Stillwagon Test 2 Electrons & Bonding
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
metalloids on table
- divide periodic table along zig zag
- diagonal, down over, down over, diagonal
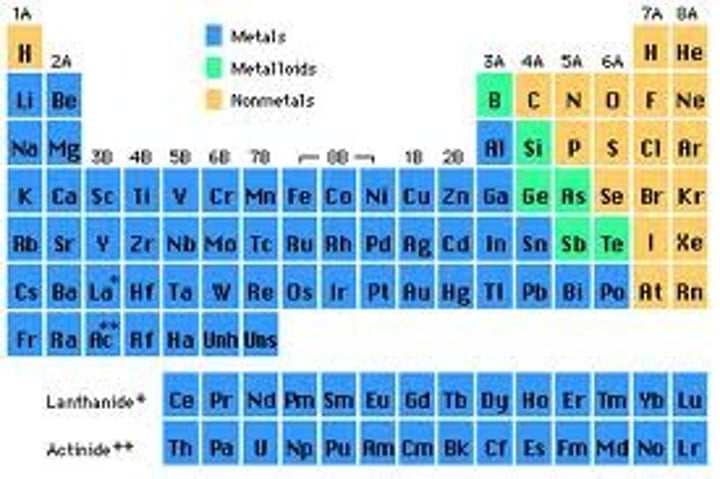
principle quantum #
n= any pos integer value
- (2n)^2 = # of e- per energy level
- describes energy level of e- (1-7)
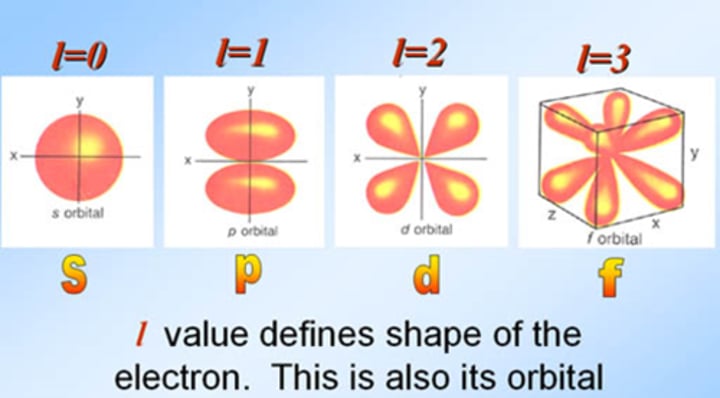
angular momentum quantum number
l < or = n-1
- indicates shape of the electron's orbital
s: sphere
p: figure 8
d: clover
f: tetrahedral
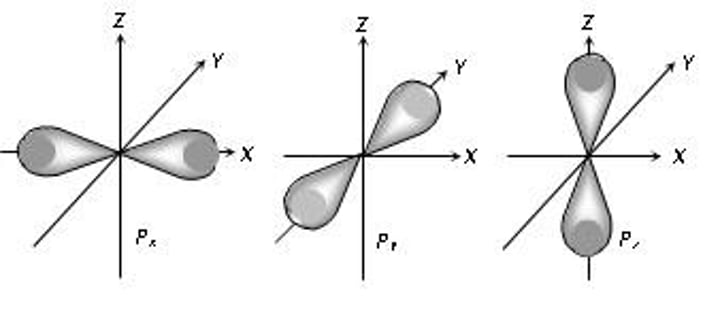
magnetic quantum number
m = values from l to -l (if l=2 m could = 2, 1, 0, -1, -2)
- describes shape of orbital in 3D around axes (x, y, z)
- indicates the orientation of the orbital around the nucleus
s: 1 orientation
p: 3 orientations
d: 5 orientations
f: 7 orientations
