BIO CHAPTER25
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Macroevolution
evolutionary change that happens above species level
first genetic material
RNA
ribozyme
an RNA molecule that functions as an enzyme.
Relative dating
uses the order of rock strata to determine the relative age of fossils.
Radiometric dating
uses the decay of radioactive isotopes to determine the age of the rocks or fossils. It is based on the rate of decay, or half-life, of the isotope.
What is the age range for which carbon-14 dating may be used?
75,000
How many years ago did prokaryotes originate on the geologic timescale?
3.5 billion
How many years ago was the colonization of land on the geologic timescale?
500million
What unique ability originated with cyanobacteria? How did this alter life on Earth and lead to a wave of mass extinctions?
oxygenic photosynthesis. The accumulating oxygen gas (O2) probably doomed many prokaryotic groups by attacking chemical bonds and damaging cells.
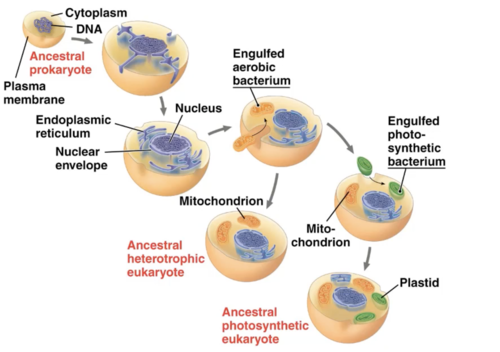
three lines of evidence that support the model of endosymbiosis.
inner membranes contain enzymes
replicate by a splitting process
contain a single circular DNA
What other life form appears to have colonized land associated with plants?
Fungi accompanied plants as they colonized land and aided in absorption of water and minerals from the soil.
What were some challenges both plants and animals had to overcome in order to colonize land?
dehydration and the need to obtain minerals.
What group of animals colonized land about 450 million years ago?
Arthropods (particularly insects and spiders)
What group of animals colonized land about 365 million years ago?
tetrapods
End of Paleozoic: all land joined in Pangea
Mid-Mesozoic: Pangea split into Laurasia (north) & Gondwana (south)
End of Mesozoic: Laurasia & Gondwana separated → present-day continents
~45 million years ago: India collided with Eurasia → formed the Himalayas
Today: continents still drifting
“Penguins Love Giant Happy Dolphins”
Describe the major events in the movement of Earth’s continents from the end of the Paleozoic to today. Include key landmasses and mountain formation.

What environmental factors have scientists worried about the potential for a sixth mass extinction?
Habitat loss, introduced species, overharvesting, with climate change being a prime facture.
What are adaptive radiations?
are periods of evolutionary change in which groups of organisms form many new species whose adaptations allow them to fill different ecological roles in their communities
Explain how heterochrony, an evolutionary change in the rate or timing of developmental events, can lead to new forms on which evolution can act.
leads to different body shapes depending on developmental growth rates of different body parts as a result of an evolutionary change
hox genes control
provide positional information in an animal embryo. This information prompts cells to develop into structures appropriate for a particular location.
Why is the four-stage hypothesis for the abiotic origin of life useful? (Concept 25.1)
It leads to predictions that can be tested.
the early atmosphere probably consisted of __________.
N2, H2O, CO2, NH3, CH4, H2 vapor
The Miller and Urey abiotic synthesis experiment (and subsequent, similar experiments) showed that __________.
simple organic molecules can form spontaneously under conditions like those thought to prevail early in Earth's history
Ancient cyanobacteria were very important in the history of life because they
produced atmospheric oxygen
What prokaryotic adaptation occurred during the oxygen revolution and opened up the possibility for energy-demanding multicellular life-forms?
Cellular respiration
mitochondria and plastids evolved from prokaryotic endosymbionts
single circular chromosome
ribosomes are more like prokaryotic ribosomes
Prior to the Cambrian explosion, most animals were small and soft-bodied. What development appears to have spurred adaptations such as sharp spines, claws, and body armor (shells)?
Predation
major "problems" that had to be solved before plants, animals, and fungi could fully move into terrestrial habitats?
Reproduction and prevention of dehydration
What evidence most strongly suggests that an impact by an asteroid or meteorite may have caused the extinction of the dinosaurs
Sedimentary rocks at the Mesozoic-Cenozoic boundary contain a layer of iridium, a mineral uncommon on Earth.
Which of the following best describes how the breakup of Pangaea affected evolution?
It separated populations, leading to the formation of new species
Lake Malawi, in the African Rift Valley, is home to more than a hundred species of cichlid fishes, each with slightly different diets and habits. All these species probably evolved from a common ancestor, making them an example of __________.
adaptive radiation
Adaptive radiations are often seen after ____
mass extinctions
180 million years ago, mammals underwent an adaptive radiation starting approximately 65 million years ago. Why?
mammals were outcompeted by the well-established dinosaurs.
How does continental drift affect speciation?
Continental drift changes where animals live, which can create new species or make others go extinct.
Mutations in what class of genes have probably been responsible for many of the changes leading to the great diversity of life existing today?
Developmental genes
The products of Hox genes __________.
provide positional information in animal embryos
exaptations: If the feathers of extant flying birds originally arose as thermoregulatory devices in ancestral reptiles, then flight feathers could be accurately described as
An exaptation is a structure that had one function originally and later evolved other functions
In the species selection model, __________ is to macroevolution as __________ is to microevolution
differential speciation success; differential reproductive success