Reproduction
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Place these words or phrases in the correct category depending on whether they apply for sexual or asexual reproduction:
2 Gametes
Genetic Variation
Large amount of Offspring
No Genetic Variation
2 Parents
0 Gametes
1 Parent
Small amount of Offspring
Sexual: 1, 2, 5, 8
Asexual: 3, 4, 6, 7
Fill in the blanks: Binary fission is a/an _______ mode of reproduction carried out by _______
First the _______ duplicates
Then the parent _______ into 2 _______ cells
Binary fission is a/an asexual mode of reproduction carried out by bacteria
First the genetic material duplicates
Then the parent divides into 2 daughter cells
Fill in the blanks: Budding is a/an _______ mode of reproduction carried out by _______ _______
A _______ grows from the parent
The _______ eventually detaches
Budding is a/an asexual mode of reproduction carried out by unicellular fungi
A bud grows from the parent
The bud eventually detaches
Fill in the blanks: Spore Production is a/an _______ mode of reproduction carried out by _______ _______
_______ are released from _______
The spores are dispersed by _______
This is different from _______ spores in _______ like mosses and ferns:
In plants, spores are _______ _______ which are eventually _______
In fungi, spores are _______. They grow into new _______
Spore Production is a/an asexual mode of reproduction carried out by filamentous fungi
Spores are released from sporangia
The spores are dispersed by wind
This is different from sexual spores in plants like mosses and ferns:
In plants, spores are sexual gametes which are eventually fertilised
In fungi, spores are asexual. They grow into new organisms/fungi
Fill in the blanks: Vegetative Propagation is a/an _______ mode of reproduction carried out by _______ _______
A part of a _______ grows away from its _______
Vegetative Propagation is a/an asexual mode of reproduction carried out by many plants
A part of a plant grows away from its parent
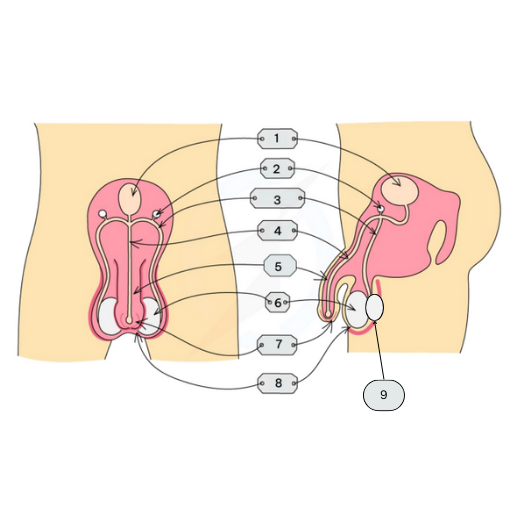
This is the Male Reproductive organ. Name labels 1-9
Bladder
Seminal Vesicles
Vas Deferens / Sperm Duct
Urethra
Penis
Testicles
Foreskin
Scrotum
Epididymis
Explain the function of the Seminal Vesicles, and its correlation with the Prostate Gland
The seminal vesicles produces secretions into the urethra alongside the prostate gland
These secretions nourish the sperm, active the sperm using enzymes, facilitates the swimming of sperm cells, and neutralises the acidity of the urethra
Explain why the Scrotum is found outside of the body
The reason for this is because the optimum temperature of sperm is lower than the internal body temperature, so if the scrotum was to be inside the body, the sperm would die out or be insufficient
What is the name of the male gamete, explain its function, and describe what semen is
