Lecture 25
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
P-factor in children
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
babies
Longitudinal
Characteristics of the Dunedin study:
1037 ______ born in New Zealand
________ study where subjects were tested at birth, age 3, every 2 years until 15, 18, 21, 26, 32, 38, 45 and ongoing
equal
Each risk factor has basically ______ association with externalizing, internalizing, and thought disorders
general
Genetic risk is specific but also _____
Homotypic continuity | Heterotypic continuity |
Disorder predicts itself over time | Disorder predicts other things over time → Common in psychopathology (Having a disorder often predicts occurrence of different disorders across time and development) |
What’s the difference between homotypic continuity and heterotypic continuity?
psychopathology
Certain disorders may run in families but _____ seems to run in families even more commonly
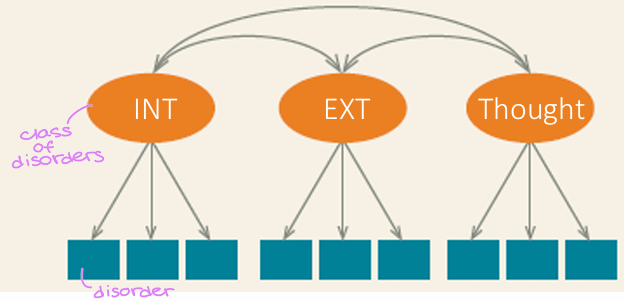
Different domains are positively associated with each other
What is the correlated-factors model?

P (general psychopathology) explains all disorders, no subtypes/classes of disorders
What is the single factor model?
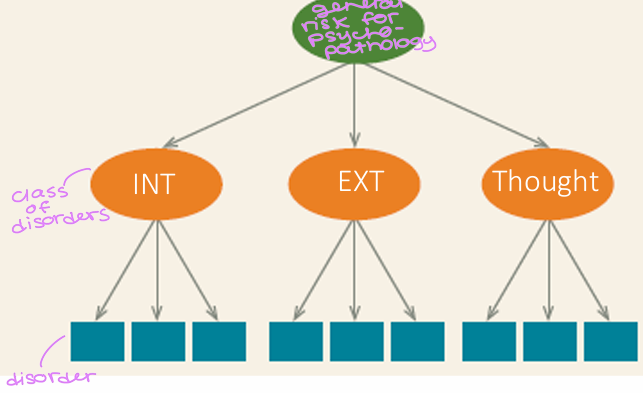
P (general psychopathology) → classes of disorders → disorders
What is the hierarchical model?
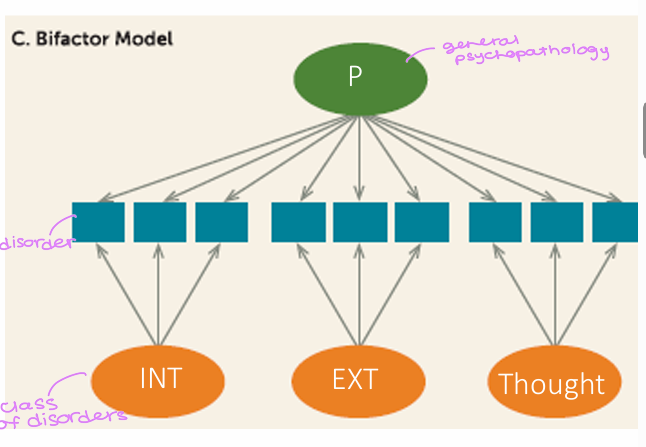
P (general psychopathology) directly causes disorders + specific factors within classes of disorders cause specific disorders
What is the bifactor model?
not, 0.95
Using a specific model is ______ relevant because scores of P are correlated at more than ___, no matter which model you use
empirically, observed
P is _____ based, meaning that it is a result of statistical modeling, not directly _______
negative
regulation
cognitive
Thought
vulnerability
Different Theories of P:
Dispositional _____ emotionality
Emotion ______ difficulties/impulsive responsivity to emotion
Low ______ functioning (not just intelligence – attention & concentration, processing speed, higher level thinking)
_____ dysfunction/aberrant thought processes
Underlying ______ to psychopathology
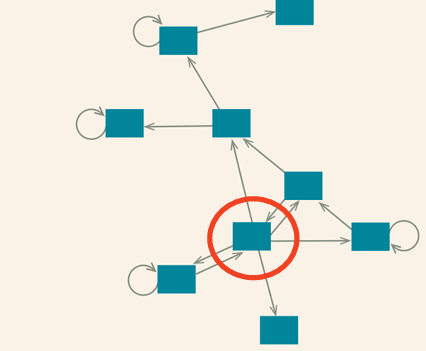
Symptoms across different disorders cause each other
There is no underlying P or risk for general psychopathology that explains everything
→ Intervening on central symptom leads to domino effect of symptom reduction in related symptoms
What is the symptom network model?
cause
It is possible that specific disorders ______ P, not the other way around
The P-factor theory doesn’t fit well with our understanding of ASD, because this disorder endures over time and has high comorbidity but doesn’t morph into other disorders
Genetic risk for autism not associated with P
How does ASD fit with the P-factor theory?
correlations
Different studies find very different strengths of ______ between a disorder and P
measurement
Better ______ is key for learning more about P and applying knowledge in real-world settings
relate
Comorbidities
different
transdiagnostic
With P, we could understand:
How disorders _____ to one another
______ between disorders
Why clinicians see kids present with ______ things over time and across development
How to treat people by using a _____ treatment, that target underlying difficulties that occur across many disorders
depression
internalizing
flowchart
trauma
Treatments:
Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders
Moderate to large effects across anxiety and _____
Most evidence for _______ symptoms
Modular treatment (Match-ADTC)
Picking a starting point based on presenting problems and then follow the ______
Useful for anxiety, depression, _____ and conduct problems