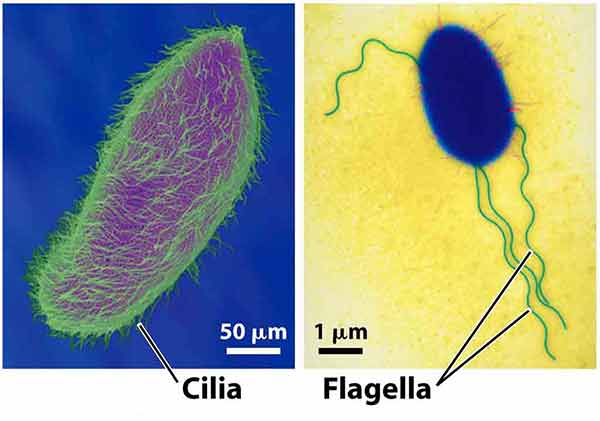
Cilia & Flagella
Motility and movement of substances across cell surface.
Composed of microtubules in a 9+2 arrangement.
AP Exam Tip (Very Important)
College Board focuses on:
Structure → function relationships
Membrane-bound vs non-membrane-bound organelles
Energy processing (mitochondria & chloroplasts)
Protein trafficking pathway:
RER → Golgi → vesicle → destination