EACH ORIENTATION CAN HOLD MAX 2 ELECTRONS!!!
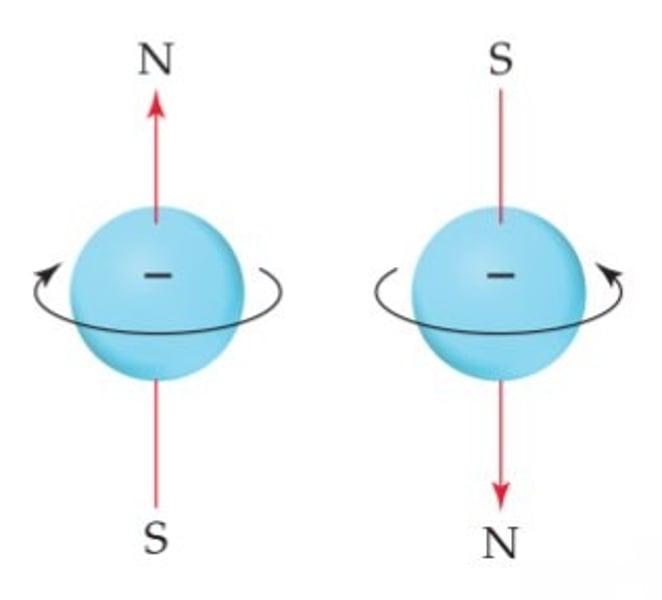
spin quantum number
- ms = 1/2 or -1/2
- indicates the spin orientation (+/- 1/2) of an electron in an orbital
- 2 e- in same orientation must spin in different directions (pos is upwards, neg is downwards)
Aufbau Principle
electrons occupy the orbitals of lowest energy levels first

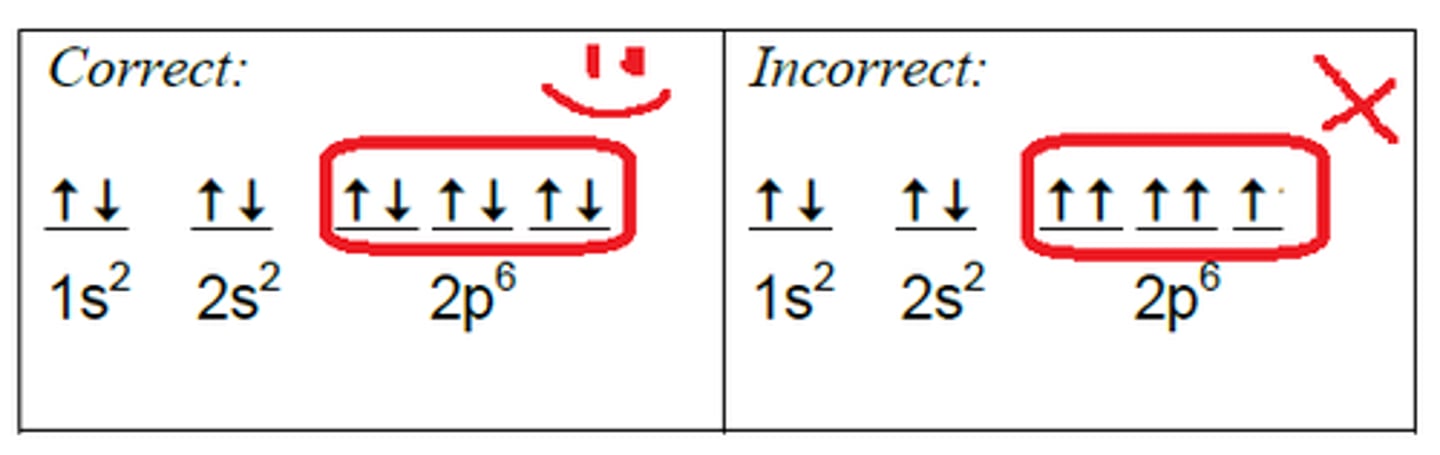
Pauli Exclusion Principle
- NO 2 ELECTRONS CAN BE IN SAME PLACE AT SAME TIME
- orbital may only contain 2 e- each w opposite spin directions
(no two electrons in the same atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers)
Hund's Rule
e- will fill up each orientation once before pairing up
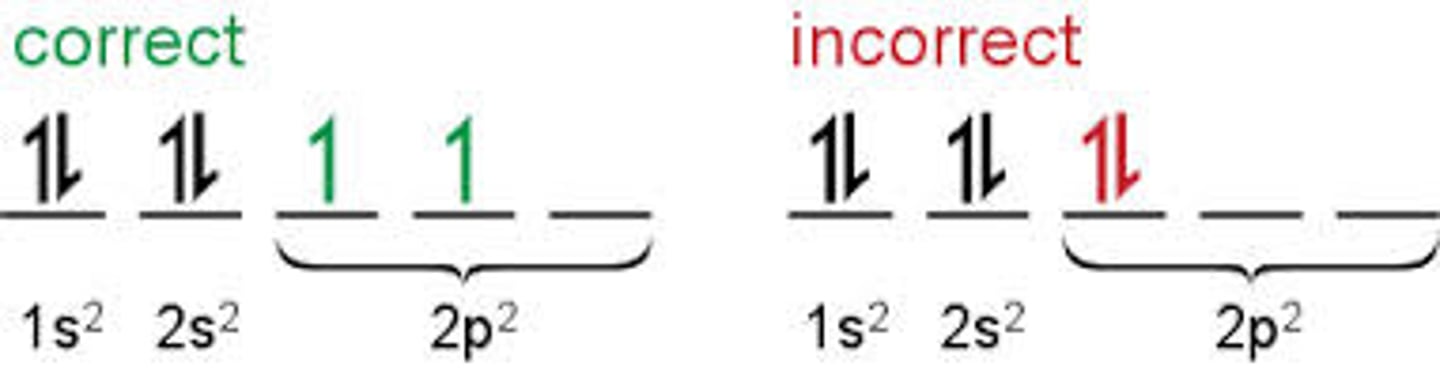
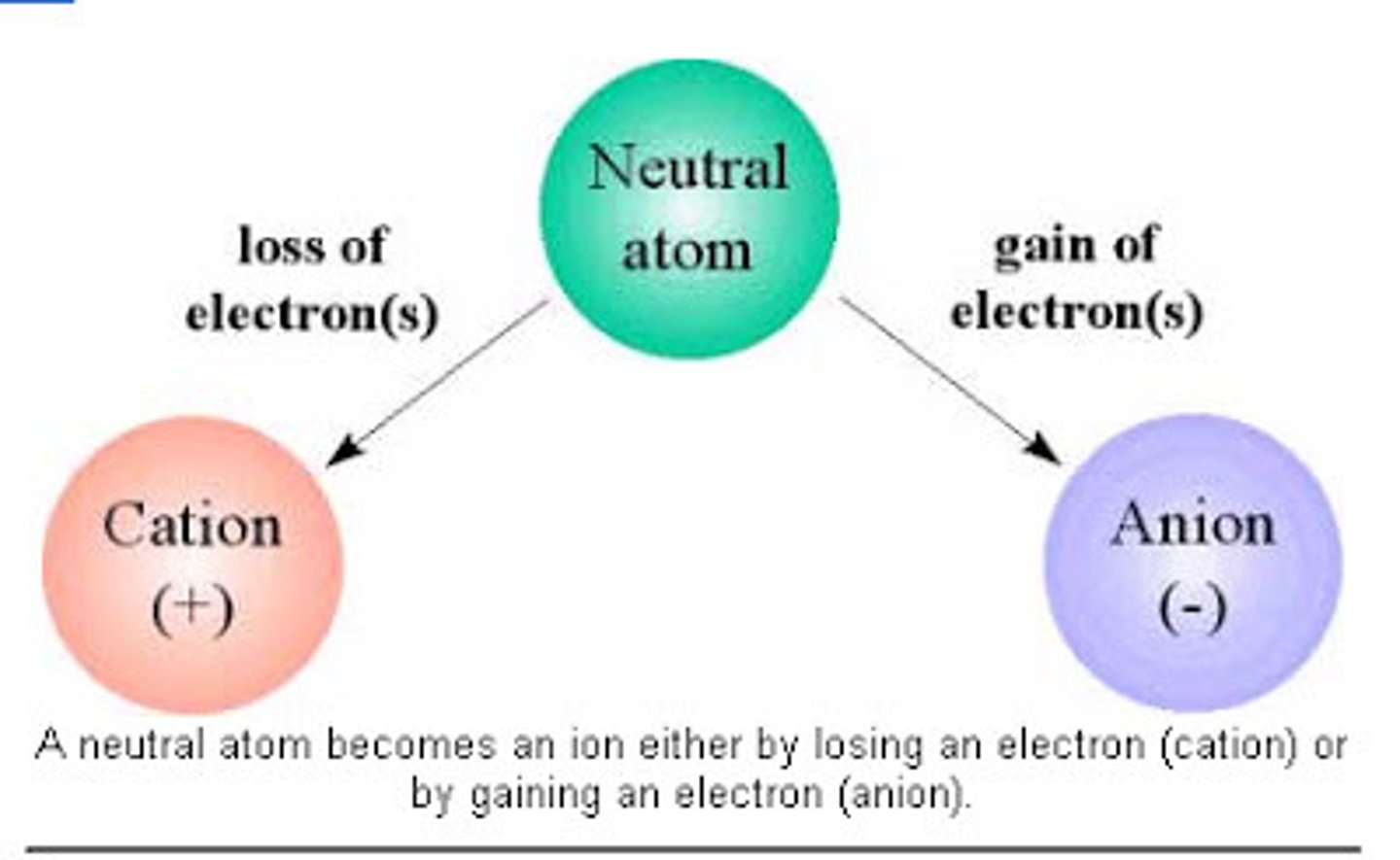
cations and anions
cations gain e-, anions lose e-
how many VSEPR models are there?
