Cariology Lecture 8
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
lesions on unrestored surfaces
primary caries
lesions that develop adjacent to a restoration
recurrent or secondary lesions
why are you more likely to get secondary caries with composite vs amalgam
amalgam has silver in it which has anti-caries properties
(active/inactive) caries lesion is considered to have a greater likelihood of transition (progress, arrest, or regress)
active
(active/inactive) caries lesion is considered to have less likelihood of transition to a carious state
inactive
In active caries rate of progression is ____
rapid
in active caries, the floor of the cavity is ____ to touch
soft
in inactive caries, the caries progress is ____
slow
inactive caries often involves the collapse of enamel that may result in an open cavity that is ____-______
self -cleansing
How does the cavity floor look in inactive caries
hard and leathery
what color is the cavity in inactive caries
dark in color
an inactive cavity was _____ at one time
active
initial lesion
First sign of enamel lesion that can be detected with the naked eye
a non-cavitated lesion
white spot lesion
incipient lesion
Rampant caries
patient has multiple active extensive carious lesions
examples of rampant caries
early childhood caries
bottle or nursing caries
mountain dew mouth
meth mouth (dry mouth that causes increase in pH)
soft/infected zone of the lesion involves the (outer/inner) layers
outer
the soft/infected zone characteristics
high level of contamination
complete demineralization of the dentin
how does the soft affected zone affect the dentin tubular structure
collapse of tubular structures
leathery/firm affected zone includes the deeper _____ area
pulpal
