Mechatronics devices 6: Servo Systems
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is a servo motor, and how does it achieve precise position control?
A servo motor is a linear or rotary actuator designed for fast, precise position control in closed-loop applications. It achieves this by using a feedback mechanism that compares the actual position to the desired position, generating an error signal that drives the motor until the error is zero. Internally, it combines a motor, feedback circuit, controller, and other electronics
What are the main components and roles in a servo system?
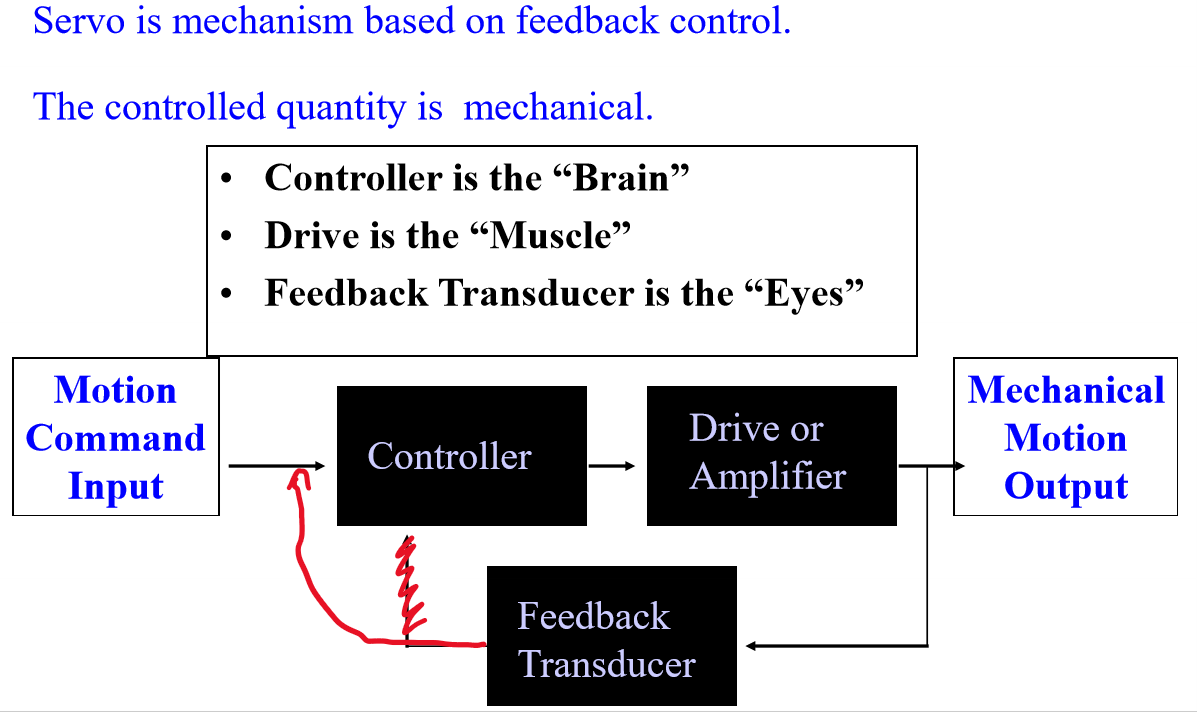
How does a closed-loop control system work in servo mechanisms?
The system compares the feedback signal (actual position) with the input command (desired position). If there’s a difference, an error signal is generated, amplified, and used to drive the motor until the desired position is reached
How are servo motors classified, and what are their typical applications?
Servo motors are classified as AC or DC based on their power supply. AC servos are used for high-accuracy control in automation and robotics, while DC servos are used for simpler, smaller applications. RC servos are common in hobby robotics due to their simplicity and affordability
What are the differences between positional rotation, continuous rotation, and linear servo motors?
Positional rotation servos rotate about 180°, used in RC vehicles and robots.
Continuous rotation servos rotate indefinitely, with the control signal determining speed and direction.
Linear servos convert circular motion to back-and-forth motion, often used as actuators in model airplanes
What is the working principle of a servo motor?