6 (or 5 with bent having 2 possible bond angles)
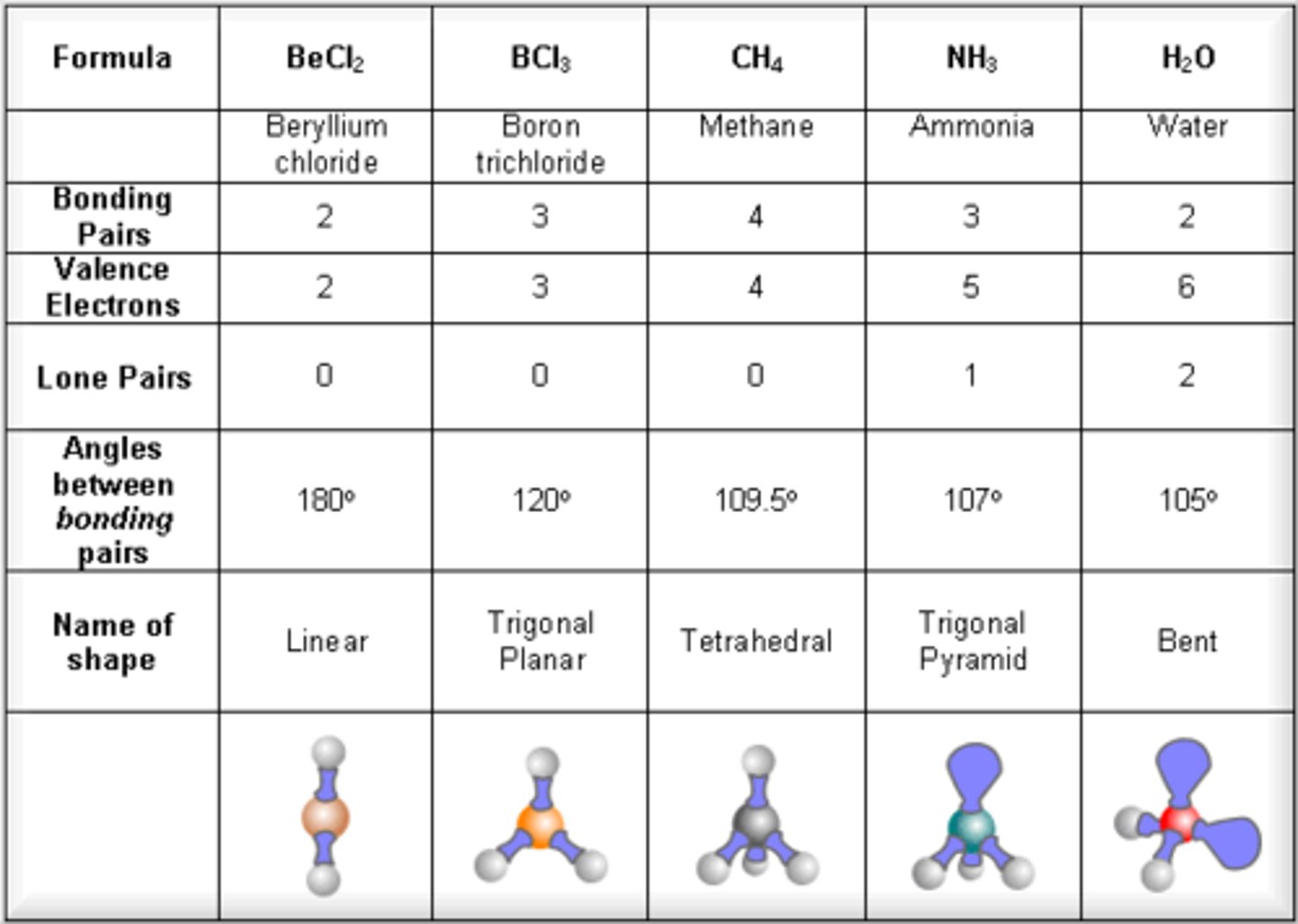
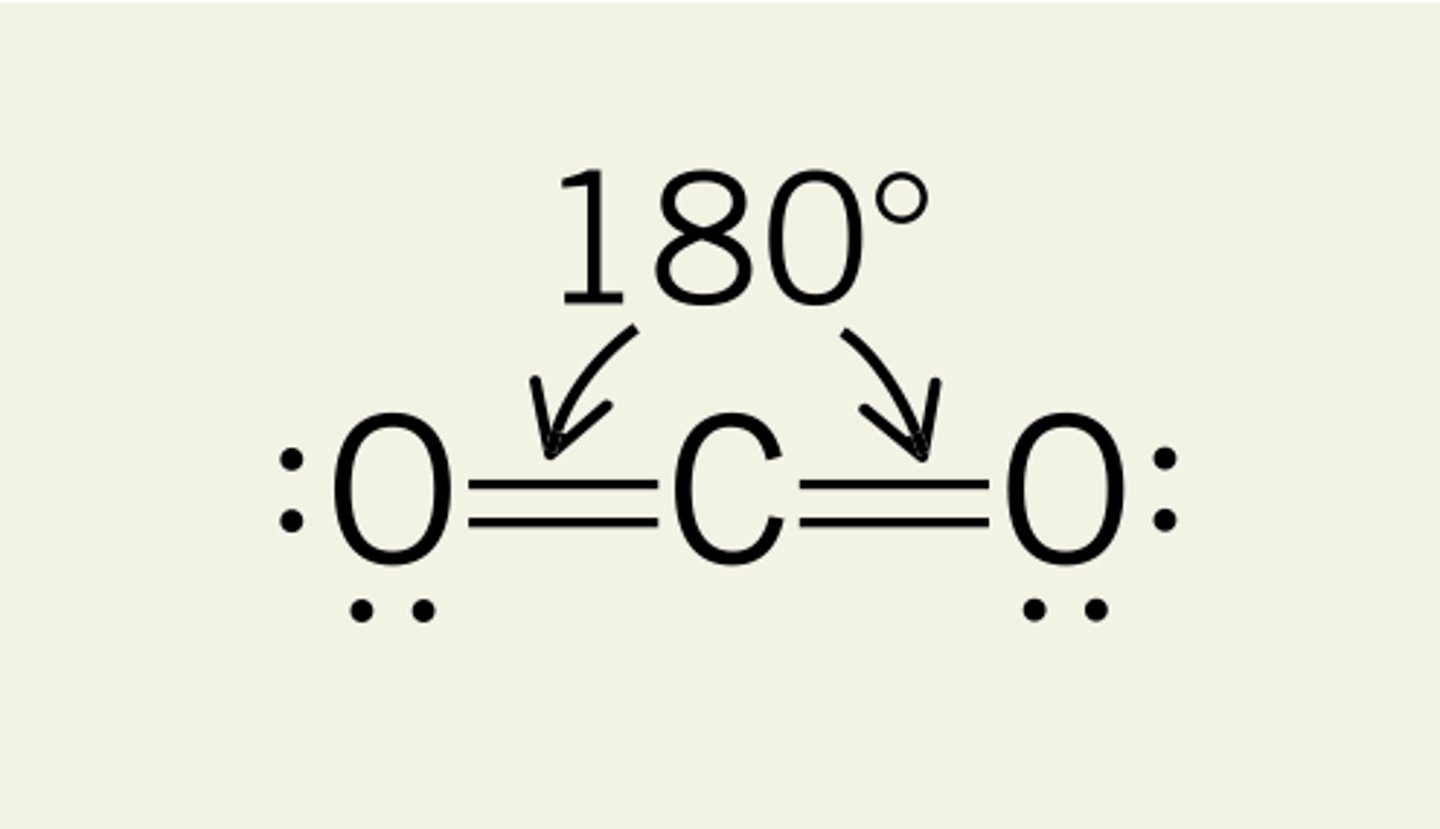
linear
bond angle 180 degrees
bent 1 pair
IF 1 PAIR OF LONE ELECTRONS:
- bond angle 120 degrees
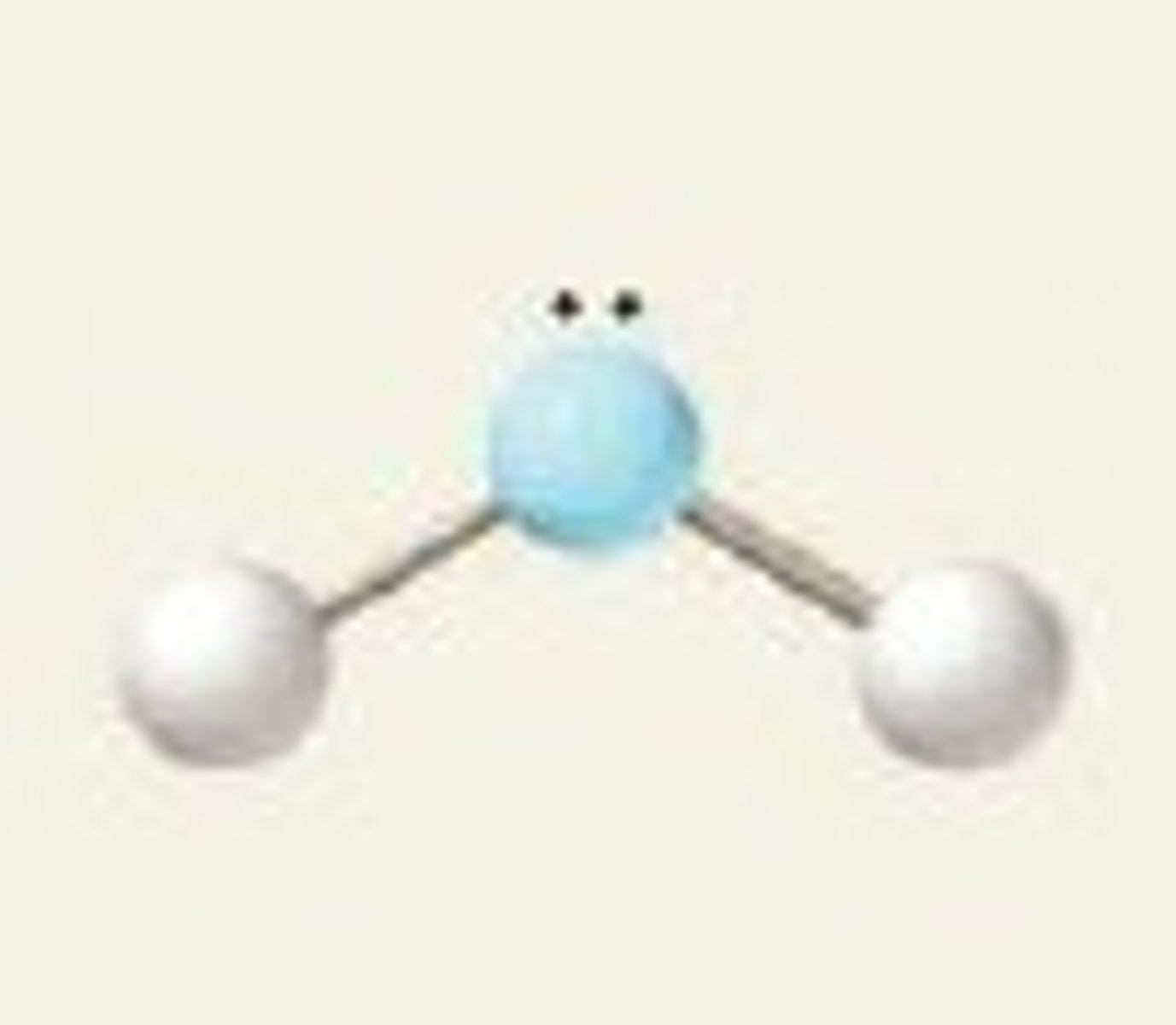

