Cell Size and Plasma Membrane
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Metabolism
The process by which the body converts the food and drinks you consume into energy
Cell Size
Cellular metabolism depends on the cell size
Cellular waste must leave
Dissipates thermal energy
Nutrients and other resources must enter
Surface Area to Volume
Size dictates function
Cells need a high sa/v ratio to optimize exchange of materials through plasma membrane (higher efficiency)
High sa/v
Efficient at transport
Smaller cell
Low sa/v
Efficient at storage
Larger cell
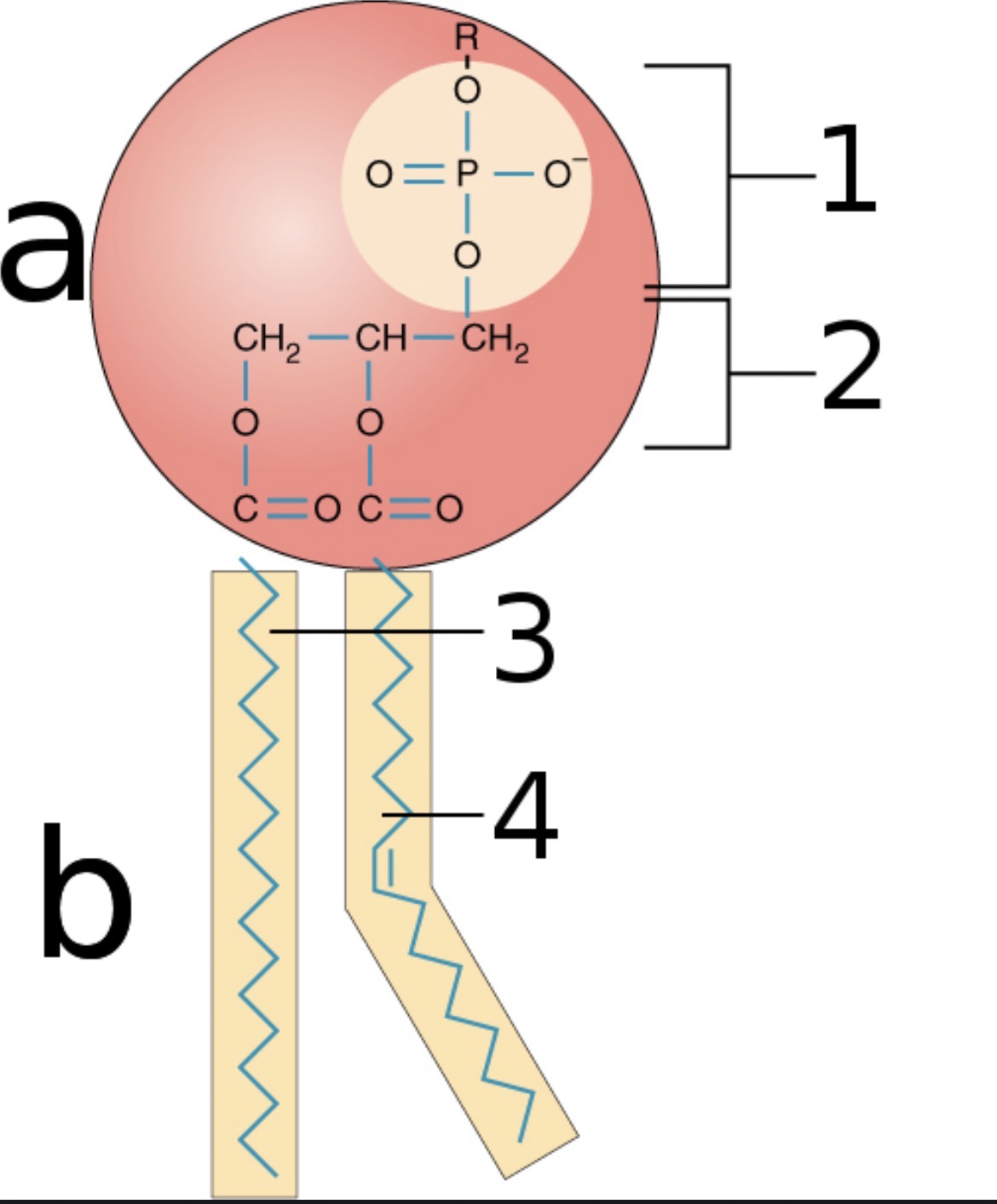
Parts of a phospholipid
A: hydrophilic head
B: hydrophobic tails
1: phosphate group
2: glycerol
3: saturated fatty acid chain
4: unsaturated fatty acid chain
Plasma membrane
Separates internal cell environment from external environment
Made primarily of phospholipids
Amphipathic
Having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
Phospholipids form a bilayer to avoid their hydrophobic tails from interacting with water while hydrophilic heads face water on both sides