affect of the affected zome on the dentin tubular structure
it has sufficient mineral context to retain dentin tubular structure
____ dentin will deform when a hard instrument is pressed into it and can be easily scooped up with little force being required
soft
Although the dentin does not deform when an instrument is pressed into it, ______ dentin can still be easily lifted without much force being required
leathery
there may be little difference between leathery and firm dentin with leathery being the transition between soft and firm dentin
____ dentin is physically resistant to hand excavation and some pressure needs to be exerted through an instrument to lift it
firm
for ____ dentin, a pushing force needs to be used with a hand instrument to engage the dentin and only a sharp cutting edge or a bur can lift it
hard
Non surgical goals
prevention and remineralization
surgical goals
tooth preserving selective removal and replacement of tooth structure
Steps of a visual examination
clean the teeth (note plaque buildup)
Thoroughly dry teeth (5 seconds each)
magnigication visualization with light
probe/explorer (consistency/texture of the lesion
why should you not use an explorer to determine softness within the tooth structure?
can damage the enamel
can transfer microorganisms from one spot to another
using an explorer has/has not shown to improve the accuracy of caries diagnosis
has not
visual appearance of pit and fissure lesions
opaque
chalky
white, yellow, brown, grey discoloration
what does staining show
that demineralization did occur at some point, but did not progress further
After entry through a pit/fissure lesion, the caries progresses along ____ ____ affecting a larger area of the ___ than a smooth surface lesion