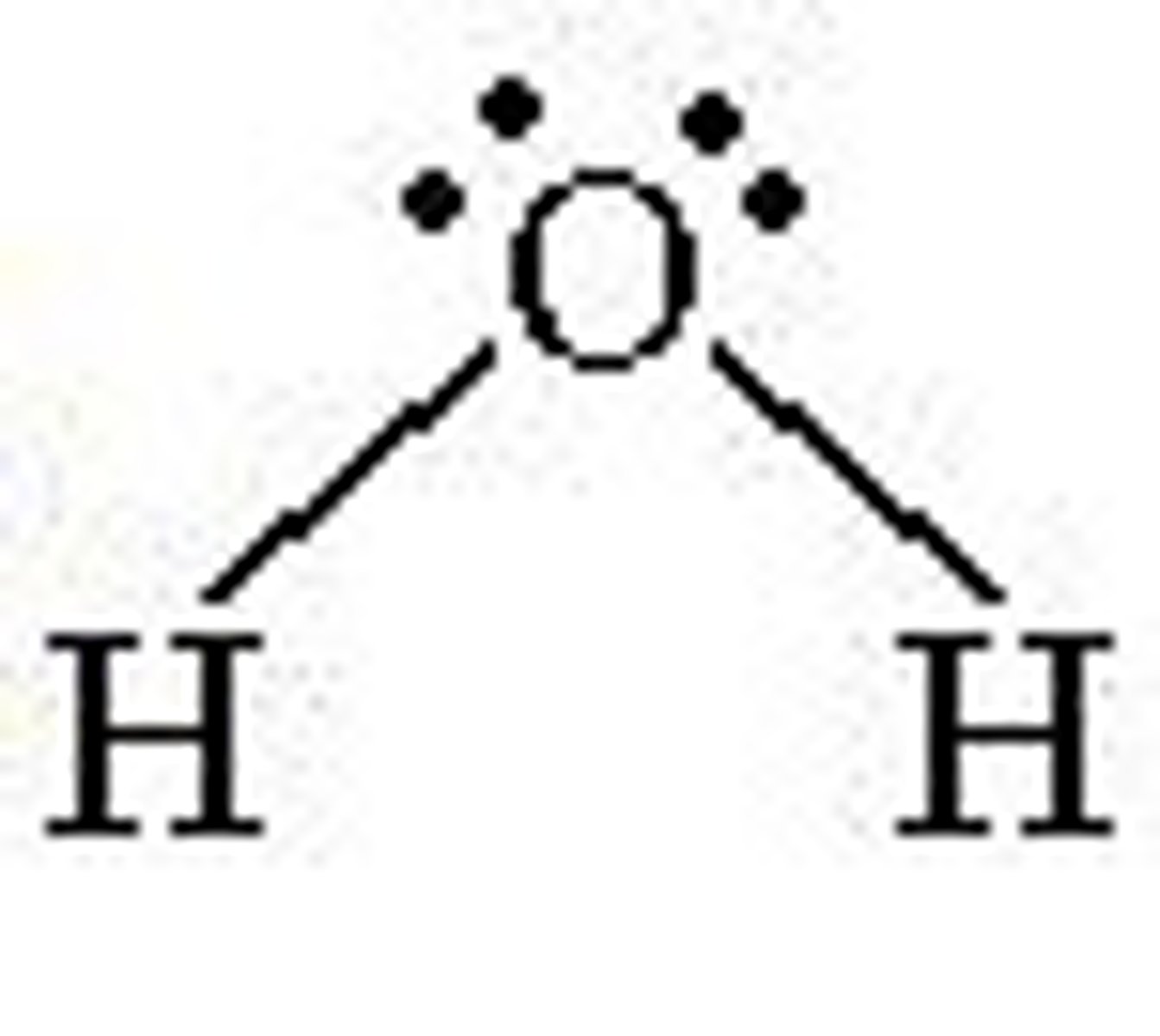
bent 2 pairs
IF 2 PAIRS OF LONE ELECTRONS:
- bond angle 105 degrees
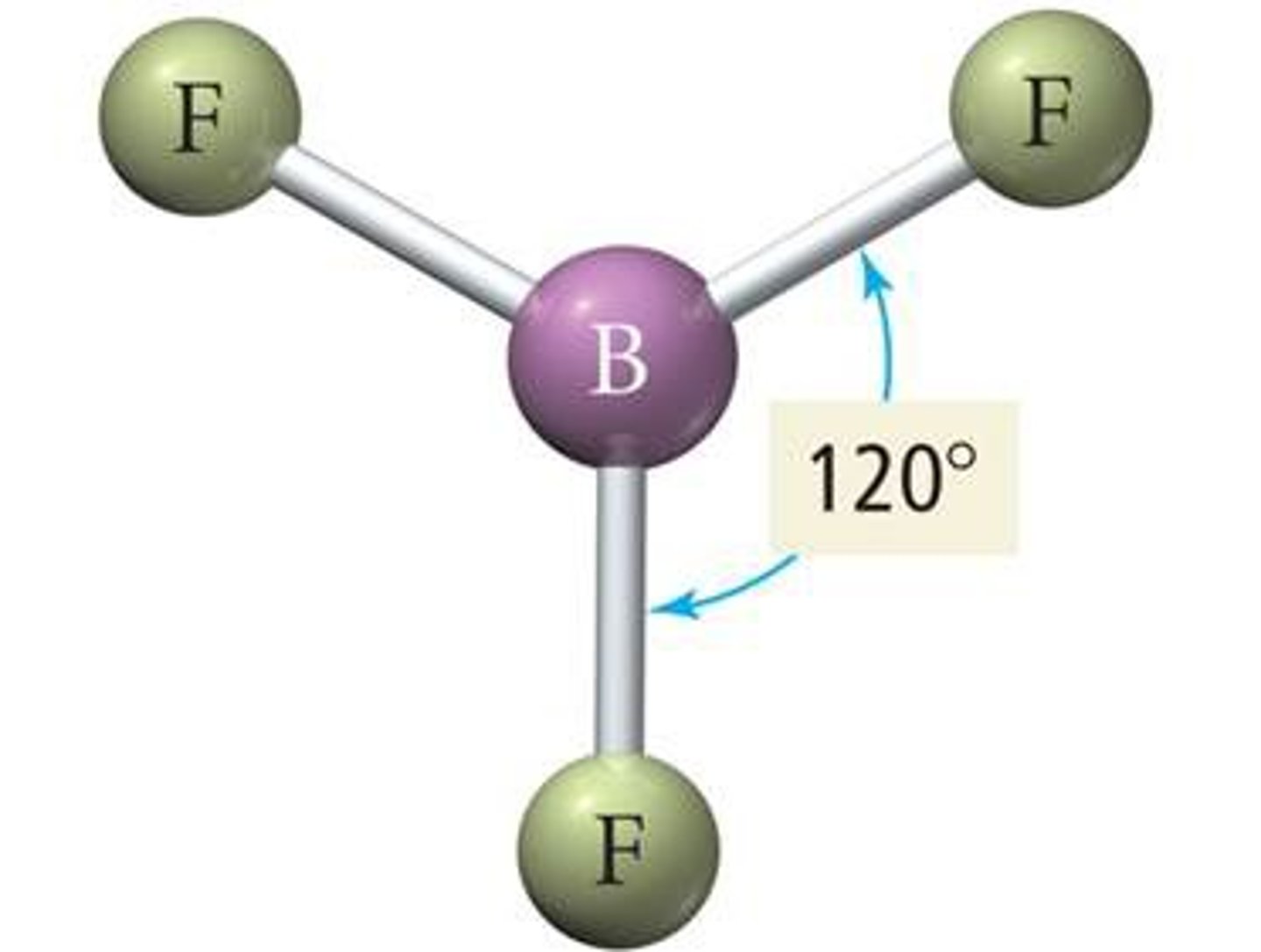
trigonal planar
3 bonds, 0 lone pairs, bond angle 120 degrees
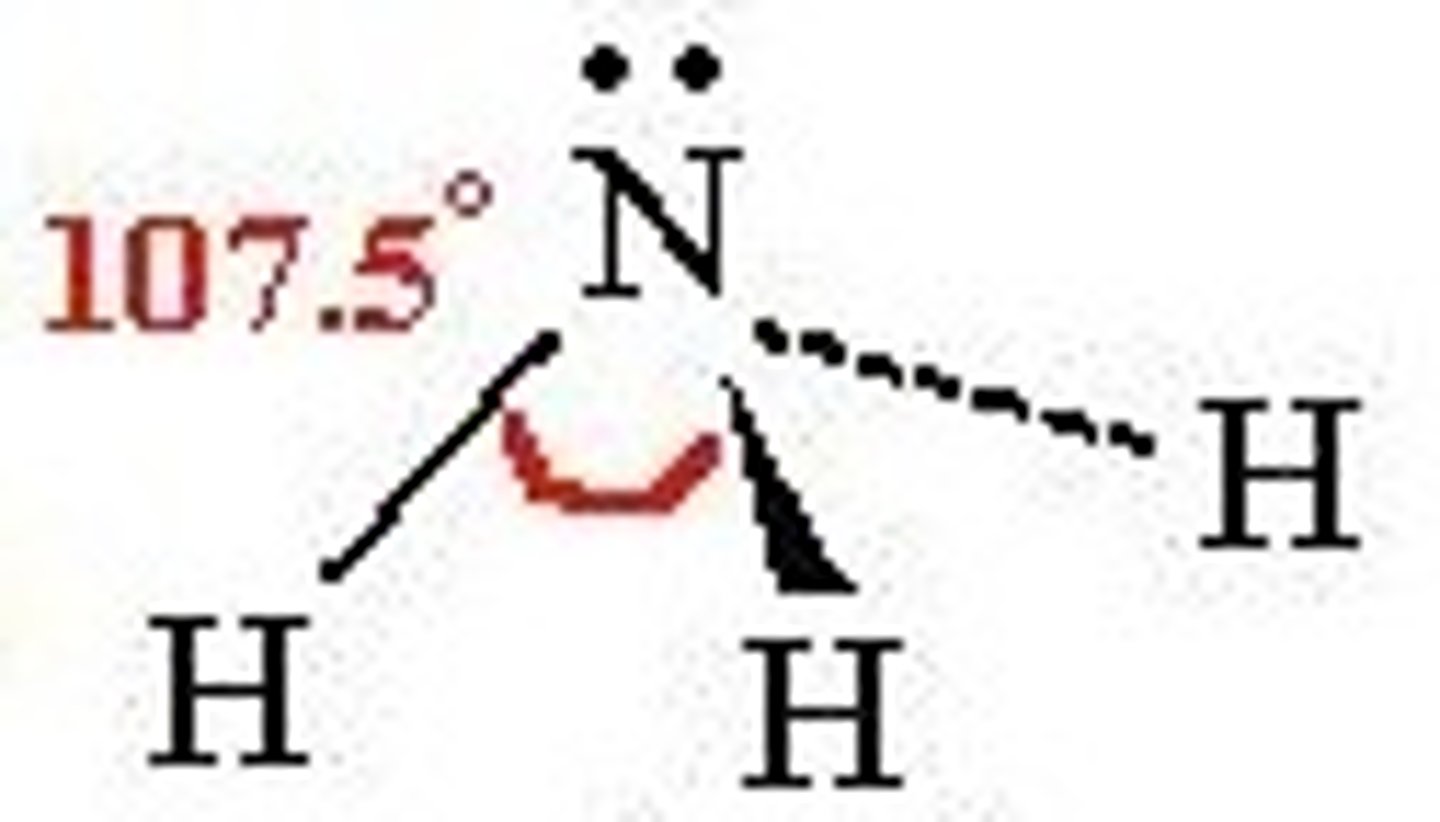
trigonal pyramidal