Fluid mosaic model
Many macromolecules held together by weak hydrophobic interactions which allow the cell membrane to move and shift
Temp affects fluidity
Unsaturated/kinked tails prevents tight packing of phospholipids
Cholesterol
Lipid helping to maintain fluidity at high and low temps
Reduces movement at high temps
Reduces tight packing of phospholipids at low temps
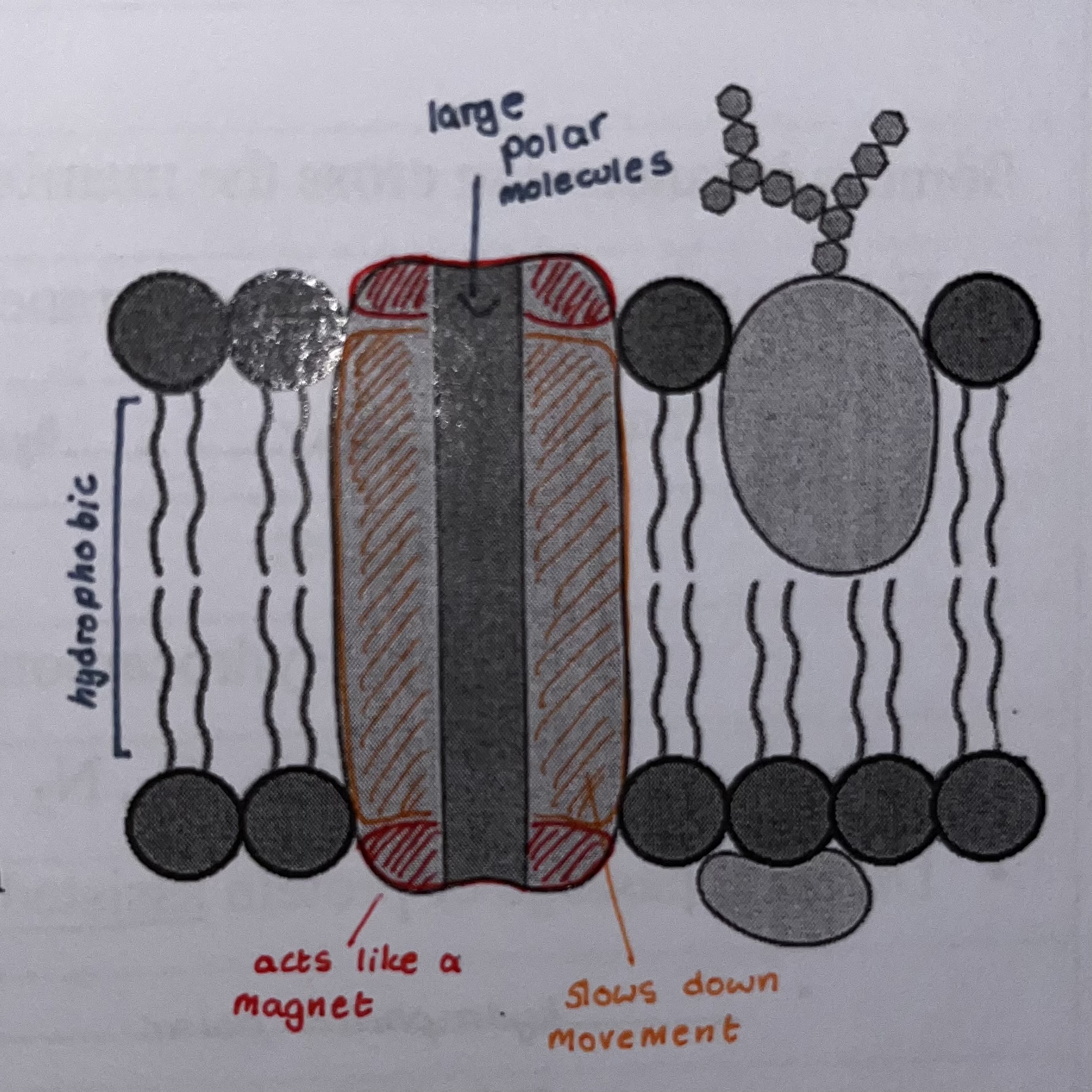
Peripheral proteins
Proteins not embedded into the lipid bilayer
Loosely bonded to surface