The male game is the Sperm Cell. Its job is to locate the female gamete, penetrate through its membrane and fertilise it
Semen is the fluid containing both the secretions release and the sperm cells
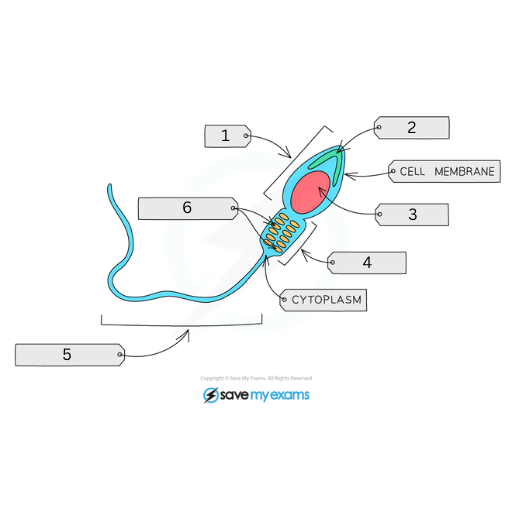
This is the male gamete (sperm cell). Name labels 1-6 and explain the function of all the labels, but 1 and 4
Head
Acrosome: Contains enzymes to break the female gamete’s membrane
Haploid Nucleus: Contains either an X or Y chromosome
Mid-Piece
Tail / Flagellum: Enables swimming of the cell
Mitochondria: Provide the energy to the cell to help it swim
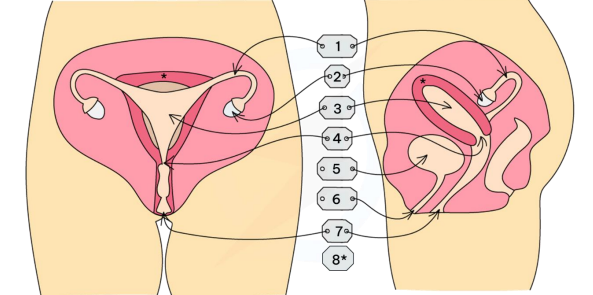
This is the Female Reproductive organ. Name labels 1-8. Explain the 2 functions of label 7
Fallopian Tube
Ovaries
Uterus
Cervix
Bladder
Urethra
Vagina: The point of entry of the penis during copulation (sex) and the point of exit of the baby at the end of pregnancy
Endometrium
Fill in the blanks: Ovulation occurs as follows:
_______ are produced in the _______. An _______ is released approximately every _______ days
Upon ovulation, the _______ may be fertilised within _______ hours
The _______ travels to the _______ _______ (the site of fertilisation)
If the _______ is fertilised by the _______ _______, a _______ forms and settles in the _______, if not, the _______ is released (by menstruation) through the _______
Ovulation occurs as follows:
Ova are produced in the ovaries. An ovum is released approximately every 28 days
Upon ovulation, the ovum may be fertilised within 36 hours
The ovum travels to the fallopian tube (the site of fertilisation)
If the ovum is fertilised by the sperm cell / male gamete, a zygote forms and settles in the uterus, if not, the ovum is released (by menstruation) through the vagina
Fill in the blanks: The Menstrual Cycle:
Days 1-5: The _______ sheds its _______ lining, resulting in bleeding. The _______ _______ starts releasing _______-_______ hormones, the rise in these hormones stimulates the development of _______ in the _______
Days 1-13: The _______ fully develops. _______ stimulates the _______ to produce _______ which causes the _______ to thicken as well as the _______ _______ to decrease _______ production and stimulate _______ hormones production
Day 14: Around this day, the _______ moves to the edge of the _______ and bursts, releasing the _______ into the fallopian tube by _______, stimulated by _______ hormones
Days 15-28: The _______ hormones then converts the empty _______ into the _______ _______, secreting _______ which prevents the breakdown of the _______ (in preparation of pregnancy) and causes the _______ _______ to stop _______ and _______-_______ hormones production
If the released _______ isn’t fertilised, the _______ _______ dies, the _______ levels fall and the cycle restarts
The Menstrual Cycle:
Days 1-5: The uterus sheds its endometrium lining, resulting in bleeding. The pituitary gland starts releasing follicle-stimulating hormones, the rise in these hormones stimulates the development of follicles in the ovaries
Days 1-13: The follicle fully develops. FSH stimulates the ovaries to produce oestrogen which causes the endometrium to thicken as well as the pituitary gland to decrease FSH production and stimulate luteinising hormones production
Day 14: Around this day, the follicle moves to the edge of the ovary and bursts, releasing the ovum into the fallopian tube by ovulation, stimulated by luteinising hormones
Days 15-28: The luteinising hormones then converts the empty follicle into the corpus luteum, secreting progesterone which prevents the breakdown of the endometrium (in preparation of pregnancy) and causes the pituitary gland to stop luteinising and follicle-stimulating hormones production
If the released ovum isn’t fertilised, the corpus luteum dies, the hormone levels fall and the cycle restarts
What is the name of the female gamete and explain its function
The female gamete is the egg cell or the ovum. It is the largest cell and its job is to be fertilised by a sperm cell, developing into the zygote
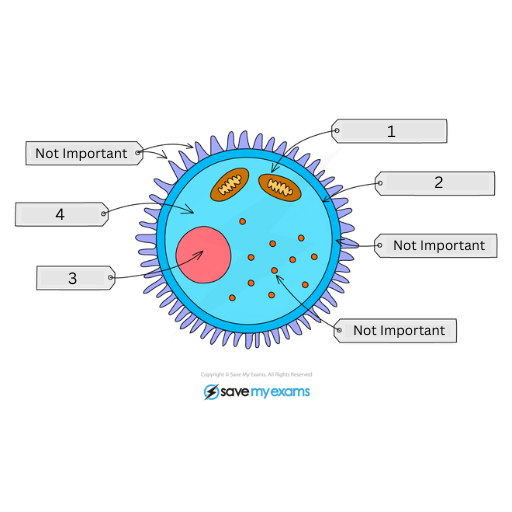
This is the female gamete (egg cell / ovum). Name labels 1-4
Mitochondria
Cell Membrane
Haploid Nucleus: Contains the X chromosome
Cytoplasm
Fertilisation
Fertilisation is when both haploid nuclei (from each gamete) fuse together to form a zygote. Each nucleus contains 23 chromosome, when the chromosomes from each nucleus fuse, 46 are formed. One chromosome from each nucleus is a sex-chromosome. The ovum’s sex-chromosome is always an X, whilst the sperm’s sex-chromosome can be either an X or a Y. When the sex-chromosome fuse they can be either XX (the baby’s gender would be female) or XY (the baby’s gender would be male)
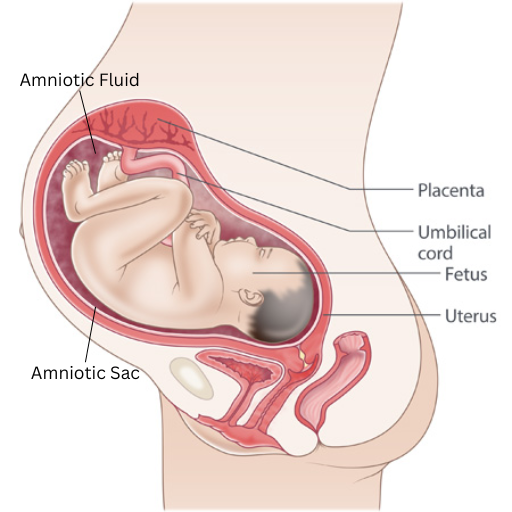
The foetus is enclosed in an (1), filled with (2)
State the function of (1), (2), the placenta, and the umbilical cord
(1) - Amniotic Sac: Grows with the foetus, providing space and protection
(2) - Amniotic Fluid: Provides a warm body temperature and protection
Placenta: Absorbs water (by osmosis), removes waste (CO2, urea), protects the foetus from harmful substances (from the mother), and produces oestrogen and progesterone to sustain pregnancy
Umbilical Cord: Absorbs oxygen and nutrients (by diffusion) from the mother’s blood
What are the 10 main birth control methods and classify them into the categories; Chemical, Natural, Barrier, and Surgical
Chemical: Contraceptive Implants, Contraceptive Pill, IUD / IUS
Natural: Abstinence, Monitoring Body Temperature, Monitoring Changes in Cervical Mucus
Barrier: Condom, Diaphragm
Surgical: Vasectomy, Female Sterilisation