3 bonds, 1 lone pair, bond angle 107 degrees
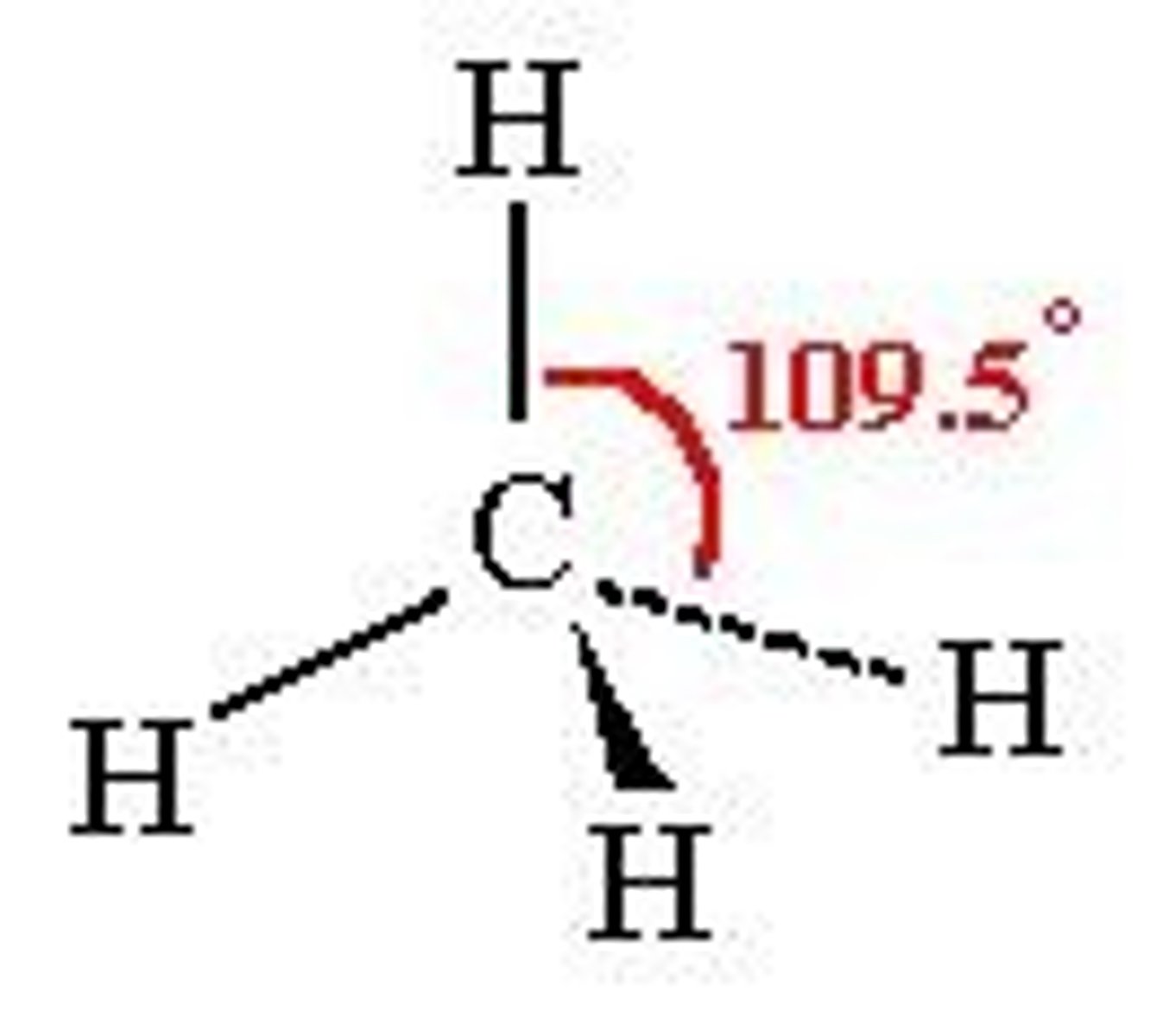
tetrahedral
bond angle 109.5 degrees
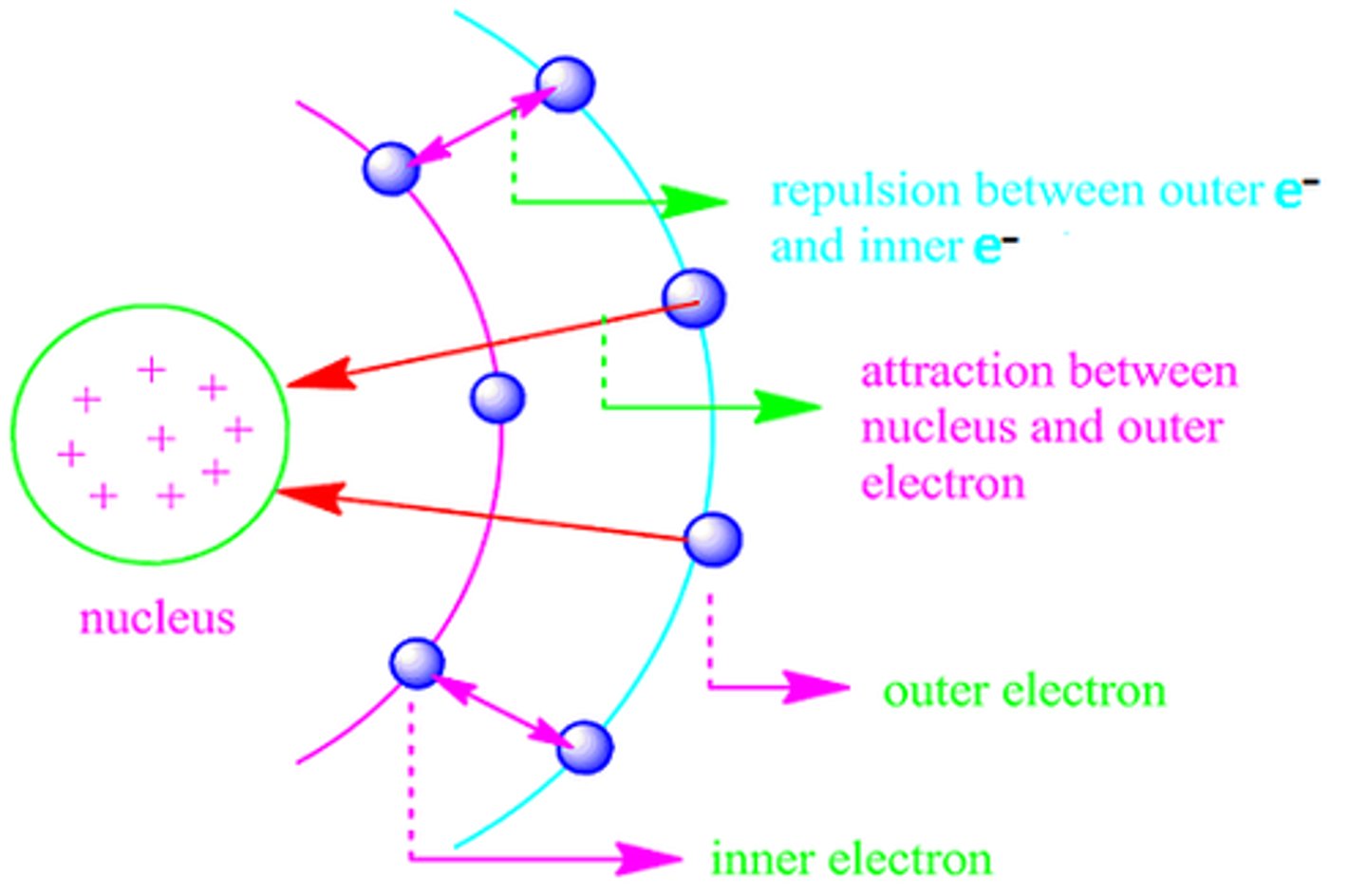
Sheilding
core electrons partially block the attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons
Periodicity