enamel rods
DEJ
in a cross section of a pit/fissure lesion, the enamel appears as an ______ __ with a narrow entrance and wider area of development closer to the DEJ
inverted V
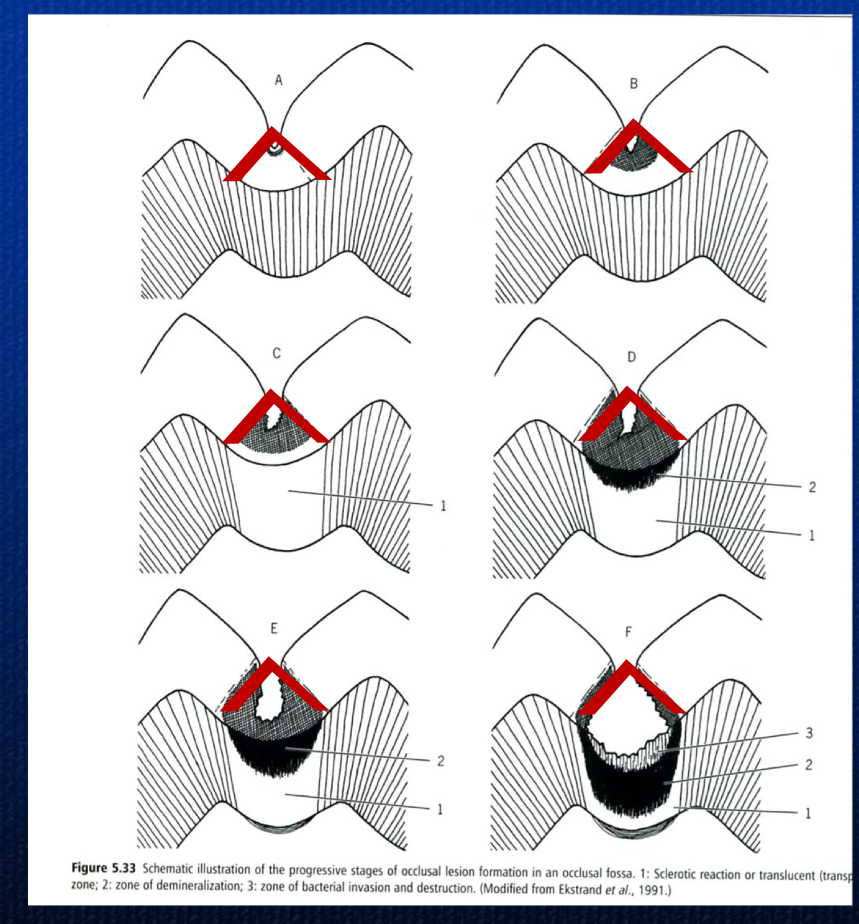
In pit/fissure lesions, a cross section of the lesion in the dentin appears as a __ from dentin to pulp
V
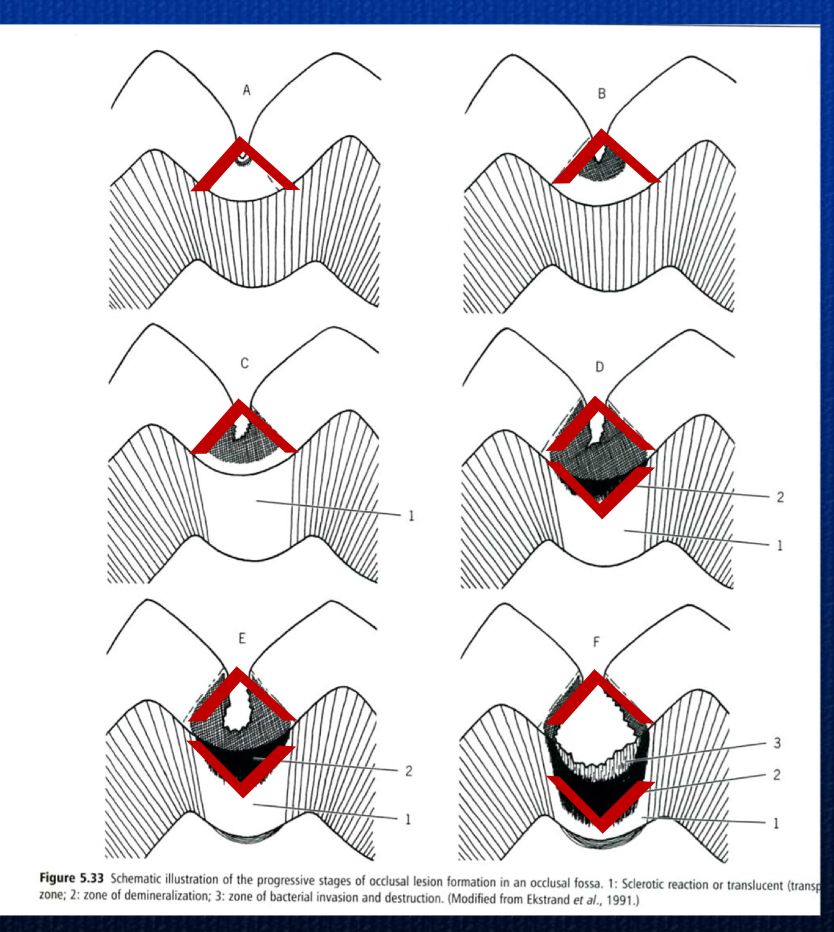
_____ lesions within the enamel and outer dentin are difficult to detect radiographically
small
____ lesions may appear as a radiolucent area spreading laterally under the occlusal enamel
Large
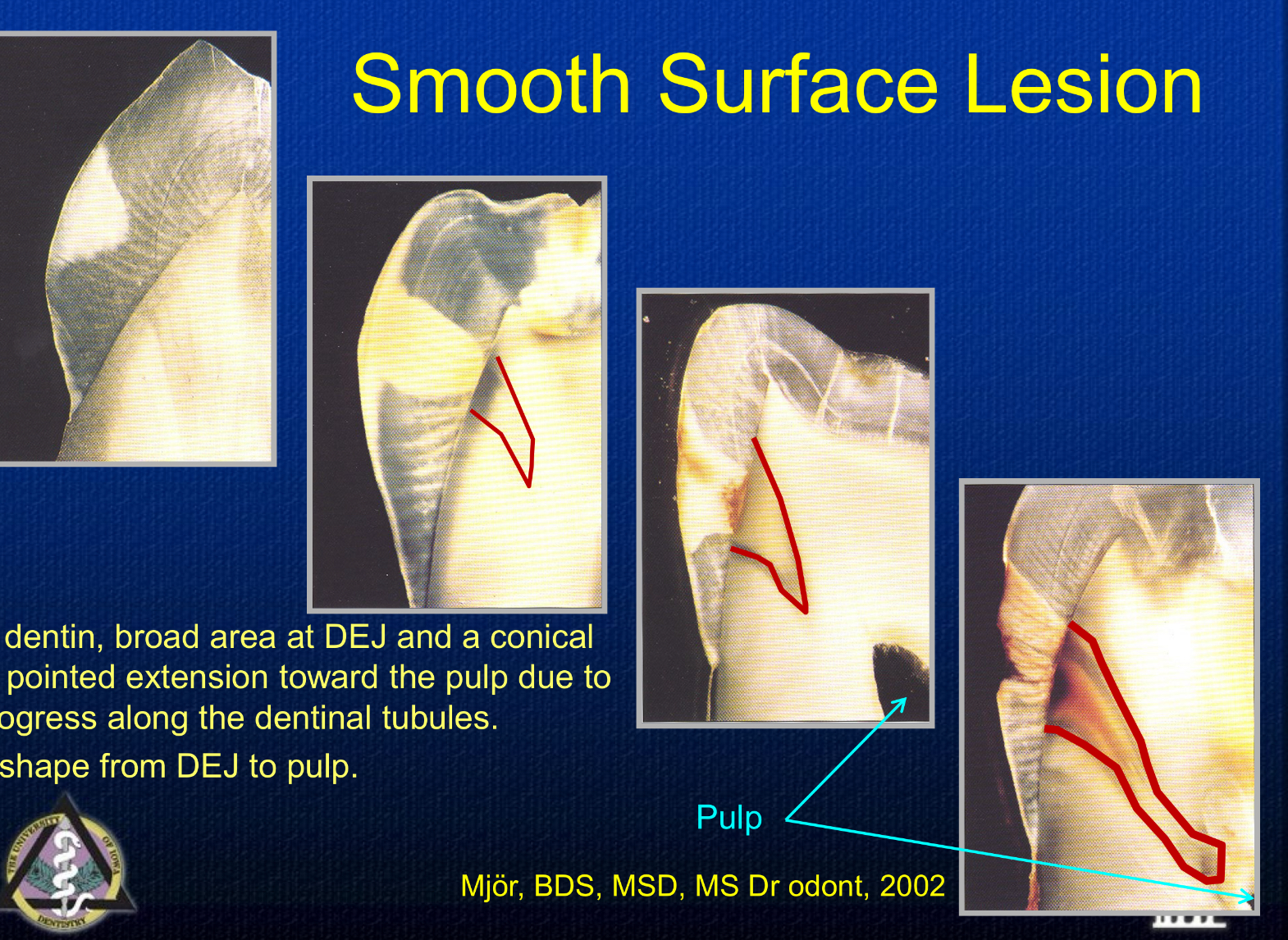
Where are you most likely to find caries on a smooth surface?
In plaque stagnant areas
What are plaque stagnation areas?
gingival to proximal contact area that can only be reach by floss
ginigival surface to the height of contour on the buccal and lingual (anything along the gumline)
erupting posterior teeth (occlusal surface)
shape of smooth surface lesion
progresses from the surface towards the DEJ due to progression along enamel rods in a V shape
root surface active lesions look
soft and leathery, may be discolored
Root surface inactive caries looks
commonly discolored, the darker the color the greater the greater the remineralization
dark and shiny
Caries code ___ and __ = initial caries
1 and 2
Caries code ___ and __ = moderate caries
3 and 4
Caries code ___ and __ = initial caries
5 and 6
Initial stage caries
first or distinct visual changes in enamel seen as a carious opacity or visible discoloration
moderate stage caries
a white or brown spot lesion with localized enamel breakdown without visible dentin exposure
extensive stage caries
a distinct cavity in opaque or discolored enamel with visible dentin