Structures and Features of Eukaryotic Cells
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What defines a eukaryotic cell?
It contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
From what are eukaryotic cells believed to have evolved?
From prokaryotic cells via endosymbiosis
What are the main kingdoms of eukaryotes
Animals, Plants, Fungi, and Protists
What are the main features of animal cells
No cell wall; feeds by ingestion
What are the main features of plant cells
Cell wall made of cellulose; feeds by photosynthesis
What are the main features of fungi
Cell wall made of chitin; absorbs food.
Where is genetic material located in eukaryotic cells
Inside a double-membrane nucleus
What size are eukaryotic ribosomes
80S — larger than prokaryotic ribosomes
Name four common membrane-bound organelles found in all eukaryotes
Mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and vesicles
What additional structures are unique to plant cells
Chloroplasts, a large central vacuole, and a tonoplast membrane
What structural feature is common in multicellular fungi
Filamentous hyphae separated by septa
Why is separating transcription and translation beneficial
It allows mRNA modification (capping, polyadenylation, splicing) before translation, improving stability and control of gene expression
Why is compartmentalisation important in eukaryotic cells
It allows organelles to maintain unique internal environments suited to specific functions.
How does compartmentalisation improve efficiency
Allows enzymes and materials to stay close together for faster reactions
What do lysosomes and phagocytic vacuoles demonstrate about compartmentalisation
hey safely contain hydrolytic enzymes, preventing damage to the rest of the cell
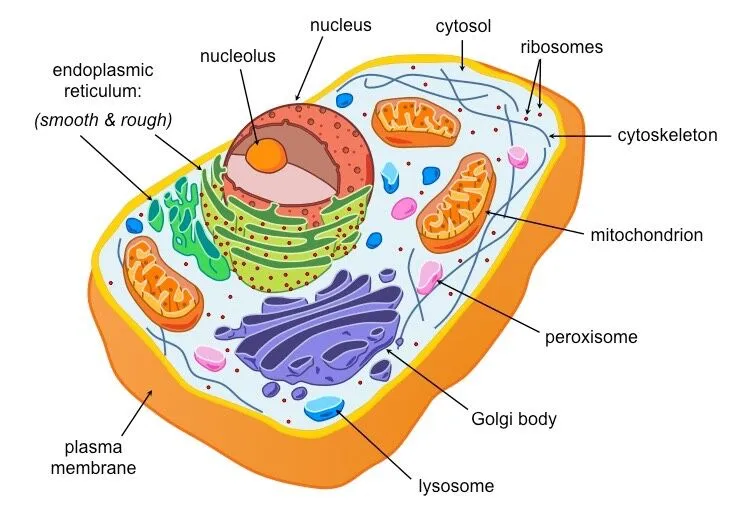
Draw a Eukaryotic include labelling