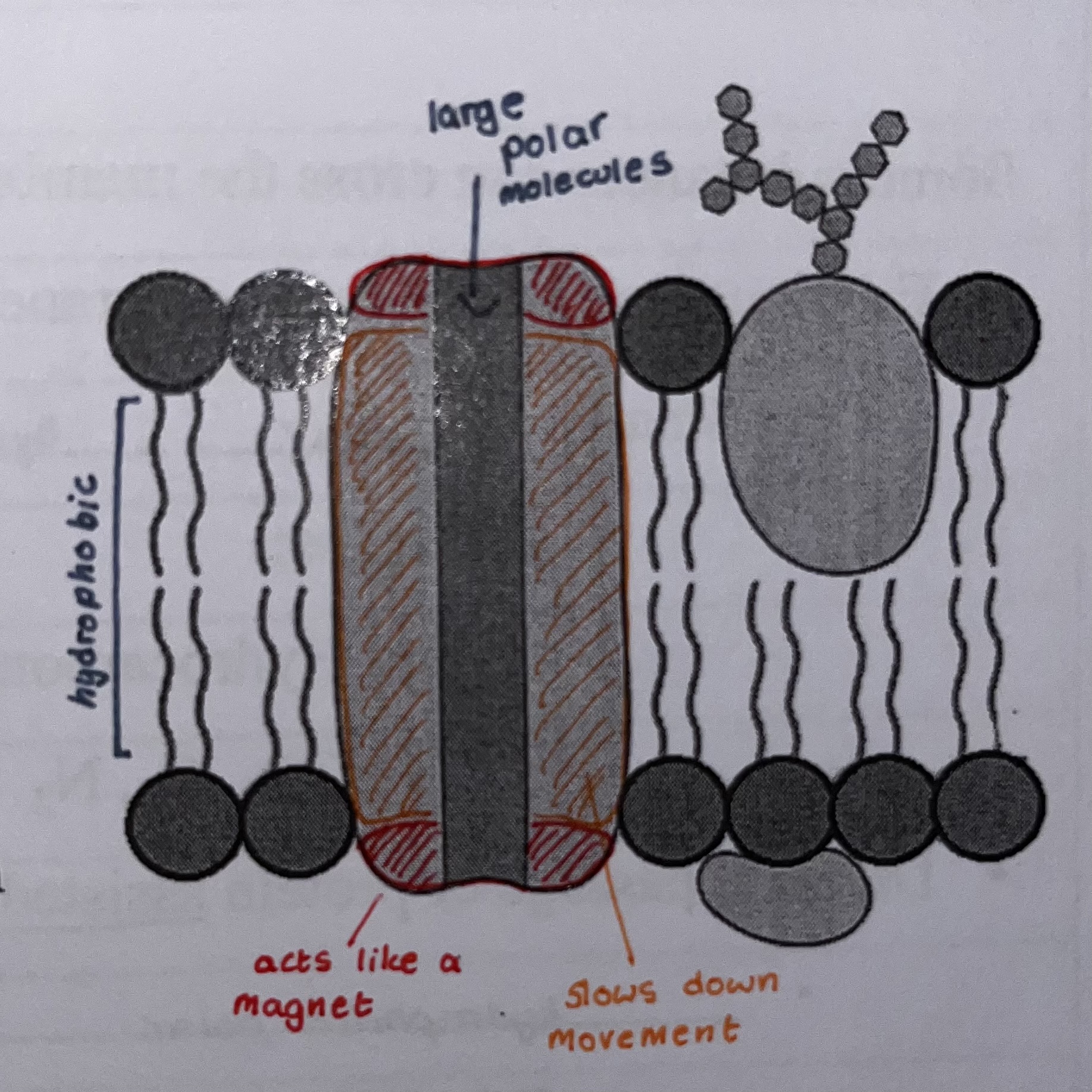
Integral proteins
Proteins embedded into the lipid bilayer (Integrated)
Can by hydrophobic, hydrophilic or both
Determined by A groups (side chains)
Hydrophilic regions make up interior of channel or pore, exposed to cytosol
Hydrophobic regions makeup up surface of protein and interact with fatty acids on interior
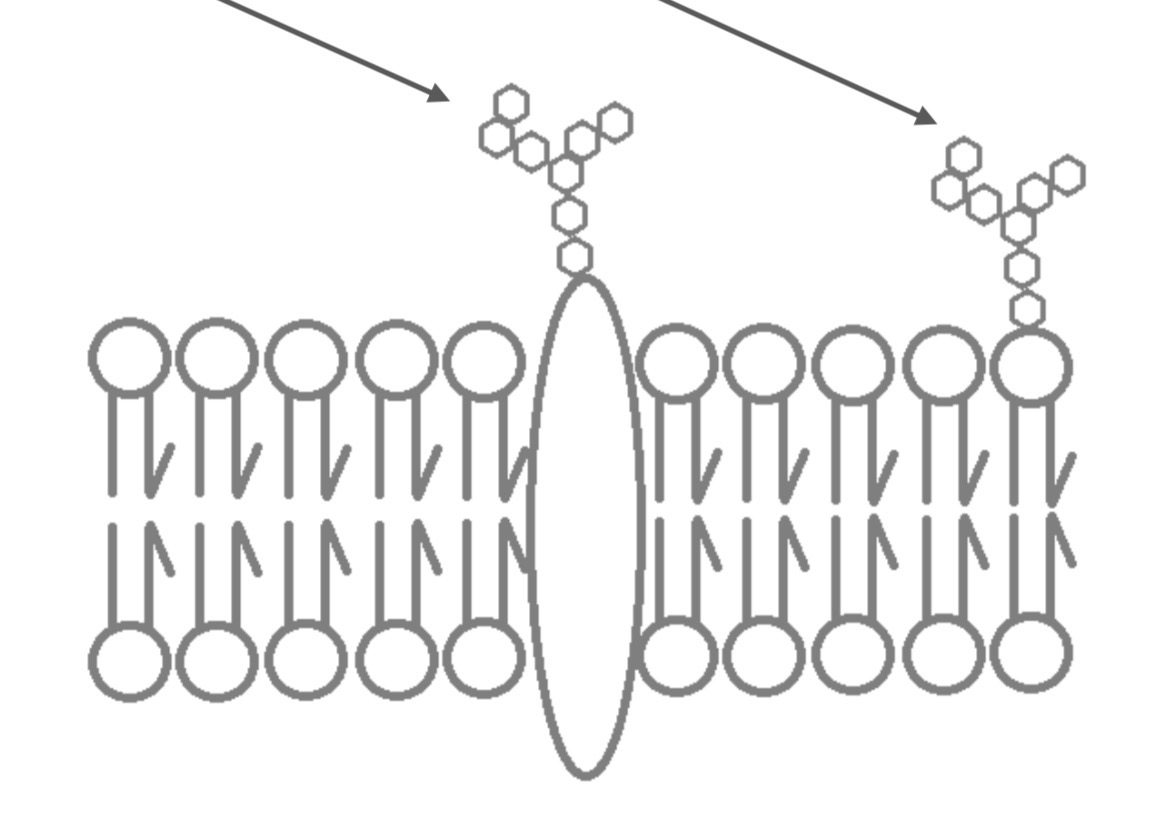
Glycolipids
Important for cell to cell recognition
Carbohydrates bonded to lipids
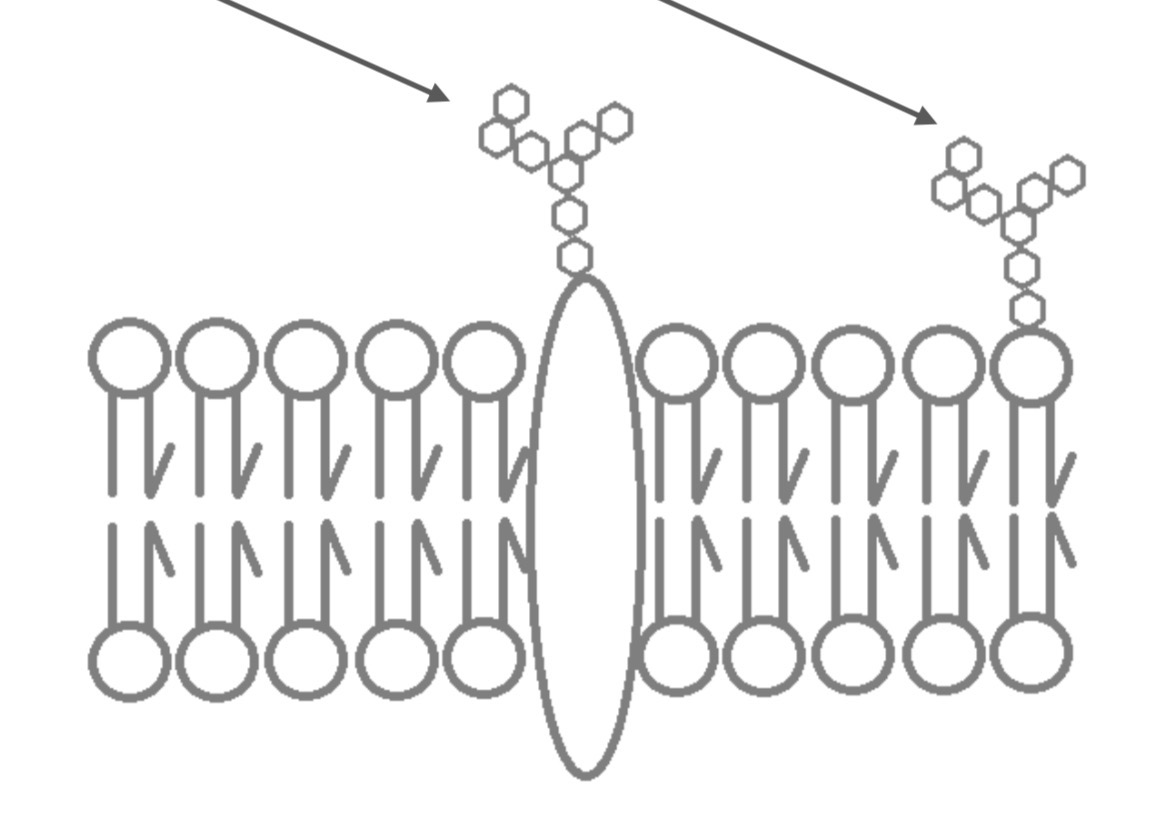
Glycoproteins
Important for cell to cell recognition
Carbohydrates bonded to proteins
Hydrophillic
Attracted to water
Charged or polar
Hydrophobic
Not attracted to water/ repels
nonpolar or no charge
Selective permeability
The ability to regulate the substances that enter and exit
Due to hydrophobic interior (nonpolar hydrophobic tails)
Polar
Molecule with uneven distribution of electrons/electrical charge
Hydrophilic
Nonpolar
Molecule with even distribution of electrons/electrical charge, neutral
Hydrophobic
Charged
Being either positive or negative in polarity