A position sensor (like a potentiometer) senses the shaft’s position, converting it to an electrical signal. This is compared to the command input; if different, an error signal is generated, amplified, and applied to the motor until the desired position is reached
Describe the typical layout of a servo mechanism.
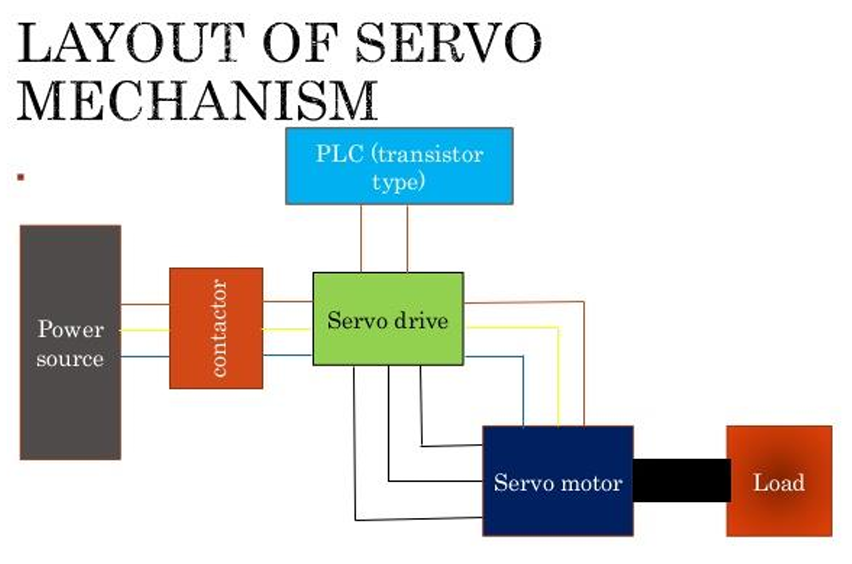
How is position control achieved in servo motors using PWM?
Position control uses Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), where the width of the pulse determines the angular position.

List several practical applications of servo motors.
robotics (precise arm movement)
conveyor belts (manufacturing)
camera lens correction
robotic vehicles (wheel control)
solar tracking systems
metal forming/cutting machines
textile machinery
automatic door openers
What are key properties and design considerations for servo systems?
Servo systems require high maximum and zero-speed torque, high bandwidth for fast/accurate control, robustness, and the ability to handle high intermittent torque. A high torque-to-inertia ratio is desirable for responsiveness, and the system must react to small voltage variations
What is the standard interface and feedback mechanism for hobby/RC servos?
Most hobby servos use a three-wire interface: Power (5-6V), Ground, and Control Line. The control signal (desired position) is compared with feedback from a position sensor, generating an error signal to drive the motor. Gear reduction and feedback complete the loop
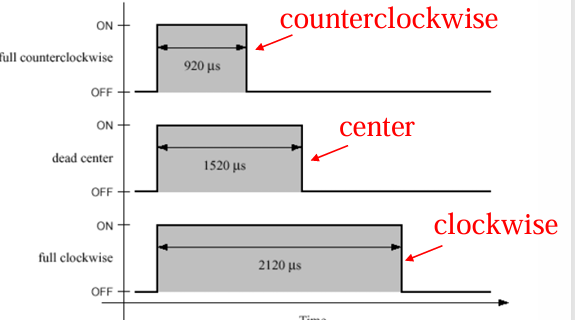
How does PWM control differ for servos versus speed control?
Servo PWM uses the length of the pulse to encode position, while speed control PWM uses the overall duty cycle to determine speed. Typical pulse widths: 920 µs (full counterclockwise), 1520 µs (center), 2120 µs (full clockwise)
What must be considered when writing software to control servos?
Control pulses must be repeated at regular intervals (14-20 ms) for the servo to maintain position. If pulses stop, the servo turns off. Mechanical limits should be considered to avoid damage, and pulse width accuracy is crucial to prevent jitter
What is a winch servo, and how can a standard servo be converted for continuous rotation?
A winch servo rotates continuously, with the control signal specifying speed and direction. To convert a standard servo, replace the feedback potentiometer with fixed resistors mimicking the center position, causing the servo to spin continuously as the control signal moves away from center