the repeating patterns of chemical and physical properties of the elements moving down/across periodic table
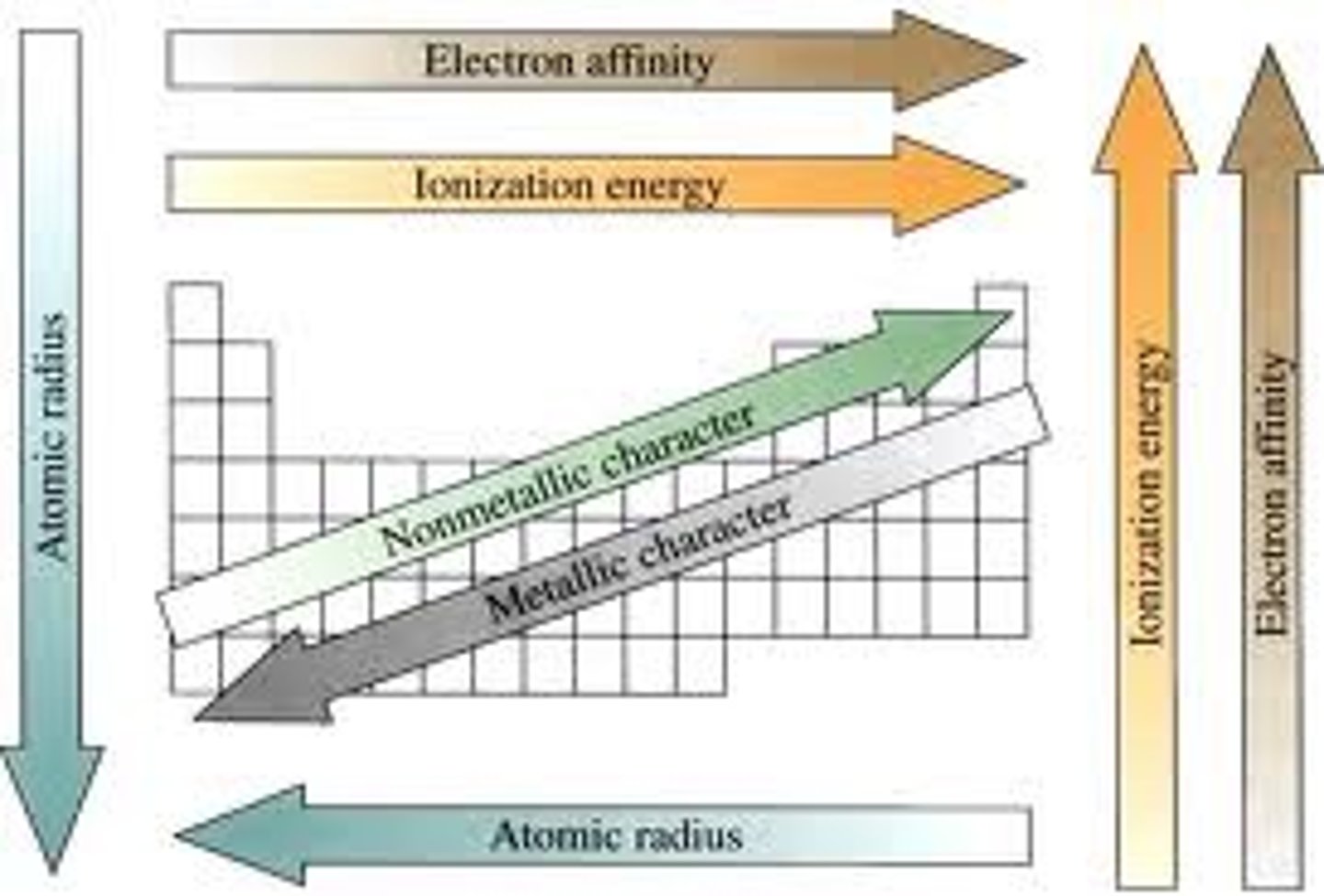
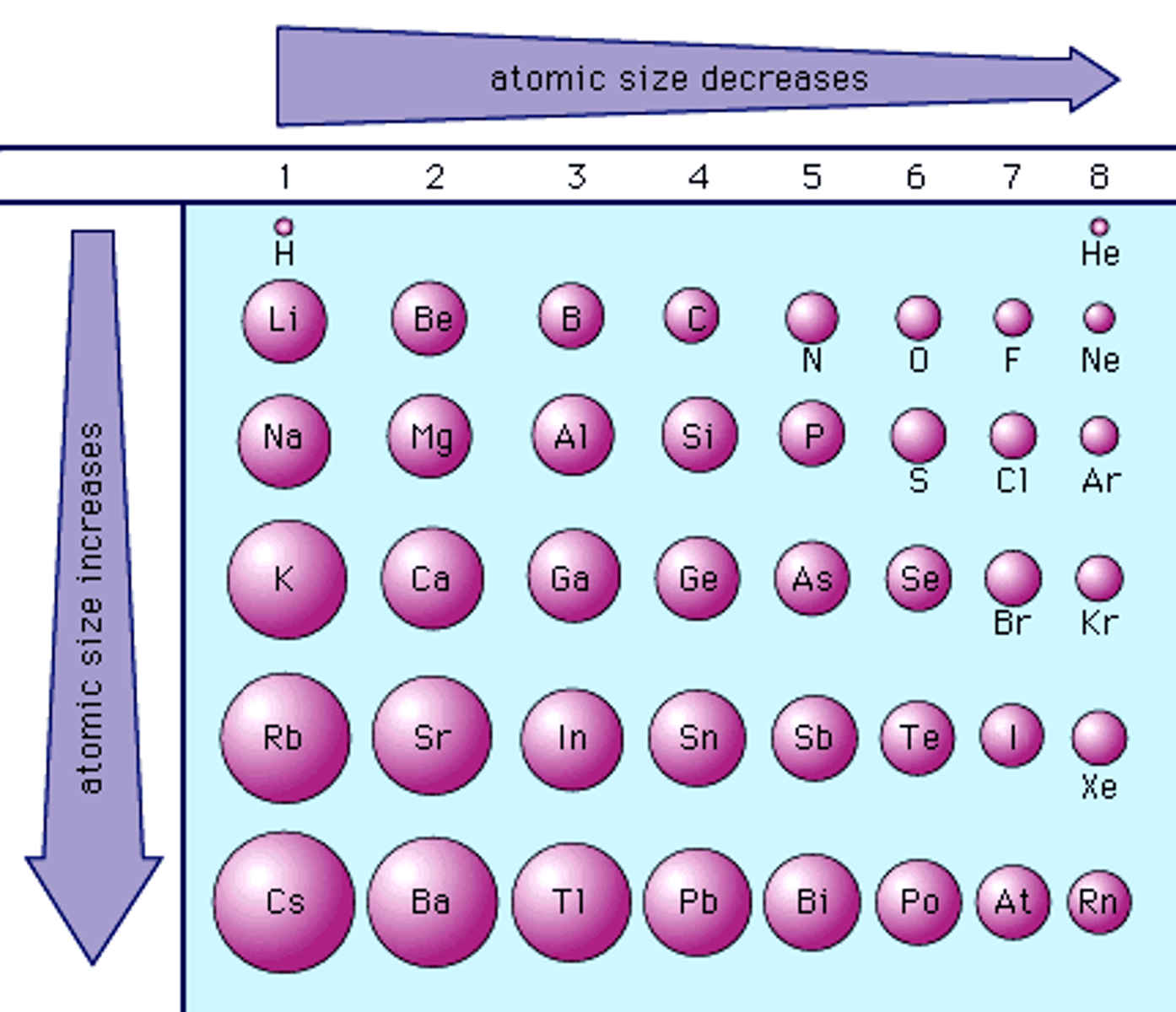
atomic radius
- 1/2 distance between 2 nuclei in molecule with identical atoms
- gets bigger as you go down (energy levels increase size)
- gets smaller as you go across (adds p+, force becomes strong)
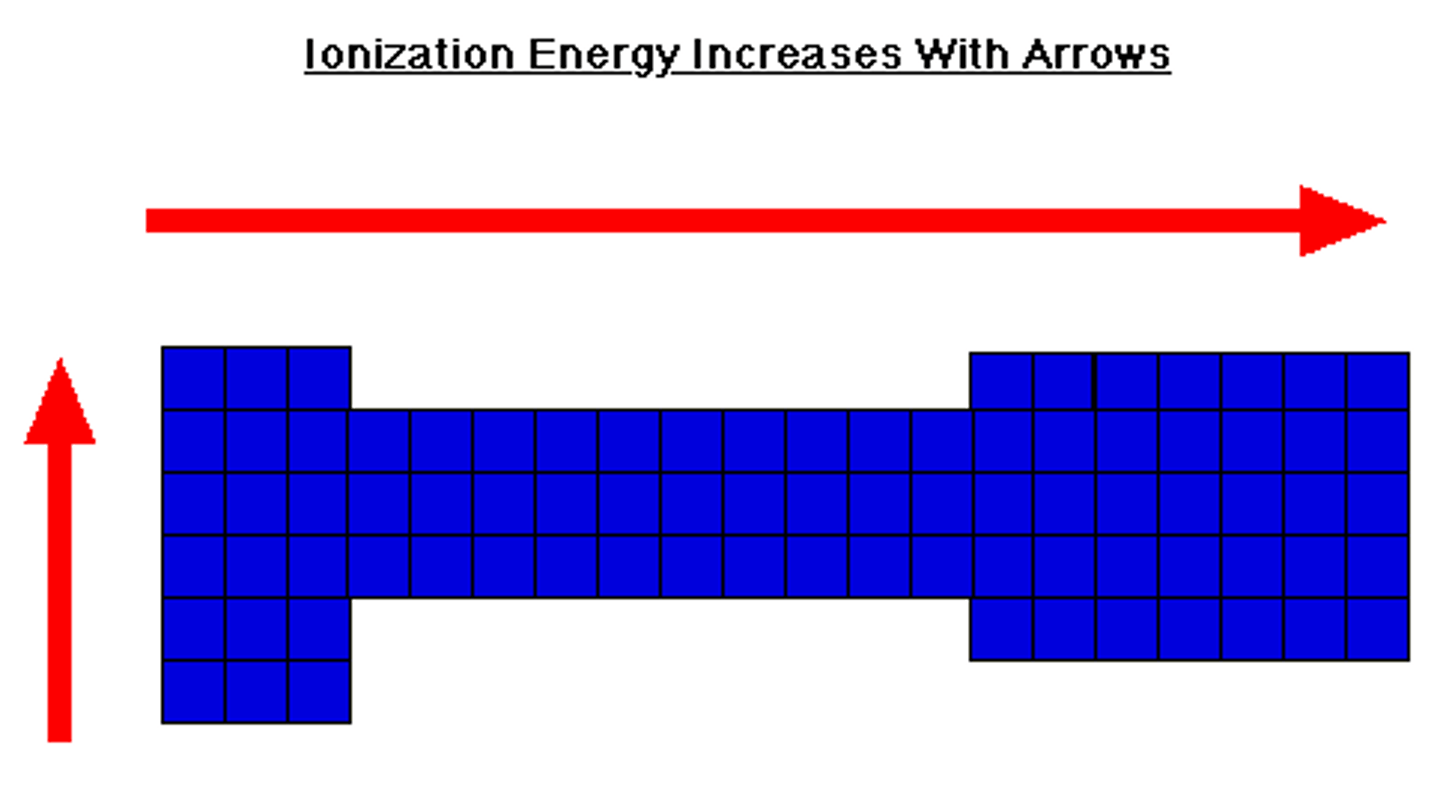
ionization energy
- energy required to lose e-
- gets smaller as you go down table (shielding makes losing e- easier)
- gets bigger as you go across table (harder to lose e- closer you are to 8)
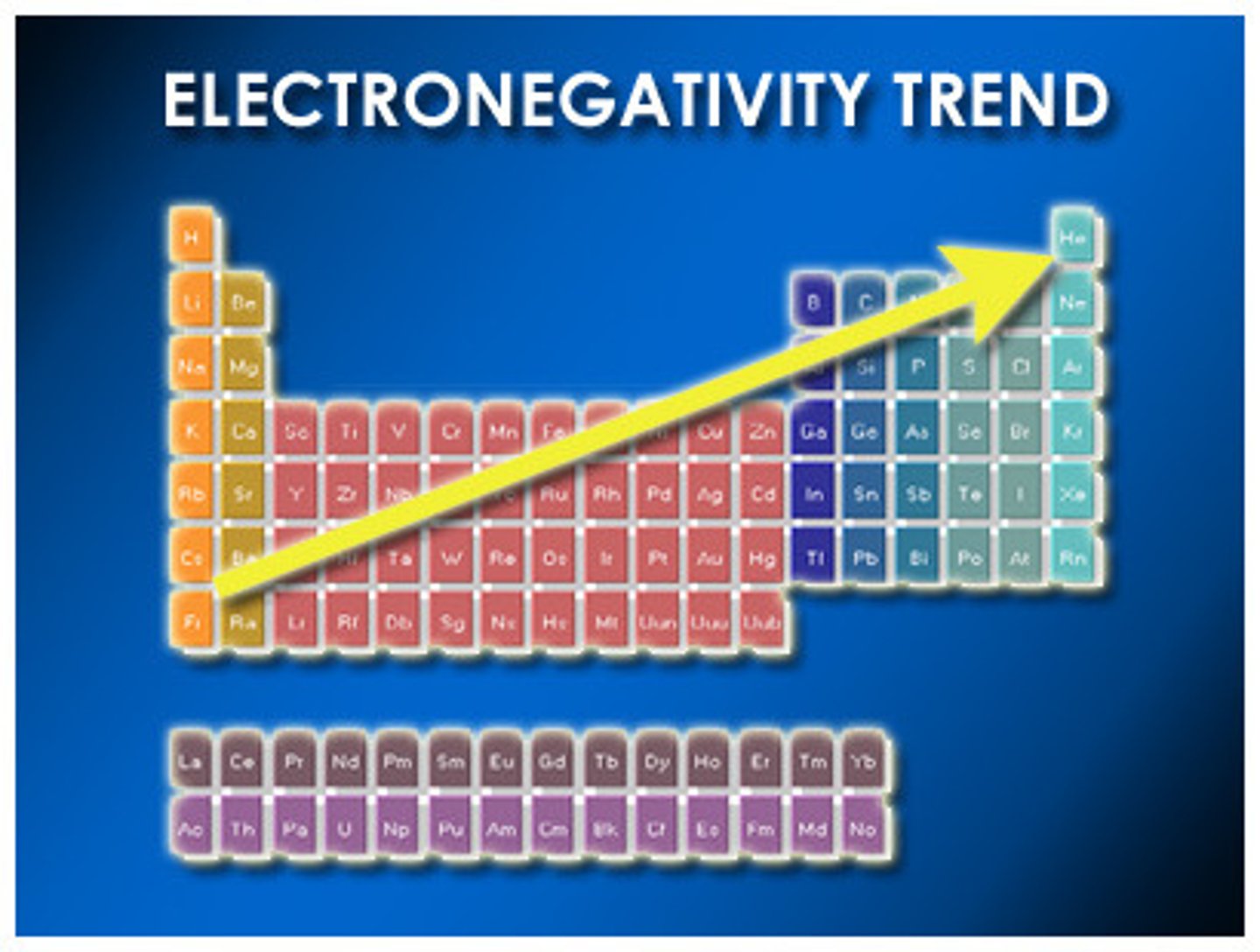
Electronegativity
- the ability of an atom to attract shared electrons when the atom is in a compound
- gets smaller going down table
-gets larger going across table (nonmetals want to attract e-)